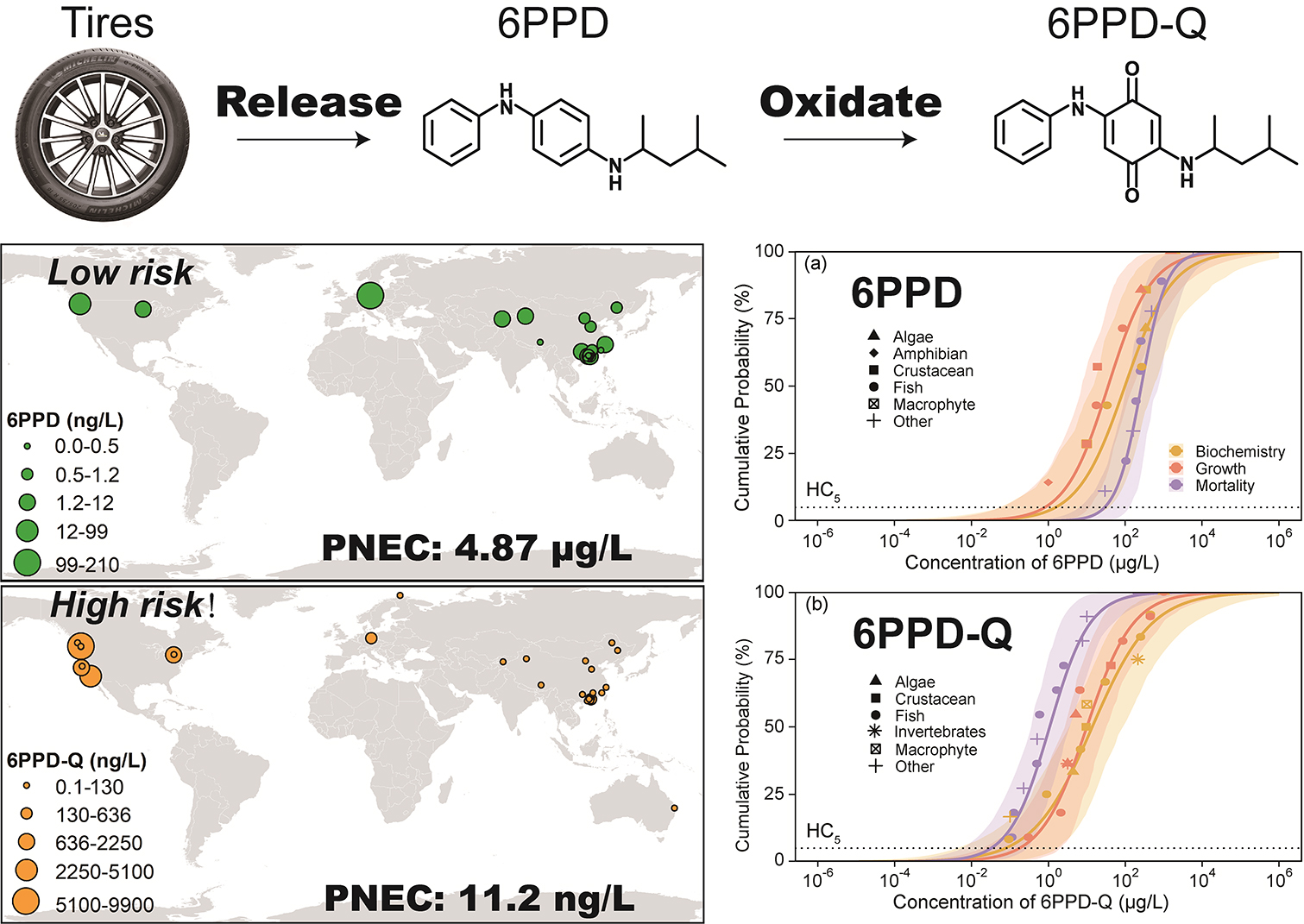
- Global SSD-based PNECs were derived for 6PPD and 6PPD-Q
- 6PPD-Q showed much higher toxicity than 6PPD, with extreme sensitivity in salmonids
- 6PPD-Q exhibited elevated probabilistic ecological risk in surface waters
- Open Access
- Article
Global Occurrence and Ecological Risk Assessment of 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone: Derivation of PNECs Using Species Sensitivity Distribution
- Yingjie Chen 1, 2, 3, †,
- Zhuo-Ying Du 3, †,
- Xiang-Yu Liu 3,
- Han-Qi Zhang 3,
- Jing-Jing Wang 3,
- Jing-Yang Wu 3,
- Bo Pang 3,
- Guang-Guo Ying 3,
- Jian-Liang Zhao 1, 2, 3, *
Author Information
Received: 15 Dec 2025 | Revised: 14 Jan 2026 | Accepted: 19 Jan 2026 | Published: 30 Jan 2026
Highlights
Abstract
Tire antioxidant N-(1,3-dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine (6PPD) and its transformation product 6PPD-quinone (6PPD-Q) have recently been recognized as emerging contaminants of global concern due to their widespread occurrence and high toxicity to aquatic organisms. Although the rapidly accumulating monitoring and toxicological data suggesting substantial ecological risks, a quantitative and cross-species assessment framework remains lacking. Here, we compiled 77 reported concentration records of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q from 21 studies worldwide and assembled 991 toxicity endpoints across 34 species to derive Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs) by species sensitivity distributions (SSDs) and probabilistic ecological risk estimates. Both compounds were ubiquitously detected in surface waters, with 6PPD-Q frequently exceeding the concentration of its parent compound. Salmonids exhibited exceptional sensitivity to 6PPD-Q, with lethal thresholds in the nanogram-per-liter range, whereas tolerance varied markedly among non-salmonid taxa. Model-averaged SSDs yielded mortality-based hazardous concentrations for 5% of species (HC5) of 24.3 µg/L for 6PPD and 0.0559 µg/L for 6PPD-Q, corresponding to PNECs of 4.87 and 0.0112 µg/L, respectively. Probabilistic risk characterization indicated negligible global risk for 6PPD, whereas 6PPD-Q exhibited elevated risk potential, with mortality-based overall risk probabilities reaching 11.4%. Risk levels followed the pattern of surface runoff > river waters > wastewater effluent, and were higher in North America and Europe than in Asia. Regional differences in species sensitivity and environmental exposure contributed to substantial uncertainties, underscoring the need for localized PNEC derivation and expanded toxicity datasets, particularly for transformation products. This study provides the first integrated global SSD-based benchmarks for 6PPD and 6PPD-Q, offering a quantitative foundation for monitoring, regulation, and ecological protection of tire-derived contaminants.
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
6PPD | 6PPD-Q | species sensitivity distribution (SSD) | Probabilistic ecological risk assessment | tire-derived contaminants
References
- 1.
Liu, Y.-H.; Mei, Y.-X.; Liang, X.-N.; et al. Small-Intensity Rainfall Triggers Greater Contamination of Rubber-Derived Chemicals in Road Stormwater Runoff from Various Functional Areas in Megalopolis Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 13056–13064.
- 2.
Liu, Y.-H.; Mei, Y.-X.; Wang, J.-Y.; et al. Precipitation Contributes to Alleviating Pollution of Rubber-Derived Chemicals in Receiving Watersheds: Combining Confluent Stormwater Runoff from Different Functional Areas. Water Res. 2024, 264, 122240.
- 3.
Chen, X.; He, T.; Yang, X.; et al. Analysis, Environmental Occurrence, Fate and Potential Toxicity of Tire Wear Compounds 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 452, 131245.
- 4.
Du, B.; Liang, B.; Li, Y.; et al. First Report on the Occurrence of N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-Phenyl-p-Phenylenediamine (6PPD) and 6PPD-Quinone as Pervasive Pollutants in Human Urine from South China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 1056–1062.
- 5.
Zeng, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; et al. Widespread Occurrence and Transport of P-Phenylenediamines and Their Quinones in Sediments across Urban Rivers, Estuaries, Coasts, and Deep-Sea Regions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2393–2403.
- 6.
Tian, Z.; Gonzalez, M.; Rideout, C.A.; et al. 6PPD-Quinone: Revised Toxicity Assessment and Quantification with a Commercial Standard. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 140–146.
- 7.
Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; et al. A Ubiquitous Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical Induces Acute Mortality in Coho Salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189.
- 8.
Ge, Y.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; et al. Environmental Concentrations of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q Cause Oxidative Damage and Alter Metabolism in Eichhornia Crassipes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175736.
- 9.
Yang, B.; Yang, Q.; Dong, J.; et al. Toxicity of 6PPD to the Stony Coral Pocillopora Damicornis in Different Developmental Stages. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 496, 139214.
- 10.
Peng, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, D.; et al. Exposure to N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-Phenyl-p-Phenylenediamine (6PPD) Affects the Growth and Development of Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113221.
- 11.
Hua, X.; Feng, X.; Liang, G.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Tire-Derived 6-PPD Quinone Causes Intestinal Toxicity by Affecting Functional State of Intestinal Barrier in Caenor-habditis Elegans. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160591.
- 12.
Fang, C.; Fang, L.; Di, S.; et al. Characterization of N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-Phenyl-p-Phenylenediamine (6PPD)-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Larval Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163595.
- 13.
Wu, J.; Cao, G.; Zhang, F.; et al. A New Toxicity Mechanism of N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-Phenyl-p-Phenylenediamine Quinone: Formation of DNA Adducts in Mammalian Cells and Aqueous Organisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161373.
- 14.
He, W.; Chao, J.; Gu, A.; et al. Evaluation of 6-PPD Quinone Toxicity on Lung of Male BALB/c Mice by Quantitative Proteomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171220.
- 15.
Klauschies, T.; Isanta-Navarro, J. The Joint Effects of Salt and 6PPD Contamination on a Freshwater Herbivore. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154675.
- 16.
Cao, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Occurrence and Fate of Substituted P-Phenylenediamine-Derived Quinones in Hong Kong Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15635–15643.
- 17.
Rauert, C.; Charlton, N.; Okoffo, E.D.; et al. Concentrations of Tire Additive Chemicals and Tire Road Wear Particles in an Australian Urban Tributary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2421–2431.
- 18.
Zhang, R.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; et al. Aquatic Environmental Fates and Risks of Benzotriazoles, Benzothiazoles, and p-Phenylenediamines in a Catchment Providing Water to a Megacity of China. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114721.
- 19.
Peter, K.T.; Gilbreath, A.; Gonzalez, M.; et al. Storms Mobilize Organophosphate Esters, Bisphenols, PFASs, and Vehicle-Derived Contaminants to San Francisco Bay Watersheds. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2024, 26, 1760–1779.
- 20.
Wei, L.-N.; Wu, N.-N.; Xu, R.; et al. First Evidence of the Bioaccumulation and Trophic Transfer of Tire Additives and Their Transformation Products in an Estuarine Food Web. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 6370–6380.
- 21.
Gredelj, A.; Barausse, A.; Grechi, L.; et al. Deriving Predicted No-Effect Concentrations (PNECs) for Emerging Contaminants in the River Po, Italy, Using Three Approaches: Assessment Factor, Species Sensitivity Distribution and AQUATOX Ecosystem Modelling. Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 66–78.
- 22.
Yanagihara, M.; Hiki, K.; Iwasaki, Y. Which Distribution to Choose for Deriving a Species Sensitivity Distribution? Implications from Analysis of Acute and Chronic Ecotoxicity Data. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116379.
- 23.
Zhang, J.; Ye, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Derivation of Hexachlorocyclohexane Toxicity Thresholds for Assessing Ecological Risks in the Surface Waters of China. Water Res. 2026, 288, 124651.
- 24.
Zeng, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Ecological Risk of Phenol on Typical Biota of the Northern Chinese River from an Integrated Probability Perspective: The Hun River as an Example. Env. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1512.
- 25.
Tao, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. ICE-SSD Model: Bridging the Ecological Risk Assessment Gap between Plasticizer and the Substitute. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 727–737.
- 26.
Binet, M.T.; Golding, L.A.; Adams, M.S.; et al. Advantages of Model Averaging of Species Sensitivity Distributions Used for Regulating Produced Water Discharges. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2024, 20, 498–517.
- 27.
Fox, D.R.; Van Dam, R.A.; Fisher, R.; et al. Recent Developments in Species Sensitivity Distribution Modeling. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 40, 293–308.
- 28.
Belanger, S.E.; Carr, G.J. SSDs Revisited: Part II—Practical Considerations in the Development and Use of Application Factors Applied to Species Sensitivity Distributions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 1526–1541.
- 29.
Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; et al. Which Micropollutants in Water Environments Deserve More Attention Globally? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13–29.
- 30.
Karjalainen, J.; Hu, X.; Mäkinen, M.; et al. Sulfate Sensitivity of Aquatic Organism in Soft Freshwaters Explored by Toxicity Tests and Species Sensitivity Distribution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 258, 114984.
- 31.
Yang, Y.; Zhao, X.-M.; Lai, R.W.S.; et al. Decoding Adverse Effects of Organic Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment: A Meta-Analysis of Species Sensitivity, Hazard Prediction, and Ecological Risk Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 18122–18132.
- 32.
Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ma, L.; et al. Environmental Profiles, Hazard Identification, and Toxicological Hallmarks of Emerging Tire Rubber-Related Contaminants 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108677.
- 33.
Yan, X.; Xiao, J.; Kiki, C.; et al. Unraveling the Fate of 6PPD-Q in Aquatic Environment: Insights into Formation, Dissipation, and Transformation under Natural Conditions. Environ. Int. 2024, 191, 109004.
- 34.
Zhang, P.; Tang, X.; Qin, N.; et al. Advanced Understanding of the Natural Forces Accelerating Aging and Release of Black Microplastics (Tire Wear Particles) Based on Mechanism and Toxicity Analysis. Water Res. 2024, 266, 122409.
- 35.
Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, C.; et al. Occurrence, Fate and Chiral Signatures of p-Phenylenediamines and Their Quinones in Wastewater Treatment Plants, China. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123272.
- 36.
Maurer, L.; Carmona, E.; Machate, O.; et al. Contamination Pattern and Risk Assessment of Polar Compounds in Snow Melt: An Integrative Proxy of Road Runoffs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 4143–4152.
- 37.
Wang, B.; Sun, W.; Ye, X.; et al. Occurrence, Analytical Methods, and Ecotoxicological Effects of 6PPD-Quinone in Aquatic Environments: A Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2025, 193, 118449.
- 38.
Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Shi, R.; et al. Comparative Toxic Effect of Tire Wear Particle-Derived Compounds 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone to Chlorella Vulgaris. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175592.
- 39.
Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Sun, W.; et al. Environmental Concentrations of 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone Induce Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Disorders in Male Black-Spotted Frogs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136400.
- 40.
Shen, D.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Transformations of 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in Soil under Redox-Driven Conditions: Kinetics, Product Identification, and Environmental Implications. Environ. Int. 2025, 200, 109532.
- 41.
Di, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; et al. Chiral Perspective Evaluations: Enantioselective Hydrolysis of 6PPD and 6PPD-Quinone in Water and Enantioselective Toxicity to Gobiocypris Rarus and Oncorhynchus Mykiss. Environ. Int. 2022, 166, 107374.
- 42.
Grasse, N.; Seiwert, B.; Massei, R.; et al. Reemtsma, T. Uptake and Biotransformation of the Tire Rubber-Derived Contaminants 6-PPD and 6-PPD Quinone in the Zebrafish Embryo (Danio rerio). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15598–15607.
- 43.
Greer, J.B.; Dalsky, E.M.; Lane, R.F.; et al. Establishing an In Vitro Model to Assess the Toxicity of 6PPD-Quinone and Other Tire Wear Transformation Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2023, 10, 533–537.
- 44.
Ahi, E.P.; Lindeza, A.S.; Miettinen, A.; et al. Transcriptional Responses to Changing Environments: Insights from Salmonids. Rev. Fish. Biol. Fish. 2025, 35, 681–706.
- 45.
Greer, J.B.; Dalsky, E.M.; Lane, R.F.; et al. Tire-Derived Transformation Product 6PPD-Quinone Induces Mortality and Transcriptionally Disrupts Vascular Permeability Pathways in Developing Coho Salmon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10940–10950.
- 46.
Li, R.; Barrett, H.; Nair, P.; et al. Enantioselectivity in Metabolism and Toxicity of 6PPD-Quinone in Salmonids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 12878–12888.
- 47.
Hiki, K.; Yamamoto, H. The Tire-Derived Chemical 6PPD-Quinone Is Lethally Toxic to the White-Spotted Char Salvelinus Leucomaenis Pluvius but Not to Two Other Salmonid Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 1050–1055.
- 48.
Brinkmann, M.; Montgomery, D.; Selinger, S.; et al. Acute Toxicity of the Tire Rubber-Derived Chemical 6PPD-Quinone to Four Fishes of Commercial, Cultural, and Ecological Importance. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 333–338.
- 49.
Jhwueng, D.-C.; Huzurbazar, S.; O’Meara, B.C.; et al. Investigating the Performance of AIC in Selecting Phylogenetic Models. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2014, 13, 459–475.
- 50.
Iwasaki, Y.; Yanagihara, M. Comparison of Model-Averaging and Single-Distribution Approaches to Estimating Species Sensitivity Distributions and Hazardous Concentrations for 5% of Species. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 834–840.
- 51.
Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kiki, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, G.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Q. Stepwise Screening with LC-Q/TOF-MS and Signal Subtraction with GC ×GC-TOFMS Enables Rapid Identification of 6PPD-Q and 6PPD Metabolites in Raphidocelis Subcapitata. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138805.
- 52.
Cao, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. New Evidence of Rubber-Derived Quinones in Water, Air, and Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 4142–4150.
- 53.
Zhang, H.-Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.-H.; et al. Occurrence and risks of 23 tire additives and their transformation products in an urban water system. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107715.
- 54.
Kryuchkov, F.; Foldvik, A.; Sandodden, R.; et al. Presence of 6PPD-quinone in runoff water samples from Norway using a new LC–MS/MS method. Front. Environ. Chem. 2023, 4, 1194664.
- 55.
Jaeger, A.; Monaghan, J.; Tomlin, H.; et al. Intensive Spatiotemporal Characterization of the Tire Wear Toxin 6PPD Quinone in Urban Waters. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 5566–5574.
- 56.
Black, G.P.; De Parsia, M.; Uychutin, M.; et al. 6PPD-quinone in water from the San Francisco-San Joaquin Delta, California, 2018–2024. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 369.
- 57.
Lane, R.F.; Smalling, K.L.; Bradley, P.M.; et al. Tire-derived contaminants 6PPD and 6PPD-Q: Analysis, sample handling, and reconnaissance of United States stream exposures. Chemosphere 2024, 363, 142830.
- 58.
Li, Z.-M.; Kannan, K. Mass Loading, Removal, and Emission of 1,3-Diphenylguanidine, Benzotriazole, Benzothiazole, N-(1,3-Dimethylbutyl)-N′-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, and Their Derivatives in a Wastewater Treatment Plant in New York State, USA. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 2721–2730.
- 59.
Geng, N.; Hou, S.; Sun, S.; et al. A Nationwide Investigation of Substituted p-Phenylenediamines (PPDs) and PPD-Quinones in the Riverine Waters of China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 3183–3192.
- 60.
Zhu, J.; Guo, R.; Ren, F.; et al. Occurrence and partitioning of p-phenylenediamine antioxidants and their quinone derivatives in water and sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 170046.
- 61.
Wei, L.-N.; Wu, N.-N.; Xu, R.; et al. Rainfall, seasonal variation, and stream type governing the multi-media fate and ecological risks of tire additives and their transformation products in mega-urban streams. Water Res. 2025, 287, 124366.
- 62.
Johannessen, C.; Helm, P.; Lashuk, B.; et al. The Tire Wear Compounds 6PPD-Quinone and 1,3-Diphenylguanidine in an Urban Watershed. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 82, 171–179.
- 63.
Helm, P.A.; Raby, M.; Kleywegt, S.; et al. Assessment of Tire-Additive Transformation Product 6PPD-Quinone in Urban-Impacted Watersheds. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 1422–1432.
- 64.
Halama, J.J.; McKane, R.B.; Barnhart, B.L.; et al. Watershed analysis of urban stormwater contaminant 6PPD-Quinone hotspots and stream concentrations using a process-based ecohydrological model. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1364673.
- 65.
Zhao, H.N.; Hu, X.; Tian, Z.; et al. Transformation Products of Tire Rubber Antioxidant 6PPD in Heterogeneous Gas-Phase Ozonation: Identification and Environmental Occurrence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 5621–5632.
- 66.
Zhou, L.J., Liu, S., Wang, M.; et al. Nationwide Occurrence and Prioritization of Tire Additives and Their Transformation Products in Lake Sediments of China. Environ. Int. 2024, 193, 109139.
- 67.
Liang, C., Hou, Y.Y., Li, J.Y.; et al. Occurrences, Profiles, And Mass Inventories of Sediment p-Phenylenediamine and Their Quinones in the Northern South China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 221, 118482.
- 68.
Gwak, J., Cha, J., Lee, S.; et al. Spatial Distribution, Compositional Profiles, and Potential Ecological Risks of Rubber Additives in Sediments of Lake Sihwa, South Korea: Insights into Industrial and Road-Derived Toxic Substances. ACS EST Water 2025, 5, 3953–3962.
- 69.
Varshney, S.; Gora, A.H.; Siriyappagouder, P.; et al. Toxicological effects of 6PPD and 6PPD quinone in zebrafish larvae. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127623.
- 70.
Yan, X.; Kiki, C.; Xu, Z.; et al. Comparative growth inhibition of 6PPD and 6PPD-Q on microalgae Selenastrum capricornutum, with insights into 6PPD-induced phototoxicity and oxidative stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177627.
- 71.
Li, X.; Liu, W.; Ge, Y.; et al. Response of Ceratophyllum demersum L. and its epiphytic biofilms to 6PPD and 6PPD-Q exposure: Based on metabolomics and microbial community analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136420.
- 72.
Shi, C.; Wu, F.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Effects of environmental concentrations of 6PPD and its quinone metabolite on the growth and reproduction of freshwater cladoceran. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 175018.
- 73.
Hiki, K.; Asahina, K.; Kato, K.; et al. Acute Toxicity of a Tire Rubber-Derived Chemical, 6PPD Quinone, to Freshwater Fish and Crustacean Species. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 779–784.
- 74.
Ackerly, K.L.; Roark, K.J.; Lu, K.; et al. Acute toxicity testing of 6PPD‐quinone on the estuarine-dependent sport fish, Sciaenops ocellatus. Ecotoxicology 2024, 33, 582–589.
- 75.
Montgomery, D.; Ji, X.; Cantin, J.; et al. Interspecies Differences in 6PPD-Quinone Toxicity Across Seven Fish Species: Metabolite Identification and Semiquantification. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 21071–21079.
- 76.
Lo, B.P.; Marlatt, V.L.; Liao, X.; et al. Acute Toxicity of 6PPD‐Quinone to Early Life Stage Juvenile Chinook (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and Coho (Oncorhynchus kisutch) Salmon. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 815–822.
- 77.
Obanya, H.E.; Couceiro, F.; Ford, A.T.; et al. Toxicological assessment of tyre-derived compounds: Effects of 6PPD-quinone, diphenylguanidine, and mercaptobenzothiazole on Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Aquat. Toxicol. 2025, 286, 107457.
- 78.
Prosser, R.S.; Salole, J.; Hang, S. Toxicity of 6PPD-quinone to four freshwater invertebrate species. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 337, 122512.
- 79.
Maji, U.J.; Kim, K.; Yeo, I.-C.; et al. Toxicological effects of tire rubber-derived 6PPD-quinone, a species-specific toxicant, and dithiobisbenzanilide (DTBBA) in the marine rotifer Brachionus koreanus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115002.
- 80.
Foldvik, A.; Kryuchkov, F.; Sandodden, R.; et al. Acute Toxicity Testing of the Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical 6PPD‐quinone on Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) and Brown Trout (Salmo trutta). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2022, 41, 3041–3045.
- 81.
Calle, L.; Le Du-Carrée, J.; Martínez, I.; et al. Toxicity of tire rubber-derived pollutants 6PPD-quinone and 4-tert-octylphenol on marine plankton. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 484, 136694.
- 82.
Botelho, M.T.; Militão, G.G.; Brinkmann, M.; et al. Toxicity and mutagenicity studies of 6PPD-quinone in a marine invertebrate species and bacteria. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2023, 64, 335–341.
- 83.
Shankar, P.; Dalsky, E.M.; Salzer, J.E.; et al. Evaluation of 6PPD-Quinone Lethal Toxicity and Sublethal Effects on Disease Resistance and Swimming Performance in Coastal Cutthroat Trout (Oncorhynchus clarkii clarkii). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 11505–11514.
- 84.
Philibert, D.; Stanton, R.S.; Tang, C.; et al. The lethal and sublethal impacts of two tire rubber-derived chemicals on brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis) fry and fingerlings. Chemosphere 2024, 360, 142319.
- 85.
Anderson-Bain, K.; Roberts, C.; Kohlman, E.; et al. Apical and mechanistic effects of 6PPD-quinone on different life-stages of the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 271, 109697.
- 86.
Huang, Z.; Chen, C.; Guan, K.; et al. Protective role of ghrelin against 6PPD-quinone-induced neurotoxicity in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio) via the GHSR pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 285, 117031.
- 87.
Zhou, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. 6PPD-quinone exposure induces oxidative damage and physiological disruption in Eisenia fetida: An integrated analysis of phenotypes, multi-omics, and intestinal microbiota. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 493, 138334.
- 88.
Roberts, C.; Kohlman, E.; Jain, N.; et al. Subchronic and Acute Toxicity of 6PPD-Quinone to Early Life Stage Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 6771–6777.
- 89.
Nair, P.; Sun, J.; Xie, L.; et al. Synthesis and Toxicity Evaluation of p-Phenylenediamine-Quinones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 7485–7494.
- 90.
Foldvik, A.; Kryuchkov, F.; Ulvan, E.M.; et al. Acute Toxicity Testing of Pink Salmon (Oncorhynchus gorbuscha) with the Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical 6PPD‐Quinone. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2024, 43, 1332–1338.
- 91.
Roberts, C.; Lin, J.; Kohlman, E.; et al. Acute and Subchronic Toxicity of 6PPD-Quinone to Early Life Stage Lake Trout (Salvelinus namaycush). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 791–797.
- 92.
Di, S.; Xu, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of S-6PPD-Quinone Caused More Serious Hepatotoxicity Than R-Enantiomer and Racemate in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 17617–17628.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


