- The hetero-wetting nanofibrous membrane with sandwich structure was fabricated
- A novel "sieving-repulsion-adsorption" separation mechanism was proposed
- The membrane can efficiently remove oil droplets sub-150 nm (TOC less than 3 ppm)
- The membrane has superior cycle stability for oil/water emulsion separation
- Open Access
- Article
Hierarchical Sandwich-Type Hetero-Wetting Nanofibrous Membrane toward Nano-Scaled Oil/Water Emulsion Separation
- Linlin Yan 1,2,
- Mengmeng Zhang 1,
- Chen Chen 1,
- Mi Zhou 1,
- Kai Wang 1,2,
- Yuhua Gao 3,
- Pengcheng Liu 2,
- Dalong Li 1,
- Xiquan Cheng 1,2,*
Author Information
Received: 10 Oct 2025 | Revised: 30 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 23 Dec 2025 | Published: 14 Jan 2026
Highlights
Abstract
The ever-increasing discharge of oily sewage poses serious threats to marine ecosystem and human health, which has become a severe environmental problem globally. With high porosity, interconnected porous architectures and tunable surface wettability, superwetting nanofiber membranes have been proven effective in remediating oily sewage. However, constrained by their micron-scale pores, nanofiber membranes demonstrate insufficient separation efficiency for sub-150 nm emulsified oil droplets, making it difficult to meet the standards of regulations for discharging oily sewage in various countries and regions. Herein, a “sieving-repulsion-adsorption” mechanism was proposed to break the limitation of “trade-off” between permeability and selectivity via the designed hetero-wetting nanofiber membrane, which was engineered by intercalating discrete hydrophobic polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) microdomains between hydrophilic polyethylene oxide (PEO)-based hydrogels modified polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofiber membranes. The hetero-wetting architecture improves water transport under the synergistic effect of hydrophobic/hydrophilic layers while captures the tiny oil droplets via hydrophobic/oleophilic PDMS microdomains, thereby achieving high emulsion permeance of 22,308 L⋅m−2⋅h−1⋅bar−1 with high separation efficiency of 99.97% and total organic carbon (TOC) content less than 3 ppm. Notably, the membrane demonstrates exceptional fouling resistance (94.6% permeance recovery) and cyclic stability, outperforming most previously reported state-of-the-art nanofiber membranes. This sandwich-type hetero-wetting nanofibrous membrane provides new insights into advanced membranes fabrication for low-carbon and efficient treatment of nano-scaled oil-in-water emulsions.
Graphical Abstract
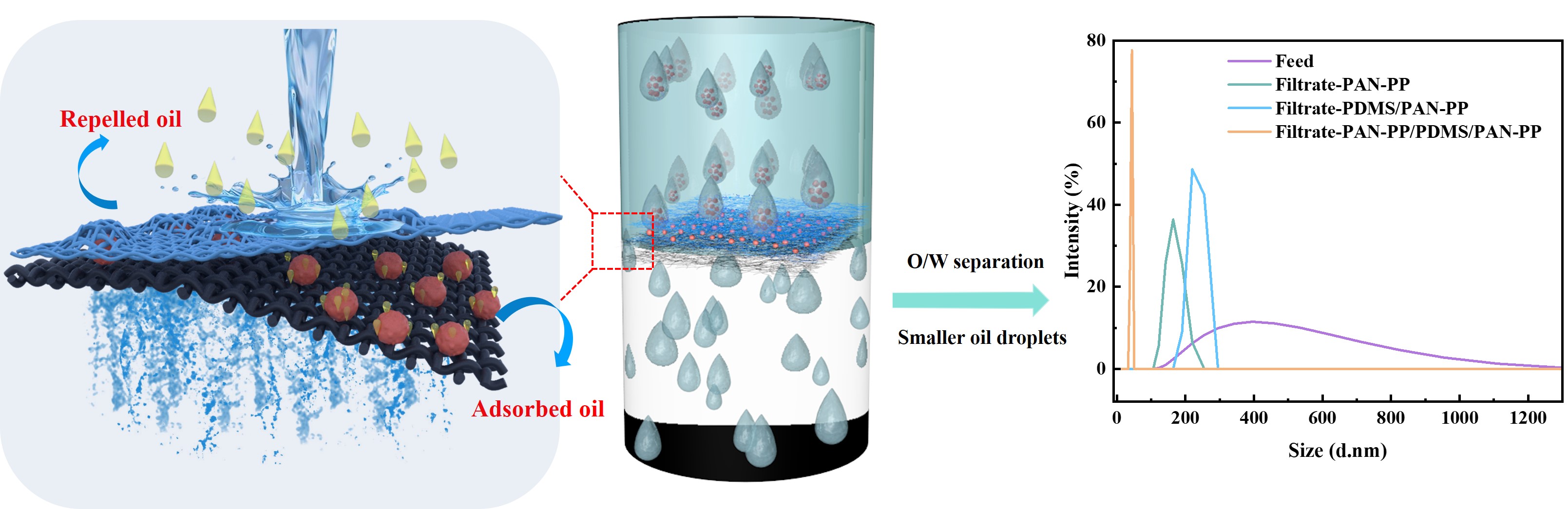
Keywords
hetero-wetting membranes | electrospinning nanofiber | sieving-repulsion-adsorption mechanism | nano-scaled oil/water emulsions separation
References
- 1.
Wang, Z.; Guo, P.; Heng, L.; et al. Nano/Submicrometer-Emulsion Oily Wastewater Treatment Inspired by Plant Transpiration. Matter 2021, 4, 1274–1286.
- 2.
He, L.; Qi, X.; Wei, W.; et al. Biomass-Activated Carbon-Based Superhydrophobic Sponge with Photothermal Properties for Adsorptive Separation of Waste Oil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 135222.
- 3.
Cui, W.; Fan, T.; Li, Y.; et al. Robust Functional Janus Nanofibrous Membranes for Efficient Harsh Environmental Air Filtration and Oil/Water Separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 121018.
- 4.
Tong, Y.; Qi, M.; Sun, P.; et al. Estimation of Unintended Treated Wastewater Contributions to Streams in the Yangtze River Basin and the Potential Human Health and Ecological Risk Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5590–5601.
- 5.
Tanudjaja, H.J.; Hejase, C.A.; Tarabara, V.V.; et al. Membrane-Based Separation for Oily Wastewater: A Practical Perspective. Water Res. 2019, 156, 347–365.
- 6.
Peterson, C.H.; Rice, S.D.; Short, J.W.; et al. Long-Term Ecosystem Response to the Exxon Valdez Oil Spill. Science 2003, 302, 2082–2086.
- 7.
Wang, Y.; Villalobos, L.F.; Liang, L.; et al. Scalable Weaving of Resilient Membranes with On-Demand Superwettability for High-Performance Nanoemulsion Separations. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadn3289.
- 8.
Wu, S.; Lu, F.; Deng, R.; et al. Solar-Driven Evaporators with Thin-Film-Composite Architecture Inspired by Plant Roots for Treating Concentrated Nano-/Submicrometer Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 51555–51563.
- 9.
Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; et al. A Simple One-Step Method to Synthesize PVDF-PG/KH792 Membrane for Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 101996.
- 10.
Lin, Y.; Yu, F.; Yu, Z.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Superhydrophilic and Antibacterial Membranes for Effective Gravity-Driven Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126919.
- 11.
Wang, B.; Luo, X.; Feng, Y.; et al. Turbo Synergistic Oily Wastewater Remediation in Bio Inspired Cone Array Barrel. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2204244.
- 12.
Chen, D.; Bao, M.; Ge, H.; et al. A Hydrogel Coated Wood Membrane with Intelligent Oil Pollution Detection for Emulsion Separation. Small 2024, 20, 2401719.
- 13.
Zhang, J.; Peng, K.; Xu, Z.-K.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on the Behavior and Evolution of Oil Droplets during Oil/Water Separation by Membranes. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 319, 102971.
- 14.
Ge, J.; Zong, D.; Jin, Q.; et al. Biomimetic and Superwettable Nanofibrous Skins for Highly Efficient Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705051.
- 15.
Guo, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, H.; et al. Janus Channel of Membranes Enables Concurrent Oil and Water Recovery from Emulsions. Science 2024, 386, 654–659.
- 16.
Meng, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Electrospun Nanofibrous Composite Membranes for Separations. Acc. Mater. Res. 2023, 4, 180–192.
- 17.
Cheng, X.; Li, T.; Yan, L.; et al. Biodegradable Electrospinning Superhydrophilic Nanofiber Membranes for Ultrafast Oil-Water Separation. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadh8195.
- 18.
Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Nanofibres Intercalated Multilayer Membrane with Hierarchical Structure for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 288, 120672.
- 19.
Ge, J.; Ye, Y.; Yao, H.; et al. Pumping through Porous Hydrophobic/Oleophilic Materials: An Alternative Technology for Oil Spill Remediation. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 3686–3690.
- 20.
Yang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. Janus Membranes with Controllable Asymmetric Configurations for Highly Efficient Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 7907–7917.
- 21.
Hu, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, Z. Janus Hollow Fiber Membranes with Functionalized Outer Surfaces for Continuous Demulsification and Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 648, 120388.
- 22.
Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Qu, R.; et al. Asymmetric Superwetting Configuration of Janus Membranes Based on Thiol-Ene Clickable Silane Nanospheres Enabling On-Demand and Energy-Efficient Oil-Water Remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10047–10057.
- 23.
Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Gao, M.; et al. Fabrication of Janus Cellulose Nanocomposite Membrane for Various Water/Oil Separation and Selective One-Way Transmission. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106016.
- 24.
Qin, Y.; Shen, H.; Han, L.; et al. Mechanically Robust Janus Poly (Lactic Acid) Hybrid Fibrous Membranes toward Highly Efficient Switchable Separation of Surfactant-Stabilized Oil/Water Emulsions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50879–50888.
- 25.
Huang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, S.; et al. Mechanically Robust Janus Nanofibrous Membrane with Asymmetric Wettability for High Efficiency Emulsion Separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128250.
- 26.
Zeng, X.; Qian, L.; Yuan, X.; et al. Inspired by Stenocara Beetles: From Water Collection to High-Efficiency Water-in-Oil Emulsion Separation. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 760–769.
- 27.
Jiang, X.; Yang, F.; Xu, G.; et al. Smart NiAl-LHDs-Based Superwetting Janus Membrane Based on Charge Demulsification for Efficient Separation of Multiple Emulsions and Mixtures via Multi-Strategy Synergy. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124350.
- 28.
Du, L.; Quan, X.; Fan, X.; et al. Electro-Responsive Carbon Membranes with Reversible Superhydrophobicity/Superhydrophilicity Switch for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 891–899.
- 29.
Wei, X.; Naraginti, S.; Yang, X.; et al. Polydopamine Functionalized FeVO4@PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane with Superior Antifouling and Detoxification Properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154718.
- 30.
Zou, D.; Nie, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Fabrication of a MoS2@PAN Composite Membrane for Efficient Removal of Toxic Cr (VI). Desalination 2025, 600, 118460.
- 31.
Cheng, X.; Sun, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. Construction of Superhydrophilic Hierarchical Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Membranes by in Situ Asymmetry Engineering for Unprecedently Ultrafast Oil-Water Emulsion Separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 16933–16942.
- 32.
Cheng, X.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Constructing Scalable Superhydrophobic Membranes for Ultrafast Water-Oil Separation. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3500–3508.
- 33.
Zhou, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Plasma Modification of Substrate with Poly(Methylhydrosiloxane) for Enhancing the Interfacial Stability of PDMS/PAN Composite Membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 779–789.
- 34.
Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; et al. Hydrophobic Modified Activated Carbon Using PDMS for the Adsorption of VOCs in Humid Condition. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116517.
- 35.
Wang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Dufresne, A.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of Compatibility and Dispersibility in Nanocellulose-Reinforced Composites: Hansen Solubility and Raman Mapping. ACS Nano 2021, 12, 20148–20163.
- 36.
Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, S. Nonflammable and Magnetic Sponge Decorated with Polydimethylsiloxane Brush for Multitasking and Highly Efficient Oil–Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1902488.
- 37.
Shen, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, S.; et al. One-Step Electrospinning Membranes with Gradual-Transition Wettability Gradient for Directional Fluid Transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 644, 120091.
- 38.
Yang, X.; Wen, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Engineering in Situ Catalytic Cleaning Membrane via Prebiotic-Chemistry-Inspired Mineralization. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2306626.
- 39.
Zhuang, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhang, T.; et al. One-Step Fabrication of Robust Stenocara Beetle-Inspired Membrane Deriving from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Waste for Enhancing Emulsion Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 351, 128128.
- 40.
Ge, J.; Jin, Q.; Zong, D.; et al. Biomimetic Multilayer Nanofibrous Membranes with Elaborated Superwettability for Effective Purification of Emulsified Oily Wastewater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16183–16192.
- 41.
Zhong, X.; Shi, Q.; Guo, Z. Synergistic Construction of Superhydrophilic PVDF Membranes by Dual Modification Strategies for Efficient Emulsion Separation. Small 2024, 20, e2402538.
- 42.
Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, L.; et al. Biodegradable Nanofiber Membranes Based on Interpenetrating Network for Highly Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2024, 7, 197.
- 43.
Ning, D.; Lu, Z.; Tian, C.; et al. Hierarchical and Superwettable Cellulose Acetate Nanofibrous Membranes Decorated via 3D Flower-Like Layered Double Hydroxides for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127052.
- 44.
Zhou, M.; Zhou, J.; Yan, L.; et al. Engineering Superhydrophilic and Fouling-Free COF Armor for Ultrafast Oil–Water Separation. Small 2025, 21, 2505330.
- 45.
Feng, L.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Dual-Functional Layer Modified GO@SiO2 Membrane with Excellent Anti-Fouling Performance for Continuous Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126681.
- 46.
Xu, L.; Xu, T.; Liu, W.; et al. Heterogeneous Wettability Membrane for Efficient Demulsification and Separation of Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 489, 151466.
- 47.
Li, X.; Gui, Q.; Wei, Y.; et al. Novel Superwetting Nanofibrous Skins for Removing Stubborn Soluble Oil in Emulsified Wastewater. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 26127–26134.
- 48.
Zhou, M.; Tong, J.; Zhou, F.; et al. Constructing Heterogeneously Wettable Nanofiber Membrane for Highly Efficient Oil Refining. Adv. Membr. 2025, 5, 100135.
- 49.
Wu, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, L.; et al. Unidirectional Water-Penetration Composite Fibrous Film via Electrospinning. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 5996–5999.
- 50.
Yang, H.; Hou, J.; Chen, V.; et al. Janus Membranes: Exploring Duality for Advanced Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 13398–13407.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


