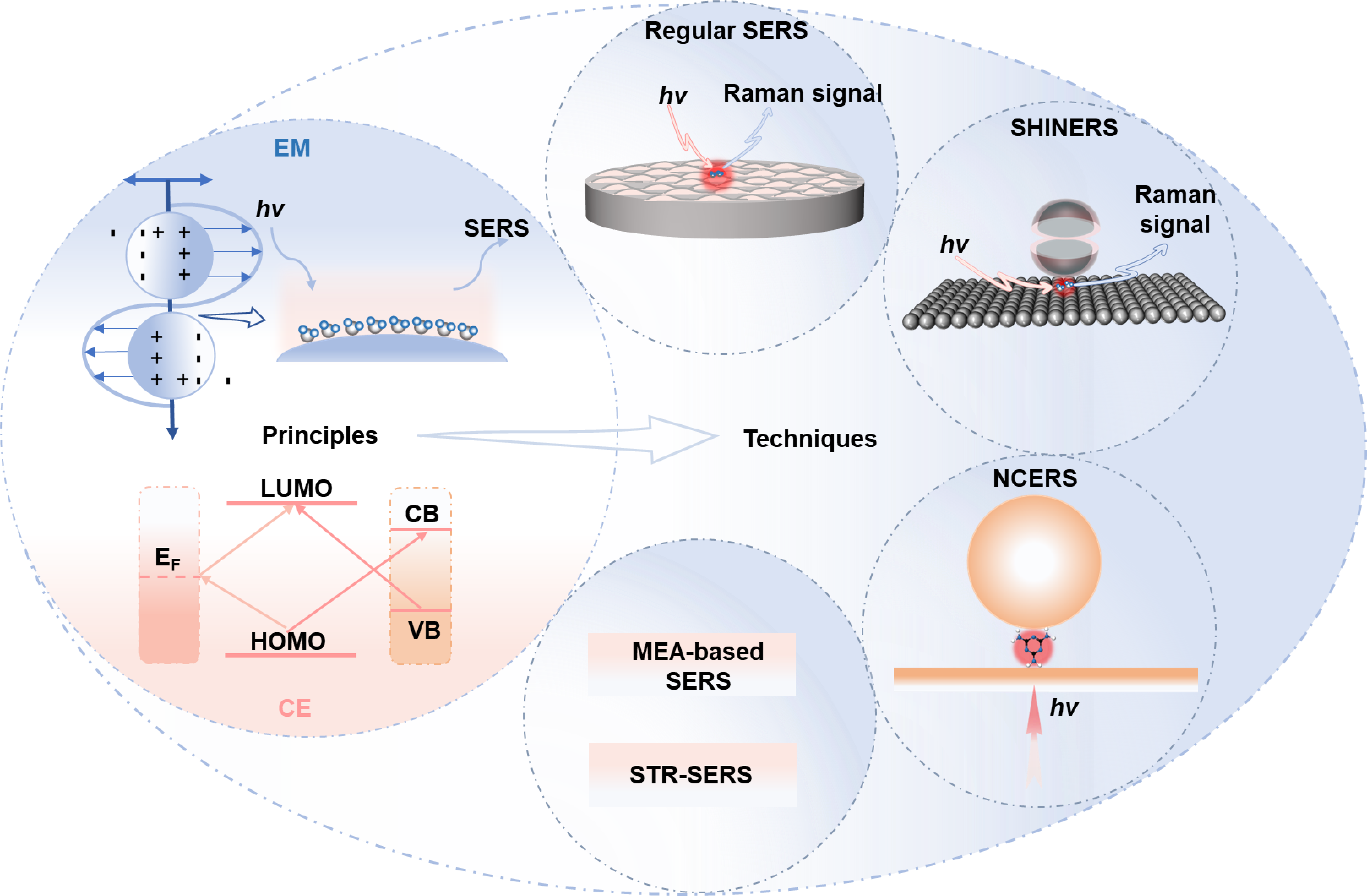
Electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction reaction (eCO2RR) is a pivotal negative carbon technology that converts greenhouse gas CO2 into value-added chemicals using renewable energy. However, its selectivity and efficiency are still limited by an incomplete understanding of active-phase dynamics, key intermediate formation, and reaction-pathway identification. Due to its molecular-level structural sensitivity and real-time monitoring capability, in-situ Raman spectroscopy has become a powerful tool for decoupling eCO2RR mechanisms by providing surface/interface-specific molecular fingerprints. This minireview systematically classifies and summarizes recent advances of in-situ Raman techniques applied to eCO2RR, emphasizing the enhancement principles and design strategies of each technique. The discussed approaches include surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, nanoconfinement-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, membrane electrode assembly-based Raman spectroscopy, and sub-second time-resolved surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Representative examples highlight how these techniques decouple complex mechanisms, from active-phase evolution to intermediate identification and pathway elucidation. Furthermore, we provided a mechanism map linking Raman-observable intermediates to elementary reaction steps, highlighted recent innovations in Raman cell design, and discussed future directions toward multimodal integration and quantitative analysis. This focused and critical perspective provides a practical roadmap for researchers aiming to apply in-situ Raman spectroscopy in complex electrocatalytic systems.
- Open Access
- Review
In-Situ/Operando Raman Spectroscopy Techniques for In-Depth Decoupling CO2 Reduction Reaction Mechanisms
- Jinxia Xue,
- Ruixin Yang,
- Zixuan Chen *
Author Information
Received: 28 Sep 2025 | Revised: 16 Oct 2025 | Accepted: 17 Oct 2025 | Published: 27 Oct 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
in-situ Raman spectroscopy | electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction reaction | reaction mechanism | reaction intermediate | Raman cell innovations
References
- 1.
O’Brien, C.P.; Miao, R.K.; Shayesteh Zeraati, A.; et al. CO2 Electrolyzers. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 3648–3693.
- 2.
Sun, Q.; Jia, C.; Lu, H.; et al. Ampere-Level Electroreduction of CO2 and CO. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2025, 54, 6973–7016.
- 3.
Nitopi, S.; Bertheussen, E.; Scott, S.B.; et al. Progress and Perspectives of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper in Aqueous Electrolyte. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672.
- 4.
Guan, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; et al. Promotion of C-C Coupling in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction to Valuable C2+ Products: From Micro-Foundation to Macro-Application. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2417567.
- 5.
Song, Y.F.; Zhang, X.M.; Xie, K.; et al. High-Temperature CO2 Electrolysis in Solid Oxide Electrolysis Cells: Developments, Challenges, and Prospects. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902033.
- 6.
Firet, N.J.; Smith, W.A. Probing the Reaction Mechanism of CO2 Electroreduction over Ag Films via Operando Infrared Spectroscopy. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 606–612.
- 7.
Yao, Z.; Cheng, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Hydrogen Radical-Boosted Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Using Ni-Partnered Heteroatomic Pairs. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9881.
- 8.
Lim, C.Y.J.; Yilmaz, M.; Arce-Ramos, J.M.; et al. Surface Charge as Activity Descriptors for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Multi-Carbon Products on Organic-Functionalised Cu. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 335.
- 9.
Liu, H.M.; Yan, T.; Tan, S.D.; et al. Observation on Microenvironment Changes of Dynamic Catalysts in Acidic CO2 Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5333–5342.
- 10.
Zhang, W.; Yu, A.; Mao, H.Y.; et al. Dynamic Bubbling Balanced Proactive CO2 Capture and Reduction on a Triple-Phase Interface Nanoporous Electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 21335–21347.
- 11.
Hsu, C.S.; Wang, J.; Chu, Y.C.; et al. Activating Dynamic Atomic Configuration for Single-Site Electrocatalyst in Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5245.
- 12.Phong Duong, H.; Rivera de la Cruz, J.G.; Portehault, D.; et al. Incorporation of Isolated Ag Atoms and Au Nanoparticles in Copper Nitride for Selective CO Electroreduction to Multicarbon Alcohols. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 900–906.
- 13.
Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; et al. Tuning Catalyst-Support Interactions Enable Steering of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Pathways. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eado5000.
- 14.
Zang, Y.; Wang, S.; Sang, J.; et al. Illustration of the Intrinsic Mechanism of Reconstructed Cu Clusters for Enhanced CO2 Electroreduction to Ethanol Production with Industrial Current Density. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 7261–7268.
- 15.Hou, J.; Chang, X.; Li, J.; et al. Correlating CO Coverage and CO Electroreduction on Cu via High-Pressure in Situ Spectroscopic and Reactivity Investigations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 22202–22211.
- 16.
Gao, W.; Xu, Y.; Fu, L.; et al. Experimental Evidence of Distinct Sites for CO2-to-CO and CO Conversion on Cu in the Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Reaction. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 885–894.
- 17.Luo, Y.; Sheng, S.; Pisarra, M.; et al. Selective excitation of vibrations in a single molecule. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6983.
- 18.
Li, J.; Chen, G.X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; et al. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction on a Three-Phase Interface. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 592–600.
- 19.
Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. In situ Raman Spectroscopic Studies of CO2 Reduction Reactions: From Catalyst Surface Structures to Reaction Mechanisms. Chem. Sci. 2025, 16, 4916–4936.
- 20.Pérez-Jiménez, A.I.; Lyu, D.; Lu, Z.X.; et al. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Benefits, Trade-Offs and Future Developments. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4563–4577.
- 21.Zhao, Y.; Chang, X.; Malkani, A.S.; et al. Speciation of Cu Surfaces During the Electrochemical CO Reduction Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9735–9743.
- 22.
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Bodappa, N.; et al. Elucidating Electrochemical CO2 Reduction Reaction Processes on Cu(hkl) Single-Crystal Surfaces by in Situ Raman Spectroscopy. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 3968–3977.
- 23.Wright, D.; Lin, Q.; Berta, D.; et al. Mechanistic Study of an Immobilized Molecular Electrocatalyst by in Situ Gap-Plasmon-Assisted Spectro-Electrochemistry. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 157–163.
- 24.
Yang, R.; Cai, Y.; Qi, Y.; et al. How Local Electric Field Regulates C-C Coupling at a Single Nanocavity in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7140.
- 25.
Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Xiao, L.; et al. Operando Spectroscopic Insights into CO2 Reduction at Electrode/Polyelectrolyte Interfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202509423.
- 26.
Fu, L.; He, P.; Wu, C.; et al. Distribution of Speciation and Activity Across the Catalyst Layer during CO2 Electroreduction in Membrane Electrode Assembly. ACS Energy Lett. 2025, 10, 3445–3450.
- 27.
An, H.; Wu, L.; Mandemaker, L.D.B.; et al. Sub-Second Time-Resolved Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Reveals Dynamic CO Intermediates during Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16576–16584.
- 28.Chen, H.Q.; Zou, L.; Wei, D.Y.; et al. In Situ Studies of Energy-Related Electrochemical Reactions Using Raman and X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy. Chin. J. Catal. 2022, 43, 33–46.
- 29.He, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, Z.L.; et al. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Principles, Methods, and Applications in Energy Systems. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 355–369.
- 30.He, Q.F.; Yu, J.; Dong, J.C.; et al. Recent Advances in Raman Spectroelectrochemistry on Single-Crystal Surfaces. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 3360–3371.
- 31.Song, J.T.; Qian, Z.X.; Yang, J.; et al. In Situ/Operando Investigation for Heterogeneous Electro-Catalysts: From Model Catalysts to State-of-the-Art Catalysts. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 4414–4440.
- 32.Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhou, R.Y.; Hu, S.; et al. Shell-Isolated Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy: Toward High Sensitivity and Broad Applicability. ACS Nano, 2024, 18, 32287–32298.
- 33.Wang, Y.H.; Zheng, S.; Yang, W.M.; et al. In Situ Raman Spectroscopy Reveals the Structure and Dissociation of Interfacial Water. Nature 2021, 600, 81–85.
- 34.
Bao, H.M.; Motobayashi, K.; Zhang, H.W.; et al. In Situ Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Reveals a Mars-van Krevelen-Type Gas Sensing Mechanism in Au@SnO2 Nanoparticle-Based Chemiresistors. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 4113–4118.
- 35.Ze, H.J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.T.; et al. Molecular Insight of the Critical Role of Ni in Pt-Based Nanocatalysts for Improving the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Probed Using an in Situ SERS Borrowing Strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1318–1322.
- 36.Li, J.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Ding, S.Y.; et al. Core-Shell Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5002–5069.
- 37.Chen, M.; Liu, D.; Du, X.; et al. 2D Materials: Excellent Substrates for Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering in Chemical Sensing and Biosensing. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2020, 130, 115983.
- 38.Wang, X.; Huang, S.C.; Hu, S.; et al. Fundamental Understanding and Applications of Plasmon-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2020, 2, 253–271.
- 39.
Yang, P.P.; Zhang, X.L.; Gao, F.Y.; et al. Protecting Copper Oxidation State via Intermediate Confinement for Selective CO2 Electroreduction to C2+ Fuels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 6400–6408.
- 40.
Yang, F.; Jiang, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Dynamics of Bulk and Surface Oxide Evolution in Copper Foams for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 66.
- 41.Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; et al. Shell-Isolated Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395.
- 42.
Hansen, K.U.; Cherniack, L.H.; Jiao, F. Voltage Loss Diagnosis in CO2 Electrolyzers Using Five-Electrode Technique. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 4504–4511.
- 43.
Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, P. Address the “Alkalinity Problem” in CO2 Electrolysis with Catalyst Design and Translation. Joule 2021, 5, 737–742.
- 44.
Mi, Z.; Wang, T.; Xiao, L.; et al. Catalytic Peculiarity of Alkali Metal Cation-Free Electrode/Polyelectrolyte Interfaces Toward CO2 Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 17377–17383.
- 45.Hartman, T.; Geitenbeek, R.G.; Wondergem, C.S.; et al. Operando Nanoscale Sensors in Catalysis: All Eyes on Catalyst Particles. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 3725–3735.
- 46.Dong, J.C.; Zhang, X.G.; Briega-Martos, V.; et al. In Situ Raman Spectroscopic Evidence for Oxygen Reduction Reaction Intermediates at Platinum Single-Crystal Surfaces. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 60–67.
- 47.
Yang, S.Y.; Jiang, M.H.; Zhang, W.J.; et al. In Situ Structure Refactoring of Bismuth Nanoowers for Highly Selective Electrochemical Reduction of CO2 to Formate, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301984.
- 48.Handoko, A.D.; Wei, F.; Jenndy; et al. Understanding Heterogeneous Electrocatalytic Carbon Dioxide Reduction through Operando Techniques. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 922–934.
- 49.Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, H.L.; et al. In Situ Dynamic Tracking of Heterogeneous Nanocatalytic Processes by Shell-Isolated Nanoparticle-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15447.
- 50.You, X.Q.; Zhang, D.A.; Zhang, X.G.; et al. Exploring the Cation Regulation Mechanism for Interfacial Water Involved in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction by in Situ Raman Spectroscopy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 53.
- 51.Gunathunge, C.M.; Ovalle, V.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Existence of an Electrochemically Inert CO Population on Cu Electrodes in Alkaline pH. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7507–7516.
- 52.
Lees, E.W.; Mowbray, B.A.W.; Parlane, F.G.L.; et al. Gas Diffusion Electrodes and Membranes for CO2 Reduction Electrolysers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 55–64.
- 53.
Tan, X.; Sun, K.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Stabilizing Copper by a Reconstruction-Resistant Atomic Cu-O-Si Interface for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8656–8664.
- 54.
Kibria, M.G.; Edwards, J.P.; Gabardo, C.M.; et al. Electrochemical CO2 Reduction into Chemical Feedstocks: From Mechanistic Electrocatalysis Models to System Design. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807166.
- 55.
Sun, Q.; Wang, J.; Fu, L.; et al. Probing Inside the Catalyst Layer on Gas Diffusion Electrodes in Electrochemical Reduction of CO and CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202504715.
- 56.
Chernyshova, I.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Ponnurangam, S. On the Origin of the Elusive First Intermediate of CO2 Electroreduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9261–E9270.
- 57.
Bohra, D.; Ledezma-Yanez, I.; Li, G.; et al. Lateral Adsorbate Interactions Inhibit HCOO@ while Promoting CO Selectivity for CO2 Electrocatalysis on Silver. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1520–1520.
- 58.
Zhan, C.; Dattila, F.; Rettenmaier, C.; et al. Key Intermediates and Cu Active Sites for CO2 Electroreduction to Ethylene and Ethanol. Nature Energy, 2024, 9, 1485–1496.
- 59.
Xie, Y.; Ou, P.; Wang, X.; et al. High Carbon Utilization in CO2 Reduction to Multi-Carbon Products in Acidic Media. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 564–570.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.