- Exposure routes influence the internal dose, distribution, and metabolism of pollutants
- Aggregate exposure assessment calls for weight-based integration of multiple routes
- Probabilistic parameters and bioavailability data improve the accuracy of risk assessment
- Open Access
- Perspective
Advancing Health Risk Assessment: Integrating Exposure Routes and Bioavailability to Quantify Internal Dose
Author Information
Received: 04 Oct 2025 | Revised: 20 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 21 Nov 2025 | Published: 24 Nov 2025
Highlights
Abstract
As the linkage between environmental pollution and health outcomes, exposure routes characterize how pollutants enter the human body, constituting the foundation of health risk assessment. Pollutants primarily enter body through three major routes: ingestion, inhalation, and dermal contact. The exposure routes govern the internal dose, tissue distribution, and metabolic fate of various environmental pollutants, fundamentally shaping the nature and magnitude of associate health risks. From the perspective of exposure routes, current risk assessment models exist several limitations, including the lack of systematic integration across multiple exposure routes; reliance on fixed default exposure parameters that fail to reflect population heterogeneity; dependence on external exposure dose such as daily intake, without accounting for bioavailability; and omission of special exposure routes. Therefore, modern health risk assessment frameworks must evolve to incorporate: integrated multi-route exposure assessments, probabilistic parameter distributions, and bioavailability-corrected effective dose. Only through such comprehensive improvements can achieve accurate characterization of exposure risks and provide a robust scientific basis for precision prevention and control.
Graphical Abstract
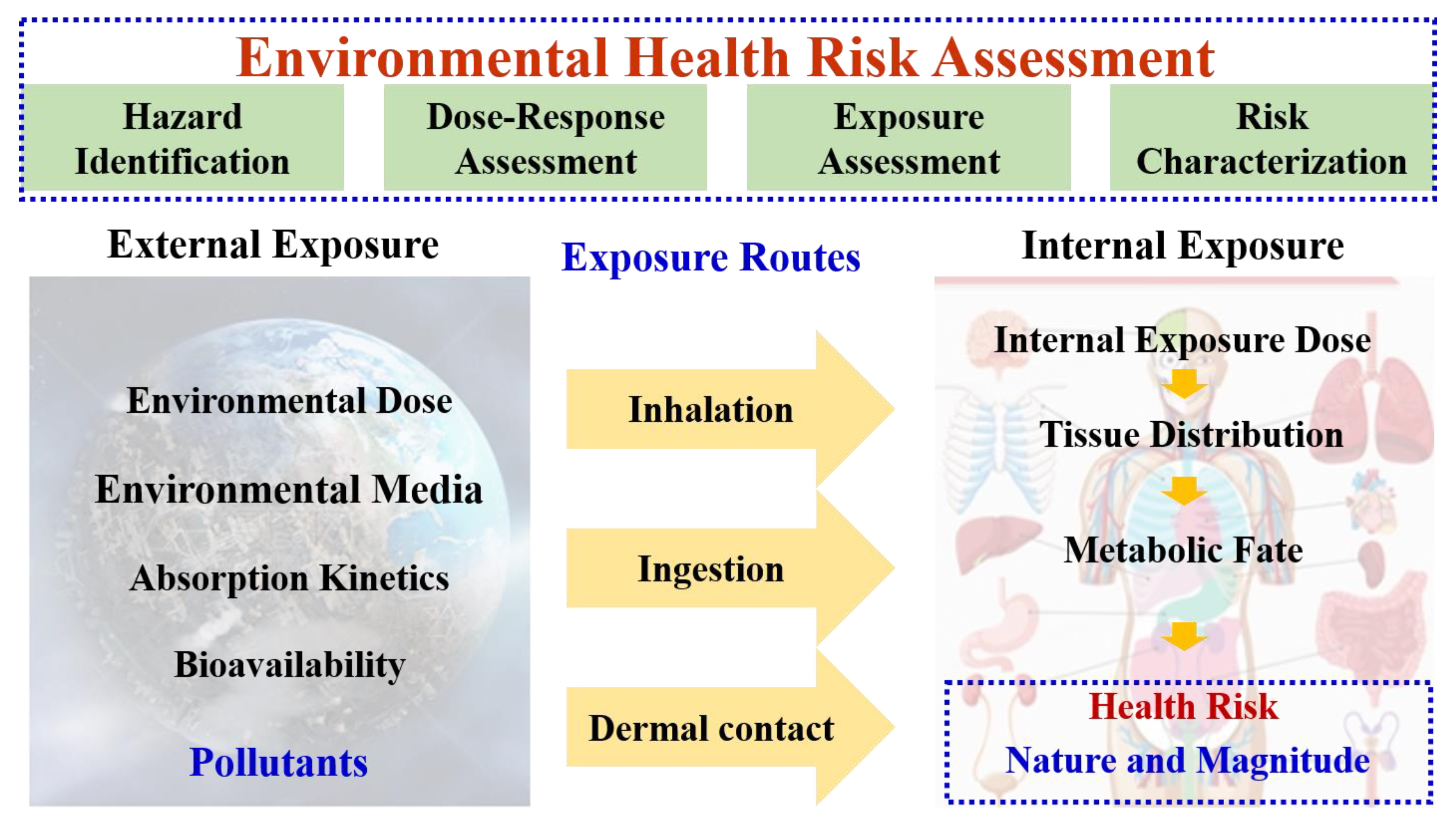
Keywords
exposure route | health risk assessment | environmental pollutant | exposure parameter | bioavailability
References
- 1.Fuller, R.; Landrigan, P.J.; Balakrishnan, K. Pollution and health: A progress update. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, E535–E547.
- 2.Argentieri, M.A.; Amin, N.; Nevado-Holgado, A.J.; et al. Integrating the environmental and genetic architectures of aging and mortality. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1016–1025.
- 3.Nawab, A.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, M.T.; et al. Human exposure to microplastics: A review on exposure routes and public health impacts. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100487.
- 4.He, A.; Liang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. A critical review of populations with occupational exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances: External exposome, internal exposure levels, and health effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 10715–10733.
- 5.Weschler, C.J.; Bekö, G.; Koch, H.M.; et al. Transdermal uptake of diethyl phthalate and di(n-butyl) phthalate directly from air: Experimental verification. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 928–934.
- 6.González, N.; Domingo, J.L. PFC/PFAS concentrations in human milk and infant exposure through lactation: A comprehensive review of the scientific literature. Arch. Toxicol. 2025, 99, 1843–1864.
- 7.Bhardwaj, A.; Verma, S.; Agnihotri, A.; et al. Protein based nanoparticles for pulmonary drug delivery: Advances, challenges, and future perspectives. J. Nanopart. Res. 2025, 27, 176.
- 8.Oberdörster, C.; Maynard, A.; Donaldson, K.; et al. Principles for characterizing the potential human health effects from exposure to nanomaterials: Elements of a screening strategy. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2005, 2, 8.
- 9.Zhu, Y.M.; Pan, X.Y.; Jia, Y.B.; et al. Exploring route-specific pharmacokinetics of PFAS in mice by coupling in vivo tests and physiologically based toxicokinetic models. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 127012.
- 10.Luo, N.; Gao, Y.P.; Wang, M.; et al. Bidirectional role of synthetic musk tonalide as photosensitizer and activator on amino acids: Formation of sensitizer imine at aqueous chemistry interface of skin. Eco-Environ. Health 2023, 2, 32–39.
- 11.Zhang, Y.; Hu, Q.; Fu, J.Q.; et al. Influence of exposure pathways on tissue distribution and health impact of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon derivatives. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 150–167.
- 12.Tang, J.; Ma, S.T.; Hu, X.; et al. Handwipes as indicators to assess organophosphate flame retardants exposure and thyroid hormone effects in e-waste dismantlers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130248.
- 13.Kornbausch, N.; Debong, M.W.; Buettner, A.; et al. Odorant metabolism in humans. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202202866.
- 14.Wang, M.; Gao, Y.P.; Li, G.Y.; et al. Increased adverse effects during metabolic transformation of short-chain chlorinated paraffins by cytochrome P450: A theoretical insight into 1-chlorodecane. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124391.
- 15.Ding, X.X.; Kaminsky, L.S. Human extrahepatic cytochromes P450: Function in xenobiotic metabolism and tissue-selective chemical toxicity in the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 43, 149–173.
- 16.Castell, J.V.; Donato, M.T.; Gómez-Lechón, M.J. Metabolism and bioactivation of toxicants in the lung: The in vitro cellular approach. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2005, 57, 189–204.
- 17.Shin, D.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Jang, Y.; et al. Adverse human health effects of chromium by exposure route: A comprehensive review based on toxicogenomic approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3410.
- 18.Yao, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.L.; et al. A review of sources, pathways, and toxic effects of human exposure to benzophenone ultraviolet light filters. Eco-Environ. Health 2024, 3, 30–44.
- 19.Tian, X.W.; Yang, Q.Q.; Zhao, Y.Q.; et al. Comprehensive multidimensional analysis of metal(loid)-containing dust in plastic sports facilities: Insights into the potential sources and health risks. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 23212–23221.
- 20.Wang, M.M.; Li, Y.Y.; Lv, Y.Y.; et al. Quantitative characterization of resident' exposure to typical semi-volatile organic compounds (SVOCs) around a non-ferrous metal smelting plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133353.
- 21.Juhasz, A.L.; Smith, E.; Weber, J.; et al. In vitro assessment of arsenic bioaccessibility in contaminated (anthropogenic and geogenic) soils. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 69–78.
- 22.Zhu, Y.M.; Jia, Y.B.; Wang, X.; et al. Mechanisms underlying the impacts of lipids on the diverse bioavailability of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in foods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 3613–3622.
- 23.Kreyling, W.G.; Möller, W.; Holzwarth, U.; et al. Age-dependent rat lung deposition patterns of inhaled 20 manometer gold nanoparticles and their quantitative biokinetics in adult rats. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7771–7790.
- 24.Lacroix, G.; Koch, W.; Ritter, D.; et al. Air-liquid interface in vitro models for respiratory toxicology research: Consensus workshop and recommendations. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 4, 91–106.
- 25.Zheng, J.Y.; Ding, L.X.; Yi, J.J.; et al. Revealing the potential effects of oil phase on the stability and bioavailability of astaxanthin contained in Pickering emulsions: In vivo, in vitro and molecular dynamics simulation analysis. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139935.
- 26.Zhang, Y.; Tang, M.; Zhang, S.; et al. Mapping blood lead levels in China during 1980–2040 with machine learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 7270–7278.
- 27.Gansu Provincial Investigation Team. Report on the Investigation and Handling of Abnormal Blood Lead Levels in Children at Heshi Peixin Kindergarten in Maiji District, Tianshui City. 2025. Available online: https://www.gansu.gov.cn/gsszf/gsyw/202507/174177765.shtml (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- 28.Tang, J.; Lin, M.Q.; Ma, S.T.; et al. Identifying dermal uptake as a significant pathway for human exposure to typical semivolatile organic compounds in an e-waste dismantling site: The relationship of contaminant levels in handwipes and urine metabolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14026–14036.
- 29.Li, Q.L.; Yuan, M.; Shangguan, J.F.; et al. Insights into Persistent Toxic Substances in Protective Cases of Mobile Phones: Occurrence, Health Risks, and Implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6076–6086.
- 30.Pouzou, J.G.; Cullen, A.C.; Yost, M.G.; et al. Comparative probabilistic assessment of occupational pesticide exposures based on regulatory assessments. Risk Anal. 2018, 38, 1223–1238.
- 31.An, T.; Gu, J.; Li, G. Toward an environmentally friendly and healthier world. Global Environ. Sci. 2025, 1, 1–2.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


