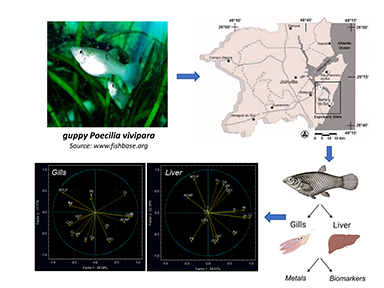
We aimed to select reliable biomarkers of metal exposure in the eurhalyne guppy Poecilia vivipara. Individuals were exposed to three different sites in a coastal bay (i.e., Linguado Channel, Babitonga Bay, Southern Brazil), a coastal environment with a long history of metal contamination. Temperature, salinity, pH, dissolved oxygen, and dissolved organic carbon) were measured in seawater from the exposure sites. After exposure, fish were anesthetized and their tissues (i.e., gill and liver) were dissected to evaluate the Ag, Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn concentrations, as well as a suite of biomarkers: antioxidant capacity against peroxyl radicals (ACAP), antioxidant enzyme activities (catalase and glutathione S-transferase), metallothionein-like protein (MTLP) concentration, and lipid peroxidation level (LPO). Seawater physicochemical conditions were similar in the exposure sites. Metal concentrations in tissues did not differ significantly between exposure sites. Principal component analysis indicated close correlations between Ni and ACAP, Ag/Cd and MTLPs, and Zn and LPO in the gills. In the liver, there was a close correlation between Pb and LPO. These findings highlight the importance and need for selecting relevant and suitable tissues and biomarkers for biomonitoring programs that aim to assess and monitor fish exposure to metal contamination in coastal waters. The findings also point to the need for future research focused on the response of oxidative stress‒related biomarkers to long-term in situ exposure of fish to coastal waters contaminated with metals and other inorganic and organic pollutants.
- Open Access
- Article
Oxidative Stress-Related Biomarkers in Tissues of the Euryhaline Guppy Poecilia Vivipara Exposed In Situ to a Coastal Water Environment with a Long History of Metal Contamination
- Arthur Juan Costa Mathias 1,
- Anderson Abel de Souza Machado 1,
- Marianna Basso Jorge 2,
- Mariana Machado Lauer 2,
- Juliana da Silva Fonseca 2,
- Claudia Bueno dos Reis Martinez 3,
- Adalto Bianchini 1, 2, *
Author Information
Received: 05 Aug 2025 | Revised: 27 Aug 2025 | Accepted: 03 Sep 2025 | Published: 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
biomarkers | ecotoxicology | fish | metals | oxidative stress | pollution
References
- 1.Henseler, C.; Nordström, M.C.; Törnroos, A.; et al. Coastal habitats and their importance for the diversity of benthic communities: A species- and trait-based approach. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 226, 106272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2019.106272.
- 2.Pinheiro, G.D.S.; Tupiassu, L.; Reymão, A.E.N. Coastal management in Brazil from the perspective of the public policy cycle: Analysis of the “multiscale management” proposed in the National Coastal Management Plan. Camb. Prism. Coast. Futures 2023, 1, e41. https://doi.org/10.1017/cft.2023.28.
- 3.Kennish, M. Drivers of change in estuarine and coastal marine environments: An overview. Open J. Ecol. 2021, 11, 224‒239. https://doi.org/10.4236/oje.2021.113017.
- 4.Pereira, R.D.; Brazílio, L.P.; Trejo-Rangel, M.A.; et al. Traditional and local communities as key actors to identify climate-change impacts: A citizen science approach in Southeast Brazilian coastal areas. Front. Clim. 2023, 5, 1‒16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fclim.2023.1243008.
- 5.Pereira, C.D.S.; Maranho, L.A.; Cortez, F.S.; et al. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and cocaine in a Brazilian coastal zone. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 148‒154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.051.
- 6.Perina, F.C.; Abessa, D.M.S. Contamination and toxicity in a subtropical Estuarine Protected Area influenced by former mining activities. Ocean Coast. Res. 2020, 68, 1‒29. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2675-28242020068313.
- 7.Marson, E.O.; Paniagua, C.E.S.; Gomes Júnior, O.; et al. A review toward contaminants of emerging concern in Brazil: Occurrence, impact and their degradation by advanced oxidation process in aquatic matrices. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155605.
- 8.Escrobot, M.; Pagioro, T.; Martins, L.; et al. Microplastics in Brazilian coastal environments: A systematic review. RBCIAMB 2024, 59, e-1719. https://doi.org/10.5327/Z2176-94781719.
- 9.El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi; M.O.; Li, J.; et al. Heavy metal pollution in coastal environments: Ecological implications and management strategies: A review. Sustainability 2025, 17, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17020701.
- 10.FAO. Integrated Management of Coastal Zones. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/t0708e/T0708E01.htm (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- 11.Jablonski, S.; Filet, M. Coastal management in Brazil—A political riddle. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2008, 51, 536‒543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2008.06.008.
- 12.Roussiez, V.; Ludwig, W.L.; Monaco, A.; et al. Sources and sinks of sediment-bound contaminants in the Gulf of Lions (NW Mediterranean Sea): A multi-tracer approach. Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1843‒1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csr.2006.04.010.
- 13.Costa, P.G.; Marube, L.C.; Artifon, V.; et al. Temporal and spatial variations in metals and arsenic contamination in water, sediment and biota of freshwater, marine and coastal environments after the Fundão dam failure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151340.
- 14.Hayat, M.; Khan, B.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Evidence of microplastic contamination in the food chain: An assessment of their presence in the gastrointestinal tract of native fish. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2024, 36, 40‒49. https://doi.org/10.15586/ijfs.v36i3.2532.
- 15.Dhineka, K.; Kaviarasan, T.; Sambandam, M.; et al. Coastal Lagoon’s dual role as a sink and source for microplastics: A case study from India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 211, 117480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117480.
- 16.Khan, B.N.; Ullah, H.; Ashfaq, Y.; et al. Elucidating the effects of heavy metals contamination on vital organ of fish and migratory birds found at fresh water ecosystem. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20968.
- 17.Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 730305. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305.
- 18.Zhang, M.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Heavy metal pollution in the East China Sea: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111473.
- 19.Li, C.; Wang, H.; Liao, X.; et al. Heavy metal pollution in coastal wetlands: A systematic review of studies globally over the past three decades. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127312.
- 20.Martins, I.; Guerra, A.; Azevedo, A.; et al. A modelling framework to assess multiple metals impacts on marine food webs: Relevance for assessing the ecological implications of deep-sea mining based on a systematic review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114902.
- 21.Ahamad, M.I.; Yao, Z.; Ren, L.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on aquatic life and human health: A case study of River Ravi Pakistan. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1374835. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1374835.
- 22.Santhosh, K.; Kamala, K.; Ramasamy, P.; et al. Unveiling the silent threat: Heavy metal toxicity devastating impact on aquatic organisms and DNA damage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116139.
- 23.Khawar, M.; Masood, Z.; Ul Hasan, H.; et al. Trace metals and nutrient analysis of marine fish species from the Gwadar coast. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6548. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57335-0.
- 24.Oros, A. Bioaccumulation and trophic transfer of heavy metals in marine fish: Ecological and ecosystem-level impacts. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/jox15020059.
- 25.Taslima, K.; Al-Emran, M.; Rahman, M.S.; et al. Impacts of heavy metals on early development, growth and reproduction of fish—A review. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 858‒868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.04.013.
- 26.Gashkina, N.A. Metal toxicity: Effects on energy metabolism in fish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms25095015.
- 27.Naz, S.; Chatha, A.; Tellez, G.; et al. A comprehensive review on metallic trace elements toxicity in fishes and potential remedial measures. Water 2023, 15, 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w15163017.
- 28.Kumar, M.; Singh, S.; Jain, A.; et al. A review on heavy metal-induced toxicity in fishes: Bioaccumulation, antioxidant defense system, histopathological manifestations, and transcriptional profiling of genes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 83, 127377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127377.
- 29.Averill-Bates, D.A. The antioxidant glutathione. In Vitamins and Hormones: Antioxidants; Litwack, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; Volume 121, pp. 109‒141. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.vh.2022.09.002.
- 30.Yang, R.; Roshani, D.; Gao, B.; et al. Metallothionein: A comprehensive review of its classification, structure, biological functions, and applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox13070825.
- 31.Ševčíková, M.; Modrá, H.; Slaninova, A.; et al. Metals as a cause of oxidative stress in fish: A review. Vet. Med. 2011, 56, 537‒546. https://doi.org/10.17221/4272-VETMED.
- 32.Das, J.N.; Saikia, S. Metal induced oxidative stress in fishes: A review. J. Adv. Zool. 2024, 45, 434‒449. https://doi.org/10.53555/jaz.v45i1.3582.
- 33.Wang, Y.; Noman, A.; Zhang, C.; et al. Effect of fish-heavy metals contamination on the generation of reactive oxygen species and its implications on human health: A review. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1500870. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2024.1500870.
- 34.Magnuson, J.T.; Sandheinrich, M.B. Relation among mercury, selenium, and biomarkers of oxidative stress in Northern Pike (Esox lucius). Toxics 2023, 11, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11030244.
- 35.Paylar, B.; Bezabhe, Y.H.; Mangu, J.C.K.; et al. Assessing organism differences in mixed metal sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167340.
- 36.Fettweis, M.; Riethmüller, R.; Van der Zande, D.; et al. Sample based water quality monitoring of coastal seas: How significant is the information loss in patchy time series compared to continuous ones? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162273.
- 37.Franco, T.; Zorzal-Almeida, S.; Sá, F.; et al. Ex-post impact assessment on a large environmental disaster. Environ. Chall. 2024, 15, 100889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2024.100889.
- 38.Monserrat, J.M.; Martínez, P.E.; Geracitano, L.A.; et al. Pollution biomarkers in estuarine animals: Critical review and new perspectives. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 221‒234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.08.012.
- 39.Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Giordano, M.E. Pollution biomarkers in the framework of marine biodiversity conservation: State of art and perspectives. Water 2021, 13, 1847. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13131847.
- 40.Calisi, A. Integrating bioindicators and biomarkers in aquatic ecotoxicology: An overview. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11920. https://doi.org/10.3390/app132111920.
- 41.Lionetto, M.G.; Matozzo, V. Editorial: The physiological response of aquatic invertebrates to pollution. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1295636. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1295636.
- 42.El-SiKaily, A.; Shabaka, S. Biomarkers in aquatic systems: Advancements, applications and future directions. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2025, 50, 169‒182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejar.2024.05.002.
- 43.Bodou, A.; Ribeyre, F. Fish as “biological model” for experimental studies in ecotoxicology. In Aquatic Ecotoxicology, 1st ed.; Bodou, A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989; Volume 2, pp. 127‒162. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781351069861.
- 44.Norrgren, L. Fish models for ecotoxicology. Acta Vet. Scand. 2012, 54, S14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1751-0147-54-S1-S14.
- 45.Desforges, J.P.; Weijs, L.; Hickie, B.; et al. Models as much needed tools in ecotoxicology: Integrative approaches to cross barriers. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 83, 295‒298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-022-00964-1.
- 46.Inwati, P.; Yadav, B.; Aitwar, V.; et al. Review on fish as bio-indicators: Assessing the health of river ecosystems. UPJOZ. 2025, 46, 168–180. https://doi.org/10.56557/upjoz/2025/v46i74874.
- 47.Bevitório, L.Z.; Silva, N.G.; Pirovani, J.C.M.; et al. Impacts of tailings of Fundão dam (Brazil) rupture on marine fish: Metals bioaccumulation and physiological responses. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113511.
- 48.Vieira, C.E.D.; Marques, J.A.; Silva, N.G.; et al. Ecotoxicological impacts of the Fundão dam failure in freshwater fish community: Metal bioaccumulation, biochemical, genetic and histopathological effects. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 832, 154878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154878.
- 49.Kocalar, K.; Canli, E.G.; Canli, M. Responses of oxidative stress biomarkers of freshwater fish (Oreochromis niloticus) exposed to Cr6+, Hg2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ in differing calcium levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 267, 109577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2023.109577.
- 50.Yamamoto, F.Y.; Onishi, K.; Ralha, T.R.; et al. Earlier biomarkers in fish evidencing stress responses to metal and organic pollution along the Doce River Basin. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121720.
- 51.Macedo, G.H.R.V.; Castro, J.S.; Jesus, W.B.; et al. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in an estuarine catfish species caught near a port complex on the Brazilian Amazon coast. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 69, 103306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsma.2023.103306.
- 52.Zahran, E.; Mamdouh, AZ.; Elbahnaswy, S.; et al. The impact of heavy metal pollution: Bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, and histopathological alterations in fish across diverse habitats. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-025-02045-1.
- 53.Machado, A.A.S. Biomarcadores de Contaminação Aquática em Poecilia vivipara. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande, Rio Grande, RS, Brazil, 2012.
- 54.Machado, A.A.S.; Hoff, M.L.M.; Cardoso, J.G.; et al. Biomarkers of waterborne copper exposure in the guppy Poecilia vivipara acclimated to salt water. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 138, 60‒69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.04.009.
- 55.Fehrenbach, G.W.; Murphy, E.; Tanoeiro, J.R.; et al. Monitoring water contamination through shellfish: A systematic review of biomarkers, species selection, and host response. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 295, 118120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.118120.
- 56.Louvise, J.; Monteiro, L. Morphological divergence patterns among populations of Poecilia vivipara (Teleostei Poeciliidae): Test of an ecomorphological paradigm. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2008, 93, 799‒812. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.2007.00945.x.
- 57.Rocha, T.L.; Carvalho, R.; Yamada, Á.T.; et al. Morphologic analysis of developmental phases and gill ontogenesis in neotropical species Poecilia vivipara (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) exposed to different salinities. Zoologia 2010, 27, 554‒562. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-46702010000400007.
- 58.Bolasina, S.N.; Azevedo, A.; Petry, A.C. Comparative efficacy of benzocaine, tricaine methanesulfonate and eugenol as anesthetic agents in the guppy Poecilia vivipara. Aquac. Rep. 2017, 6, 56‒60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aqrep.2017.04.002.
- 59.Mattos, J.J.; Siebert, M.N.; Luchmann, K.H.; et al. Differential gene expression in Poecilia vivipara exposed to diesel oil water accommodated fraction. Mar. Environ. Res. 2010, 69, S31‒S33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2009.11.002.
- 60.Paulo, D.V.; Fontes, F.; Flores-Lopes, F. Histopathological alterations observed in the liver of Poecilia vivipara (Cyprinodontiformes: Poeciliidae) as a tool for the environmental quality assessment of the Cachoeira River, BA. Braz. J. Biol. 2012, 72, 131‒140. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1519-69842012000100015.
- 61.Machado, A.A.S.; Hoff, M.L.M.; Klein, R.D.; et al. Oxidative stress and DNA damage responses to phenanthrene exposure in the estuarine guppy Poecilia vivipara. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 98, 96‒105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2014.03.013.
- 62.Piazza, C.E.; Mattos, J.J.; Lima, D.; et al. Hepatic transcriptome, transcriptional effects and antioxidant responses in Poecilia vivipara exposed to sanitary sewage. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 203, 116426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.116426.
- 63.Chung, K.S. Lethal effects of cadmium in tropical fishes. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1983, 49, 1565‒1568. https:// doi.org/10.2331/suisan.49.1565.
- 64.Araújo, E.; Morais, J.; Souza, P.; et al. Efeitos de poluentes químicos cumulativos e mutagênicos durante o desenvolvimento ontogenético de Poecilia vivipara (Cyprinodontiformes, Poeciliidae). Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2001, 23, 391‒399. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v23i0.2694.
- 65.IBAMA. Proteção e Controle de Ecossistemas Costeiros: Manguezal da Baía de Babitonga; Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais Renováveis: Brasília, DF, Brazil, 1998; p. 145.
- 66.Bonatti-Chaves, M.; Barros, V.; Manente, S.; et al. Study of the Anthropogenic Contamination of Babitonga Bay, Brazil. In Understanding the Complexity of Environmental Issues: A Way to Sustainability, Proceedings of the SETAC Europe 13th Annual Meeting, Hamburg, Germany, 27 April‒1 May 2023; Volume 1.
- 67.Oliveira, T.M.N.; Tureck, C.R.; Bassfeld, J.C.; et al. Integridade ambiental da Baía da Babitonga: Características físico-químicas, microbiológicas e ecotoxicidade. In Diagnóstico Ambiental da Baía da Babitonga; Cremer, M.J.; Morales, P.R.D.; Oliveira, T.M.N., Eds.; Editora da Univille: Joinville, SC, Brazil, 2006; pp. 20‒80.
- 68.Cremer, M.J.; Simões-Lopes, P.C. Distribution, abundance and density estimates of franciscanas, Pontoporia blainvillei (Cetacea: Pontoporiidae), in Babitonga bay, southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2008, 25, 397‒402. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-81752008000300003.
- 69.Mazzer, A.M.; Gonçalves, M.L. Aspectos geomorfológicos da Baía da Babitonga, Santa Catarina, Brasil: Caracterização morfométrica. Rev. Bras. Geomorfol. 2011, 12, 115–120.
- 70.Filgueras, A.S.; Silva, T.S.; Correa, I.C.S. Impacts of sea level rise and land use on coastal wetlands: Methodology applied to Baía da Babitonga (SC). Soc. Nat. 2023, 36, e69403 https://doi.org/10.14393/SN-v36-2024-69403x.
- 71.Vieira, C.V.; Haponiuk, R.R.; Horn Filho, N.O. Ilhas da Baía Babitonga, Santa Catarina, Brasil: Caracterização geológica, geomorfológica e do uso e cobertura do solo. GEOgraphia 2024, 26, 1‒20. https://doi.org/10.22409/GEOgraphia2024.v26i57.a55902.
- 72.Demori, J. Análise Histórica da Contaminação por Metais Pesados na Baía da Babitonga—SC. Master’s Thesis, Universidade do Vale do Itajaí, Itajaí, SC, Brazil, 2008.
- 73.Destefani, A. Avaliação de Riscos Ecológicos Associados aos Sedimentos Superficiais Acumulado no Dique do Canal do Linguado Sul (Baía de Babitonga—SC). Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade do Vale do Itajaí, Itajaí, SC, Brazil, 2017.
- 74.Benedetti, B. Geoquímica de Metais e Outros Elementos em Sedimentos da Baía da Babitonga (SC): Uma Caracterização Ambiental. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, SP, Brazil, 2023. https://doi.org/10.11606/D.21.2023.tde-18102023-180027.
- 75.Tureck, C.R.; Haak, L.; Cunha, S.M.B.; et al. Qualidade de sedimentos na Baía da Babitonga e sua implicação na reabertura do Canal do Linguado (SC), Brasil. Acta Biol. Catarin. 2024, 11, 46‒61. https://doi.org/10.21726/abc.v11i1.2173.
- 76.Amado, L.L.; Garcia, M.L.; Ramos, P.B.; et al. A method to measure total antioxidant capacity against peroxyl radicals in aquatic organisms: Application to evaluate microcystins toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2115‒2123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.11.038.
- 77.Beutler, E. Red Cell Metabolism: A Manual of Biochemical Methods; Grune & Straton: New York, NY, USA, 1975.
- 78.Keen, J.H.; Habig, W.H.; Jakoby, W.B. Mechanism for several activities of the glutathione-S-transferase. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 20, 6183‒6188. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(20)81842-0.
- 79.Viarengo, A.; Ponzano, E.; Dondero, F.; et al. A simple spectophotometric method for metallothionein evaluation in marine organisms: An application to Mediterranean and Antarctic molluscs. Mar. Environ. Res. 1997, 44, 69‒84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(96)00103-1.
- 80.Oakes, K.D.; Van Der Kraak, G.J. Utility of the TBARS assay in detecting oxidative stress in white sucker (Catostomus commersoni) populations exposed to pulp mill effluent. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 63, 447‒463. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0166-445X(02)00204-7.
- 81.Machado, A.A.S.; Spencer, K.; Kloas, W.; et al. Metal fate and effects in estuaries: A review and conceptual model for better understanding of toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 268‒281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.09.045.
- 82.Moiseenko, T.I.; Gashkina, N.A. Distribution and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Hg, Cd and Pb) in fish: Influence of the aquatic environment and climate. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 115013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/abbf7c.
- 83.Ray, S.; Vashishth, R. From water to plate: Reviewing the bioaccumulation of heavy metals in fish and unraveling human health risks in the food chain. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2024.100358.
- 84.Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, X.; et al. Nutritional value and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in nine commercial fish species from Dachen Fishing Ground, East China Sea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6927. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10975-6.
- 85.Zaghloul, G.Y.; Eissa, H.A.; Zaghloul, A.Y.; et al. Impact of some heavy metal accumulation in different organs on fish quality from Bardawil Lake and human health risks assessment. Geochem. Trans. 2024, 25, 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12932-023-00084-2.
- 86.Zhang, P.; Ye, Z.; Huang, L.; et al. Heavy metal alarm of marine fish consumption surrounding Qiongzhou Strait, the South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1557963. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1557963.
- 87.Topić Popović, N.; Čižmek, L.; Babić, S.; et al. Fish liver damage related to the wastewater treatment plant effluents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 48739‒48768. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-26187-y.
- 88.Hoseinifar, S.H.; Yousefi, S.; Van Doan, H.; et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in fish: The implications of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotics. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2021, 29, 198‒217. https://doi.org/10.1080/23308249.2020.1795616.
- 89.Mathias, A.J.C. Biomarcadores em Poecilia vivipara (Cyprinodontiformes, Poeciliidae) Exposto a Ambiente Salino Com Histórico de Contaminação por Metais. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande, Rio Grande, RS, Brazil, 2014.
- 90.Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Boucheker, A.; et al. Seasonal and spatial contamination of trace elements in sediments and fish tissues (Mugil chephalus) from Annaba gulf (North East of Algeria). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 166137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166137.
- 91.Weber, P.; Behr, E.R.; Knorr, C.L.; et al. Metals in the water, sediment, and tissues of two fish species from different trophic levels in a subtropical Brazilian river. Microchem. J. 2013, 106, 61‒66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2012.05.004.
- 92.Has-Schön, E.; Bogut, I.; Vuković, R.; et al. Distribution and age-related bioaccumulation of lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), cadmium (Cd), and arsenic (As) in tissues of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and European catfish (Sylurus glanis) from the Buško Blato reservoir (Bosnia and Herzegovina). Chemosphere 2015, 135, 289‒296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.04.015.
- 93.Koduvayur, M.V.; Vasudevan, S.; Pandey, V.; et al. Comparative evaluation of heavy metal concentration in different organs of the asian seabass: A multivariate approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1012541. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2022.1012541.
- 94.Kumar, R.D.; Pandey, V.; Jha, D.K.; et al. Comparative evaluation of heavy metal concentration in three commercially important fish: Insights from organ-specific and interspecies variability. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1634855. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2025.1634855.
- 95.Wood, C.M.; Al-Reasi, H.A.; Scott Smith, D. The two faces of DOC. Aquat. Toxicol. 2011, 105, 3‒8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2011.03.007.
- 96.Kito, H.; Tazawa, T.; Ose, Y.; et al. Formation of metallothionein in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Comp. Pharmacol. 1982, 73, 129‒134. https://doi.org/10.1016/0306-4492(82)90179-4.
- 97.Gerpe, M.; Kling, P.; Olsson, P.E. Metallothionein gene expression in arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) following metal and PCB exposure. Mar. Environ. Res. 1998, 46, 551‒554. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-1136(97)00108-6.
- 98.Cho, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; et al. Gene structure and expression of metallothionein during metal exposures in Hemibarbus mylodon. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 125‒137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2007.08.005.
- 99.Man, A.K.; Woo, N.Y. Upregulation of metallothionein and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase expression in silver sea bream, Sparus sarba exposed to sublethal levels of cadmium. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 89, 214‒221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.07.002.
- 100.De Boeck, G.; Eyckmans, M.; Lardon, I.; et al. Metal accumulation and metallothionein induction in the spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 155, 503‒508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.12.014.
- 101.Osman, A.G.M.; Wuertz, S.; Mohammed-Geba, K. Lead-induced heat shock protein (HSP70) and metallothionein (MT) gene expression in the embryos of African catfish Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Sci. Afr. 2019, 3, e00056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2019.e00056.
- 102.Crupkin, A.; Menone, M. Changes in the activities of glutathione-s-transferases, glutathione reductase and catalase after exposure to different concentrations of cadmium in Australoheros facetus (Cichlidae, Pisces). J. Braz. Soc. Ecotoxicol. 2013, 8, 21‒25. https://doi.org/10.5132/eec.2013.01.003.
- 103.Massarsky, A.; Dupuis. L.; Taylor, J.; et al. Assessment of nanosilver toxicity during zebrafish (Danio rerio) development. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 59‒66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.02.060.
- 104.Choudhury, C.; Mazumder, R.; Kumar, R.; et al. Cadmium induced oxystress alters Nrf2-Keap1 signaling and triggers apoptosis in piscine head kidney macrophages. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 231, 105739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2020.105739.
- 105.Lee, D.-C.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, J-H. Toxic effects of waterborne cadmium exposure on hematological parameters, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and heat shock protein 70 in juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 122, 476‒483. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2022.02.022.
- 106.Lee, J.-W.; Choi, H.; Hwang, U.-K.; et al. Toxic effects of lead exposure on bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and immune responses in fish: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 68, 101‒108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2019.03.010.
- 107.Lee, J.-W.; Jo, A.-H.; Lee, D.-C.; et al. Review of cadmium toxicity effects on fish: Oxidative stress and immune responses. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116600.
- 108.Ghannam, H.E.; Khedr, A.I.; El-Sayed, R.; et al. Oxidative stress responses and histological changes in the liver of Nile tilapia exposed to silver bulk and nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 15390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-97731-8.
- 109.Jebur, A.B.; El-Demerdash, F.M. Hexavalent chromium toxicity induced biochemical perturbation in Tilapia nilotica: Role of Phoenix. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 388, 012057. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/388/1/012057.
- 110.Handa, K.; Jindal, R. Estimating the hepatotoxic impact of hexavalent chromium on Ctenopharyngodon idellus through a multi-biomarker study. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envadv.2021.100108.
- 111.Zheng, J.-L.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Wu, C.-W.; et al. Zinc acclimation mitigated high zinc induced oxidative stress by enhancing antioxidant defenses in large yellow croaker Pseudosciaena crocea. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 172, 21‒29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.12.009.
- 112.Choi, C.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Song, J.A.; et al. Water hardness improves the antioxidant response of zinc-exposed goldfish (Carassius auratus). Biology 2023, 12, 289. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12020289.
- 113.Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; et al. Comprehensive assessment of detoxification mechanisms of hydrolysis fish peptides in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) under copper exposure: Tracing from bioaccumulation, oxidative stress, lipid deposition to metabolomics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115418.
- 114.Chaurasia, S.S.; Gupta, P.; Kar, A.; et al. Lead induced thyroid dysfunction and lipid peroxidation in the fish Clarias batrachus with special reference to hepatic type I-5′-monodeiodinase activity. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 56, 649‒654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001289900095.
- 115.Abdel-Aziz, R.; Elwoa, S.; Al-Megrin, W.; et al. Effects of heavy metal contamination on Oreochromis niloticus (Tilapia fish). Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e47822. https://doi.org/10.1590/fst.47822.
- 116.Atli, G. How metals directly affect the antioxidant status in the liver and kidney of Oreochromis niloticus? An in vitro study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2020, 62, 126567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126567.
- 117.Azevedo, J.S.; Serafim, A.; Company, R.; et al. Biomarkers of exposure to metal contamination and lipid peroxidation in the benthic fish Cathorops spixii from two estuaries in South America, Brazil. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 1001‒1010. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-009-0370-x.
- 118.Padmini, E.; Rani, M.U. Evaluation of oxidative stress biomarkers in hepatocytes of grey mullet inhabiting natural and polluted estuaries. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4533‒4541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.04.005.
- 119.Ferreira, C.P.; Piazza, T.B.; Souza, P.; et al. Integrated biomarker responses in oysters Crassostrea gasar as an approach for assessing aquatic pollution of a Brazilian estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2021, 165, 105252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2021.105252.
- 120.Maraschi, A.C.; Marques, J.A.; Costa, S.R.; et al. Marine shrimps as biomonitors of the Fundão (Brazil) mine dam disaster: A multi-biomarker approach. Environ Pollut. 2022, 305, 119245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119245.
- 121.Fonseca, J.S.; Marangoni, L.F.B.; Marques, J.A.; et al. Effects of increasing temperature alone and combined with copper exposure on biochemical and physiological parameters in the zooxanthellate scleractinian coral Mussismilia harttii. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 121‒132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2017.07.002.
- 122.Marques, J.A.; Abrantes, D.P.; Marangoni, L.F.; et al. Ecotoxicological responses of a reef calcifier exposed to copper, acidification and warming: A multiple biomarker approach. Environ Pollut. 2020, 257, 113572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113572.
- 123.Fonseca, J.S.; Marangoni, L.F.B.; Marques, J.A.; et al. Elevated temperature and exposure to copper leads to changes in the antioxidant defense system of the reef-building coral Mussismilia harttii. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 804678. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2021.804678.
- 124.Fonseca, J.S.; Mies, M.; Paranhos, A.; et al. Isolated and combined effects of thermal stress and copper exposure on the trophic behavior and oxidative status of the reef-building coral Mussismilia harttii. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115892.
- 125.Baag, S.; Mandal, S. Integrative biomarker approach to decode seasonal variation in biomarker responses of Scylla serrata and Penaeus monodon from Sundarbans estuarine system. Oceanologia 2025, 67, 67108. https://doi.org/10.5697/IVQW7412.
How to Cite
Mathias, A. J. C.; de Souza Machado, A. A.; Jorge, M. B.; Lauer, M. M.; da Silva Fonseca, J.; dos Reis Martinez, C. B.; Bianchini, A. Oxidative Stress-Related Biomarkers in Tissues of the Euryhaline Guppy Poecilia Vivipara Exposed In Situ to a Coastal Water Environment with a Long History of Metal Contamination. Earth: Environmental Sustainability 2025, 1 (1), 84–101. https://doi.org/10.53941/eesus.2025.100007.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


