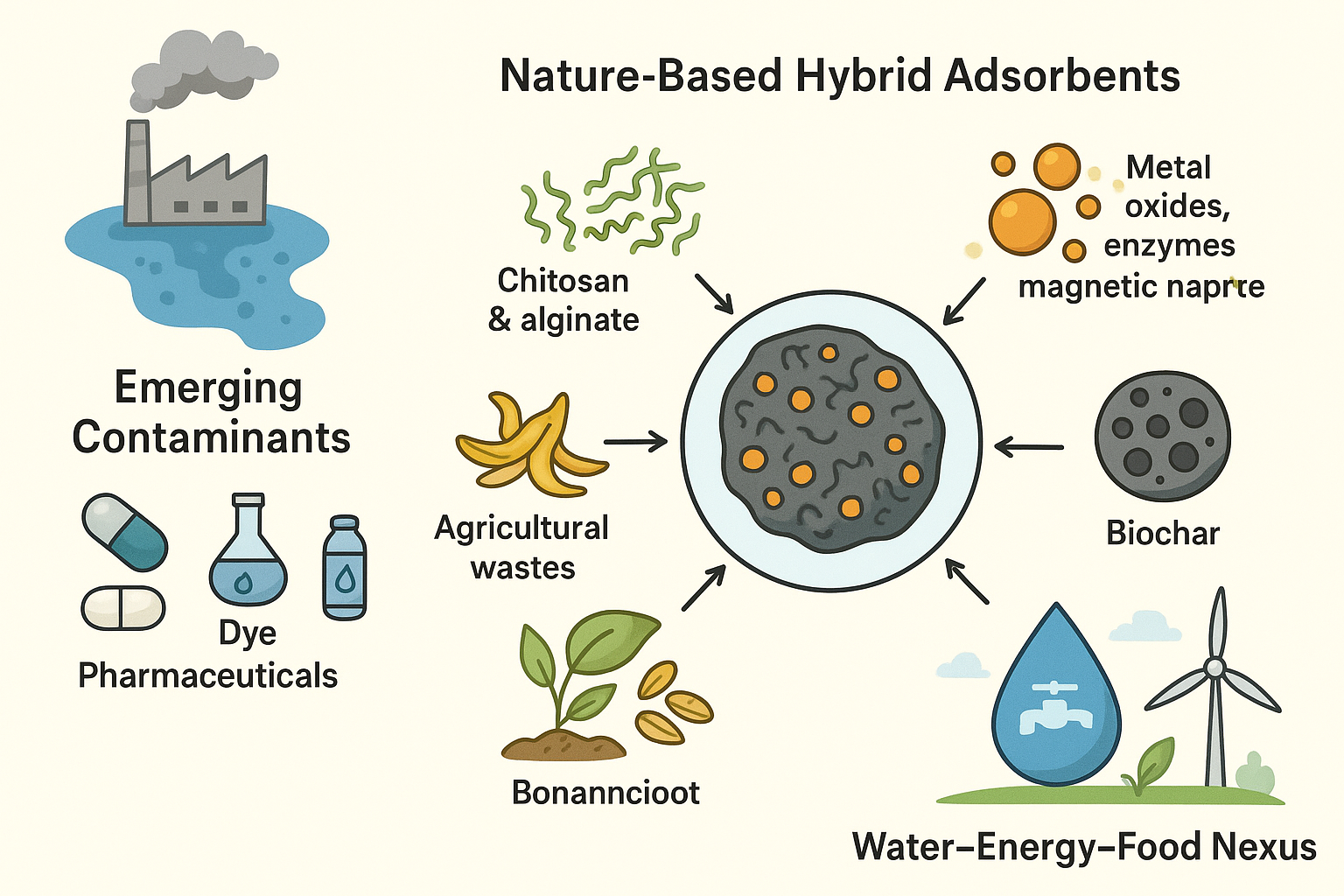
The pervasive presence of emerging contaminants (ECs), including pharmaceuticals, heavy metals, dyes, and personal care products in water systems, poses a critical threat to environmental and public health. Conventional treatment methods often fail to remove these pollutants efficiently due to high costs, energy intensity, and limited selectivity. This review highlights the transformative potential of nature-based hybrid adsorbents, which synergistically combine biopolymers such as chitosan and alginate, agricultural wastes including banana peel and rice husk, and biochar with functional components like metal oxides, enzymes, or magnetic nanoparticles. These systems achieve relatively high removal efficiencies, often exceeding 90%, and record-breaking adsorption capacities, such as 586 mg/g for lead and 394 mg/g for pharmaceuticals, far surpassing conventional alternatives. By leveraging low-cost, renewable materials, they reduce operational expenses by 30–80% and minimise energy use and secondary waste. Furthermore, their integration within the water–energy–food (WEF) nexus supports resource recovery, water reuse, and progress toward multiple UN Sustainable Development Goals. Remaining challenges, including scalability, regeneration stability, and the ecological safety of nano-enhanced adsorbents, are critically addressed, with forward-looking insights into AI-assisted design and circular economy integration. Ultimately, this work highlights how bridging natural bioresources with advanced hybrid engineering can redefine sustainable water treatment paradigms.
- Open Access
- Review
Nature-Based Hybrid Adsorbents for Emerging Contaminant Removal: Integrating Low-Cost Bioresources in the Water–Energy–Food Nexus
- Timoth Mkilima
Author Information
Received: 28 Aug 2025 | Revised: 04 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 12 Nov 2025 | Published: 18 Nov 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
nature-based adsorbents | emerging contaminants | wastewater treatment | water–energy–food nexus | sustainable technologies
References
- 1.
Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xinn.2024.100612.
- 2.
Li, X.; Shen, X.; Jiang, W.; et al. Comprehensive Review of Emerging Contaminants: Detection Technologies, Environmental Impact, and Management Strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 278, 116420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116420.
- 3.
Brack, W.; Barcelo Culleres, D.; Boxall, A.B.A.; et al. One Planet: One Health. A Call to Support the Initiative on a Global Science–Policy Body on Chemicals and Waste. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-022-00602-6.
- 4.
Arman, N.Z.; Salmiati, S.; Aris, A.; et al. A Review on Emerging Pollutants in the Water Environment: Existences, Health Effects and Treatment Processes. Water 2021, 13, 3258. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13223258.
- 5.
Zhou, Q.; Chen, H.; Liu, G.; et al. Occurrence, Sustainable Treatment Technologies, Potential Sources, and Future Prospects of Emerging Pollutants in Aquatic Environments: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1455377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2024.1455377.
- 6.
Ejiohuo, O.; Onyeaka, H.; Akinsemolu, A.; et al. Ensuring Water Purity: Mitigating Environmental Risks and Safeguarding Human Health. Water Biol. Secur. 2025, 4, 100341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watbs.2024.100341.
- 7.
Aslam, B.; Asghar, R.; Muzammil, S.; et al. AMR and Sustainable Development Goals: At a Crossroads. Global. Health 2024, 20, 73. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12992-024-01046-8.
- 8.
Ahn, C.; Jeung, E.B. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals and Disease Endpoints. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5342. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065342.
- 9.
Huang, Y.-K.; Chang, Y.-C. Oral Health: The First Step to Sustainable Development Goal 3. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, 1348–1350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2021.10.018.
- 10.
Aguda, O.N.; Lateef, A. Recent Advances in Functionalization of Nanotextiles: A Strategy to Combat Harmful Microorganisms and Emerging Pathogens in the 21st Century. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09761.
- 11.
Küfeoğlu, S. SDG-6 Clean Water and Sanitation; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 289–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07127-0_8.
- 12.
Küfeoğlu, S. SDG-12: Responsible Consumption and Production; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 409–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07127-0_14.
- 13.
Aaltonen, H. Re-Storying SDG 14: Life below Water. Nord. J. Art Res. 2023, 12. https://doi.org/10.7577/ar.5172.
- 14.
Küfeoğlu, S. SDG-14: Life Below Water; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 453–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-07127-0_16.
- 15.
Zheng, T.-H.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Recent Progress in Catalytically Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment. Catalysts 2025, 15, 761. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15080761.
- 16.
Yuan, H.; Zhai, S.; Fu, H.; et al. Environmental and Economic Life Cycle Assessment of Emerging Sludge Treatment Routes. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141792.
- 17.
Essien, A.E.; Dickson-Anderson, S.E.; Guo, Y. Utilizing Nature-Based Adsorbents for Removal of Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Controlled Polluted Aqueous Systems: A Systematic Review of Sources, Properties, Adsorption Characteristics, and Performance. Next Sustain. 2025, 5, 100119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nxsust.2025.100119.
- 18.
Alkhaldi, H.; Alharthi, S.; Alharthi, S.; et al. Sustainable Polymeric Adsorbents for Adsorption-Based Water Remediation and Pathogen Deactivation: A Review. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 33143–33190. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4RA05269B.
- 19.
Narayanan, M.; Ma, Y. Influences of Biochar on Bioremediation/Phytoremediation Potential of Metal-Contaminated Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929730. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.929730.
- 20.
Al Masud, M.A.; Shin, W.S.; Sarker, A.; et al. A Critical Review of Sustainable Application of Biochar for Green Remediation: Research Uncertainty and Future Directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166813.
- 21.
Annu, A.; Mittal, M.; Tripathi, S.; et al. Biopolymeric Nanocomposites for Wastewater Remediation: An Overview on Recent Progress and Challenges. Polymers 2024, 16, 294. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16020294.
- 22.
Javed, S.; Zulfiqar, Z.; Fatima, Z.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Plant-Based Mucilages as Promising Candidates for Water Remediation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 114035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2024.114035.
- 23.
Arumugam, A.; Lee, K.E.; Ng, P.Y.; et al. Pharmaceuticals as Emerging Pollutants: Implications for Water Resource Management in Malaysia. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2025.100470.
- 24.
Prada, A.F.; Scott, J.W.; Green, L.; et al. Microplastics and Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Landfill-Wastewater Treatment Systems: A Field Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.176751.
- 25.
Cedeño-Muñoz, J.S.; Aransiola, S.A.; Reddy, K.V.; et al. Antibiotic Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic Resistance Genes as Contaminants of Emerging Concern: Occurrences, Impacts, Mitigations and Future Guidelines. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.175906.
- 26.
Osuoha, J.O.; Anyanwu, B.O.; Ejileugha, C. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products as Emerging Contaminants: Need for Combined Treatment Strategy. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 9, 100206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2022.100206.
- 27.
Szymczycha, B.; Borecka, M.; Białk-Bielińska, A.; et al. Submarine Groundwater Discharge as a Source of Pharmaceutical and Caffeine Residues in Coastal Ecosystem: Bay of Puck, Southern Baltic Sea Case Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136522.
- 28.
Rehrl, A.L.; Golovko, O.; Ahrens, L.; et al. Spatial and Seasonal Trends of Organic Micropollutants in Sweden’s Most Important Drinking Water Reservoir. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126168.
- 29.
Jurado, A.; Margareto, A.; Pujades, E.; et al. Fate and Risk Assessment of Sulfonamides and Metabolites in Urban Groundwater. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115480.
- 30.
Fonseca, E.; Hernández, F.; Ibáñez, M.; et al. Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Pharmaceuticals in a Mediterranean River in Eastern Spain. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2020.106004.
- 31.
Richards, L.A.; Kumari, R.; White, D.; et al. Emerging Organic Contaminants in Groundwater under a Rapidly Developing City (Patna) in Northern India Dominated by High Concentrations of Lifestyle Chemicals. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115765. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115765.
- 32.
Sodré, F.F.; Sampaio, T.R. Development and Application of a SPE-LC-QTOF Method for the Quantification of Micropollutants of Emerging Concern in Drinking Waters from the Brazilian Capital. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.emcon.2020.01.001.
- 33.
Branchet, P.; Ariza Castro, N.; Fenet, H.; et al. Anthropic Impacts on Sub-Saharan Urban Water Resources through Their Pharmaceutical Contamination (Yaoundé, Center Region, Cameroon). Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 886–898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.256.
- 34.
Karimi, K.J.; Ngumba, E.; Ahmad, A.; et al. Contamination of Groundwater with Sulfamethoxazole and Antibiotic Resistant Escherichia Coli in Informal Settlements in Kisumu, Kenya. PLOS Water 2023, 2, e0000076. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pwat.0000076.
- 35.
Molnar, E.; Maasz, G.; Pirger, Z. Environmental Risk Assessment of Pharmaceuticals at a Seasonal Holiday Destination in the Largest Freshwater Shallow Lake in Central Europe. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59233–59243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09747-4.
- 36.
Bexfield, L.M.; Toccalino, P.L.; Belitz, K.; et al. Hormones and Pharmaceuticals in Groundwater Used As a Source of Drinking Water Across the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2950–2960. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b05592.
- 37.
Kibuye, F.A.; Gall, H.E.; Elkin, K.R.; et al. Occurrence, Concentrations, and Risks of Pharmaceutical Compounds in Private Wells in Central Pennsylvania. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1057–1066. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2018.08.0301.
- 38.
Thacharodi, A.; Hassan, S.; Hegde, T.A.; et al. Water a Major Source of Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals: An Overview on the Occurrence, Implications on Human Health and Bioremediation Strategies. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.116097.
- 39.
Miller, M.E.; Hamann, M.; Kroon, F.J. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Microplastics in Marine Organisms: A Review and Meta-Analysis of Current Data. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240792. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0240792.
- 40.
Naznine, F.; Shafi, Z.; Aafreen, U.; et al. Tracking Antimicrobial Resistance in River Waters: Sources, Key Microbes, and Detection Techniques. Microbe 2025, 7, 100386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microb.2025.100386.
- 41.
Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, E.; et al. Insights into the Highly Selective and Efficient Adsorption of Pb2+ by Fish Skin Collagen-Enabled Sodium Alginate-Based Composite Gel Spheres: Adsorption and Interference Mechanisms. Food Hydrocoll. 2026, 170, 111700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2025.111700.
- 42.
Liu, B.; Han, X.; Yang, K.; et al. Lignin-Intercalated WS2 with Synergistic Adsorption for Efficiency Lead Removal. Bioresour. Technol. 2026, 439, 133284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2025.133284.
- 43.
Zheng, C.; Sun, K.; Wu, Q.; et al. Green Synthesis of Robust Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Beads for Cr(VI) Removal from Water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 377, 134271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134271.
- 44.
Shamsudin, M.S.; Sellaoui, L.; Ismail, S.; et al. Mechanistic Insights of Diclofenac Adsorption on Functionalized Clay-Based Adsorptive Film: Bridging Experimental and Molecular Dynamics Findings. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 377, 134119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134119.
- 45.
Lv, P.; She, L.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Regulation Mechanism of Biochar on Cobalt-Doped Copper Oxide/Peroxymonosulfate System: Key Roles of Superoxide Radicals. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 375, 133857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.133857.
- 46.
Ben Khemis, I.; Aouaini, F.; Knani, S.; et al. A Chitosan-Lignin Biocomposite Adsorbent for RO16 Dye and Cr(VI) Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solutions: New Interpretations via Experiments and Statistical Physics Analysis. BMC Chem. 2025, 19, 259. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-025-01621-z.
- 47.
Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. One-Step Removal of Cr(VI) and As(III) from Wastewater Using Deep Eutectic Supramolecular Polymer-Modified Magnetic Cellulose Nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 379, 134895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134895.
- 48.
Yang, T.; Shao, X.; Zeng, X.; et al. Adsorption Performance and Mechanistic Study of 1D Sodium Lignosulfonate-Functionalized Fe3O4@SiO2@polypyrrole Nanochains for the Removal of Methylene Blue, Malachite Green, Mn(VII) and Crystal Violet. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 378, 134663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.134663.
- 49.
Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Highly Flexible, SnO2/BiOBr Core-Shell Heterostructured Lignin-Based Carbon Nanofibrous Membrane Driven by LED Light for Pollutant Degradation. J. Memb. Sci. 2025, 736, 124671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2025.124671.
- 50.
Alprol, A.E.; Bakr, A.; Al-Saeedi, S.I.; et al. Chitosan/Ferrous Oxide Nanocomposite for the Sunlight-Driven Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Azo Dye in Aqueous Solutions and Aquaculture Effluents Wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-04207-w.
- 51.
Gu, Y.; Tang, R.; Wang, L.; et al. Eco-Friendly Spherical Sugarcane Bagasse Biochar/Sodium Alginate Monolithic Adsorbent: A Rapid Removal of Nitrofurazone in the Aqueous Environment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2026, 380, 135298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.135298.
- 52.
Chakma, B.; Chisty, A.H.; Jawad, I.A. Development Adsorbents Derived from Waste Peels in Chromium (III) Removal: A Comparative Study. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2025, 22, 1407–1418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13738-025-03230-y.
- 53.
Baskaran, D.; Natarajan, A.P.A.; Byun, H.-S. Potential of Palm Husk Powder in the Treatment of Real Tannery Wastewater: Performance Comparison between Response Surface Methodology and Artificial Neural Network-Particle Swarm Optimization. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2024.106101.
- 54.
Gupta, S.; Kandasubramanian, B. Silk Adsorbent for Green and Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue from Wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33226-9.
- 55.
Bahadir, T.; Şimşek, İ.; Tulun, Ş.; et al. Use of Different Food Wastes as Green Biosorbent: Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies of Pb2+. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 103324–103338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-29745-6.
- 56.
Yakkerimath, S.; Kulkarni, R.M.; Divekar, S.V.; et al. Thermally Activated Natural Clay for the Removal of Pharmaceutical Drug Levofloxacin. Asian J. Chem. 2023, 35, 2161–2170. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2023.28124.
- 57.
Alobaidi, D.S.; Alwared, A.I. The Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Immobilized (Chlorophyta) Macroalgae: An Equilibrium, Kinetic, and Desorption-Regeneration Study. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 283, 141–152. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2023.29225.
- 58.
Kusuma, H.S.; Aigbe, U.O.; Ukhurebor, K.E.; et al. Biosorption of Methylene Blue Using Clove Leaves Waste Modified with Sodium Hydroxide. Results Chem. 2023, 5, 100778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rechem.2023.100778.
- 59.
Sharma, P.; Shahi, V.K. Selective Removal of Hg2+/As3+/5+ from Water System Using Suaeda maritima Plant Based Bio-Adsorbent Hybrid Electro-Deionization Process. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.107726.
- 60.
Huda, B.N.; Wahyuni, E.T.; Kamiya, Y.; et al. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Study on Adsorption of Lead(II) Ions in Water over Dithizone-Immobilized Coal Bottom Ash. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 282, 126005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.126005.
- 61.
Kumar, J.A.; Kumar, P.S.; Krithiga, T.; et al. Acenaphthene Adsorption onto Ultrasonic Assisted Fatty Acid Mediated Porous Activated Carbon-Characterization, Isotherm and Kinetic Studies. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131249.
- 62.
Ernawati, L.; Wahyuono, R.A.; Halim, A.; et al. Hierarchically 3-d Porous Structure of Silk Fibroin-Based Biocomposite Adsorbent for Water Pollutant Removal. Environments 2021, 8, 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110127.
- 63.
Sulyman, M.; Kucinska-Lipka, J.; Sienkiewicz, M.; et al. Development, Characterization and Evaluation of Composite Adsorbent for the Adsorption of Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solution: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Studies. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103115.
- 64.
Yahya, M.D.; Obayomi, K.S.; Abdulkadir, M.B.; et al. Characterization of Cobalt Ferrite-Supported Activated Carbon for Removal of Chromium and Lead Ions from Tannery Wastewater via Adsorption Equilibrium. Water Sci. Eng. 2020, 13, 202–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2020.09.007.
- 65.
Azmi, S.N.H.; Al-Balushi, M.; Al-Siyabi, F.; et al. Adsorptive Removal of Pb(II) Ions from Groundwater Samples in Oman Using Carbonized Phoenix Dactylifera Seed (Date Stone). J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2020, 32, 2931–2938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.07.015.
- 66.
Yahya, M.D.; Aliyu, A.S.; Obayomi, K.S.; et al. Column Adsorption Study for the Removal of Chromium and Manganese Ions from Electroplating Wastewater Using Cashew Nutshell Adsorbent. Cogent Eng. 2020, 7, 1748470. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2020.1748470.
- 67.
Obayomi, K.S.; Bello, J.O.; Yahya, M.D.; et al. Statistical Analyses on Effective Removal of Cadmium and Hexavalent Chromium Ions by Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes (MWCNTs). Heliyon 2020, 6, e04174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04174.
- 68.
Espinosa Rodríguez, M.Á.; Bernal-Jácome, L.A.; Gallegos García, M.; et al. Adsorption of Lead (Ii) from Aqueous Solution Using Adsorbents Obtained from Nanche Stone (Byrsonima Crassifolia). J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2020, 64, 301–315. https://doi.org/10.29356/jmcs.v64i4.1201.
- 69.
Obayomi, K.S.; Bello, J.O.; Nnoruka, J.S.; et al. Development of Low-Cost Bio-Adsorbent from Agricultural Waste Composite for Pb(II) and As(III) Sorption from Aqueous Solution. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1687274. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2019.1687274.
- 70.
Tandekar, S.A.; Pande, M.A.; Shekhawat, A.; et al. Fe(III)–Chitosan Microbeads for Adsorptive Removal of Cr(VI) and Phosphate Ions. Minerals 2022, 12, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12070874.
- 71.
Daochalermwong, A.; Chanka, N.; Songsrirote, K.; et al. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions Using Modified Celluloses Prepared from Pineapple Leaf Fiber. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 5285–5296. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04326.
- 72.
Song, S.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structural Characteristics and Adsorption of Phosphorus by Pineapple Leaf Biochar at Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2923. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14122923.
- 73.
Ogheneochuko, O.; Zintle, N.; Veruscha, F. Modified Pineapple Waste as Low-Cost Biomass for Removal of Co(II) from Simulated and Real Treated Wastewater in Batch and Continuous System. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103206.
- 74.
Mahamad, M.N.; Zaini, M.A.A.; Zakaria, Z.A. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from Pineapple Waste Biomass for Dye Removal. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.03.009.
- 75.
Asnam, A.; Bouras, O.; Aouabed, A.; et al. Structuration of Biosorbents in the Form of Reinforced Gelled and Porous Composites Based on Opuntia Ficus Indica (Cactus) Extract and Sodium Alginate. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102612.
- 76.
Nazzari, E.C.; Wernke, G.; Magalhães Ghiotto, G.A.V.; et al. Hydrogel Biocomposite of Alginate and Mucilage of Opuntia Ficus-Indica Cactus in the Adsorption of Methylene Blue in Aqueous Solution. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 627–636. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.4c07325.
- 77.
Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Recent Advances in Biochar-Based Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 100059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccst.2022.100059.
- 78.
Kareem, R.; Afkhami, A.; Aziz, K.H.H. Synthesis of a Novel Magnetic Biochar Composite Enhanced with Polyaniline for High-Performance Adsorption of Heavy Metals : Focus on Hg (II) and Cu(II). RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 20309–20320. https://doi.org/10.1039/D5RA02250A.
- 79.
Soni, H.; Kanjariya, P.; Ballal, S.; et al. Recent Advances in the Synthesis of Magnetic Nanocomposites for the Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions from Wastewater. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1345, 143019. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.molstruc.2025.143019.
- 80.
Manoj, G.M.; Shalini, M.; Thenmozhi, K.; et al. Recent Advancements in the Surface Modification and Functionalization of Magnetic Nanomaterials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 21, 100608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2024.100608.
- 81.
Rezania, S.; Darajeh, N.; Rupani, P.F.; et al. Recent Advances in the Adsorption of Different Pollutants from Wastewater Using Carbon-Based and Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11492. https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411492.
- 82.
Arabzadeh Nosratabad, N.; Yan, Q.; Cai, Z.; et al. Exploring Nanomaterial-Modified Biochar for Environmental Remediation Applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37123.
- 83.
Sani, M.N.H.; Amin, M.; Siddique, A.B.; et al. Waste-Derived Nanobiochar: A New Avenue towards Sustainable Agriculture, Environment, and Circular Bioeconomy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 166881 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166881.
- 84.
Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.; et al. Scalable Nanoplastic Degradation in Water with Enzyme-Functionalized Porous Hydrogels. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 487, 137196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137196.
- 85.
Bittencourt, G.A.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Martínez-Burgos, W.J.; et al. Emerging Contaminants Bioremediation by Enzyme and Nanozyme-Based Processes—A Review. iScience 2023, 26, 106785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2023.106785.
- 86.
Sinharoy, A.; Kumar, M.; Chaudhuri, R.; et al. Simultaneous Removal of Selenite and Heavy Metals from Wastewater and Their Recovery as Nanoparticles Using an Inverse Fluidized Bed Bioreactor. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134248.
- 87.
Aguilar-Rosero, J.; Urbina-López, M.E.; Rodríguez-González, B.E.; et al. Development and Characterization of Bioadsorbents Derived from Different Agricultural Wastes for Water Reclamation: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2740. https://doi.org/10.3390/app12052740.
- 88.
Karić, N.; Maia, A.S.; Teodorović, A.; et al. Bio-Waste Valorisation: Agricultural Wastes as Biosorbents for Removal of (in)Organic Pollutants in Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 9, 100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceja.2021.100239.
- 89.
Teklemedhin, T.B.; Wan, Z.; Hossain, N.; et al. Bio-Adsorbents Derived from Carbohydrates, Lignin, and Protein Biomass as Potential Environmental Remediation: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 320, 145861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145861.
- 90.
Samuel Olugbenga, O.; Goodness Adeleye, P.; Blessing Oladipupo, S.; et al. Biomass-Derived Biochar in Wastewater Treatment- a Circular Economy Approach. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wmb.2023.07.007.
- 91.
Madeła, M.; Skuza, M. Towards a Circular Economy: Analysis of the Use of Biowaste as Biosorbent for the Removal of Heavy Metals. Energies 2021, 14, 5427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175427.
- 92.
Alameri, A.A.; Alfilh, R.H.C.; Awad, S.A.; et al. Ciprofloxacin Adsorption Using Magnetic and ZnO Nanoparticles Supported Activated Carbon Derived from Azolla Filiculoides Biomass. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 27001–27014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03372-6.
- 93.
Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Biochar Nanoparticles Reduce Ciprofloxacin Accumulation and Restore Growth and Hormonal Balance in Rice Seedlings. Plants 2025, 14, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants14030380.
- 94.
Wei, J.; Song, M.; Zhang, D. Study on the Preparation of Modified Coconut Shell Biochar and Its Adsorption Performance for Sulfadiazine. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2025, 3013, 012029. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/3013/1/012029.
- 95.
Collivignarelli, M.C.; Bellazzi, S.; Caccamo, F.M.; et al. Removal of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances by Adsorption on Innovative Adsorbent Materials. Sustainability 2023. 15, 13056. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151713056.
- 96.
Wu, Y.; Pei, K.; Zhou, J.; et al. Coconut Shell Activated Carbon Engineered for Triphasic Adsorption and Multimechanistic Removal of Emerging Contaminant F-53B. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 26141. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-11051-5.
- 97.
Xia, H.; Duan, N.; Song, B.; et al. Efficient Removal of Micro-Sized Degradable PHBV Microplastics from Wastewater by a Functionalized Magnetic Nano Iron Oxides-Biochar Composite: Performance, Mechanisms, and Material Regeneration. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15120915.
- 98.
Li, J.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; et al. Removal of Pristine and Aged Microplastics from Water by Magnetic Biochar: Adsorption and Magnetization. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 875, 162647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162647.
- 99.
Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Qin, X.; et al. An Updated Review on How Biochar May Possess Potential in Soil ARGs Control on Aspects of Source, Fate and Elimination. Biochar 2024, 6, 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42773-024-00319-0.
- 100.
Ezra, R.; Vanti, G.; Masaphy, S. Sustainable, Targeted, and Cost-Effective Laccase-Based Bioremediation Technologies for Antibiotic Residues in the Ecosystem: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 1138. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom15081138.
- 101.
Madhogaria, B.; Banerjee, S.; Kundu, A.; et al. Efficacy of New Generation Biosorbents for the Sustainable Treatment of Antibiotic Residues and Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Polluted Waste Effluent. Infect. Med. 2024, 3, 100092. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imj.2024.100092.
- 102.
Wei, L.; Zheng, J.; Han, Y.; et al. Insights into the Roles of Biochar Pores toward Alleviating Antibiotic Resistance Genes Accumulation in Biofiltration Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 394, 130257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2023.130257.
- 103.
Khraisheh, M.; Kim, J.; Campos, L.; et al. Removal of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) Pollutants from Water by Novel TiO2-Coconut Shell Powder (TCNSP) Composite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 979–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.06.032.
- 104.
Li, K.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; et al. Heterogeneous Photocatalytic Degradation of Selected Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) Using Tungsten Doped TiO2: Effect of the Tungsten Precursors and Solvents. Molecules 2024, 29, 4164. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174164.
- 105.
Rohmah, D.N.; Saputro, S.; Masykuri, M.; et al. Combination of Rice Husk and Coconut Shell Activated Adsorbent to Adsorb Pb(II) Ionic Metal and It’s Analysis Using Solid-Phase Spectrophotometry (Sps). In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; Surakarta, Indonesia, 4–5 September 2017. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/333/1/012056.
- 106.
Vázquez-Guerrero, A.; Cortés-Martínez, R.; Alfaro-Cuevas-villanueva, R.; et al. CD(II) and PB(II) Adsorption Using a Composite Obtained from Moringa Oleifera Lam. Cellulose Nanofibrils Impregnated with Iron Nanoparticles. Water 2021, 13, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13010089.
- 107.
Bée, A.; Obeid, L.; Mbolantenaina, R.; et al. Magnetic Chitosan/Clay Beads: A Magsorbent for the Removal of Cationic Dye from Water. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 421, 59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.07.022.
- 108.
Khanday, W.A.; Asif, M.; Hameed, B.H. Cross-Linked Beads of Activated Oil Palm Ash Zeolite/Chitosan Composite as a Bio-Adsorbent for the Removal of Methylene Blue and Acid Blue 29 Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 95, 895–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.10.075.
- 109.
Lahgui, F.; Delgado Cano, B.; Avalos Ramirez, A.; et al. Development of New Biosorbent Based on Crosslinked Chitosan Beads with High Brilliant Blue FCF Removal Efficiency. Molecules 2025, 30, 292. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020292.
- 110.
Shakoor, M.B.; Ye, Z.-L.; Chen, S. Engineered Biochars for Recovering Phosphate and Ammonium from Wastewater: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146240.
- 111.
Takaya, C.A.; Fletcher, L.A.; Singh, S.; et al. Phosphate and Ammonium Sorption Capacity of Biochar and Hydrochar from Different Wastes. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 518–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.052.
- 112.
Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Efficient Simultaneous Phosphate and Ammonia Adsorption Using Magnesium-Modified Biochar Beads and Their Recovery Performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2023.110875.
- 113.
Campos, E.V.R.; Proença, P.L.F.; Oliveira, J.L.; et al. Chitosan Nanoparticles Functionalized with β-Cyclodextrin: A Promising Carrier for Botanical Pesticides. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2067. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20602-y.
- 114.
Gonçalves, J.O.; Leones, A.R.; de Farias, B.S.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Agricultural Residue-Derived Bioadsorbents for Emerging Contaminant Removal. Water 2025, 17, 2141. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17142141.
- 115.
Ng, Y.J.; Lim, H.R.; Khoo, K.S.; et al. Recent Advances of Biosurfactant for Waste and Pollution Bioremediation: Substitutions of Petroleum-Based Surfactants. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113126.
- 116.
Lei, X.; Lian, Q.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Review of PFAS Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions: Current Approaches, Engineering Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 321, 121138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121138.
- 117.
Karbassiyazdi, E.; Kasula, M.; Modak, S.; et al. A Juxtaposed Review on Adsorptive Removal of PFAS by Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) with Carbon-Based Materials, Ion Exchange Resins, and Polymer Adsorbents. Chemosphere 2023, 311, 136933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.136933.
- 118.
Chambers, C.; Grimes, S.; Fire, S.; et al. Influence of Biochar on the Removal of Microcystin-LR and Saxitoxin from Aqueous Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11058. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61802-z.
- 119.
Abbas, T.; Kajjumba, G.W.; Ejjada, M.; et al. Recent Advancements in the Removal of Cyanotoxins from Water Using Conventional and Modified Adsorbents—A Contemporary Review. Water 2020, 12, 2756. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12102756.
- 120.
Akhtar, K.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.B.; et al. Scanning Electron Microscopy: Principle and Applications in Nanomaterials Characterization. In Handbook of Materials Characterization; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp 113–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92955-2_4.
- 121.
Biessikirski, A.; Dworzak, M.; Kaczmarczyk, G.P.; et al. Evaluation of the Porosity and Morphology of Microstructured Charcoal. Materials 2025, 18, 1730. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081730.
- 122.
Jafari Eskandari, M.; Gostariani, R.; Asadi Asadabad, M. Transmission Electron Microscopy of Nanomaterials. In Electron Crystallography; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.92212.
- 123.
Malatesta, M. Transmission Electron Microscopy as a Powerful Tool to Investigate the Interaction of Nanoparticles with Subcellular Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312789.
- 124.
Virtanen, T.; Rudolph, G.; Lopatina, A.; et al. Analysis of Membrane Fouling by Brunauer-Emmett-Teller Nitrogen Adsorption/Desorption Technique. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3427. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-59994-1.
- 125.
Sinha, P.; Datar, A.; Jeong, C.; et al. Surface Area Determination of Porous Materials Using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Method: Limitations and Improvements. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 20195–20209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b02116.
- 126.
Tan, Y.H.; Davis, J.A.; Fujikawa, K.; et al. Surface Area and Pore Size Characteristics of Nanoporous Gold Subjected to Thermal, Mechanical, or Surface Modification Studied Using Gas Adsorption Isotherms, Cyclic Voltammetry, Thermogravimetric Analysis, and Scanning Electron Microscopy. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6733. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm16633j.
- 127.
Yang, M.; Wang, Y. D-BJH: The Intrinsic Model for Characterizing the Pore Size Distribution of Porous Materials. Langmuir 2024, 40, 20368–20378. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01548.
- 128.
Pasieczna-Patkowska, S.; Cichy, M.; Flieger, J. Application of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy in Characterization of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles. Molecules 2025, 30, 684. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30030684.
- 129.
Dittmann, D.; Saal, L.; Zietzschmann, F.; et al. Characterization of Activated Carbons for Water Treatment Using TGA-FTIR for Analysis of Oxygen-Containing Functional Groups. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01723-2.
- 130.
Krishna, D.N.G.; Philip, J. Review on Surface-Characterization Applications of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS): Recent Developments and Challenges. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2022, 12, 100332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsadv.2022.100332.
- 131.
Lefebvre, J.; Galli, F.; Bianchi, C.L.; et al. Experimental Methods in Chemical Engineering: X‐ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy‐XPS. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 2588–2593. https://doi.org/10.1002/cjce.23530.
- 132.
Chukhchin, D.G.; Malkov, A.V.; Tyshkunova, I.V.; et al. Diffractometric Method for Determining the Degree of Crystallinity of Materials. Crystallogr. Rep. 2016, 61, 371–375. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1063774516030081.
- 133.
Farivar, F.; Lay Yap, P.; Karunagaran, R.U.; et al. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) of Graphene Materials: Effect of Particle Size of Graphene, Graphene Oxide and Graphite on Thermal Parameters. C 2021, 7, 41. https://doi.org/10.3390/c7020041.
- 134.
Mohammadi-Jam, S.; Greenwood, R.W.; Waters, K.E. An Overview of the Temperature Dependence of the Zeta Potential of Aqueous Suspensions. Results Eng. 2025, 27, 105698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2025.105698.
- 135.
Ismail, R.; Ibrahim, A.; Mohamed, H.M.S.; et al. Experimental Data for the Magnetic Properties of Vulcanized Natural Rubber Nanocomposites Using Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM). Data Br. 2023, 46, 108872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2022.108872.
- 136.
Crovella, T.; Paiano, A.; Falciglia, P.P.; et al. Wastewater Recovery for Sustainable Agricultural Systems in the Circular Economy—A Systematic Literature Review of Life Cycle Assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.169310.
- 137.
Garcia, X.; Pargament, D. Reusing Wastewater to Cope with Water Scarcity: Economic, Social and Environmental Considerations for Decision-Making.Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 101, 154–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.05.015.
- 138.
Badran, A.M.; Utra, U.; Yussof, N.S.; et al. Advancements in Adsorption Techniques for Sustainable Water Purification: A Focus on Lead Removal. Separations 2023, 10, 565. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10110565.
- 139.
Kunwar, P.J.; Luukkonen, T.; Haapasalo, H.; et al. Addressing Adsorbent Materials Commercialization Challenges for Water Treatment in European Markets through Productization. Cogent Eng. 2024, 11, 2320952 https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2024.2320952.
- 140.
Faheem, M.; Azher Hassan, M.; Du, J.; et al. Harnessing Potential of Smart and Conventional Spent Adsorbents: Global Practices and Sustainable Approaches through Regeneration and Tailored Recycling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 128907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.128907.
- 141.
Wang, G.; Kumar, S.; Huang, Z.; et al. Water Resource Management and Policy Evaluation in Middle Eastern Countries: Achieving Sustainable Development Goal 6. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dwt.2024.100829.
- 142.
Wang, M.; Janssen, A.B.G.; Bazin, J.; et al. Accounting for Interactions between Sustainable Development Goals Is Essential for Water Pollution Control in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 730. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28351-3.
- 143.
Islam, M.A.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Mozumder, M.S.I.; et al. Langmuir Adsorption Kinetics in Liquid Media: Interface Reaction Model. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 14481–14492. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c01449.
- 144.
Chang, C.-K.; Tun, H.; Chen, C.-C. An Activity-Based Formulation for Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm. Adsorption 2020, 26, 375–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-019-00185-4.
- 145.
Ao, D.; AP, L.; AM, O. Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherms Studies of Equilibrium Sorption of Zn2+ Unto Phosphoric Acid Modified Rice Husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 3, 38–45. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845.
- 146.
Vigdorowitsch, M.; Pchelintsev, A.; Tsygankova, L.; et al. Freundlich Isotherm: An Adsorption Model Complete Framework. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11178078.
- 147.
Obaid, S.A. Langmuir, Freundlich and Tamkin Adsorption Isotherms and Kinetics For The Removal Aartichoke Tournefortii Straw From Agricultural Waste. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1664, 012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1664/1/012011.
- 148.
Mahanty, B.; Behera, S.K.; Sahoo, N.K. Misinterpretation of Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherm and Its Implications on Adsorption Parameter Estimates. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2023, 58, 1275–1282. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2023.2189050.
- 149.
Chu, K.H.; Hashim, M.A.; Hayder, G.; et al. Comparative Evaluation of the Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherm and Its Variants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 15002–15011. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.4c01895.
- 150.
Feng, Q.; Fan, B.; He, Y.-C. Antibacterial, Antioxidant, Cr(VI) Adsorption and Dye Adsorption Effects of Biochar-Based Silver Nanoparticles‑sodium Alginate-Tannic Acid Composite Gel Beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 271, 132453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132453.
- 151.
Perumal, M.K.K.; Gandhi, D.; Renuka, R.R.; et al. Advanced Nano-Based Adsorbents for Purification of Pharmaceutical Residue Polluted Water: A Critical Review. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 186, 552–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2024.04.011.
- 152.
Kumar, R.; Qureshi, M.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; et al. A Review on Emerging Water Contaminants and the Application of Sustainable Removal Technologies. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2022.100219.
- 153.
Samadi, A.; Kong, L.; Guo, W.; et al. Standardized Methodology for Performance Evaluation in Using Polyaniline-Based Adsorbents to Remove Aqueous Contaminants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2024.112650.
- 154.
Mahlangu, O.T.; Motsa, M.M.; Richards, H.; et al. The Impact of Nanoparticle Leach on Sustainable Performance of the Membranes—A Critical Review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2024.100984.
- 155.
Falinski, M.M.; Turley, R.S.; Kidd, J.; et al. Doing Nano-Enabled Water Treatment Right: Sustainability Considerations from Design and Research through Development and Implementation. Environ. Sci. Nano, 2020, 7, 3255–3278. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN00584C.
- 156.
Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and Challenges in Adsorption-Based Wastewater Remediation: A Comprehensive Review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29573.
- 157.
Akhtar, M.S.; Ali, S.; Zaman, W. Innovative Adsorbents for Pollutant Removal: Exploring the Latest Research and Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 4317. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29184317.
- 158.
Mansour, M.; Bassyouni, M.; Abdel-Kader, R.F.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Predicting the Performance of Adsorption Processes in Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 153–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-46491-1_10.
- 159.
Kumari, S.; Chowdhry, J.; Chandra Garg, M. AI-Enhanced Adsorption Modeling: Challenges, Applications, and Bibliographic Analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119968.
- 160.
de Araujo, L.G.; Vilcocq, L.; Fongarland, P.; et al. Recent Developments in the Use of Machine Learning in Catalysis: A Broad Perspective with Applications in Kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.160872.
- 161.
Alam, G.; Ihsanullah, I.; Naushad, M.; et al. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Water Treatment for Optimization and Automation of Adsorption Processes: Recent Advances and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130011.
- 162.
Marín Díaz, G. Comparative Analysis of Explainable AI Methods for Manufacturing Defect Prediction: A Mathematical Perspective. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13152436.
- 163.
Van Fan, Y.; Lee, C.T.; Lim, J.S.; et al. Cross-Disciplinary Approaches towards Smart, Resilient and Sustainable Circular Economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1482–1491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.266.
- 164.
Compagnucci, L.; Spigarelli, F. Fostering Cross-Sector Collaboration to Promote Innovation in the Water Sector. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4154. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114154.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


