This review addresses the critical issue of microplastic (MP) pollution in aquatic environments, with an emphasis on the potential role of MPs as vectors for pathogens. The persistence of MPs, resulting from their strong resistance to degradation, poses major global environmental and public-health challenges. Their inherent stability and large surface area promote pathogen adhesion, rendering MPs a favorable medium for the adsorption and transport of both pollutants and microorganisms. This review first explores the key physicochemical properties of MPs and the decisive factors that influence pathogen adhesion to MP surfaces. It then examines the environmental impacts and associated health risks of MP pollution in marine and freshwater ecosystems, along with its implications for human exposure through the food chain. A critical analysis and discussion of the multiple dimensions of MPs as potential vectors for pathogens highlight the urgent need to implement advanced waste-management strategies and water-treatment technologies. Furthermore, the review emphasizes the necessity of an integrated research approach to elucidate the mechanisms and impacts of MPs as pathogen carriers in aquatic ecosystems.
- Open Access
- Review
Microplastics: A Potential Vector for Pathogens in Aquatic Ecosystems
- Behnam Nayebi,
- Sepideh Nasrollahpour,
- Juviya Mathew,
- Rama Pulicharla,
- Ratul Kumar Das,
- Satinder Kaur Brar *
Author Information
Received: 16 Aug 2025 | Revised: 15 Oct 2025 | Accepted: 16 Oct 2025 | Published: 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
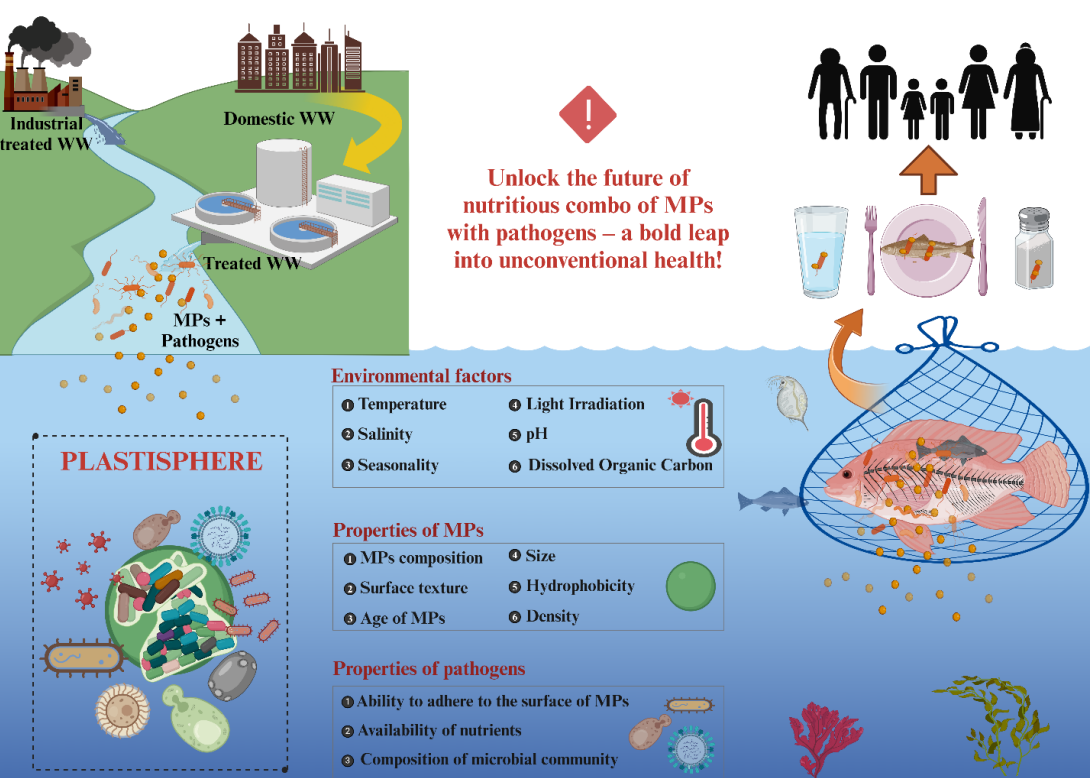
Keywords
microplastics | pathogens | carrier | adsorption | water
References
- 1.
Nayebi, B.; Khurana, P.; Pulicharla, R.; et al. Preservation, storage, and sample preparation methods for freshwater microplastics—A comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 1060–1081. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3VA00043E.
- 2.
Pham, D.N.; Clark, L.; Li, M. Microplastics as hubs enriching antibiotic-resistant bacteria and pathogens in municipal activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2021, 2, 100014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazl.2021.100014.
- 3.
Mishra, S.; Swain, S.; Sahoo, M.; et al. Microbial Colonization and Degradation of Microplastics in Aquatic Ecosystem: A Review. Geomicrobiol. J. 2022, 39, 259–269. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490451.2021.1983670.
- 4.
Song, J.; Beule, L.; Jongmans-Hochschulz, E.; et al. The travelling particles: Community dynamics of biofilms on microplastics transferred along a salinity gradient. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 35. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43705-022-00117-4.
- 5.
Gkoutselis, G.; Rohrbach, S.; Harjes, J.; et al. Microplastics accumulate fungal pathogens in terrestrial ecosystems. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13214. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92405-7.
- 6.
Mathew, J.; Pulicharla, R.; Rezai, P.; et al. Microplastics in wastewaters: Pretreatment to detection trail. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.105702.
- 7.
Chen, Y.-N.; Rani, A.; Chiang, C.-Y.; et al. Monitoring, control and assessment of microplastics in bioenvironmental systems. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103250.
- 8.
Lamichhane, G.; Acharya, A.; Marahatha, R.; et al. Microplastics in environment: Global concern, challenges, and controlling measures. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 4673–4694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04261-1.
- 9.
Athey, S.N.; Albotra, S.D.; Gordon, C.A.; et al. Trophic transfer of microplastics in an estuarine food chain and the effects of a sorbed legacy pollutant. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2020, 5, 154–162. https://doi.org/10.1002/lol2.10130.
- 10.
Hurley, R.R.; Woodward, J.C.; Rothwell, J.J. Ingestion of Microplastics by Freshwater Tubifex Worms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12844–12851. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03567.
- 11.
Hamilton, B.; Rochman, C.; Hoellein, T.; et al. Prevalence of microplastics and anthropogenic debris within a deep-sea food web. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2021, 675, 23–33. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps13846.
- 12.
Joo, S.H.; Liang, Y.; Kim, M.; et al. Microplastics with adsorbed contaminants: Mechanisms and Treatment. Environ. Chall. 2021, 3, 100042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100042.
- 13.
Zhang, Q.; He, Y.; Cheng, R.; et al. Recent advances in toxicological research and potential health impact of microplastics and nanoplastics in vivo. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 40415–40448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19745-3.
- 14.
Rice, J.; Westerhoff, P. Spatial and Temporal Variation in De Facto Wastewater Reuse in Drinking Water Systems across the USA. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 982–989. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5048057.
- 15.
Negrete Velasco, A.; Ramseier Gentile, S.; Zimmermann, S.; et al. Contamination and Removal Efficiency of Microplastics and Synthetic Fibres in a Conventional Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Front. Water 2022, 4, 835451.
- 16.
Vercauteren, M.; Semmouri, I.; Van Acker, E.; et al. Toward a Better Understanding of the Contribution of Wastewater Treatment Plants to Microplastic Pollution in Receiving Waterways. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 642–654.
- 17.
Murphy, L.; Germaine, K.; Dowling, D.N.; et al. Association of Potential Human Pathogens with Microplastics in Freshwater Systems. In Springer Water, Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Microplastic Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea, Capri, Italy, 15–18 September 2019; Cocca, M., Di Pace, E., Errico, M.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 112–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-45909-3_19.
- 18.
Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Li, M.; et al. Selective enrichment of bacterial pathogens by microplastic biofilm. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.114979.
- 19.
Naik, R.K.; Naik, M.M.; D’Costa, P.M.; et al. Microplastics in ballast water as an emerging source and vector for harmful chemicals, antibiotics, metals, bacterial pathogens and HAB species: A potential risk to the marine environment and human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110525.
- 20.
Junaid, M.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Sadaf, M.; et al. Enrichment and dissemination of bacterial pathogens by microplastics in the aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154720.
- 21.
BugBitten Terrestrial Pathogens and Microplastics: Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Ocean. Available online: https://blogs.biomedcentral.com/bugbitten/2022/09/09/terrestrial-pathogens-and-microplastics/ (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- 22.
Hou, D.; Hong, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Assessing the Risks of Potential Bacterial Pathogens Attaching to Different Microplastics during the Summer-Autumn Period in a Mariculture Cage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1909.
- 23.
Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Dai, M.; et al. Microplastic pollution and its relationship with the bacterial community in coastal sediments near Guangdong Province, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144091.
- 24.
Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; et al. Ingested Microscopic Plastic Translocates to the Circulatory System of the Mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800249a.
- 25.
Li, H.X.; Ma, L.S.; Lin, L.; et al. Microplastics in oysters Saccostrea cucullata along the Pearl River Estuary, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 619–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.01.083.
- 26.
Tata, T.; Belabed, B.E.; Bououdina, M.; et al. Occurrence and characterization of surface sediment microplastics and litter from North African coasts of Mediterranean Sea: Preliminary research and first evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136664.
- 27.
Zhong, H.; Wu, M.; Sonne, C.; et al. The hidden risk of microplastic-associated pathogens in aquatic environments. Eco Environ. Health 2023, 2, 142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eehl.2023.07.004.
- 28.
Jeong, E.; Lee, J.-Y.; Redwan, M. Animal exposure to microplastics and health effects: A review. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2024.100369.
- 29.
Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Boraschi, D. Association between Microorganisms and Microplastics: How Does It Change the Host–Pathogen Interaction and Subsequent Immune Response? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4065.
- 30.
Rummel, C.D.; Jahnke, A.; Gorokhova, E.; et al. Impacts of Biofilm Formation on the Fate and Potential Effects of Microplastic in the Aquatic Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 258–267.
- 31.
Liu, P.; Dai, J.; Bie, C.; et al. Bioaccessibility of Microplastic-Associated Antibiotics in Freshwater Organisms: Highlighting the Impacts of Biofilm Colonization via an In Vitro Protocol. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 12267–12277.
- 32.
McFall, A.; Coughlin, S.A.; Hardiman, G.; et al. Strategies for biofilm optimization of plastic-degrading microorganisms and isolating biofilm formers from plastic-contaminated environments. Sustain. Microbiol. 2024, 1, qvae012.
- 33.
Cheng, J.; Jacquin, J.; Conan, P.; et al. Relative Influence of Plastic Debris Size and Shape, Chemical Composition and Phytoplankton-Bacteria Interactions in Driving Seawater Plastisphere Abundance, Diversity and Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 610231. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.610231.
- 34.
Cloutman-Green, E.; Barbosa, V.L.; Jimenez, D.; et al. Controlling Legionella pneumophila in water systems at reduced hot water temperatures with copper and silver ionization. Am. J. Infect. Control 2019, 47, 761–766.
- 35.
Parrish, K.; Fahrenfeld, N.L. Microplastic biofilm in fresh- and wastewater as a function of microparticle type and size class. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 495–505. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8EW00712H.
- 36.
Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Plastisphere enrich antibiotic resistance genes and potential pathogenic bacteria in sewage with pharmaceuticals. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 144663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144663.
- 37.
Silva, V.; Pérez, V.; Gillanders, B.M.; et al. Short-Term Plastisphere Colonization Dynamics across Six Plastic Types. Environ Microbiol. 2023, 25, 2732–2745
- 38.
Kye, H.; Kim, J.; Ju, S.; et al. Microplastics in water systems: A review of their impacts on the environment and their potential hazards. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14359.
- 39.
Sun, X.D.; Yuan, X.Z.; Jia, Y.; et al. Differentially charged nanoplastics demonstrate distinct accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 755–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-020-0707-4.
- 40.
Vigeant, M.A.-S.; Ford, R.M.; Wagner, M.; et al. Reversible and Irreversible Adhesion of Motile Escherichia coli Cells Analyzed by Total Internal Reflection Aqueous Fluorescence Microscopy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2794–2801. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.68.6.2794-2801.2002.
- 41.
Schäfer, A.; Harms, H.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Bacterial Accumulation at the Air—Water Interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3704–3712. https://doi.org/10.1021/es980191u.
- 42.
He, L.; Rong, H.; Li, M.; et al. Bacteria have different effects on the transport behaviors of positively and negatively charged microplastics in porous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125550.
- 43.
Shen, H.; Yang, M.; Yin, K.; et al. Size- and surface charge-dependent hormetic effects of microplastics on bacterial resistance and their interactive effects with quinolone antibiotic. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 903, 166580.
- 44.
Ustabasi, G.S.; Baysal, A. Bacterial interactions of microplastics extracted from toothpaste under controlled conditions and the influence of seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135024.
- 45.
Xu, J.; Zhou, T.; Tang, C.; et al. Characterization and tolerance of foodborne pathogenic bacteria in microplastic biofilm. LWT 2024, 200, 116168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116168.
- 46.
Arias-Andres, M.; Klümper, U.; Rojas-Jimenez, K.; et al. Microplastic pollution increases gene exchange in aquatic ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 237, 253–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.058.
- 47.
He, S.; Jia, M.; Xiang, Y.; et al. Biofilm on microplastics in aqueous environment: Physicochemical properties and environmental implications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127286.
- 48.
Sanni, O.; Chang, C.Y.; Anderson, D.G.; et al. Bacterial Attachment to Polymeric Materials Correlates with Molecular Flexibility and Hydrophilicity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 695–701.
- 49.
Hossain, M.R.; Jiang, M.; Wei, Q.; et al. Microplastic surface properties affect bacterial colonization in freshwater. J. Basic Microbiol. 2019, 59, 54–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.201800174.
- 50.
Mathew, J.; Warraich, H.; Das, R.K.; et al. Curcumin-based-fluorescent staining and microfluidic detection of microplastics in wastewater effluent. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 16242–16245. https://doi.org/10.1039/D5CC02304A.
- 51.
Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Microplastics as contaminants in the soil environment: A mini-review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 848–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.209.
- 52.
Elimelech, M.; Gregory, J.; Jia, X. Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modelling and Simulation, 1st ed.; Williams, R.A.F., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013.
- 53.
Fotopoulou, K.N.; Karapanagioti, H.K. Surface Properties of Beached Plastics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11022–11032.
- 54.
Ferris, F.G.; Fyfe, W.S.; Witten, T.; et al. Effect of mineral substrate hardness on the population density of epilithic microorganisms in two Ontario rivers. Can. J. Microbiol. 1989, 35, 744–747.
- 55.
Tuson, H.H.; Weibel, D.B. Bacteria–surface interactions. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 4368–4380.
- 56.
Crawford, C.B.; Quinn, B. Physiochemical Properties and Degradation. In Microplastic Pollutants; Crawford, C.B., Quinn, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 57–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-809406-8.00004-9.
- 57.
Mammo, F.K.; Amoah, I.D.; Gani, K.M.; et al. Microplastics in the environment: Interactions with microbes and chemical contaminants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140518.
- 58.
Ermis, H.; Collins, C.; Saha, S.K.; et al. Beyond Visibility: Microorganisms for tackling plastic and microplastic problems for cleaner future. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 497, 154585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154585.
- 59.
Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; et al. Sorption of Four Hydrophobic Organic Compounds by Three Chemically Distinct Polymers: Role of Chemical and Physical Composition. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 7252–7259.
- 60.
Liu, G.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Sorption behavior and mechanism of hydrophilic organic chemicals to virgin and aged microplastics in freshwater and seawater. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.100.
- 61.
Forero-López, A.D.; Brugnoni, L.I.; Abasto, B.; et al. Plastisphere on microplastics: In situ assays in an estuarine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129737.
- 62.
Van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. The role of van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds in ‘hydrophobic interactions’ between biopolymers and low energy surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 111, 378–390.
- 63.
Monika, M.; Sharma, K. Challenges Associated with Preventive Measures and Environmentally Acceptable Techniques to Control Microplastics. In Microplastics; Singh, B., Upadhyay, S.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 317–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-443-29804-2.00013-5.
- 64.
Kirstein, I.V.; Kirmizi, S.; Wichels, A.; et al. Dangerous hitchhikers? Evidence for potentially pathogenic Vibrio spp. on microplastic particles. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.07.004.
- 65.
Bowley, J.; Baker-Austin, C.; Porter, A.; et al. Oceanic Hitchhikers—Assessing Pathogen Risks from Marine Microplastic. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2020.06.011.
- 66.
Are Microplastics Spreading Infectious Disease? Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.2311253120 (accessed on 2 August 2025).
- 67.
Ortiz, D.; Munoz, M.; Nieto-Sandoval, J.; et al. Insights into the degradation of microplastics by Fenton oxidation: From surface modification to mineralization. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136809.
- 68.
Dey, S.; Rout, A.K.; Behera, B.K.; et al. Plastisphere community assemblage of aquatic environment: Plastic-microbe interaction, role in degradation and characterization technologies. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 32.
- 69.
Koelmans, A.A.; Nor, N.H.M.; Hermsen, E.; et al. Microplastics in freshwaters and drinking water: Critical review and assessment of data quality. Water Res. 2019, 155, 410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.02.054.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


