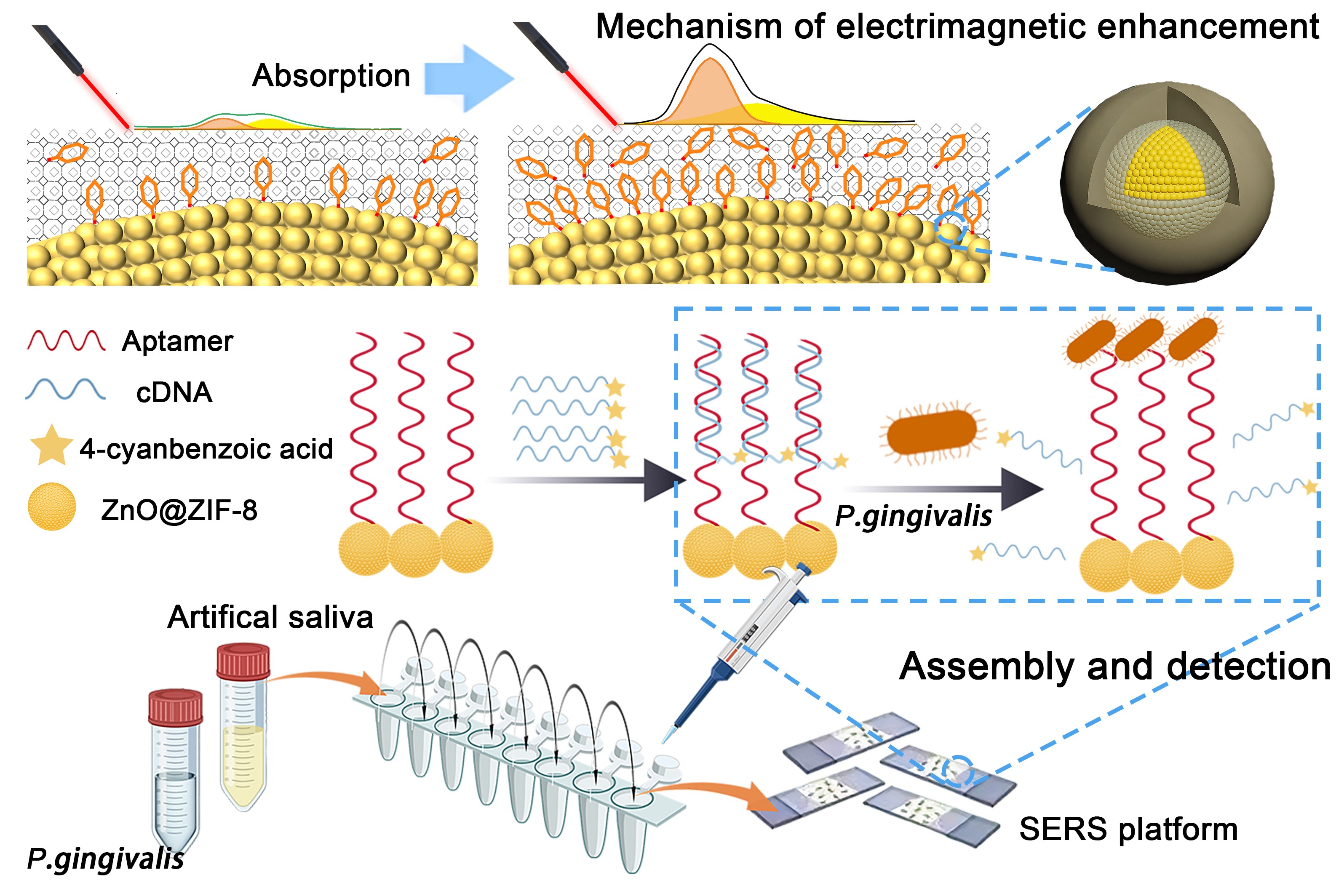
Periodontitis, which owns a significant prevalence rate, is a chronic inflammatory disorder caused by the infection of multiple microorganisms. Porphyromonas gingivalis (P. gingivalis) serves as a key pathogenic biomarker for periodontitis. However, currently, there is a lack of diagnostic tools that are able to quickly and precisely quantify levels of P. gingivalis. Therefore, developing a quantitative detection method for this pathogenic bacterium is critical for the diagnosis and management of this disease. Herein, based on the petal-like spherical ZnO@ZIF-8 composite substrate, we built an innovative semiconductor surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) platform specifically engineered for the detection of P. gingivalis with high speed, sensitivity, and stability. The detection of P. gingivalis on this SERS platform takes only 30 min. It also has excellent long-term stability for over 60 days. This platform exhibits an extensive linear range from 4 × 103 CFU/mL to 4 × 108 CFU/mL, while also owning a low limit of detection (LOD) of 38 CFU/mL for P. gingivalis. The developed method provides a novel pathway for precise diagnosis and efficient screening of periodontitis, and explores new directions for detecting other disease-related biomolecules, including proteins, small molecules, peptides, and miRNAs at the same time.
- Open Access
- Article
Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Platform Based on ZnO@ZIF-8 Composite for the Detection of Periodontal Pathogens
- Xinyi Zhang 1,
- Zhenhuan Liu 1,
- Qing Liu 1,
- Xuan Xu 2,
- Tingting Zheng 1,*
Author Information
Received: 30 Sep 2025 | Revised: 30 Oct 2025 | Accepted: 07 Nov 2025 | Published: 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
zinc oxide | Porphyromonas gingivalis | semiconductor | bacterial detection | electromagnetic enhancement
References
- 1.
Xin, X.R.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, X.C.; et al. Melatonin-Derived Carbon Dots with Free Radical Scavenging Property for Effective Periodontitis Treatment via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 8307–8324.
- 2.
Huang, H.Y.; Pan, W.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. Nanoparticulate Cell-free DNA Scavenger for Treating Inflammatory Bone Loss in Periodontitis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 13, 5925.
- 3.
Ray, R.R. 2D MOF Periodontitis Photodynamic Ion Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 15427–15439.
- 4.
Hajishengallis, G. Periodontitis: From Microbial Immune Subversion to Systemic Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 30–44.
- 5.
Potempa, J.; Mydel, P.; Koziel, J. The Case for Periodontitis in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 606–620.
- 6.
Nazir, M.; Al-Ansari, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.; et al. Global Prevalence of Periodontal Disease and Lack of Its Surveillance. Sci. World J. 2020, 2146160. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2146160.
- 7.
Jia, L.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Wu, L.L.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis Aggravates Colitis Via a Gut Microbiota-linoleic Acid Metabolism-Th17/Treg Cell Balance Axis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1617.
- 8.
Sands, K.; Carvalho, M.J.; Portal, E.; et al. Characterization of Antimicrobial-resistant Gram-negative Bacteria that Cause Neonatal Sepsis in Seven Low-and middle-income Countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 512–532.
- 9.
Murugaiyan, V.; Utreja, S.; Hovey, K.M.; et al. Defining Porphyromonas gingivalis Strains Associated with Periodontal Disease. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6222.
- 10.
Quick, J.; Grubaugh, N.D.; Pullan, S.T.; et al. Multiplex PCR Method for MinION and Illumina Sequencing of Zika and Other Virus Genomes Directly from Clinical Samples. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 25, 266–271.
- 11.
Weng, Z.Y.; You, Z.; Yang, J.; et al. CRISPR-Cas Biochemistry and CRISPR-Based Molecular Diagnostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214987.
- 12.
Smyrlaki, I.; Ekman, M.; Lentini, A.; et al. Massive and Rapid COVID-19 Testing is Feasible by Extraction-free SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4812.
- 13.
Qian, X.M.; Nie, S.M. Single-molecule and Single-nanoparticle SERS: From Fundamental Mechanisms to Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 912–920.
- 14.
Su, X.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Ouyang, Y.Z.; et al. SERS Lateral Flow Strip Detection of Serum Biomarkers for Noninvasive Assessment of Operative Microwave Ablation Outcomes of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149833.
- 15.
Shin, H.; Choi, B.H.; Shim, O.; et al. Single Test-based Diagnosis of Multiple Cancer Types Using Exosome-SERS-AI for Early Stage Cancers. Nat. Commun. 2024, 14, 1644.
- 16.
Bi, X.Y.; Daniel, M.C.; Shao, Z.F.; et al. Digital Colloid-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy by Single-molecule Counting. Nature 2024, 628, 771–775.
- 17.
Evelin, W.; Anna, M.L.; Krzysztof, N.; et al. In Search of Spectroscopic Signatures of Periodontitis: A SERS-Based Magnetomicrofluidic Sensor for Detection of Porphyromonas gingivalis and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1621–1635.
- 18.
Prince, K.J.; Mirletz, H.M.; Gaulding, E.A.; et al. Sustainability Pathways for Perovskite Photovoltaics. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 22–33.
- 19.
Song, G.; Gong, W.B.; Cong, S.; et al. Ultrathin Two-Dimensional Nanostructures: Surface Defects for Morphology-Driven Enhanced Semiconductor SERS. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5505–5511.
- 20.
Han, S.W.; Han, H.S.; Kim, K. Potassium Ion Assisted Regeneration of Active Cyano Groups in Carbon Nitride Nanoribbons: Visible Light Driven Photocatalytic Nitrogen Reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16644–16650.
- 21.
Wang, Y.G.; Zhou, K.J.; Huang, G.; et al. A Nanoparticle-based Strategy for the Imaging of a Broad Range of Tumours by Nonlinear Amplification of Microenvironment signals. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 204–212.
- 22.
Liu, X.Y.; Ye, Z.W.; Xiang, Q.; et al. Boosting Electromagnetic Enhancement for Detection of Non-adsorbing Analytes on Semiconductor SERS Substrates. Chem 2023, 9, 1464–1476.
- 23.
Tuncel, D.; Ökte, A.N. Improved Adsorption Capacity and Photoactivity of ZnO-ZIF-8 Nanocomposites. Catal. Today 2021, 361, 191–197.
- 24.
Liang, W.L.; Cheng, J.L.; Zhang, J.D.; et al. pH-Responsive On-Demand Alkaloids Release from Core-Shell ZnO@ZIF-8 Nanosphere for Synergistic Control of Bacterial Wilt Disease. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 2762–2773.
- 25.
Liang, W.L.; Wang, B.; Cheng, J.L.; et al. 3D, Eco-Friendly Metal-Organic Frameworks@carbon Nanotube Aerogels Composite Materials for Removal of Pesticides in Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123718.
- 26.
Jiang, S.Q.; Li, W.D.; Liu, J.Y.; et al. ZnO@ZIF-8 Core-shell Structure Nanorods Superhydrophobic Coating on Magnesium Alloy with Corrosion Resistance and Self-cleaning. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 3287–3301.
- 27.
Lai, Y.J.; Dong, L.J.; Liu, R.; et al. Synthesis of Highly-branched Au@AgPd Core/shell Nanoflowers for in situ SERS Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2437–2441.
- 28.
Li, S.K.; Li, Z.Y.; Hao, Q.; et al. Ultrastable Graphene Isolated AuAg Nanoalloy for SERS Biosensing and Photothermal Therapy of Bacterial Infection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108636.
- 29.
Quan, Y.N.; Tang, X.H.; Lu, W.J.; et al. Amorphous/Crystal Heterostructure Coupled Oxygen Vacancies-Sensitized TiO2 with Conspicuous Charge-Transfer Resonance for Efficient Sers Detection of Chloramphenicol. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2301609.
- 30.
Xu, Y.C.; Li, C.L.; Li, Z.Q.; et al. Constructing Charge-Transfer Excited States Based on Frontier Molecular Orbital Engineering: Narrowband Green Electroluminescence with High Color Purity and Efficiency. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17442–17446.
- 31.
Cheng, H.; Chen, R.J.; Zhan, Y.Q.; et al. Novel Ratiometric Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Quantitative Monitoring of Human Carboxylesterase-1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Using Ag-Au Nanoflowers as SERS Substrate. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 18555–18563.
- 32.
Sibug-Torres, S.M.; Grys, D.B.; Kang, G.; et al. In Situ Electrochemical Regeneration of Nanogap Hotspots for Continuously Reusable Ultrathin SERS Sensors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2022.
- 33.
Lin, X.M.; Sun, Y.L.; Chen, Y.X.; et al. Insights into Electrocatalysis through in situ Electrochemical Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. eScience 2024, 7, 100352.
- 34.
Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; et al. Generic Diagramming Platform (GDP): A comprehensive database of high-quality biomedical graphics. NAR 2025, 53, 1670–1676.
- 35.
Ji, W.; Li, L.; Song, W.; et al. Enhanced Raman Scattering by ZnO Superstructures: Synergistic Effect of Charge Transfer and Mie Resonances. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14452–14456.
- 36.
Wang, W.; Deng, C.; Xie, S.; et al. Photocatalytic C-C Coupling from Carbon Dioxide Reduction on Copper Oxide with Mixed-valence Copper(I)/Copper(II). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2984–2993.
- 37.
Gomes, B.P.F.A.; Pinheiro, E.T.; Gadê-Neto, C.R.; et al. Microbiological Examination of Infected Dental Root Canals. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2004, 19, 71–76.
- 38.
Gu, B.L.; Qi, Y.J.; Kong, J.Y.; et al. An Evaluation of Direct PCR Assays for the Detection and Quantification of P. gingivalis. Epidemiol. Infect. 2020, 148, e107.
- 39.
Ingalagi, P.; Bhat, K.G.; Kulkarni, R.D.; et al. Detection and Comparison of Prevalence of Porphyromonas gingivalis through Culture and Real Time-polymerase Chain Reaction in Subgingival Plaque Samples of Chronic Periodontitis and Healthy Individuals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2022, 26, 288.
- 40.
Su, Y.X.; Huang, S.M.; Hong, L.; et al. Establishment of the Molecular Beacon-loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification Method for the Rapid Detection of P. gingivalis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 160, 68–72.
- 41.
Shin, H.Y.; Shim, E.L.; Choi, Y.J.; et al. Giant enhancement of the Raman response due to one-dimensional ZnO nanostructures. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 14622–14626.
- 42.
Wang, Y.; Ruan, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Direct observation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in ZnO nanocrystals. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2009, 40, 1072–1077.
- 43.
Luo, Y.W.; Niu, L.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; et al. Experimental and theoretical evaluation of crystal facet exposure on the charge transfer and SERS activity of ZnO films. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 16220–16232.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.