- Systematically defined SDI and its core concepts
- Summarized existing SDIR methods and key influencing factors
- Discussed SDIR calculation limitations and proposed improvement
- Open Access
- Review
- Peiyao Yun 1, †,
- Xu Han 1, 2, †,
- Huiji Liu 1, 2,
- Yun Jia 1,
- Zhiguo Cao 1, 2, *
Author Information
Received: 29 Apr 2025 | Revised: 17 Jun 2025 | Accepted: 20 Jun 2025 | Published: 27 Jun 2025
Highlights
Abstract
Soil and dust particulate matter is a sink of various environmental pollutants, and people are exposed to the pollutants they contain through accidental soil and dust ingestion (SDI). However, up to now, the description of SDI in relevant studies is relatively vague and lacks systematic understanding. Therefore, this review sorts out the definition of SDI, analyzes and summarizes existing research methods, data and relevant influencing factors on the soil and dust ingestion rate (SDIR). The SDI refers to the ingestion of soil and dust particles adhering to hand and object surfaces, primarily through hand-to-mouth and object-to-mouth contact. The main methods for determining SDIR include tracer element methodology (TEM), biokinetic model comparison methodology (BMCM), activity pattern methodology (APM), and dust/soil loading-activity pattern-based parametric formula methodology (LPFM), with the third method being comparatively more accurate. According to the limited available data, the SDIR ranged from 0 to 483 mg/d globally for all populations, and most particles adhering to human hands were below 250 µm. Specifically, in economically underdeveloped areas, the SDIR is relatively higher and tends to increase with increasing in microenvironmental contamination. Comparatively, the SDIR tends to decrease initially and then increase with age. Summer has a higher SDIR compared to other seasons. In addition, this review also provides an outlook on the shortcomings and future directions of existing studies. This review will help to improve the understanding of SDI by scholars in related fields, and will help to adopt the correct methodology and obtain more realistic results in contaminant exposure assessment.
Graphical Abstract
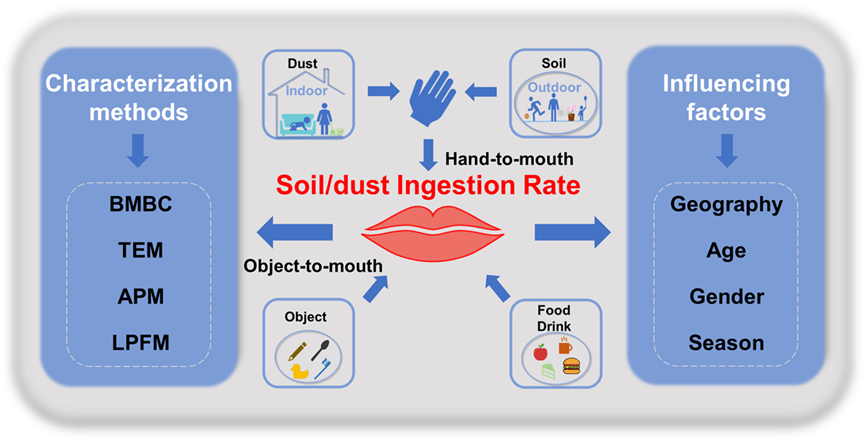
Keywords
soil and dust | hand-to-mouth | ingestion rate | particle size
References
- 1.Tsou, M.C.; Hu, C.Y.; Hsi, H.C.; Hu, H.J.; Özkaynak, H.; Hseu, Z.Y.; Dang, W.; Bradham, K.D.; Chien, L.C. Soil-to-skin adherence during different activities for children in Taiwan. Environ. Res. 2018, 167, 240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2018.07.028.
- 2.Zartarian, V.; Xue, J.P.; Tornero-Velez, R.; Brown, J. Children’s Lead Exposure: A Multimedia Modeling Analysis to Guide Public Health Decision-Making. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097009. https://doi.org/10.1289/Ehp1605.
- 3.Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Xu, M.H.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wei, P.K.; Fan, Y.J.; Yan, G.X.; et al. A systematic characterization of soil/dust ingestion for typical subpopulations in China. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2023, 45, 6199–6214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-023-01634-4.
- 4.Song, Z.D.; Shi, M.; Ren, X.P.; Wang, L.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Fan, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.P.; Xu, Y. An integrated non-targeted and targeted analysis approach for identification of semi-volatile organic compounds in indoor dust. J. Hazar. Mater. 2023, 459, 132202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132202.
- 5.Roosens, L.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Harrad, S.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Current Exposure to Persistent Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene (p,p′-DDE) of Belgian Stude. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 2870–2875. https://doi.org/10.1021/es9021427.
- 6.Dong, T.; Zhang, Y.D.; Jia, S.L.; Shang, H.T.; Fang, W.J.; Chen, D.; Fang, M.L. Human Indoor Exposome of Chemicals in Dust and Risk Prioritization Using EPA’s ToxCast Database. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7045–7054. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b00280.
- 7.Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Li, H.; He, H.; Han, J. The association between metal exposure and body mass index of preschool children of Shaanxi, China. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2024, 10, 100094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heha.2024.100094.
- 8.Kadi, M.W.; Ali, N.; Albar, H. Phthalates and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the indoor settled carpet dust of mosques, health risk assessment for public. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 627, 134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.01.146.
- 9.Lehmler, H.J.; Simonsen, D.; Garcia, A.Q.; Irfan, N.M.; Dean, L.; Wang, H.; von Elsterman, M.; Li, X. A systematic review of human biomonitoring studies of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid, a urinary biomarker pyrethroid insecticide exposure, 1997 to 2019. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2022, 4, 100018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heha.2022.100018.
- 10.Lupolt, S.N.; Agnew, J.; Burke, T.A.; Kennedy, R.D.; Nachman, K.E. Key considerations for assessing soil ingestion exposures among agricultural workers. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 32, 481–492. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-021-00339-z.
- 11.Li, J.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Dong, W. A systematic review of global distribution, sources and exposure risk of phthalate esters (PAEs) in indoor dust. J. Hazar. Mater. 2024, 471, 134423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134423.
- 12.Zhou, L.; Liu, G.J.; Shen, M.C.; Liu, Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Characteristics of indoor dust in an industrial city: Comparison with outdoor dust and atmospheric particulates. Chemosphere 2021, 272, 129952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129952.
- 13.Cohen, J.; Hubbard, H.; Ozkaynak, H.; Thomas, K.; Phillips, L.; Tulve, N. Meta-analysis of soil and dust ingestion studies. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.119649.
- 14.Hubbard, H.; Özkaynak, H.; Glen, G.; Cohen, J.; Thomas, K.; Phillips, L.; Tulve, N. Model-based predictions of soil and dust ingestion rates for U.S. adults using the stochastic human exposure and dose simulation soil and dust model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 846, 157501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.157501.
- 15.Xu, R.B.; Zheng, X.B.; Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.M.; Guo, Y.F.; Huo, X. Assessment of dust trace elements in an e-waste recycling area and related children’s health risks. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 791, 148154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148154.
- 16.Raffy, G.; Mercier, F.; Glorennec, P.; Mandin, C.; Le Bot, B. Oral bioaccessibility of semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) in settled dust: A review of measurement methods, data and influencing factors. J. Hazar. Mater. 2018, 352, 215–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.03.035.
- 17.U.S. EPA. Update for Chapter 5 of the Exposure Factors Handbook: Soil and Dust Ingestion; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. https://doi.org/2018-01/documents/efh-chapter05_2017.pdf.
- 18.Özkaynak, H.; Cohen, J.; Hubbard, H.; Thomas, K.; Phillips, L.; Tulve, N. Advancing Methodologies Used in Trace Element-Based Mass Balance Studies to Separately Estimate Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates for Children. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 107983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2023.107983.
- 19.Tu, J.W.; Fuller, W.; Feldpausch, A.M.; Van Landingham, C.; Schoof, R.A. Objective ranges of soil-to-dust transfer coefficients for lead-impacted sites. Environ. Res. 2020, 184, 109349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109349.
- 20.Fergusson, J.E.; Kim, N.D. Trace elements in street and house dusts: Sources and speciation. Sci. Total. Environ. 1991, 100, 125–150.
- 21.Kademoglou, K.; Xu, F.; Padilla-Sanchez, J.A.; Haug, L.S.; Covaci, A.; Collins, C.D. Legacy and alternative flame retardants in Norwegian and UK indoor environment: Implications of human exposure via dust ingestion. Environ. Int. 2017, 102, 48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2016.12.012.
- 22.Yang, C.; Harris, S.A.; Jantunen, L.M.; Kvasnicka, J.; Nguyen, L.V.; Diamond, M.L. Phthalates: Relationships between Air, Dust, Electronic Devices, and Hands with Implications for Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8186–8197. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00229.
- 23.Binder, S.; Sokal, D.; Maughan, D. Estimating Soil Ingestion: The Use of Tracer Elements in Estimating the Amount of Soil Ingested by Young Children. Arch. Environ. Health 1986, 41, 341–345. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1986.9935776.
- 24.Moya, J.; Phillips, L. A review of soil and dust ingestion studies for children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 545–554. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2014.17.
- 25.Van Wijnen, J.H.; Clausing, P.; Brunekreef, B. Estimated Soil Ingestion by Children. Environ. Res. 1990, 51, 147–162. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp930.
- 26.Calabrese, E.; Barnes, R.; Stanek, E.; Pastides, H.; Gilbert, C.; Veneman, P.; Wang, X.; Lásztity, A.; Kostecki, P. How much soil do young children ingest: An epidemiologic study. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1989, 10, 123−137. https://doi.org/10.1016/0273-2300(89)90019-6.
- 27.Von Lindern, I.; Spalinger, S.; Stifelman, M.L.; Stanek, L.W.; Bartrem, C. Estimating Children’s Soil/Dust Ingestion Rates through Retrospective Analyses of Blood Lead Biomonitoring from the Bunker Hill Superfund Site in Idaho. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1462–1470. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1510144.
- 28.Wilson, R.; Jones-Otazo, H.; Petrovic, S.; Mitchell, I.; Bonvalot, Y.; Williams, D.; Richardson, G.M. Revisiting Dust and Soil Ingestion Rates Based on Hand-to-Mouth Transfer. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2013, 19, 158–188. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2012.685807.
- 29.Kwong, L.H.; Ercumen, A.; Pickering, A.J.; Unicomb, L.; Davis, J.; Luby, S.P. Age-related changes to environmental exposure: Variation in the frequency that young children place hands and objects in their mouths. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 30, 205–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-019-0115-8.
- 30.Smolders, E.; Roels, L.; Kuhangana, T.C.; Coorevits, K.; Vassilieva, E.; Nemery, B.; Lubaba Nkulu, C.B. Unprecedentedly High Dust Ingestion Estimates for the General Population in a Mining District of DR Congo. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 7851–7858. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b01973.
- 31.Ali, N.; Ali, L.; Mehdi, T.; Dirtu, A.C.; Al-Shammari, F.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Levels and profiles of organochlorines and flame retardants in car and house dust from Kuwait and Pakistan: Implication for human exposure via dust ingestion. Environ. Int. 2013, 55, 62–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2013.02.001.
- 32.Chen, H.; Han, X.; Zhu, C.; Du, B.; Tan, L.; He, R.; Shen, M.; Liu, L.-Y.; Zeng, L. Identification of Fluorescent Brighteners as Another Emerging Class of Abundant, Ubiquitous Pollutants in the Indoor Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10131–10140. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c03082.
- 33.Balza, J.; Awoyinka, I.; Kaeppler, C.; Cusatis, R.; Flynn, K.E. Lead poisoning in refugee children living in the United States: A systematic review of case studies. Hyg. Environ. Health Adv. 2023, 6, 100057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heha.2023.100057.
- 34.Ogunbiyi, O.D.; Cappelini, L.T.D.; Monem, M.; Mejias, E.; George, F.; Gardinali, P.; Bagner, D.M.; Quinete, N. Innovative non-targeted screening approach using High-resolution mass spectrometry for the screening of organic chemicals and identification of specific tracers of soil and dust exposure in children. J. Hazar. Mater. 2024, 469, 134025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134025.
- 35.Doyle, J.R.; Blais, J.M.; Holmes, R.D.; White, P.A. A soil ingestion pilot study of a population following a traditional lifestyle typical of rural or wilderness areas. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 424, 110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.043.
- 36.Jones-Otazo, H.A.; Clarke, J.P.; Diamond, M.L.; Archbold, J.A.; Ferguson, G.; Harner, T.; Richardson, G.M.; Ryan, J.J.; Wilford, B. Is House Dust the Missing Exposure Pathway for PBDEs? An Analysis of the Urban Fate and Human Exposure to PBDEs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5121–5130. https://doi.org/10.1021/es048267b.
- 37.Li, L.; Hughes, L.; Arnot, J.A. Addressing uncertainty in mouthing-mediated ingestion of chemicals on indoor surfaces, objects, and dust. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106266.
- 38.Davis, S.; Mirick, D.K. Soil ingestion in children and adults in the same family. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 63–75. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jea.7500438.
- 39.Özkaynak, H.; Xue, J.; Zartarian, V.G.; Glen, G.; Smith, L. Modeled Estimates of Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates for Children. Risk Anal. 2011, 31, 592–608. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2010.01524.x.
- 40.Kwong, L.H.; Ercumen, A.; Pickering, A.J.; Unicomb, L.; Davis, J.; Leckie, J.O.; Luby, S.P. Soil ingestion among young children in rural Bangladesh. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 31, 82–93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-019-0177-7.
- 41.Wang, Y.L.; Tsou, M.C.M.; Pan, K.H.; Özkaynak, H.; Dang, W.; Hsi, H.C.; Chien, L.C. Estimation of Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates from the Stochastic Human Exposure and Dose Simulation Soil and Dust Model for Children in Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 11805–11813. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c00706.
- 42.Gong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Lin, C.; Xu, D.; Duan, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J. Is hand-to-mouth contact the main pathway of children’s soil and dust intake? Environ. Geochem. Health. 2022, 44, 1567–1580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-021-00830-4.
- 43.Özkaynak, H.; Glen, G.; Cohen, J.; Hubbard, H.; Thomas, K.; Phillips, L.; Tulve, N. Model based prediction of age-specific soil and dust ingestion rates for children. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 32, 472–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41370-021-00406-5.
- 44.Stanek III, E.J.; Calabrese, E.J.; Xu, B. Meta-Analysis of Mass-Balance Studies of Soil Ingestion in Children. Risk Anal. 2012, 32, 433–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2011.01673.x.
- 45.Davis, S.; Waller, P.; Buschbom, R.; Ballou, J.; White, P. Quantitative Estimates of Soil Ingestion in Normal Children between the Ages of 2 and 7 Years: Population-based Estimates Using Aluminum, Silicon, and Titanium as Soil Tracer Elements. Arch. Environ. Health 1990, 45, 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1080/00039896.1990.9935935.
- 46.Stanek, E.J.; Calabrese, E.J. Daily Estimates of Soil Ingestion in Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 276–285. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.95103276.
- 47.Calabrese, E.J.; Stanek III, E.J.; Pekow, P.; Barnes, R.M. Soil ingestion estimates for children residing on a superfund site. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 36, 258–268. https://doi.org/10.1006/eesa.1996.1511.
- 48.Irvine, G.; Doyle, J.R.; White, P.A.; Blais, J.M. Soil ingestion rate determination in a rural population of Alberta, Canada practicing a wilderness lifestyle. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470, 138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.037.
- 49.Chien, L.-C.; Tsou, M.-C.; Hsi, H.-C.; Beamer, P.; Bradham, K.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Jien, S.-H.; Jiang, C.-B.; Dang, W.; Özkaynak, H. Soil ingestion rates for children under 3 years old in Taiwan. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 27, 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2015.61.
- 50.Lin, C.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Cui, X.Y.; Xu, D.Q.; Cheng, H.G.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Chai, T.Y.; Duan, X.L.; Liu, X.T.; et al. Estimates of Soil Ingestion in a Population of Chinese Children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 077002. https://doi.org/10.1289/Ehp930.
- 51.Wang, B.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.Q.; Cheng, H.G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.T.; Ma, J. Effects of geography, age, and gender on Chinese children’s soil ingestion rate. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1983–1989. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1435255.
- 52.Wang, B.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, X.L.; Xu, D.Q.; Cheng, H.G.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.T.; Ma, J.; Ma, J.W.; et al. A soil ingestion pilot study for teenage children in China. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.067.
- 53.Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Qi, Z.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Tao, L. Estimation of Children’s Soil and Dust Ingestion Rates and Health Risk at E-Waste Dismantling Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7332. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19127332.
- 54.Beamer, P.; Key, M.E.; Ferguson, A.C.; Canales, R.A.; Auyeung, W.; James, O. Quantified activity pattern data from 6 to 27-month-old farmworker children for use in exposure assessment. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2008.07.007.
- 55.Lopez-Galvez, N.; Claude, J.; Wong, P.T.Y.; Bradman, A.; Hyland, C.; Castorina, R.; Canales, R.A.; Billheimer, D.; Torabzadeh, E.; Leckie, J.O.; et al. Quantification and Analysis of Micro-Level Activities Data from Children Aged 1–12 Years Old for Use in the Assessments of Exposure to Recycled Tire on Turf and Playgrounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042483.
- 56.Wang, S.Y.; Ma, L.; Pan, L.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Wang, B.B.; Duan, X.L. Quantification of soil/dust (SD) on the hands of children from Hubei Province, China using hand wipes. Ecotox Environ Safe 2015, 120, 193–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.06.006.
- 57.Doyle, J.R.; Blais, J.M.; White, P.A. A survey of the traditional food consumption that may contribute to enhanced soil ingestion in a Canadian First Nation community. Sci. Total. Environ. 2012, 424, 104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.044.
- 58.Geissler, P.W.; Mwaniki, D.L.; Thiong’o, F.; Friis, H. Geophagy among school children in Western Kenya. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2008, 2, 624–630. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3156.1997.d01-345.x.
- 59.Kwong, L.H.; Ercumen, A.; Pickering, A.J.; Unicomb, L.; Davis, J.; Luby, S.P. Hand- and Object-Mouthing of Rural Bangladeshi Children 3-18 Months Old. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph13060563.
- 60.Day, J.P.; Hart, M.; Robinson, M.S. Lead in urban street dust. Nature 1975, 253, 343–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/253343a0.
- 61.Duggan, M.J.; William, S. Lead in dust in city sereets. Sci. Total Environ. 1977, 7, 91–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-9697(77)90019-5.
- 62.Clausing, P.; Brunekreef, B.; van Wijnen, J.H. A method for estimating soil ingestion by children. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1987, 59, 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00377681.
- 63.Bothe, M. Quantifizierung der Ingestion von Boden durch Kinder; Bundesministerium für Umwelt, Naturschutz und Reaktorsicherheit: Dresden, Germany, 2004; p. 647. https://doi.org/2004-647-quantifizierung-der-ingestion-von-boden-durch-kinder.
- 64.Xue, J.P.; Zartarian, V.; Moya, J.; Freeman, N.; Beamer, P.; Black, K.; Tulve, N.; Shalat, S. A meta-analysis of children’s hand-to-mouth frequency data for estimating nondietary ingestion exposure. Risk Anal. 2007, 27, 411–420. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2007.00893.x.
- 65.Tsou, M.-C.; Özkaynak, H.; Beamer, P.; Dang, W.; Hsi, H.-C.; Jiang, C.-B.; Chien, L.-C. Mouthing activity data for children age 3 to < 6 years old and fraction of hand area mouthed for children age <6 years old in Taiwan. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 28, 182–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2016.87.
- 66.Cao, Z.G.; Xu, F.C.; Li, W.C.; Sun, J.H.; Shen, M.H.; Su, X.F.; Feng, J.L.; Yu, G.; Covaci, A. Seasonal and Particle Size-Dependent Variations of Hexabromocyclododecanes in Settled Dust: Implications for Sampling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11151–11157. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01717.
- 67.Cao, Z.G.; Yu, G.; Chen, Y.S.; Cao, Q.M.; Fiedler, H.; Deng, S.B.; Huang, J.; Wang, B. Particle size: A missing factor in risk assessment of human exposure to toxic chemicals in settled indoor dust. Environ. Int. 2012, 49, 24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2012.08.010.
- 68.Cohen Hubal, E.A.; Sheldon, L.S.; Burke, J.M.; McCurdy, T.R.; Berry, M.R.; Rigas, M.L.; Zartarian, V.G.; Freeman, N.C. Children’s Exposure Assessment: A Review of Factors Influencing Children’s Exposure, and the Data Available to Characterize and Assess That Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 475–486. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.108-1638158.
- 69.Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Yoshinaga, J.; Tanaka, A.; Shibata, Y. Size distributions of soil particles adhered to children’s hands. Arch. Environ. Con. Tox. 2006, 51, 157–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-005-7012-y.
- 70.Ma, J.; Pan, L.B.; Wang, Q.; Lin, C.Y.; Duan, X.L.; Hou, H. Estimation of the daily soil/dust (SD) ingestion rate of children from Gansu Province, China via hand-to-mouth contact using tracer elements. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2018, 40, 295–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-016-9906-1.
- 71.Cao, Z.G.; Wang, M.M.; Chen, Q.Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Dong, W.J.; Yang, T.F.; Yan, G.X.; Zhang, X.; Pi, Y.Q.; Xi, B.Y.; et al. Preliminary assessment on exposure of four typical populations to potentially toxic metals by means of skin wipes under the influence of haze pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 886–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.181.
- 72.Man, M.Q.; Xin, S.J.; Song, S.P.; Cho, S.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Tu, C.X.; Feingold, K.R.; Elias, P.M. Variation of Skin Surface pH, Sebum Content and Stratum Corneum Hydration with Age and Gender in a Large Chinese Population. Skin Pharmacol. Phys. 2009, 22, 190–199. https://doi.org/10.1159/000231524.
- 73.Doyle, J.R.; Blais, J.M.; White, P.A. Mass balance soil ingestion estimating methods and their application to inhabitants of rural and wilderness areas: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 2181–2188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.02.007.
- 74.Hogan, K.; Marcus, A.; Smith, R.; White, P. Integrated exposure uptake biokinetic model for lead in children: Empirical comparisons with epidemiologic data. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106, 1557–1567. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.98106s61557.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


