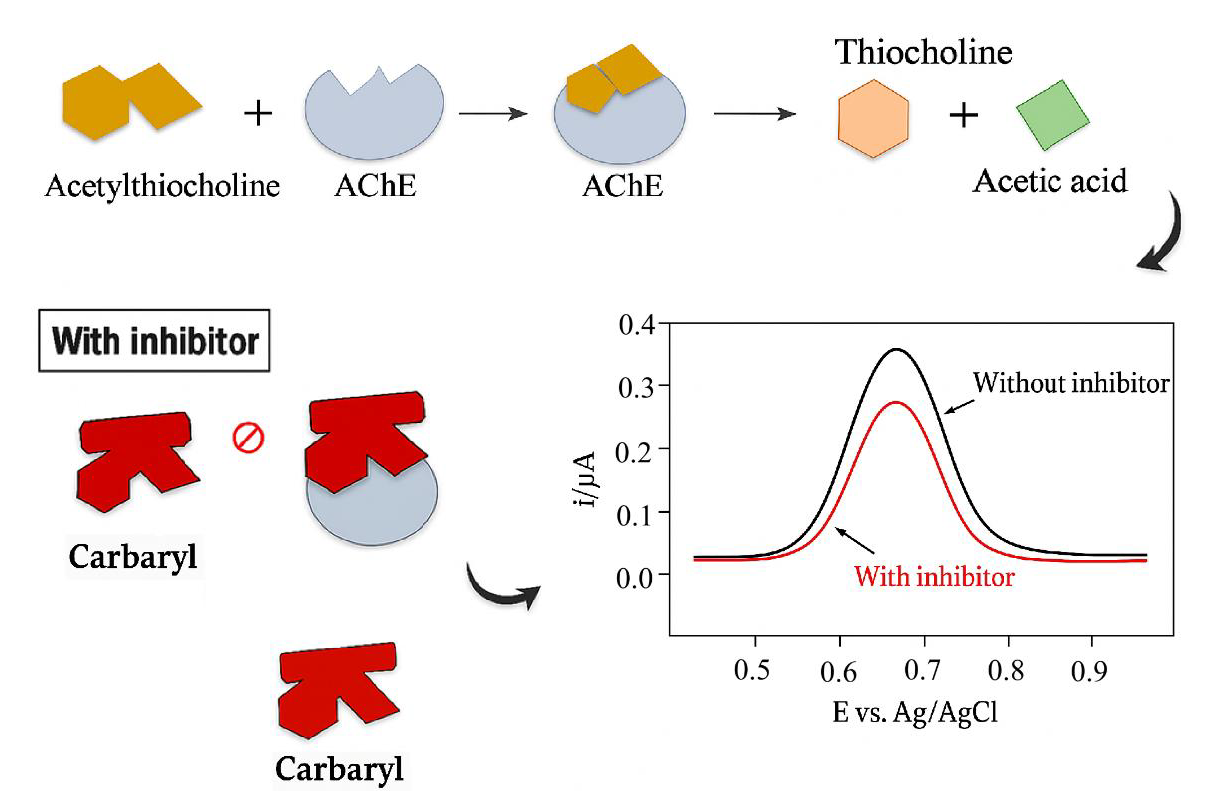
Pest-control chemicals are widely used to increase agricultural productivity; however, their extensive application raises concerns regarding food safety, occupational health, and environmental contamination. Therefore, the development of efficient and reliable technologies for pesticide detection, particularly in environmental samples, remains a key research priority. In this study, an electrochemical biosensor based on square-wave voltammetry was developed by immobilizing acetylcholinesterase onto hydrothermally synthesized gold nanoparticles, using the cysteine–diphenylalanine (CFF) peptide as both a reducing and stabilizing agent. The CFF peptide enabled excellent morphological control of the gold nanostructures (hydrodynamic radius, 16 nm) and a uniform size distribution (polydispersity index, PDI = 0.322). Carbamate detection was performed by square-wave voltammetry, yielding a highly sensitive analytical response. The calibration curve exhibited a linear range up to 10-9 M, with a correlation coefficient (R2) of 0.99 and a detection limit of 0.94 nM. The use of the CFF peptide and its self-assembling properties enabled the fabrication of an efficient and low-cost biosensor for carbamate detection, representing a promising approach for future environmental and agricultural monitoring applications.
- Open Access
- Article
- Marcos R. de A. Silva 1,
- Barbara B. Gerbelli 2,
- Ana Cristina H. Castro-Kochi 1,3,
- Andrea M. Aguilar 4,
- Wendel A. Alves 1,*
Author Information
Received: 31 Oct 2025 | Revised: 18 Dec 2025 | Accepted: 06 Jan 2026 | Published: 16 Jan 2026
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
electrochemical biosensor | pesticide detection | gold nanoparticles | cysteine–diphenylalanine peptide | environmental monitoring
References
- 1.
Xiumei, H.; Vimal, K, B.; Vanloon, W.G.; et al. Degradation of the Pesticide Fenitrothion as Mediated by Cationic Surfactants and α-Nucleophilic Reagents. Langmuir 2006, 22, 9009–9017.
- 2.
Scognamiglio, V.; Rea, G.; Arduini, F.; et al. Biosensors for Sustainable Food-New Opportunities and Technical Challenges; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 74, pp. 3–342.
- 3.
Gerbelli, B.B.; Sodre, P.T.; Filho, P.L.O.; et al. Enhancing pesticide detection: The role of serine in lipopeptide nanostructures and their self-assembly dynamics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 690, 137271.
- 4.
Gerbelli, B.B.; Filho, P.L.O.; Cortez, B.; et al. Interaction between glyphosate pesticide and amphiphilic peptides for colorimetric analysis. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 3592–3599.
- 5.
Tankiewicz, M.; Fenik, J.; Biziuk, M. Determination of organophosphorus and organonitrogen pesticides in water samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1050–1063.
- 6.
Oliveira, T.M.B.F.; Ribeiro, F.W.P.; Souza, C. P.; et al. Current overview and perspectives on carbon-based (bio)sensors for carbamate pesticides electroanalysis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115779.
- 7.
Kim, K.; Tsay, O.G.; Atwood, D.A.; et al. Destruction and detection of chemical warfare agents. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5345–5403.
- 8.
Aragay, G.; Pino, F.; Merkoçi, A. Nanomaterials for sensing and destroying pesticides. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 5317–5338.
- 9.
Kundu, M.; Krishnan, P.; Kotnala, R.K.; et al. Recent developments in biosensors to combat agricultural challenges and their future prospects. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 88, 157–178.
- 10.
Fang, Y.; Ramasamy, R.P. Current and prospective methods for plant disease detection. Biosensors 2015, 5, 537–561.
- 11.
Bakker, E.; Qin, Y. Electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3965–3984.
- 12.
Singh, P.; Kamble, G.S.; Ghodake, G.K.; et al. A Newly Emerging Trend of Chitosan-Based Sensing Platform for the Organophosphate Pesticide Detection Using Acetylcholinesterase: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 78–91.
- 13.
Sgobbi, L.F.; Machado, S.A.S. Functionalized polyacrylamide as an acetylcholinesterase-inspired biomimetic device for electrochemical sensing of organophosphorus pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 290–297.
- 14.
Ristori, C.; Del Carlo, C.; Martini, M.; et al. Potentiometric detection of pesticides in water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 1996, 325, 151–160.
- 15.
Cabral, M.F.; Sgobbi, L.F.; Kataoka, E.M.; et al. On the behavior of acetylcholinesterase immobilized on carbon nanotubes in the presence of inhibitors. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 111, 30–35.
- 16.
Sgobbi, L.F.; Zibordi-Besse, L.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; et al. Polyhydroxamicalkanoate as a bioinspired acetylcholinesterase-based catalyst for acetylthiocholine hydrolysis and organophosphorus dephosphorylation: Experimental studies and theoretical insights. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 3388–3398.
- 17.
Teixeira, S.C.; Gomes, N.O.; Calegaro, M.L.; et al. Sustainable plant-wearable sensors for on-site, rapid decentralized detection of pesticides toward precision agriculture and food safety. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 155, 213676–213686.
- 18.
Caetano, J.; Machado, S.A.S. Determination of carbaryl in tomato in natura using an amperometric biosensor based on the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase activity. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 129, 40–46.
- 19.
Patel, H.; Rawtani, D.; Agrawal, Y.K. A newly emerging trend of chitosan-based sensing platform for the organophosphate pesticide detection using acetylcholinesterase—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 78–91.
- 20.
Periasamy, A.P.; Umasankar, Y.; Chen, S.-M. Nanomaterials–acetylcholinesterase enzyme matrices for organophosphorus pesticides electrochemical sensors: A review. Sensors 2009, 9, 4034–4055.
- 21.
Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Li, H.; et al. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 230–249.
- 22.
Wang, J. Nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors. Analyst 2005, 130, 421–426.
- 23.
Pumera, M.; Sanchez, S.; Ichinose, I.; et al. Electrochemical nanobiosensors. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 123, 1195–1205.
- 24.
Du, D.; Chen, S.; Cai, J.; et al. Immobilization of acetylcholinesterase on gold nanoparticles embedded in sol–gel film for amperometric detection of organophosphorous insecticide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 130–134.
- 25.
Castro, F.L.; Castro, A.C.H.; Silva, M.R.A.; et al. Electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva using ZnO nanorods functionalized with gold-conjugated anti-RBD antibodies. ChemNanoMat 2025, 12, e202500411.
- 26.
Sabaine, A.E.; Castro, A.C.H.; Mancini, R.S.N.; et al. Peptide-based biosensors for variant-specific detection of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 7090–7103.
- 27.
Nicoliche, C.Y.N.; Pascon, A.M.; Bezerra, Í.R. S.; et al. In situ nanocoating on porous pyrolyzed paper enables antibiofouling and sensitive electrochemical analyses in biological fluids. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 2522–2533.
- 28.
Liu, G.; Wang, J.; Barry, R.; et al. Nanoparticle-based electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of phosphorylated acetylcholinesterase: An exposure biomarker of organophosphate pesticides and nerve agents. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 9951–9959.
- 29.
Du, D.; Ding, J.; Cai, J.; et al. Electrochemical thiocholine inhibition sensor based on biocatalytic growth of Au nanoparticles using chitosan as template. Sens. Actuators B 2007, 127, 317–322.
- 30.
Du, D.; Chen, S.; Song, D.; et al. Development of acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on CdTe quantum dots/gold nanoparticles modified chitosan microspheres interface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 475–479.
- 31.
Gong, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L. Electrochemical biosensing of methyl parathion pesticide based on acetylcholinesterase immobilized onto Au–polypyrrole interlaced network-like nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 2285–2288.
- 32.
Alves, W.A.; Pelin, J.N.B.D.; Edwards-Gayle, C.J.C.; et al. Self-assembled gold nanoparticles and amphiphile peptides: A colorimetric probe for copper(II) ion detection. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16226–16237.
- 33.
Gerbelli, B.B.; Vassilaides, S.V.; Rojas, J.E.U.; et al. Hierarchical self-assembly of peptides and its applications in bionanotechnology. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900085.
- 34.
Pelin, J.N.B.D.; Gatto, E.; Venanzi, M.; et al. Hybrid conjugates formed between gold nanoparticles and an amyloidogenic diphenylalanine-cysteine peptide. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 6756–6765.
- 35.
Karpel, R.L.; Liberato, M.S.; Campeiro, J.D.; et al. Design and characterization of crotamine-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 163, 1–8.
- 36.
Wang, S.S. p-Alkoxybenzyl alcohol resin and p-alkoxybenzyloxycarbonylhydrazide resin for solid-phase synthesis of protected peptide fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1973, 95, 1328–1333.
- 37.
Turkevich, J.; Stevenson, P.C.; Hillier, J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1951, 11, 55–75.
- 38.
Laviron, E. General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionless electrochemical systems. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1979, 101, 19–28.
- 39.
Wessler, I.; Michel-Schmidt, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. pH-dependent hydrolysis of acetylcholine: Consequences for non-neuronal acetylcholine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 29, 27–30.
- 40.
Štěpánek, P. Data analysis in dynamic light scattering. In Dynamic Light Scattering; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023.
- 41.
Hunter, R.J. Zeta Potential in Colloid Science: Principles and Applications; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981.
- 42.
Hackley, V.A.; Premachandran, R.S.; Malghan, S.G.; et al. A standard reference material for the measurement of particle mobility by electrophoretic light scattering. Colloids Surf. A 1995, 98, 195–203.
- 43.
Carone, A.; Emilsson, S.; Mariani, P.; et al. Gold nanoparticle shape dependence of colloidal stability domains. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 5, 2017–2026.
- 44.
Väli, R.; Jänes, A.; Lust, E. Alkali-metal insertion processes on nanospheric hard carbon electrodes: An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, E3429–E3436.
- 45.
Phongphut, A.; Chayasombat, B.; Cass, A.E.; et al. Biosensors based on acetylcholinesterase immobilized on clay–gold nanocomposites for the discrimination of chlorpyrifos and carbaryl. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 39848–39859.
- 46.
Nunes, E.W.; Silva, M.K.; Rascón, J.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on functionalized renewable carbon platform for detection of carbaryl in food. Biosensors 2022, 12, 486.
- 47.
Pohanka, M. Electrochemical biosensors based on acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase: A review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 7440–7452.
- 48.
Tun, W.S.T.; Saenchoopa, A.; Daduang, S.; et al. Electrochemical biosensor based on cellulose nanofibers/graphene oxide and acetylcholinesterase for the detection of chlorpyrifos pesticide in water and fruit juice. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 9603–9614.
- 49.
Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Hu, H.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase electrochemical biosensors with graphene-transition metal carbides nanocomposites modified for detection of organophosphate pesticides. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231981.
- 50.
Hart, J.P.; Hartley, I.C. Voltammetric and amperometric studies of thiocholine at a screen-printed carbon electrode chemically modified with cobalt phthalocyanine: Studies towards a pesticide sensor. Analyst 1994, 119, 259–263.
- 51.
Oliveira, A.C.; Mascaro, L.H. Evaluation of acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on carbon nanotube paste in the determination of chlorphenvinphos. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2011, 2011, 974216.
- 52.
Sucheta, A.; Cammack, R.; Weiner, J.; et al. Reversible electrochemistry of fumarate reductase immobilized on an electrode surface: Direct voltammetric observations of redox centers and their participation in rapid catalytic electron transport. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 5455–5465.
- 53.
Liu, Q.; Fei, A.; Huan, J.; et al. Effective amperometric biosensor for carbaryl detection based on covalent immobilization of acetylcholinesterase on multiwall carbon nanotubes/graphene oxide nanoribbons nanostructure. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 740, 8–13.
- 54.
Badawy, M.E.I.; El-Aswad, A.F. Bioactive paper sensor based on acetylcholinesterase for the rapid detection of organophosphate and carbamate pesticides. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2014, 2014, 536823.
- 55.
Timur, S.; Telefoncu, A. Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) electrodes based on gelatin and chitosan matrices for pesticide detection. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Biotechnol. 2004, 32, 427–442.
- 56.
Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; et al. An acetylcholinesterase inhibition biosensor based on a reduced graphene oxide/silver nanocluster/chitosan nanocomposite for detection of organophosphorus pesticides. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 6213–6219.
- 57.
Gong, J.; Liu, T.; Song, D.; et al. One-step fabrication of three-dimensional porous calcium carbonate–chitosan composite film as the immobilization matrix of acetylcholinesterase and its biosensing on pesticide. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1873–1876.
- 58.
Cui, H.-F.; Wu, W.-W.; Li, M.-M.; et al. A highly stable acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on chitosan–TiO₂–graphene nanocomposites for detection of organophosphate pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 223–229.
- 59.
Song, D.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Palladium–copper nanowires-based biosensor for the ultrasensitive detection of organophosphate pesticides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 982, 168–175.
- 60.
Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Wang, B.; et al. An ultra-sensitive acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on reduced graphene oxide–Au nanoparticles–β-cyclodextrin/Prussian blue–chitosan nanocomposites for organophosphorus pesticides detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 23–30.
- 61.
Nesakumar, N.; Ramachandra, B.L.; Sethuraman, S.; et al. Evaluation of inhibition efficiency for the detection of captan, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin, pentachlorophenol, and carbosulfan in water: An electrochemical approach. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 217–223.
- 62.
Guo, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; et al. A miniaturized portable instrument for rapid determination of pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 4046–4052.
- 63.
Du, D.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; et al. Comparison of pesticide sensitivity by electrochemical test based on acetylcholinesterase biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2007, 23, 285–289.
- 64.
Du, D.; Ding, J.; Tao, Y.; et al. Application of chemisorption/desorption process of thiocholine for pesticide detection based on acetylcholinesterase biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2008, 134, 908–912.
- 65.
Sun, X.; Wang, X. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on Prussian blue–modified electrode for detecting organophosphorous pesticides. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2611–2614.
- 66.
Yan, J.; Guan, H.; Yu, J.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on assembly of multiwall carbon nanotubes onto liposome bioreactors for detection of organophosphate pesticides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2013, 105, 197–202.
- 67.
Guan, H.; Zhang, F.; Yu, J.; et al. Novel acetylcholinesterase biosensors based on liposome bioreactors–chitosan nanocomposite film for detection of organophosphate pesticides. Food Res. Int. 2012, 49, 15–21.
- 68.
Sun, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. AChE biosensor based on aniline–MWNTs modified electrode for the detection of pesticides. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering, Harbin, China, 22–25 May 2011; pp 441–444.
- 69.
Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Ma, J.; et al. Determination of carbamate pesticide methomyl using acetylcholinesterase/MWNTs–chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 8856–8867.
- 70.
Dong, J.; Zhao, H.; Qiao, F.; et al. Quantum dot immobilized acetylcholinesterase for the determination of organophosphate pesticides using graphene–chitosan nanocomposite modified electrode. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 2866–2872.
- 71.
Du, D.; Wang, M.; Cai, J.; et all. One-step synthesis of multiwalled carbon nanotubes–gold nanocomposites for fabricating amperometric acetylcholinesterase biosensor. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 143, 524–529.
- 72.
Zhai, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, W.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on chitosan/Prussian blue/multiwall carbon nanotubes/hollow gold nanospheres nanocomposite film by one-step electrodeposition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 42, 124–130.
- 73.
Kandimalla, V.B.; Ju, H. Binding of acetylcholinesterase to multiwall carbon nanotube–cross-linked chitosan composite for flow-injection amperometric detection of an organophosphorous insecticide. Chem. Eur. J. 2006, 12, 1074–1080.
- 74.
El-Moghazy, A.Y.; Soliman, E.A.; Ibrahim, H.Z.; et al. Biosensor based on electrospun blended chitosan–poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibrous enzymatically sensitized membranes for pirimiphos-methyl detection in olive oil. Talanta 2016, 155, 258–264.
- 75.
Talarico, D.; Arduini, F.; Amine, A.; et al. Screen-printed electrode modified with carbon black and chitosan: A novel platform for acetylcholinesterase biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7299–7309.
- 76.
Du, D.; Ding, J.; Cai, J.; et al. One-step electrochemically deposited interface of chitosan–gold nanoparticles for acetylcholinesterase biosensor design. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 605, 53–60.
- 77.
Yang, Y.; Guo, M.; Yang, M.; et al. Determination of pesticides in vegetable samples using an acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on nanoparticles ZrO₂/chitosan composite film. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2005, 85, 163–175.
- 78.
Liu, T.; Su, H.; Qu, X.; et al. Acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on 3-carboxyphenylboronic acid/reduced graphene oxide–gold nanocomposites modified electrode for amperometric detection of organophosphorus and carbamate pesticides. Sens. Actuators B 2011, 160, 1255–1261.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


