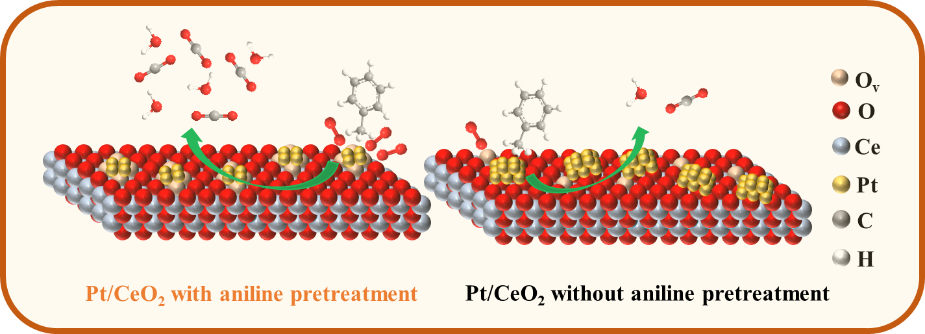
- The aniline was effectively utilized to modify various Pt/CeO₂ catalysts
- Aniline pretreatment strengthens the SMSI in Pt/CeO₂ catalyst
- The 0.9Pt/CeO₂-A catalyst exhibits excellent activity and stability for toluene catalytic oxidation
- Open Access
- Article
- Dengfeng Yan 1, *, †,
- Zhentao Feng 2, †,
- Yuhao Wang 3,
- Xudong Li 1,
- Siyuan Gao 1,
- Daiqi Ye 4, *
Author Information
Received: 28 May 2025 | Revised: 08 Jul 2025 | Accepted: 29 Jul 2025 | Published: 07 Aug 2025
Highlights
Abstract
A comprehensive study was conducted to explore an innovative strategy aimed at enhancing the catalytic activity and longevity of Pt-supported CeO2 nanocatalysts through the pretreatment with aniline. The introduction of aniline was found to effectively induce and strengthen the strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) within the Pt-supported CeO2 nanocatalysts, yielding a substantial increase in catalytic performance. Specifically, the T90 value for the 0.9Pt/CeO2-A catalyst was determined to be 149 °C when subjected to a toluene concentration of 1000 ppm in a dry air mixture at a weight hourly space velocity of 48,000 mL g−1 h−1. Extensive experimental analyses conducted using techniques such as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and visible Raman spectroscopy revealed that the modification via aniline significantly alters the physicochemical properties of the Pt/CeO2 system. Notable changes included an increase in the concentration of Pt0 and Ce3+ ions, a reduction in Pt particle size, and a corresponding increase in surface oxygen vacancies. These modifications are posited to be pivotal in the enhancement of both catalytic activity and durability. The findings of this investigation suggest that the methodological approach delineated herein may represent a universal strategy for augmenting the activity and stability of other noble metal-supported CeO2 nanocatalysts.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
volatile organic compounds | Pt/CeO2 | metal-support interaction | catalytic combustion | aniline pretreatment
References
- 1.Mu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Z.; et al. Two-year online measurements of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at four sites in a Chinese city: Significant impact of petrochemical industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159951.
- 2.Liu, Y.; Yin, S.; Zhang, S.; et al. Drivers and impacts of decreasing concentrations of atmospheric volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in Beijing during 2016–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167847.
- 3.Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Environmental and human health impacts of volatile organic compounds: A perspective review. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137489.
- 4.Pye, H.O.T.; Appel, K.W.; Seltzer, K.M.; et al. Human-Health Impacts of Controlling Secondary Air Pollution Precursors. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 96–101.
- 5.Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Nie, L.; et al. A review of whole-process control of industrial volatile organic compounds in China. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 123, 127–139.
- 6.Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wei, L.; et al. Recent progress on VOC pollution control via the catalytic method. Chin. J. Catal. 2024, 61, 71–96.
- 7.Kim, H.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; et al. Noble-Metal-Based Catalytic Oxidation Technology Trends for Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Removal. Catalysts 2022, 12, 63.
- 8.Lou, B.; Shakoor, N.; Adeel, M.; et al. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds by non-noble metal catalyst: Current advancement and future prospectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132523.
- 9.
Yan, D.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; et al. Tuning the Metal–Support Interaction by Modulating CeO2 Oxygen Vacancies to Enhance the Toluene Oxidation Activity of Pt/CeO2 Catalysts. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 11393–11405.
- 10.
Peng, R.; Wen, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. Catalytic Oxidation of Toluene over Pt/CeO2 Catalysts: A Double-Edged Sword Effect of Strong Metal–Support Interaction. Langmuir 2024, 40, 13984–13994.
- 11.
Peng, R.; Sun, X.; Li, S.; et al. Shape effect of Pt/CeO2 catalysts on the catalytic oxidation of toluene. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1234–1246.
- 12.van Deelen, T.W.; Hernández Mejía, C.; de Jong, K.P. Control of metal-support interactions in heterogeneous catalysts to enhance activity and selectivity. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 955–970.
- 13.Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, K.; et al. Metal–Support Interactions in Metal/Oxide Catalysts and Oxide–Metal Interactions in Oxide/Metal Inverse Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 1268–1287.
- 14.Luo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Pan, H.; et al. Strong Metal–Support Interaction in Heterogeneous Catalysts. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201395.
- 15.
Zhang, J.; Qin, X.; Chu, X.; et al. Tuning Metal–Support Interaction of Pt-CeO2 Catalysts for Enhanced Oxidation Reactivity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16687–16698.
- 16.Eliasson, H.; Niu, Y.; Palmer, R.E.; et al. Support-facet-dependent morphology of small Pt particles on ceria. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 19091–19098.
- 17.Castro-Latorre, P.; Neyman, K.M.; Bruix, A. Systematic Characterization of Electronic Metal–Support Interactions in Ceria-Supported Pt Particles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 17700–17710.
- 18.Ge, S.; Fan, W.; Tang, X.; et al. Revealing the Size Effect of Ceria Nanocube-Supported Platinum Nanoparticles in Complete Propane Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 2532–2544.
- 19.Yang, B.; Chen, X.; Guo, L.; et al. Catalyst architecture for metal–support interactions and its effects on heterogeneous reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 19861–19884.
- 20.Wang, T.; Hu, J.; Ouyang, R.; et al. Nature of metal-support interaction for metal catalysts on oxide supports. Science 2024, 386, 915–920.
- 21.Pu, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, M. Engineering Heterogeneous Catalysis with Strong Metal–Support Interactions: Characterization, Theory and Manipulation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202212278.
- 22.Ye, S.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Highly stable single Pt atomic sites anchored on aniline-stacked graphene for hydrogen evolution reaction. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 1000–1007.
- 23.Zhan, W.; He, Q.; Liu, X.; et al. A Sacrificial Coating Strategy Toward Enhancement of Metal–Support Interaction for Ultrastable Au Nanocatalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16130–16139.
- 24.
Sun, X.-C.; Yuan, K.; Hua, W.-D.; et al. Weakening the Metal–Support Interactions of M/CeO2 (M = Co, Fe, Ni) Using a NH3-Treated CeO2 Support for an Enhanced Water–Gas Shift Reaction. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 11942–11954.
- 25.Matsubu, J.C.; Zhang, S.; DeRita, L.; et al. Adsorbate-mediated strong metal–support interactions in oxide-supported Rh catalysts. Nat. Chem. 2016, 9, 120–127.
- 26.
Paladugu, S.; Metz, P.C.; Luo, S.; et al. In Situ Neutron Scattering Studies on the Oxidation and Reduction of CeO2 and Pt–CeO2 Nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 3689–3697.
- 27.
Huang, H.; Dai, Q.; Wang, X. Morphology effect of Ru/CeO2 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 158, 96–105.
- 28.
Yang, Q.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Tunable metal-support interaction of Pt/CeO2 catalyst via surfactant-assisted strategy: Insight into the total oxidation of CO and toluene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127601.
- 29.Chen, P.; Khetan, A.; Yang, F.; et al. Experimental and Theoretical Understanding of Nitrogen-Doping-Induced Strong Metal–Support Interactions in Pd/TiO2 Catalysts for Nitrobenzene Hydrogenation. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 1197–1206.
- 30.
Chu, Y. Y.; Cao, J. ; Daia, Z.; et al. A novel Pt/CeO2 catalyst coated with nitrogen-doped carbon with excellent performance for DMFCs. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4038–4044.
- 31.Bi, W.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; et al. In-situ synthesized surface N-doped Pt/TiO2 via flame spray pyrolysis with enhanced thermal stability for CO catalytic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 481, 360–368.
- 32.
Yan, D.; Li, T.; Liu, P.; et al. In-situ atmosphere thermal pyrolysis of spindle-like Ce(OH)CO3 to fabricate Pt/CeO2 catalysts: Enhancing Pt–O–Ce bond intensity and boosting toluene degradation. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130658.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


