Microplastics have raised serious environmental and health concerns worldwide due to their widespread presence as a common pollutant in aquatic environments. This study offers a comprehensive examination of microplastic pollution in river basins in Vietnam, drawing on global studies to assess its potential impact on water resources. The results indicate that microplastic pollution is present in significant concentrations in surface water, sediments, Aquatic organisms, and mangrove ecosystems throughout Vietnam, particularly in coastal areas such as Da Nang and Thanh Hoa, as well as in urban rivers like the Saigon River, with the highest concentration found being 519,000 pieces per cubic meter of water. Urban runoff, wastewater, and plastic waste from domestic, manufacturing, and tourism activities are important sources of emissions. High concentrations of microplastics, primarily fibers and debris such as nylon, PE, and PP, are highly persistent and bioaccumulate in Aquatic organisms, posing potential problems due to the presence of chemical additives. Comparative data from around the world also show similar environmental risks, including microplastic consumption by marine life, possible impacts on ecosystem function, biodiversity, and ultimately human health risks through the food chain. The study also highlights the importance of improving waste management, enhancing pollution monitoring, and implementing sustainable measures to mitigate microplastic pollution in various areas of Vietnam.
- Open Access
- Review
A Review of Microplastics Pollution in the River Basin of Vietnam in Comparison with the World Context
Author Information
Received: 16 Jul 2025 | Revised: 09 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 10 Nov 2025 | Published: 24 Nov 2025
Abstract
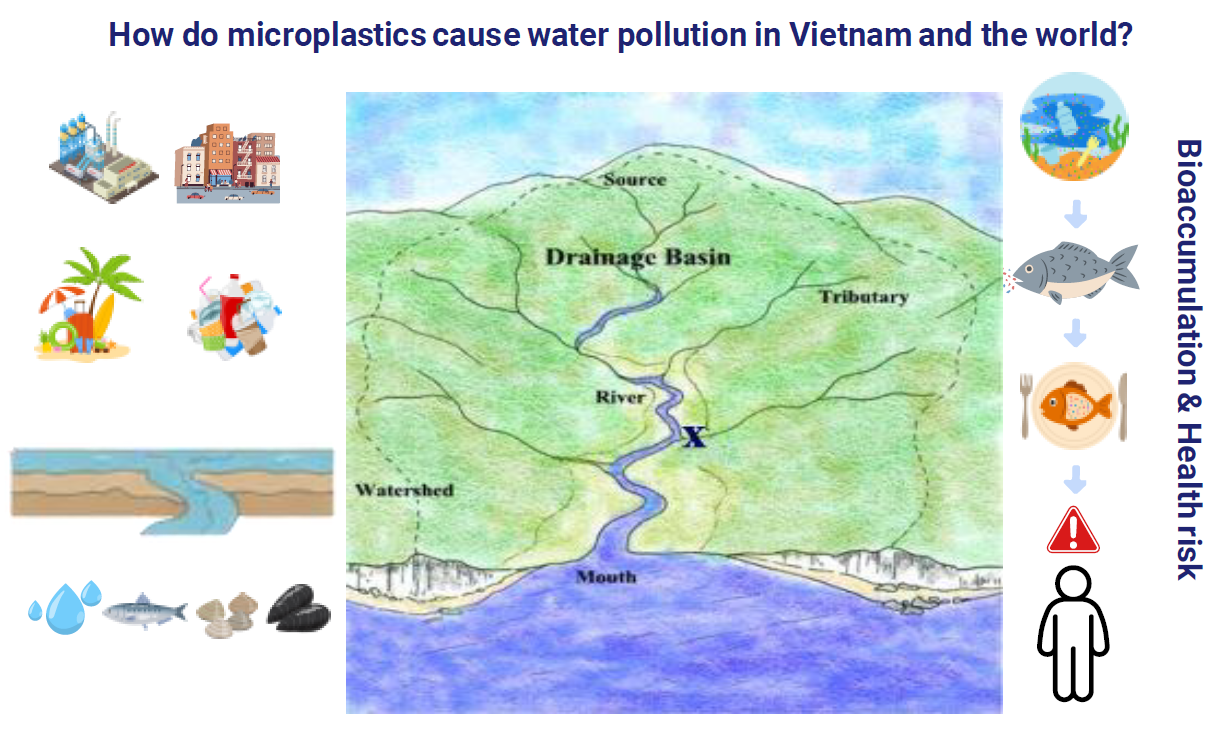
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
microplastic pollution | river basin | environmental impact | Vietnam | aquatic ecosystems
References
- 1.Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1700782.
- 2.Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; et al. Microplastics as Contaminants in the Marine Environment: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.09.025.
- 3.De Melo Nobre, F.S.; Santos, A.A.; Nilin, J. What Remains on the Beach after Tourists Leave? The Case of Abaís Beach (Sergipe, Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112700.
- 4.Caldwell, J.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; et al. Assessing Meso- and Microplastic Pollution in the Ligurian and Tyrrhenian Seas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 149, 110572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.110572.
- 5.Eriksen, M.; Lebreton, L.C.M.; Carson, H.S.; et al. Plastic Pollution in the World’s Oceans: More than 5 Trillion Plastic Pieces Weighing over 250,000 Tons Afloat at Sea. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111913. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0111913.
- 6.Van Melkebeke, M.; Janssen, C.; De Meester, S. Characteristics and Sinking Behavior of Typical Microplastics Including the Potential Effect of Biofouling: Implications for Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8668–8680. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b07378.
- 7.Hale, R.C.; Seeley, M.E.; La Guardia, M.J.; et al. A Global Perspective on Microplastics. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2020, 125, e2018JC014719. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JC014719.
- 8.Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Microplastic--an Emerging Contaminant of Potential Concern? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2007, 3, 559–561. https://doi.org/10.1002/ieam.5630030412.
- 9.Duis, K.; Coors, A. Microplastics in the Aquatic and Terrestrial Environment: Sources (with a Specific Focus on Personal Care Products), Fate and Effects. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2016, 28, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-015-0069-y.
- 10.Freshwater Microplastics: Emerging Environmental Contaminants? Wagner, M., Lambert, S., Eds.; The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 58; ISBN 978-3-319-61614-8.
- 11.Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; et al. Microplastic Ingestion by Zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. https://doi.org/10.1021/es400663f.
- 12.Lozano, R.L.; Mouat, J.; International, K. Marine Litter in the North-East Atlantic Region; OSPAR Commission: London, UK, 2009.
- 13.Campanale, C.; Massarelli, C.; Savino, I.; et al. A Detailed Review Study on Potential Effects of Microplastics and Additives of Concern on Human Health. IJERPH 2020, 17, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17041212.
- 14.Chang, X.; Xue, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Potential Health Impact of Environmental Micro- and Nanoplastics Pollution. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2020, 40, 4–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.3915.
- 15.Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; et al. Potential Toxicity of Polystyrene Microplastic Particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7391. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64464-9.
- 16.Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; et al. Plastic Waste Inputs from Land into the Ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1260352.
- 17.Hien, T.T.; Nhon, N.T.T.; Thu, V.T.M.; et al. The Distribution of Microplastics in Beach Sand in Tien Giang Province and Vung Tau City, Vietnam. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2020, 52, 208–221. https://doi.org/10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2020.52.2.6.
- 18.Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Thuong, Q.-T.; Truong, T.-N.-S.; et al. Baseline Concentration of Microplastics in Surface Water and Sediment of the Northern Branches of the Mekong River Delta, Vietnam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.114605.
- 19.Strady, E.; Dang, T.H.; Dao, T.D.; et al. Baseline Assessment of Microplastic Concentrations in Marine and Freshwater Environments of a Developing Southeast Asian Country, Viet Nam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111870.
- 20.Tran Nguyen, Q.A.; Nguyen, H.N.Y.; Strady, E.; et al. Characteristics of Microplastics in Shoreline Sediments from a Tropical and Urbanized Beach (Da Nang, Vietnam). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111768.
- 21.Viet Dung, L.; Huu Duc, T.; Thi Khanh Linh, L.; et al. Depth Profiles of Microplastics in Sediment Cores from Two Mangrove Forests in Northern Vietnam. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 1381. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9121381.
- 22.Do, V.M.; Dang, T.T.; Le, X.T.T.; et al. Abundance of Microplastics in Cultured Oysters (Crassostrea Gigas) from Danang Bay of Vietnam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.113800.
- 23.Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; et al. Microplastic and Mesoplastic Contamination in Canned Sardines and Sprats. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 1380–1386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.005.
- 24.Nam, P.N.; Tuan, P.Q.; Thuy, D.T.; et al. Contamination of Microplastic in Bivalve: First Evaluation in Vietnam. Vietnam. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 41, 252–258. https://doi.org/10.15625/0866-7187/41/3/13925.
- 25.Linh, L.T.K.; Duong, H.A.; Duc, T.H.; et al. Contamination of Microplastics in Mangrove Sediment Cores from Lach Huyen Area, Hai Phong City, Vietnam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1226, 012005. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/1226/1/012005.
- 26.Nguyễn, H.N.Ý.; Linh P.T.T.; Linh V.Đ.H.; et al. Ô nhiễm vi nhựa trong nước mặt hồ nội thành tại thành phố Đà Nẵng, Việt Nam. UD-JST 2022, 8, 88–92.
- 27.Lahens, L.; Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.-C.; et al. Macroplastic and Microplastic Contamination Assessment of a Tropical River (Saigon River, Vietnam) Transversed by a Developing Megacity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 661–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.02.005.
- 28.Strady, E.; Kieu-Le, T.-C.; Gasperi, J.; et al. Temporal Dynamic of Anthropogenic Fibers in a Tropical River-Estuarine System. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113897.
- 29.Nguyen, T.-T.T.; Ha, N.-H.; Bui, T.-K.L.; et al. Baseline Marine Litter Surveys along Vietnam Coasts Using Citizen Science Approach. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4919. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094919.
- 30.Dao Dinh, C.; Duong Thi, L.; Nguyen Quang, B.; et al. Distribution and Characteristics of Microplastics in Surface Water at Some Beaches in Thanh Hoa Province, Viet Nam. Vietnam J. Catal. Adsorpt. 2021, 10, 193–200. https://doi.org/10.51316/jca.2021.120.
- 31.Dao, C.D.; Duong, L.T.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; et al. Plastic Waste in Sandy Beaches and Surface Water in Thanh Hoa, Vietnam: Abundance, Characterization, and Sources. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10868-1.
- 32.Do, V.M.; Dang, T.T.; Le, X.T.T.; et al. Characterisation of Microplastic Debris in Beach Sediment of the Coastal Zone in Vietnam: A Preliminary Study in Da Nang. VMOST 2021, 63, 7–13. https://doi.org/10.31276/VJST.63(11DB).07-13.
- 33.Bui, T.-K.L.; Pham, Q.-K.; Doan, N.-T.; et al. Marine Litter Pollution along Sandy Beaches of Can Gio Coast, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 964, 012017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/964/1/012017.
- 34.Fruergaard, M.; Laursen, S.N.; Larsen, M.N.; et al. Abundance and Sources of Plastic Debris on Beaches in a Plastic Hotspot, Nha Trang, Viet Nam. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2022.114394.
- 35.Le, N.D.; Hoang, T.T.H.; Duong, T.T.; et al. Microplastics in the Surface Sediment of the Main Red River Estuary. Vietnam. J. Earth Sci. 2023, 45, 19–32. https://doi.org/10.15625/2615-9783/17486.
- 36.Trinh, B.-S.; Le, L.T.; Tran, L.M.; et al. Comparative Accumulation and Effects of Microplastics and Microplastic-Associated PCB-153 in the White Hard Clam (Meretrix lyrata) and Giant River Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) Following Chronic Exposure. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 34, 103581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2024.103581.
- 37.Phung, N.H.T.; Lien, L.T.; Nguyen Ha, K.-B.; et al. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Microplastics and Microplastics Associated with Polychlorinated Biphenyl 153 on Daphnia Magna. Hum. Ecol. RiskAssess. Int. J. 2024, 30, 22–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2023.2268217.
- 38.Wang, T.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; et al. Accumulation, Transformation and Transport of Microplastics in Estuarine Fronts. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 795–805. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43017-022-00349-x.
- 39.Owuor, M.A.; Icely, J.; Newton, A. Community Perceptions of the Status and Threats Facing Mangroves of Mida Creek, Kenya: Implications for Community Based Management. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 175, 172–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2019.03.027.
- 40.Maghsodian, Z.; Sanati, A.M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Study of Microplastics Pollution in Sediments and Organisms in Mangrove Forests: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.112725.
- 41.Deng, H.; He, J.; Feng, D.; et al. Microplastics Pollution in Mangrove Ecosystems: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 142041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142041.
- 42.Deng, J.; Guo, P.; Zhang, X.; et al. Microplastics and Accumulated Heavy Metals in Restored Mangrove Wetland Surface Sediments at Jinjiang Estuary (Fujian, China). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111482.
- 43.Hitchcock, J.N. Microplastics Can Alter Phytoplankton Community Composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153074. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153074.
- 44.Van Bijsterveldt, C.E.J.; van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Ramadhani, S.; et al. Does Plastic Waste Kill Mangroves? A Field Experiment to Assess the Impact of Macro Plastics on Mangrove Growth, Stress Response and Survival. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143826.
- 45.Kumar, R.; Ivy, N.; Bhattacharya, S.; et al. Coupled Effects of Microplastics and Heavy Metals on Plants: Uptake, Bioaccumulation, and Environmental Health Perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155619.
- 46.Kumar, R.; Sinha, R.; Refat Jahan Rakib, M.; et al. Microplastics Pollution Load in Sundarban Delta of Bay of Bengal. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100099.
- 47.Maghsodian, Z.; Sanati, A.M.; Ramavandi, B.; et al. Microplastics Accumulation in Sediments and Periophthalmus Waltoni Fish, Mangrove Forests in Southern Iran. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128543. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128543.
- 48.Carson, H.S.; Colbert, S.L.; Kaylor, M.J.; et al. Small Plastic Debris Changes Water Movement and Heat Transfer through Beach Sediments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1708–1713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.05.032.
- 49.Shaw, D.G.; Day, R.H. Colour- and Form-Dependent Loss of Plastic Micro-Debris from the North Pacific Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1994, 28, 39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-326X(94)90184-8.
- 50.Ryan, P.G.; Moore, C.J.; van Franeker, J.A.; et al. Monitoring the Abundance of Plastic Debris in the Marine Environment. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1999–2012. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0207.
- 51.van Franeker, J.A.; Blaize, C.; Danielsen, J.; et al. Monitoring Plastic Ingestion by the Northern Fulmar Fulmarus Glacialis in the North Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2609–2615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.06.008.
- 52.Boerger, C.M.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, S.L.; et al. Plastic Ingestion by Planktivorous Fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2275–2278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.08.007.
- 53.Davison, P.; Asch, R. Plastic Ingestion by Mesopelagic Fishes in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 432, 173–180. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09142.
- 54.Murray, F.; Cowie, P.R. Plastic Contamination in the Decapod Crustacean Nephrops Norvegicus (Linnaeus, 1758). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1207–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2011.03.032.
- 55.Frias, J.P.G.L.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, A.M. Organic Pollutants in Microplastics from Two Beaches of the Portuguese Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 1988–1992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2010.07.030.
- 56.Law, K.L.; Morét-Ferguson, S.; Maximenko, N.A.; et al. Plastic Accumulation in the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre. Science 2010, 329, 1185–1188. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1192321.
- 57.Güven, O.; Gökdağ, K.; Jovanović, B.; et al. Microplastic Litter Composition of the Turkish Territorial Waters of the Mediterranean Sea, and Its Occurrence in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Fish. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 286–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.01.025.
- 58.Köhler, A. Cellular Fate of Organic Compounds in Marine Invertebrates. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, S8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.06.020.
- 59.Ren, P.; Dou, M.; Wang, C.; et al. Abundance and Removal Characteristics of Microplastics at a Wastewater Treatment Plant in Zhengzhou. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 36295–36305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09611-5.
- 60.Tang, N.; Liu, X.; Xing, W. Microplastics in Wastewater Treatment Plants of Wuhan, Central China: Abundance, Removal, and Potential Source in Household Wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141026.
- 61.Beaumont, N.J.; Aanesen, M.; Austen, M.C.; et al. Global Ecological, Social and Economic Impacts of Marine Plastic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 189–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2019.03.022.
- 62.McIlgorm, A.; Campbell, H.F.; Rule, M.J. The Economic Cost and Control of Marine Debris Damage in the Asia-Pacific Region. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2011, 54, 643–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2011.05.007.
- 63.Qiang, M.; Shen, M.; Xie, H. Loss of Tourism Revenue Induced by Coastal Environmental Pollution: A Length-of-Stay Perspective. J. Sustain. Tour. 2020, 28, 550–567. https://doi.org/10.1080/09669582.2019.1684931.
- 64.Santos, I.R.; Friedrich, A.C.; Wallner-Kersanach, M.; et al. Influence of Socio-Economic Characteristics of Beach Users on Litter Generation. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2005, 48, 742–752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocecoaman.2005.08.006.
- 65.Iñiguez, M.E.; Conesa, J.A.; Fullana, A. Marine Debris Occurrence and Treatment: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 64, 394–402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.031.
- 66.Arcadis; Directorate-General for Environment (European Commission); Van Acoleyen, M.; et al. Marine Litter Study to Support the Establishment of an Initial Quantitative Headline Reduction Target; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2014; ISBN 978-92-79-40845-8.
- 67.Mouat, J.; Lozano, R.; Bateson, H. Economic Impacts of Marine Litter; Kommunenes Internasjonale Miljøorganisasjon (KIMO): Lerwick, UK, 2010. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Economic-impacts-of-marine-litter-Mouat-Lozano/ceb36c1bb00080deefb19d5e01ff0b58acf3c489 (accessed on 2 October 2025).
- 68.Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.S.; Thompson, R.C. Spatial Patterns of Plastic Debris along Estuarine Shorelines. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3404–3409. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903784e.
- 69.Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; et al. Transport and Release of Chemicals from Plastics to the Environment and to Wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0284.
- 70.vom Saal, F.S.; Myers, J.P. Bisphenol A and Risk of Metabolic Disorders. JAMA 2008, 300, 1353–1355. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.300.11.1353.
- 71.Lithner, D.; Damberg, J.; Dave, G.; et al. Leachates from Plastic Consumer Products—Screening for Toxicity with Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 1195–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.022.
- 72.Lithner, D.; Larsson, Å.; Dave, G. Environmental and Health Hazard Ranking and Assessment of Plastic Polymers Based on Chemical Composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3309–3324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.038.
- 73.Oehlmann, J.; Schulte-Oehlmann, U.; Kloas, W.; et al. A Critical Analysis of the Biological Impacts of Plasticizers on Wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2047–2062. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2008.0242.
- 74.Galloway, T.; Cipelli, R.; Guralnik, J.; et al. Daily Bisphenol A Excretion and Associations with Sex Hormone Concentrations: Results from the InCHIANTI Adult Population Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1603–1608. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1002367.
- 75.Zhang, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Microplastic Pollution in Water, Sediment, and Fish from Artificial Reefs around the Ma’an Archipelago, Shengsi, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134768.
- 76.Statista Cumulative Plastic Production Volume Worldwide from 1950 to 2050 Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1019758/plastics-production-volume-worldwide/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- 77.Pazos, R.S.; Bauer, D.E.; Gómez, N. Microplastics Integrating the Coastal Planktonic Community in the Inner Zone of the Río de La Plata Estuary (South America). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.064.
- 78.Zaki, M.R.M.; Zaid, S.H.M.; Zainuddin, A.H.; et al. Microplastic Pollution in Tropical Estuary Gastropods: Abundance, Distribution and Potential Sources of Klang River Estuary, Malaysia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111866.
- 79.Luo, W.; Su, L.; Craig, N.J.; et al. Comparison of Microplastic Pollution in Different Water Bodies from Urban Creeks to Coastal Waters. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 174–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.081.
- 80.He, H.; Cai, S.; Chen, S.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Distribution Characteristics and Potential Sources of Microplastic Pollution in China’s Freshwater Environments. Water 2024, 16, 1270. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16091270.
- 81.Thankamony, R.; Hashmi, A.H.A.; Hammadi, H.A.A.; et al. A First Study on the Distribution of Microplastics in Sea Water and Sediments of Abu Dhabi Emirate, U.A.E. Eur. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 6, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejgeo.2025.6.4.530.
- 82.Klein, S.; Worch, E.; Knepper, T.P. Occurrence and Spatial Distribution of Microplastics in River Shore Sediments of the Rhine-Main Area in Germany. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6070–6076. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b00492.
- 83.Babel S.; Ta A.T.; Loan N.T.P.; et al. Microplastics pollution in selected rivers from Southeast Asia. APN Sci. Bull. 2022. https://doi.org/10.30852/sb.2022.1741.
How to Cite
Hieu Nhu, H. D.; Luu, T. L. A Review of Microplastics Pollution in the River Basin of Vietnam in Comparison with the World Context. Earth: Environmental Sustainability 2025, 1 (2), 343–355. https://doi.org/10.53941/eesus.2025.100026.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


