In the face of growing environmental pressures, enzymes are emerging as powerful and versatile tools for combating pollution. With their exceptional specificity, ability to function under mild conditions, and minimal environmental impact, enzymes offer a sustainable alternative to traditional remediation methods. They can effectively break down and neutralize a wide range of pollutants—including pesticides, pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, dyes, and microplastics—without generating toxic by-products. Innovations such as enzyme immobilization, microbial consortia, and hybrid technologies have significantly enhanced their stability and performance in real-world conditions. Advances in protein engineering and the use of artificial intelligence now enable the design of tailor-made enzymes with improved resilience and substrate range. Enzymes also play a vital role in the circular economy by transforming waste into valuable secondary raw materials, biofuels, and biodegradable products. While challenges remain in scaling up these technologies and reducing costs, the potential of enzyme-based biotechnologies is immense, positioning them as a promising path toward environmentally friendly and efficient solutions for pollution control, resource recovery, climate-resilient development, and as a cornerstone of future environmental strategies.
- Open Access
- Review
Enzymes in the Removal of Harmful Substances: The Potential of Biotechnology in Environmental Protection
- Agnieszka Rybarczyk *,
- Jakub Zdarta *
Author Information
Received: 11 Jul 2025 | Revised: 18 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 23 Sep 2025 | Published: 09 Oct 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
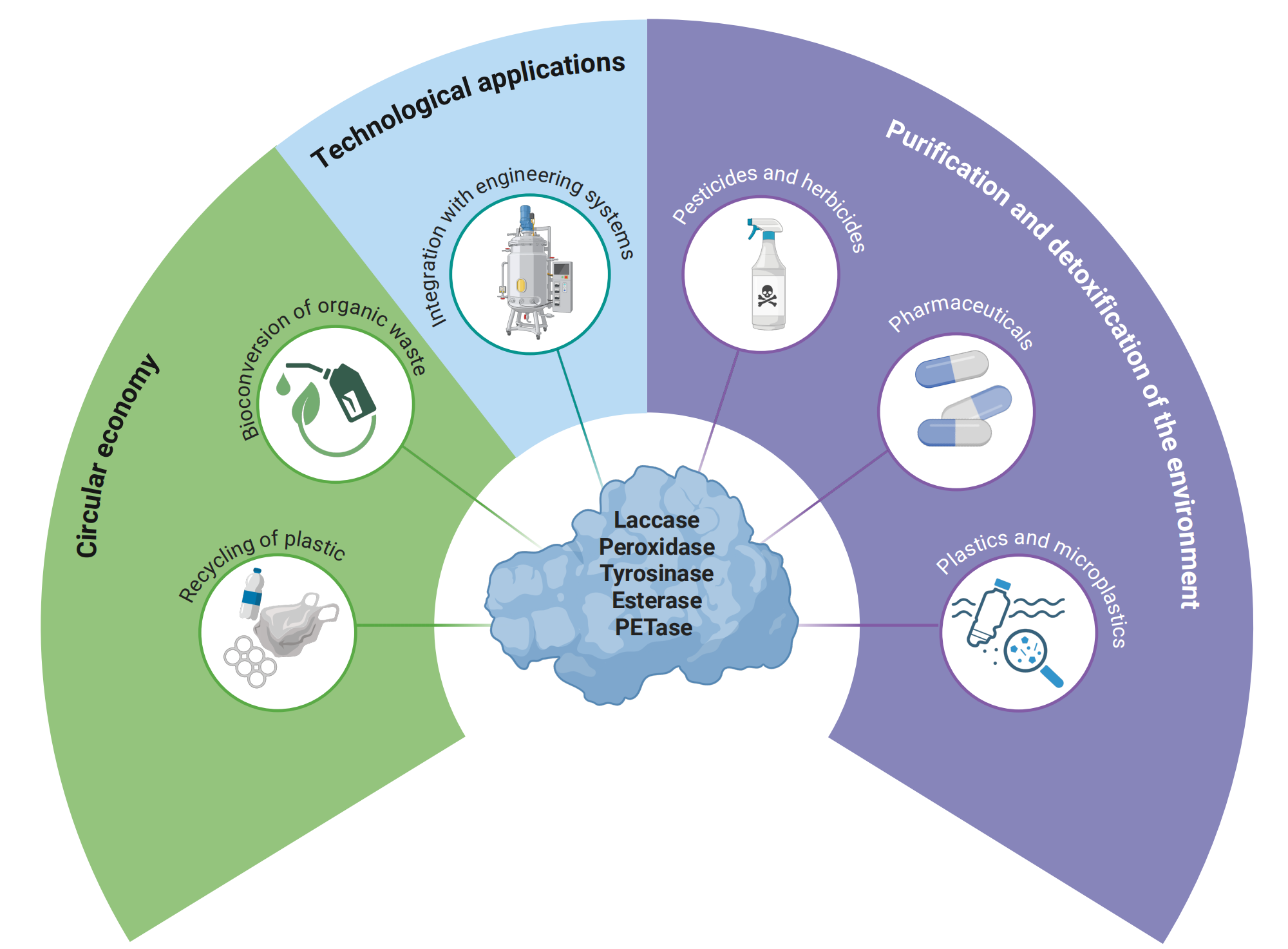
Keywords
enzymes | bioremediation | wastewater treatment | micropollutants | sustainable development
References
- 1.
Rathod, S.V.; Saras, P.; Gondaliya, S.M. Environmental Pollution: Threats and Challenges for Management. In Eco-Restoration of Polluted Environment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024. ISBN 978-1-00-342339-3.
- 2.
Mejía-Marchena, R.; Maturana-Córdoba, A.; Gómez-Cerón, D.; et al. Industrial Wastewater Treatment Technologies for Reuse, Recycle, and Recovery: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Gaps. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2023, 12, 205–250. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2023.2198147.
- 3.
Somu, P.; Narayanasamy, S.; Gomez, L.A.; et al. Immobilization of Enzymes for Bioremediation: A Future Remedial and Mitigating Strategy. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113411.
- 4.
Yaashikaa, P.R.; Devi, M.K.; Kumar, P.S. Advances in the Application of Immobilized Enzyme for the Remediation of Hazardous Pollutant: A Review. Chemosphere 2022, 299, 134390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.134390.
- 5.
Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Waswani, H.; et al. Impact of Pesticides on the Ecosystem. In Agrochemicals in Soil and Environment: Impacts and Remediation; Naeem, M., Bremont, J.F.J., Ansari, A.A., et al., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 157–181. ISBN 9789811693106.
- 6.
Sun, M.; Xu, W.; Zhang, W.; et al. Microbial Elimination of Carbamate Pesticides: Specific Strains and Promising Enzymes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 5973–5986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12141-4.
- 7.
Chia, X.K.; Hadibarata, T.; Kristanti, R.A.; et al. The Function of Microbial Enzymes in Breaking down Soil Contaminated with Pesticides: A Review. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2024, 47, 597–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-024-02978-6.
- 8.
Shukla, E.; Bendre, A.D.; Gaikwad, S.M.; et al. Hydrolases: The Most Diverse Class of Enzymes. In Hydrolases; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. ISBN 978-1-80355-163-0.
- 9.
Sharma, S.; Bhatt, K.; Shrivastava, R.; Nadda, A.K. Chapter 14-Tyrosinase and Oxygenases: Fundamentals and Applications. In Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes, 2nd ed.; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 323–340. ISBN 978-0-443-19059-9.
- 10.
Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Xin, Y.; et al. Effective Remediation and Decontamination of Organophosphorus Compounds Using Enzymes: From Rational Design to Potential Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161510.
- 11.
Sharma, A.K.; Pandit, J. Advanced Bioremediation Strategies for Organophosphorus Compounds. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2023, 51, 374–389. https://doi.org/10.48022/mbl.2308.08011.
- 12.
Łomża, P.; Krucoń, T.; Tabernacka, A. Potential of Microbial Communities to Perform Dehalogenation Processes in Natural and Anthropogenically Modified Environments—A Metagenomic Study. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1702. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11071702.
- 13.
Samadi-Maybodi, A.; Ghezel-Sofla, H.; BiParva, P. Simultaneous Removal of Phenoxy Herbicides, 2-Methyl-4-Chlorophenoxyacetic Acid and 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid from Aqueous Media by Magnetized MgAl-LDH@Fe3O4 Composite: Application of Partial Least Squares and Doehlert Experimental Design. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 97–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-023-00877-8.
- 14.
Puri, M.; Gandhi, K.; Suresh Kumar, M. A Global Overview of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in the Environment: Occurrence, Effects, and Treatment Methods. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 12875–12902. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04636-4.
- 15.
Ismanto, A.; Hadibarata, T.; Kristanti, R.A.; et al. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs) in Environmental Matrices: Occurrence, Fate, Health Impact, Physio-Chemical and Bioremediation Technology. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 302, 119061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119061.
- 16.
Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M.; Miertuš, S. Laccases as Effective Tools in the Removal of Pharmaceutical Products from Aquatic Systems. Life 2024, 14, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14020230.
- 17.
Lopes, J.M.; Marques-da-Silva, D.; Videira, P.Q.; et al. Comparison of Laccases and Hemeproteins Systems in Bioremediation of Organic Pollutants. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2022, 23, 402–423. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203723666220704090416.
- 18.
Sellami, K.; Couvert, A.; Nasrallah, N.; et al. Peroxidase Enzymes as Green Catalysts for Bioremediation and Biotechnological Applications: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150500.
- 19.
Basumatary, D.; Yadav, H.S.; Yadav, M. The Role of Peroxidases in the Bioremediation of Organic Pollutants. Nat. Prod. J. 2023, 13, 60–77. https://doi.org/10.2174/2210315512666220410132847.
- 20.
Arrighi, F. New Prospectives on the Benzo[b]Thiophene-3-Ole Scaffold: Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors & Photocatalytic Functionalization of Dehydroalanine-Derived Peptides in Batch and Flow. Available online: https://iris.uniroma1.it/handle/11573/1730176 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- 21.
Mokhosoev, I.M.; Astakhov, D.V.; Terentiev, A.A.; et al. Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase Systems: Diversity and Plasticity for Adaptive Stress Response. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2024, 193, 19–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2024.09.003.
- 22.
Li, Y.; Mu, Z.; Yuan, Y.; et al. An Enzymatic Activity Regulation-Based Clusterzyme Sensor Array for High-Throughput Identification of Heavy Metal Ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131501.
- 23.
Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Parakh, S.K.; et al. Health Hazards of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr (VI)) and Its Microbial Reduction. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4923–4938. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2037273.
- 24.
Sethi, S. Phytochelatins: Heavy Metal Detoxifiers in Plants. In Advanced and Innovative Approaches of Environmental Biotechnology in Industrial Wastewater Treatment; Shah, M.P., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 361–379. ISBN 978-981-9925-98-8.
- 25.
Huang, L.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, D.; et al. A Review of the Role of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) in Wastewater Treatment Systems. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191912191.
- 26.
Mohajan, H.K. Plastic Pollution: A Potential Threat on Health and Environment. Stud. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2025, 4, 25–30.
- 27.
Han, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, D.; et al. Enzymatic Degradation of Synthetic Plastics by Hydrolases/Oxidoreductases. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2024, 189, 105746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2024.105746.
- 28.
Khairul Anuar, N.F.S.; Huyop, F.; Ur-Rehman, G.; et al. An Overview into Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Hydrolases and Efforts in Tailoring Enzymes for Improved Plastic Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012644.
- 29.
Liu, Z.; Chang, S.H.; Mailhot, G. Emerging Biochemical Conversion for Plastic Waste Management: A Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061255.
- 30.
Ali, S.S.; Elsamahy, T.; Al-Tohamy, R.; et al. A Critical Review of Microplastics in Aquatic Ecosystems: Degradation Mechanisms and Removing Strategies. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnology 2024, 21, 100427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ese.2024.100427.
- 31.
Sodhi, A.S.; Bhatia, S.; Batra, N. Laccase: Sustainable Production Strategies, Heterologous Expression and Potential Biotechnological Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135745.
- 32.
Vijayanand, M.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Subramanian, R.; et al. Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Water Environment: A Review on Toxicity, Microbial Biodegradation, Systematic Biological Advancements, and Environmental Fate. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.115716.
- 33.
Wan, L.; Jiang, M.; Cheng, D.; et al. Continuous Flow Technology-a Tool for Safer Oxidation Chemistry. React. Chem. Eng. 2022, 7, 490–550. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RE00520K.
- 34.
Victorino da Silva Amatto, I.; Gonsales da Rosa-Garzon, N.; Antônio de Oliveira Simões, F.; et al. Enzyme Engineering and Its Industrial Applications. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 389–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2117.
- 35.
Maghraby, Y.R.; El-Shabasy, R.M.; Ibrahim, A.H.; et al. Enzyme Immobilization Technologies and Industrial Applications. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 5184–5196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c07560.
- 36.
Tadesse, M.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances in Enzyme Immobilization: The Role of Artificial Intelligence, Novel Nanomaterials, and Dynamic Carrier Systems. Catalysts 2025, 15, 571. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15060571.
- 37.
Tang, C.; Wang, L.; Zang, L.; et al. On-Demand Biomanufacturing through Synthetic Biology Approach. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 18, 100518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100518.
- 38.
Liang, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhuang, G. Construction of Environmental Synthetic Microbial Consortia: Based on Engineering and Ecological Principles. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 829717. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.829717.
- 39.
Ashokkumar, V.; Flora, G.; Venkatkarthick, R.; et al. Advanced Technologies on the Sustainable Approaches for Conversion of Organic Waste to Valuable Bioproducts: Emerging Circular Bioeconomy Perspective. Fuel 2022, 324, 124313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.124313.
- 40.
Ekeoma, B.C.; Ekeoma, L.N.; Yusuf, M.; et al. Recent Advances in the Biocatalytic Mitigation of Emerging Pollutants: A Comprehensive Review. J. Biotechnol. 2023, 369, 14–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2023.05.003.
- 41.
Zafar, M.G.; Mumtaz, A.; Akbar, A.; et al. Distinctive Role of Enzymes in Textile Industry. In Enzymes in Textile Processing: A Climate Changes Mitigation Approach: Textile Industry, Enzymes, and SDGs; Arshad, M., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2025; pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-981-9780-58-7.
- 42.
Rezvanian, K.; Shahan, H.T.; Ghofrani, D.; et al. Innovative Manufacturing and Recycling Approaches for Multilayer Polymer Packaging: A Comprehensive Review. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2025, 64, 1441–1474. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2025.2470852.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


