- EDA is increasingly combined with NTA for identifying unknown toxicants
- HRMS-based analysis enhances the reliability of compound identification
- Standardized EDA-NTA databases facilitate crossstudy comparison and data integration
- Data-driven effect attribution will enhance future mixture risk assessment
- Open Access
- Review
Integrating Bioassays and Non-Target Screening: A Review of Effect-Directed Analysis for Unknown Toxicants
Author Information
Received: 07 Dec 2025 | Revised: 30 Jan 2026 | Accepted: 06 Feb 2026 | Published: 11 Feb 2026
Highlights
Abstract
The widespread use of chemicals continues to pose significant risks to ecosystems and human health. While toxicological mechanisms of many known pollutants remain incompletely understood, the emergence of numerous unknown or poorly characterized contaminants intensifies the urgent need for robust identification strategies. Effect-directed analysis (EDA) has shown effective in detecting bioactive compounds in complex environmental matrices, yet traditional EDA approaches mainly relying on target analyses are inherently limited in uncovering new or unexpected toxicants. Integrating emerging non-target analysis (NTA) techniques with EDA offers a transformative approach, enabling comprehensive profiling of unknown compounds and improving accuracy and efficiency of environmental risk assessment. Despite this potential, the lack of standardized workflows has constrained the widespread application of NTA in EDA. The present review summarized recent developments in integrating NTA with EDA, covering key aspects from sample collection and preparation to fractionation, instrumental analysis, and toxicity confirmation, with a focus on chemical analysis for various matrices. We discuss key methodological challenges such as matrix effects and confidence levels in structural elucidation. By synthesizing current knowledge and identifying future directions, this work aims to provide actionable guidance for the identification of new or less-concerned toxicants in mixtures, ultimately advancing environmental monitoring and public health protection with integrative EDA and NTA approaches.
Graphical Abstract
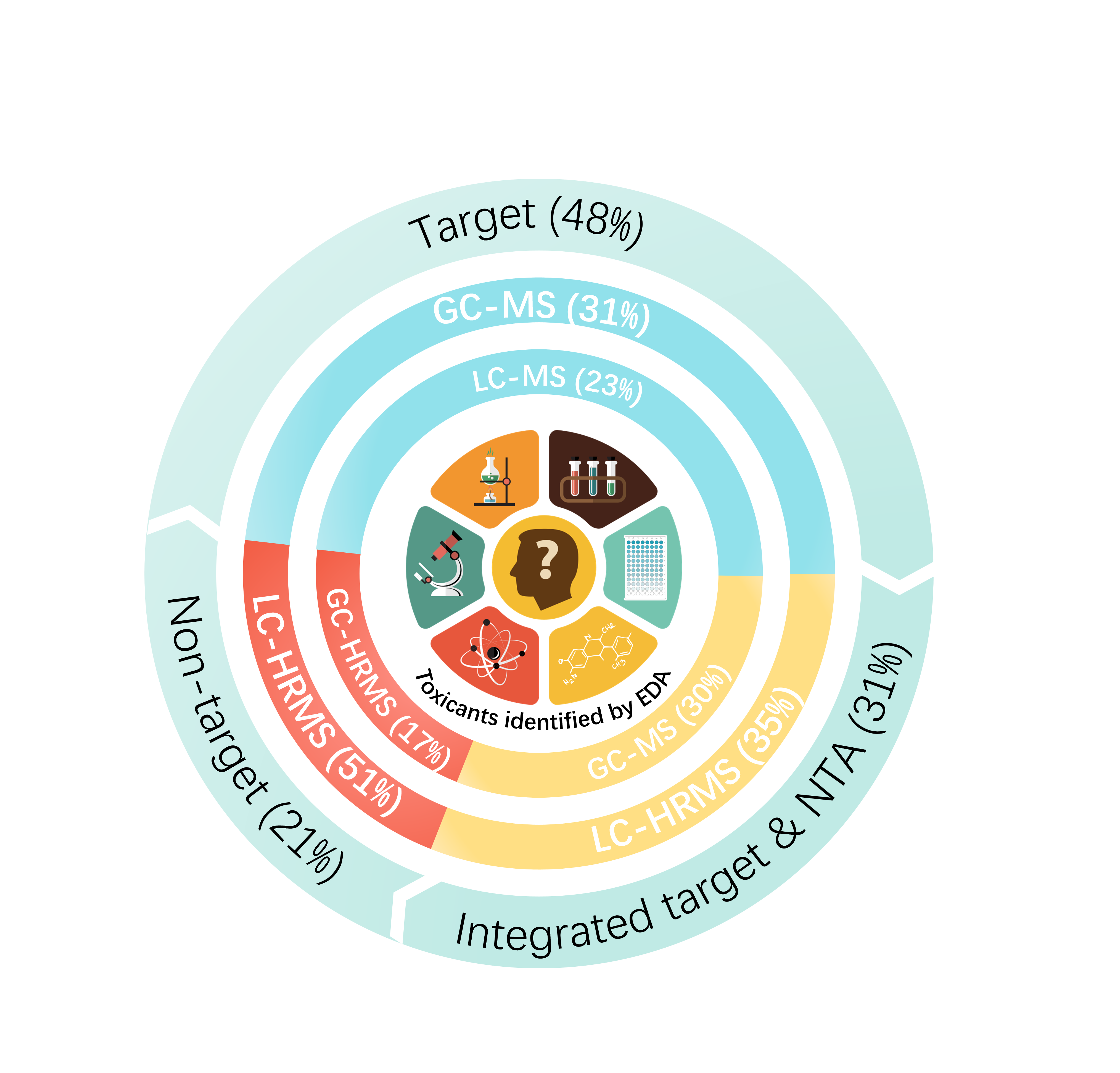
Keywords
effect-directed analysis | non-target analysis | high resolution mass spectrometry | mixture risk | toxicity identification
References
- 1.
Li, H.; Zhang, J.; You, J. Diagnosis of Complex Mixture Toxicity in Sediments: Application of Toxicity Identification Evaluation (TIE) and Effect-Directed Analysis (EDA). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 944–954.
- 2.
Brack, W. Effect-Directed Analysis: A Promising Tool for the Identification of Organic Toxicants in Complex Mixtures? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2003, 377, 397–407.
- 3.
Guo, J.; Deng, D.; Qiu, J.; et al. Biodirected Identification of Untargeted Toxicants in Industrial Wastewater Guides the Upgrading of Water Treatments. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 474–481.
- 4.
Gwak, J.; Lee, J.; Cha, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Estrogen Receptor Agonists During Sewage Treatment Processes Using Effect-Directed Analysis Combined with High-Resolution Full-Scan Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13085–13095.
- 5.
Schreiner, T.; Eggerstorfer, N.M.; Morlock, G.E. Ten-Dimensional Hyphenation Including Simulated Static Gastro-Intestinal Digestion on the Adsorbent Surface, Planar Assays, and Bioactivity Evaluation for Meal Replacement Products. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 344–353.
- 6.
Xu, E.G.; Richardot, W.H.; Li, S.; et al. Assessing Toxicity and In Vitro Bioactivity of Smoked Cigarette Leachate Using Cell-Based Assays and Chemical Analysis. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1670–1679.
- 7.
Bengtström, L.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Trier, X.; et al. Non-Targeted Screening for Contaminants in Paper and Board Food-Contact Materials Using Effect-Directed Analysis and Accurate Mass Spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 1080–1093.
- 8.
Berger, E.; Potouridis, T.; Haeger, A.; et al. Effect-Directed Identification of Endocrine Disruptors in Plastic Baby Teethers. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2015, 35, 1254–1261.
- 9.
Zhou, Q.; Shen, Y.; Chou, L.; et al. Identification of Glucocorticoid Receptor Antagonistic Activities and Responsible Compounds in House Dust: Bioaccessibility Should Not Be Ignored. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 16768–16779.
- 10.
Qi, H.; Zhao, B.; Li, L.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Toxic Organics in PM2.5 Exposure to the Cellular Bioassays In Vitro: Application in Shanxi of China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 237, 113501.
- 11.
Łata, E.; Fulczyk, A.; Ott, P.G.; et al. Thin-Layer Chromatographic Quantification of Magnolol and Honokiol in Dietary Supplements and Selected Biological Properties of These Preparations. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1625, 461230.
- 12.
Riegraf, C.; Reifferscheid, G.; Moscovici, L.; et al. Coupling High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography with a Battery of Cell-Based Assays Reveals Bioactive Components in Wastewater and Landfill Leachates. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 214, 112092.
- 13.
Stiefel, C.; Lindemann, B.; Morlock, G.E. Non-Target Bioactive Compound Profiles of Coffee Roasts and Preparations. Food Chem. 2022, 391, 133263.
- 14.
Ristivojević, P.; Morlock, G.E. Effect-Directed Classification of Biological, Biochemical and Chemical Profiles of 50 German Beers. Food Chem. 2018, 260, 344–353.
- 15.
Meyer, W.; Seiler, T.-B.; Christ, A.; et al. Mutagenicity, Dioxin-Like Activity and Bioaccumulation of Alkylated Picene and Chrysene Derivatives in a German Lignite. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 634–641.
- 16.
Bell, A.M.; Keltsch, N.; Schweyen, P.; et al. UV Aged Epoxy Coatings-Ecotoxicological Effects and Released Compounds. Water Res. X 2021, 12, 100105.
- 17.
Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Inhibition of Aged Microplastics and Leachates on Methane Production from Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge and Identification of Key Components. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130717.
- 18.
Ahmad, R.; Cho, E.; Rakhmat, S.; et al. Characterization of Structure Isomers of Ethylbenzalkyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chlorides and Quantification in Commercial Household Disinfectant Products. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 102979.
- 19.
Rosenmai, A.K.; Bengtström, L.; Taxvig, C.; et al. An Effect-Directed Strategy for Characterizing Emerging Chemicals in Food Contact Materials Made from Paper and Board. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 250–259.
- 20.
Schönlau, C.; Larsson, M.; Dubocq, F.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Ah Receptor-Mediated Potencies in Microplastics Deployed in a Remote Tropical Marine Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 120.
- 21.
Krüger, S.; Urmann, O.; Morlock, G.E. Development of a Planar Chromatographic Method for Quantitation of Anthocyanes in Pomace, Feed, Juice and Wine. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1289, 105–118.
- 22.
Tian, Z.; Zhao, H.; Peter, K.T.; et al. A Ubiquitous Tire Rubber–Derived Chemical Induces Acute Mortality in Coho Salmon. Science 2021, 371, 185–189.
- 23.
You, J.; Li, H. Improving the Accuracy of Effect-Directed Analysis: The Role of Bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2017, 19, 1484–1498.
- 24.
An, S.-A.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Identification of Potential Toxicants in Sediments from an Industrialized Area in Pohang, South Korea: Application of a Cell Viability Assay of Microalgae Using Flow Cytometry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124230.
- 25.
Weiss, J.M.; Simon, E.; Stroomberg, G.J.; et al. Identification Strategy for Unknown Pollutants Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Androgen-Disrupting Compounds Identified through Effect-Directed Analysis. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 3141–3149.
- 26.
Creusot, N.; Budzinski, H.; Balaguer, P.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Endocrine-Disrupting Compounds in Multi-Contaminated Sediment: Identification of Novel Ligands of Estrogen and Pregnane X Receptors. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2553–2566.
- 27.
Portolés, T.; Pitarch, E.; López, F.J.; et al. Use of Soft and Hard Ionization Techniques for Elucidation of Unknown Compounds by Gas Chromatography/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1589–1599.
- 28.
Muschket, M.; Di Paolo, C.; Tindall, A.J.; et al. Identification of Unknown Antiandrogenic Compounds in Surface Waters by Effect-Directed Analysis (EDA) Using a Parallel Fractionation Approach. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 288–297.
- 29.
Lübcke-von Varel, U.; Machala, M.; Ciganek, M.; et al. Polar Compounds Dominate In Vitro Effects of Sediment Extracts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2384–2390.
- 30.
Cha, J.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.; et al. Identification of Mid-Polar and Polar Ahr Agonists in Cetaceans from Korean Coastal Waters: Application of Effect-Directed Analysis with Full-Scan Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15644–15655.
- 31.
Dusza, H.M.; Janssen, E.; Kanda, R.; et al. Method Development for Effect-Directed Analysis of Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Human Amniotic Fluid. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14649–14659.
- 32.
Huang, J.; Cheng, F.; He, L.; et al. Effect Driven Prioritization of Contaminants in Wastewater Treatment Plants across China: A Data Mining-Based Toxicity Screening Approach. Water Res. 2024, 264, 122223.
- 33.
Houtman, C.J.; Brewster, K.; Ten Broek, R.; et al. Characterisation of (Anti-)progestogenic and (Anti-)androgenic Activities in Surface and Wastewater Using High Resolution Effectdirected Analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106536.
- 34.
Lopez-Herguedas, N.; Mijangos, L.; Alvarez-Mora, I.; et al. Suspect Screening of Chemicals in Hospital Wastewaters Ssing Effect-Directed Analysis Approach as Prioritization Strategy. Molecules 2023, 28, 1212.
- 35.
Cheng, F.; Li, H.; Ma, H.; et al. Identifying Bioaccessible Suspect Toxicants in Sediment Using Adverse Outcome Pathway Directed Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121853.
- 36.
Guo, J.; Deng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Extended Suspect Screening Strategy to Identify Characteristic Toxicants in the Discharge of a Chemical Industrial Park Based on Toxicity to Daphnia Magna. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 10–17.
- 37.
An, S.-A.; Lee, J.; Cha, J.; et al. Characterization of Microalgal Toxicants in the Sediments from an Industrial Area: Application of Advanced Effect-Directed Analysis with Multiple Endpoint Bioassays. Environ. Int. 2023, 173, 107833.
- 38.
Loewenthal, D.; Dagan, S.; Drug, E. Integrating Effect-Directed Analysis and Chemically Indicative Mass Spectral Fragmentation to Screen for Toxic Organophosphorus Compounds. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 2623–2627.
- 39.
Marić, P.; Ahel, M.; Senta, I.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis Reveals Inhibition of Zebrafish Uptake Transporter Oatp1d1 by Caulerpenyne, a Major Secondary Metabolite from the Invasive Marine Alga Caulerpa Taxifolia. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 643–654.
- 40.
Milman, B.L. General Principles of Identification by Mass Spectrometry. TrAC Trend. Anal. Chem. 2015, 69, 24–33.
- 41.
He, L.; Cheng, F.; Wu, F.; et al. Identifying and Prioritizing Organic Toxicants in Treated Flowback and Produced Water from Shale Gas Exploitation Sites Using an Integrative Effect-Directed Analysis and Nontarget Screening Method. Water Res. 2025, 277, 123311.
- 42.
Cheng, F.; Li, H.; Lou, X.; et al. Event-Driven Taxonomy (EDT) Screening: Leveraging Effect-Based Spectral Libraries to Accelerate Semiquantitative Nontarget Analysis of Ahr Agonists in Sediment in the Era of Big Data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 14359–14371.
- 43.
Schulze, T.; Weiss, S.; Schymanski, E.; et al. Identification of a Phytotoxic Photo-Transformation Product of Diclofenac Using Effect-Directed Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1461–1466.
- 44.
Xiao, H.; Brinkmann, M.; Thalmann, B.; et al. Toward Streamlined Identification of Dioxin-Like Compounds in Environmental Samples through Integration of Suspension Bioassay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3382–3390.
- 45.
Grote, M.; Altenburger, R.; Brack, W.; et al. Ecotoxicological Profiling of Transect River Elbe Sediments. Acta Hydroch. Hydrobiol. 2005, 33, 555–569.
- 46.
Dahl, M.; Survo, S.; Välitalo, P.; et al. Identification of Toxicants from a Highly C10–C40-Contaminated Sediment Influenced by the Wood Industry: Petroleum Hydrocarbons or Biogenic Organic Compounds? Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 936–946.
- 47.
Froment, J.; Langford, K.; Tollefsen, K.E.; et al. Identification of Petrogenic Produced Water Components as Acetylcholine Esterase Inhibitors. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 215, 18–26.
- 48.
Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, T.; et al. Identification of Ahr Agonists in Sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas Using Advanced Effect-Directed Analysis and in Silico Prediction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 128908.
- 49.
Dusza, H.M.; Manz, K.E.; Pennell, K.D.; et al. Identification of Known and Novel Nonpolar Endocrine Disruptors in Human Amniotic Fluid. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106904.
- 50.
Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis for Revealing Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonists in Sediment Samples from an Electronic Waste Recycling Town in China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119659.
- 51.
Cheng, F.; Escher, B.I.; Li, H.; et al. Deep Learning Bridged Bioactivity, Structure, and GC-Hrms-Readable Evidence to Decipher Nontarget Toxicants in Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 15415–15427.
- 52.
Radovic, J.R.; Thomas, K.V.; Parastar, H.; et al. Chemometrics-Assisted Effect-Directed Analysis of Crude and Refined Oil Using Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3074–3083.
- 53.
Muusse, M.; Langford, K.; Tollefsen, K.E.; et al. Characterization of Ahr Agonist Compounds in Roadside Snow. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 2047–2056.
- 54.
Cha, J.; Hong, S.; Gwak, J.; et al. Identification of Novel Polar Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Agonists Accumulated in Liver of Black-Tailed Gulls in Korea Using Advanced Effect-Directed Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128305.
- 55.
Stütz, L.; Leitner, P.; Schulz, W.; et al. Identification of Genotoxic Transformation Products by Effect-Directed Analysis with High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography and Non-Target Screening. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2019, 32, 173–182.
- 56.
Jonker, W.; Ballesteros-Gómez, A.; Hamers, T.; et al. Highly Selective Screening of Estrogenic Compounds in Consumer-Electronics Plastics by Liquid Chromatography in Parallel Combined with Nanofractionation-Bioactivity Detection and Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12385–12393.
- 57.
Krauss, M.; Singer, H.; Hollender, J. LC–High Resolution MS in Environmental Analysis: From Target Screening to the Identification of Unknowns. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 943–951.
- 58.
Barrett, H.; Sun, J.; Gong, Y.; et al. Triclosan Is the Predominant Antibacterial Compound in Ontario Sewage Sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 14923–14936.
- 59.
Hashmi, M.A.K.; Krauss, M.; Escher, B.I.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Progestogens and Glucocorticoids at Trace Concentrations in River Water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 189–199.
- 60.
Ouyang, X.; Leonards, P.E.; Tousova, Z.; et al. Rapid Screening of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors by Effect-Directed Analysis Using LC × LC Fractionation, a High Throughput In Vitro Assay, and Parallel Identification by Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2353–2360.
- 61.
Móricz, A.M.; Ott, P.G.; Habe, T.T.; et al. Effect-Directed Discovery of Bioactive Compounds Followed by Highly Targeted Characterization, Isolation and Identification, Exemplarily Shown for Solidago Virgaurea. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 8202–8209.
- 62.
Azadniya, E.; Morlock, G.E. Bioprofiling of Salvia miltiorrhiza via Planar Chromatography Linked to (Bio)assays, High Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1533, 180–192.
- 63.
Byer, J.D.; Siek, K.; Jobst, K. Distinguishing the C3 Vs SH4 Mass Split by Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography–High Resolution Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6101–6104.
- 64.
Dong, H.; Cuthbertson, A.A.; Plewa, M.J.; et al. Unravelling High-Molecular-Weight Dbp Toxicity Drivers in Chlorinated and Chloraminated Drinking Water: Effect-Directed Analysis of Molecular Weight Fractions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 18788–18800.
- 65.
Bataineh, M.; Lübcke-von Varel, U.; Hayen, H.; et al. HPLC/APCI-FTICR-MS as a Tool for Identification of Partial Polar Mutagenic Compounds in Effect-Directed Analysis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 21, 1016–1027.
- 66.
Zhang, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, J.; et al. Unveiling Condensed Aromatic Amines as Noteworthy Genotoxic Components in PM2.5 Dissolved Organic Matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 21015–21027.
- 67.
Ulrich, N.; Mühlenberg, J.; Schüürmann, G.; et al. Linear Solvation Energy Relationships as Classifier in Non-Target Analysis—An Approach for Isocratic Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1324, 96–103.
- 68.
Ulrich, N.; Schüürmann, G.; Brack, W. Prediction of Gas Chromatographic Retention Indices as Classifier in Non-Target Analysis of Environmental Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1285, 139–147.
- 69.
Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, T.; et al. Multiple Bioassays and Targeted and Nontargeted Analyses to Characterize Potential Toxicological Effects Associated with Sediments of Masan Bay: Focusing on Ahr-Mediated Potency. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4443–4454.
- 70.
Schulze, T.; Ahel, M.; Ahlheim, J.; et al. Assessment of a Novel Device for Onsite Integrative Large-Volume Solid Phase Extraction of Water Samples to Enable a Comprehensive Chemical and Effect-Based Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 581, 350–358.
- 71.
Gardia-Parège, C.; Kim Tiam, S.; Budzinski, H.; et al. Pesticide Toxicity Towards Microalgae Increases with Environmental Mixture Complexity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 29368–29381.
- 72.
Zwart, N.; Nio, S.L.; Houtman, C.J.; et al. High-Throughput Effect-Directed Analysis Using Downscaled In Vitro Reporter Gene Assays to Identify Endocrine Disruptors in Surface Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4367–4377.
- 73.
Booij, P.; Vethaak, A.D.; Leonards, P.E.; et al. Identification of Photosynthesis Inhibitors of Pelagic Marine Algae Using 96-Well Plate Microfractionation for Enhanced Throughput in Effect-Directed Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8003–8011.
- 74.
Gallampois, C.M.; Schymanski, E.L.; Krauss, M.; et al. Multicriteria Approach to Select Polyaromatic River Mutagen Candidates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2959–2968.
- 75.
Gallampois, C.M.; Schymanski, E.L.; Bataineh, M.; et al. Integrated Biological–Chemical Approach for the Isolation and Selection of Polyaromatic Mutagens in Surface Waters. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 9101–9112.
- 76.
Schymanski, E.L.; Gallampois, C.M.; Krauss, M.; et al. Consensus Structure Elucidation Combining GC/EI-MS, Structure Generation, and Calculated Properties. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3287–3295.
- 77.
Stütz, L.; Schulz, W.; Winzenbacher, R. Identification of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors in Water by Combining Two-Dimensional Thin-Layer Chromatography and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1624, 461239.
- 78.
Oberleitner, D.; Stütz, L.; Schulz, W.; et al. Seasonal Performance Assessment of Four Riverbank Filtration Sites by Combined Non-Target and Effect-Directed Analysis. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127706.
- 79.
Meinert, C.; Schymanski, E.; Küster, E.; et al. Application of Preparative Capillary Gas Chromatography (pcGC), Automated Structure Generation and Mutagenicity Prediction to Improve Effect-Directed Analysis of Genotoxicants in a Contaminated Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2010, 17, 885–897.
- 80.
Zwart, N.; Jonker, W.; Broek, R.T.; et al. Identification of Mutagenic and Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Surface Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents Using High-Resolution Effect-Directed Analysis. Water Res. 2020, 168, 115204.
- 81.
Tan, B.; Xiong, J.; Li, H.; et al. Simultaneous Analysis of Current-Use Pesticides and Their Transformation Products in Water Using Mixture-Sorbent Solid Phase Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 2409–2418.
- 82.
Tousova, Z.; Froment, J.; Oswald, P.; et al. Identification of Algal Growth Inhibitors in Treated Waste Water Using Effect-Directed Analysis Based on Non-Target Screening Techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 358, 494–502.
- 83.
Tousova, Z.; Oswald, P.; Slobodnik, J.; et al. European Demonstration Program on the Effect-Based and Chemical Identification and Monitoring of Organic Pollutants in European Surface Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601, 1849–1868.
- 84.
Hug, C.; Krauss, M.; Nüsser, L.; et al. Metabolic Transformation as a Diagnostic Tool for the Selection of Candidate Promutagens in Effect-Directed Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 196, 114–124.
- 85.
Tufi, S.; Wassenaar, P.N.; Osorio, V.; et al. Pesticide Mixture Toxicity in Surface Water Extracts in Snails (Lymnaea Stagnalis) by an In Vitro Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition Assay and Metabolomics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3937–3944.
- 86.
Mijangos, L.; Krauss, M.; de Miguel, L.; et al. Application of the Sea Urchin Embryo Test in Toxicity Evaluation and Effect-Directed Analysis of Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8890–8899.
- 87.
Liao, X.; Allen, J.M.; Granger, C.O.; et al. How Well Does Xad Resin Extraction Recover Halogenated Disinfection Byproducts for Comprehensive Identification and Toxicity Testing? J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 117, 264–275.
- 88.
Lau, S.S.; Forster, A.L.; Richardson, S.D.; et al. Disinfection Byproduct Recovery During Extraction and Concentration in Preparation for Chemical Analyses or Toxicity Assays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 14136–14145.
- 89.
Pinzón-Espinosa, A.; Kanda, R. Naphthenic Acids Are Key Contributors to Toxicity of Heavy Oil Refining Effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138119.
- 90.
Fang, M.; Getzinger, G.J.; Cooper, E.M.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Elizabeth River Porewater: Developmental Toxicity in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 2767–2774.
- 91.
Pochiraju, S.S.; Linden, K.; Gu, A.Z.; et al. Development of a Separation Framework for Effects-Based Targeted and Non-Targeted Toxicological Screening of Water and Wastewater. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115289.
- 92.
Qi, H.; Li, H.; Wei, Y.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Toxicants in Sediment with Combined Passive Dosing and In Vivo Toxicity Testing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6414–6421.
- 93.
Li, H.; Yi, X.; Cheng, F.; et al. Identifying Organic Toxicants in Sediment Using Effect-Directed Analysis: A Combination of Bioaccessibility-Based Extraction and High-Throughput Midge Toxicity Testing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 996–1003.
- 94.
Tian, Z.; Gold, A.; Nakamura, J.; et al. Nontarget Analysis Reveals a Bacterial Metabolite of Pyrene Implicated in the Genotoxicity of Contaminated Soil after Bioremediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7091–7100.
- 95.
Feng, Q.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; et al. Identification of the Estrogen-Active Compounds via Integrating Effect-Directed Analysis and Non-Target Screening in Soils of the Northeastern China. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2024, 36, 1–13.
- 96.
Legler, J.; van Velzen, M.; Cenijn, P.H.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis of Municipal Landfill Soil Reveals Novel Developmental Toxicants in the Zebrafish Danio Rerio. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8552–8558.
- 97.
Jondeau-Cabaton, A.; Soucasse, A.; Jamin, E.L.; et al. Characterization of Endocrine Disruptors from a Complex Matrix Using Estrogen Receptor Affinity Columns and High Performance Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 2705–2720.
- 98.
Alvarez-Muñoz, D.; Indiveri, P.; Rostkowski, P.; et al. Widespread Contamination of Coastal Sediments in the Transmanche Channel with Anti-Androgenic Compounds. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 590–597.
- 99.
Guo, J.; Shi, W.; Chen, Q.; et al. Extended Virtual Screening Strategies to Link Antiandrogenic Activities and Detected Organic Contaminants in Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12528–12536.
- 100.
Zaja, R.; Terzić, S.; Senta, I.; et al. Identification of PGlycoprotein Inhibitors in Contaminated Freshwater Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4813–4821.
- 101.
Higley, E.; Grund, S.; Jones, P.D.; et al. Endocrine Disrupting, Mutagenic, and Teratogenic Effects of Upper Danube River Sediments Using Effect-Directed Analysis. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1053–1062.
- 102.
Qu, G.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Detection of Tris-(2,3-Dibromopropyl) Isocyanurate as a Neuronal Toxicant in Environmental Samples Using Neuronal Toxicity-Directed Analysis. Sci. China Chem. 2011, 54, 1651–1658.
- 103.
Jonkers, T.J.; Meijer, J.; Vlaanderen, J.J.; et al. High-Performance Data Processing Workflow Incorporating Effect-Directed Analysis for Feature Prioritization in Suspect and Nontarget Screening. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1639–1651.
- 104.
Simon, E.; van Velzen, M.; Brandsma, S.H.; et al. Effect-Directed Analysis to Explore the Polar Bear Exposome: Identification of Thyroid Hormone Disrupting Compounds in Plasma. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8902–8912.
- 105.
Nielen, M.W.; Elliott, C.T.; Boyd, S.A.; et al. Identification of an Unknown Beta-Agonist in Feed by Liquid Chromatography/Bioassay/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Accurate Mass Measurement. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 1633–1641.
- 106.
Nielen, M.W.; Van Bennekom, E.O.; Heskamp, H.H.; et al. Bioassay-Directed Identification of Estrogen Residues in Urine by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6600–6608.
- 107.
Wong, H.; Giesy, J.; Siu, W.; et al. Estrogenic and Dioxin-Like Activities and Cytotoxicity of Sediments and Biota from Hong Kong Mudflats. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2005, 48, 575–586.
- 108.
Simon, E.; Lamoree, M.H.; Hamers, T.; et al. Testing Endocrine Disruption in Biota Samples: A Method to Remove Interfering Lipids and Natural Hormones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 8322–8329.
- 109.
Klöppel, A.; Grasse, W.; Brümmer, F.; et al. Hptlc Coupled with Bioluminescence and Mass Spectrometry for Bioactivity-Based Analysis of Secondary Metabolites in Marine Sponges. JPC J. Planar Chromatogr. Mod. TLC 2008, 21, 431–436.
- 110.
Krüzselyi, D.N.; Bakonyi, J.; Ott, P.G.; et al. Goldenrod Root Compounds Active against Crop Pathogenic Fungi. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12686–12694.
- 111.
Krstić, Đ.; Ristivojević, P.; Andrić, F.; et al. Quality Assessment of Apple and Grape Juices from Serbian and German Markets by Planar Chromatography—Chemometrics. Molecules 2022, 27, 3933.
- 112.
Peters, R.J.; Rijk, J.C.; Bovee, T.F.; et al. Identification of Anabolic Steroids and Derivatives Using Bioassay-Guided Fractionation, UHPLC/TOFMS Analysis and Accurate Mass Database Searching. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 664, 77–88.
- 113.
Houtman, C.J.; Ten Broek, R.; van Oorschot, Y.; et al. High Resolution Effect-Directed Analysis of Steroid Hormone (Ant)Agonists in Surface and Wastewater Quality Monitoring. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 80, 103460.
- 114.
Schymanski, E.L.; Jeon, J.; Gulde, R.; et al. Identifying Small Molecules via High Resolution Mass Spectrometry: Communicating Confidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2097–2098.
- 115.
Schmitt, S.; Reifferscheid, G.; Claus, E.; et al. Effect Directed Analysis and Mixture Effects of Estrogenic Compounds in a Sediment of the River Elbe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3350–3361.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


