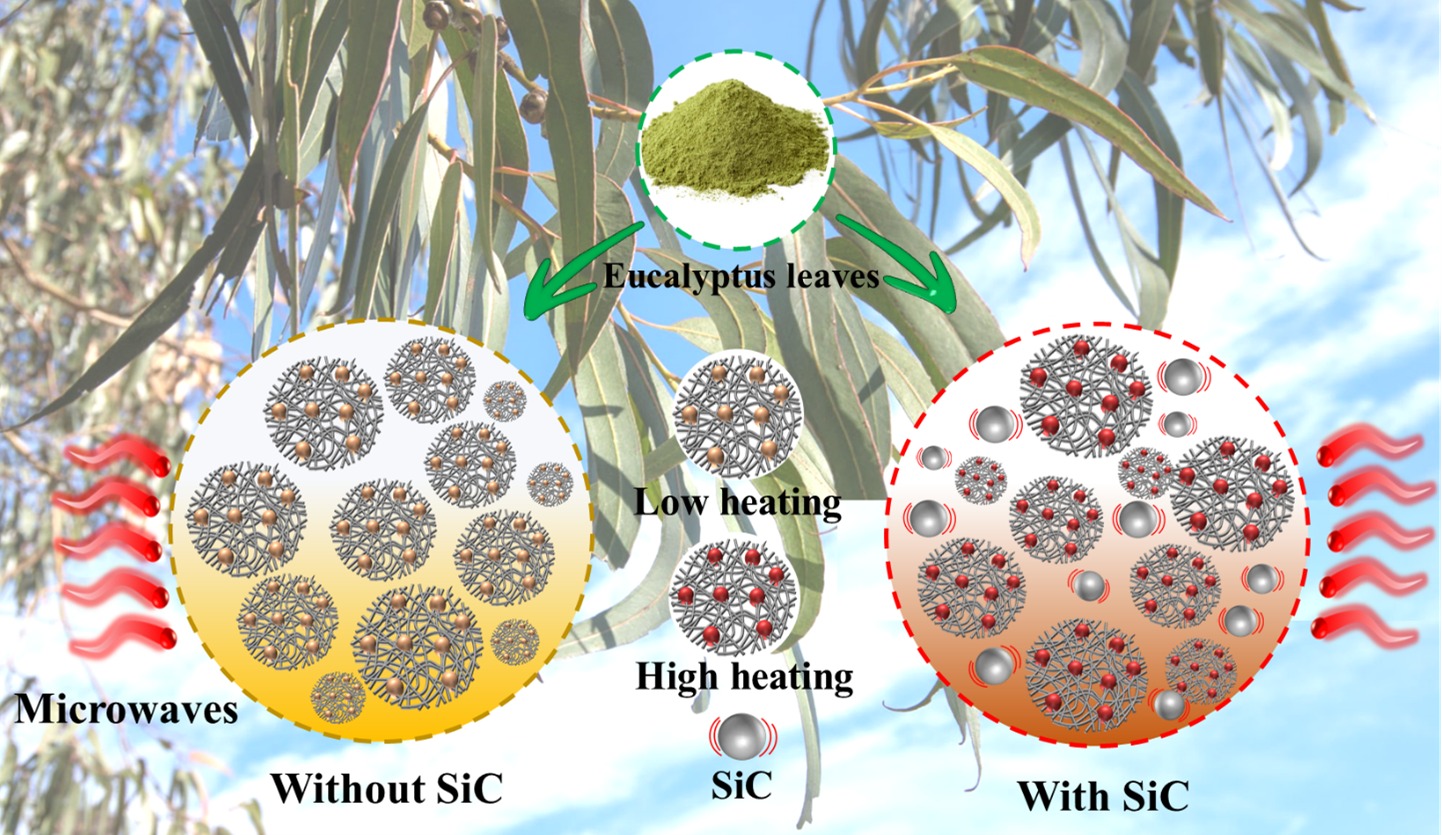
Microwave heating is an efficient and effective heating method for upgrading biofuels. This study investigated the heating performance of eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves with and without silicon carbide (SiC) in a microwave chamber. The effects of quartz reactor volume (50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mL), microwave power (400, 450, 500, 550, and 600 W), and SiC amount (0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10 g) on the heating performance were analyzed. The result showed that as the quartz reactor volume increased from 50 to 250 mL, the average heating rate of eucalyptus leaves without SiC decreased from 153.2 to 47.2 °C/min, while with SiC, it decreased from 366.8 to 106.2 °C/min. As the microwave power increased from 400 to 600 W, the average heating rate of eucalyptus leaves without SiC increased from 73.3 to 197.4 °C/min, and with SiC, it increased from 138.6 to 352.4 °C/min. When SiC amount increased from 0 to 10 g, the average heating rate of eucalyptus leaves increased from 73.9 to 352.4 °C/min. Relationships were proposed to describe the microwave heating performances of eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves with R2 of 0.9953–0.9999.
- Open Access
- Article
Microwave Heating Performances of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Leaves with Silicon Carbide for Biofuel Upgrading
- Faizan Ahmad,
- Muhammad Kashif,
- Wenke Zhao,
- Yaning Zhang *
Author Information
Received: 04 Dec 2024 | Revised: 31 Dec 2024 | Accepted: 02 Jan 2025 | Published: 09 Jan 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
heating performance | eucalyptus leave | microwave power | silicon carbide
References
- 1.Chen, W.H. Progress in Green Energy and Fuel for Sustainability. Green Energy Fuel Res. 2024, 1, 13–22.
- 2.Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Jacob, D.; Taylor, M.; et al. The human imperative of stabilizing global climate change at 1.5 °C. Science 2019, 365, eaaw6974.
- 3.Lee, J.; Im, G.; Yoo, J.H.; et al. Development of greenhouse gas (CO2) emission factor for Korean coal briquettes. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2015, 37, 1415–1423.
- 4.Zhang, C.; Fang, J.; Zhan, Y.; et al. Life Cycle Assessment of Microalgal Carbon Fixation and Torrefaction for Carbon Neutralization: A State-of-the-Art Review. Green Energy Fuel Res. 2024, 23–38.
- 5.Wu, H.; Lyu, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. Power Generation Enhancement in a Solar Energy and Biomass-Based Distributed Energy System using H2O/CO2 Hybrid Gasification. J. Therm. Sci. 2024, 33, 1657–1671.
- 6.Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Geographical spatial distribution and productivity dynamic change of eucalyptus plantations in China. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19764.
- 7.Penín, L.; López, M.; Santos, V.; et al. Technologies for Eucalyptus wood processing in the scope of biorefineries: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123528.
- 8.Seng Hua, L.; Wei Chen, L.; Antov, P.; et al. Engineering wood products from Eucalyptus spp. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1, 8000780.
- 9.Kabir, M.G.; Wang, Y.; Abuhena, M.; et al. A bio-sustainable approach for reducing Eucalyptus tree-caused agricultural ecosystem hazards employing Trichoderma bio-sustained spores and mycorrhizal networks. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1071392.
- 10.Louw, J.; Schwarz, C.E.; Burger, A.J. Supercritical water gasification of eucalyptus grandis and related pyrolysis char: Effect of feedstock composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 216, 1030–1039.
- 11.Kosanić, T.R.; Ćeranić, M.B.; Đurić, S.N.; et al. Experimental investigation of pyrolysis process of woody biomass mixture. J. Therm. Sci. 2014, 23, 290–296.
- 12.Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Yuan, X.; et al. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on composition, carbon fraction and abiotic stability of straw biochars: Correlation and quantitative analysis. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 17.
- 13.Zhang, Y.; Hong, X.; Shen, X.; et al. Heavy oil catalytic upgrading with microwave heating over a microwave absorbing catalyst USY/AC/Al2O3. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 41, 229–236.
- 14.Kostas, E.T.; Beneroso, D.; Robinson, J.P. The application of microwave heating in bioenergy: A review on the microwave pre-treatment and upgrading technologies for biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 77, 12–27.
- 15.Ho, S.H.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.H.; et al. Characterization of biomass waste torrefaction under conventional and microwave heating. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 7–16.
- 16.Sakhiya, A.K.; Anand, A.; Kaushal, P. Production, activation, and applications of biochar in recent times. Biochar 2020, 2, 253–285.
- 17.Ren, J.; Jiang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Variable frequency microwave induced CO2 Boudouard reaction over biochar. Biochar 2024, 6, 20.
- 18.Peymanfar, R.; Ershad, Z.S.; Selseleh-Zakerin, E.; et al. Graphite-like carbon nitride (g-C3N4): A promising microwave absorber. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 16461–16476.
- 19.Li, L.; Ma, X.; Xu, Q.; et al. Influence of microwave power, metal oxides and metal salts on the pyrolysis of algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 142, 469–474.
- 20.Chen, G.; Li, J.; Cheng, Z.; et al. Investigation on model compound of biomass gasification tar cracking in microwave furnace: Comparative research. Appl. Energy 2018, 217, 249–257.
- 21.Fan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; et al. Conversion of polystyrene plastic into aviation fuel through microwave-assisted pyrolysis as affected by iron-based microwave absorbents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 1054–1066.
- 22.Ke, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Energy absorption performances of silicon carbide particles during microwave heating process. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 172, 108796.
- 23.Singh, R.; Lindenberger, C.; Chawade, A.; et al. Unveiling the microwave heating performance of biochar as microwave absorber for microwave-assisted pyrolysis technology. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9222.
- 24.Tamang, S.; Aravindan, S. 3D numerical modelling of microwave heating of SiC susceptor. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 162, 114250.
- 25.Chen, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. Pyrolysis behaviors and kinetic studies on eucalyptus residues using thermogravimetric analysis. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 251–259.
- 26.Amutio, M.; Lopez, G.; Alvarez, J.; et al. Fast pyrolysis of eucalyptus waste in a conical spouted bed reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 194, 225–232.
- 27.Sánchez-Borrego, F.J.; Alvarez-Mateos, P.; Garcia-Martin, J.F. Biodiesel and other value-added products from bio-oil obtained from agrifood waste. Processes 2021, 9, 797.
- 28.Han, Y.; Paiva Pinheiro Pires, A.; Denson, M.; et al. Ternary phase diagram of water/bio-oil/organic solvent for bio-oil fractionation. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 16250–16264.
- 29.da Silveira Rossi, R.A.; Dai, L.; de Souza Barrozo, M.A.; et al. Bio-fuel production from catalytic microwave-assisted pyrolysis of the microalgae Schizochytrium limacinum in a tandem catalytic bed. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147223.
- 30.Ou, X.; Wu, C.; Shi, K.; et al. Structured ZSM-5/SiC foam catalysts for bio-oils upgrading. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 599, 117626.
- 31.Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; et al. Conversion of woody oil into bio-oil in a downdraft reactor using a novel silicon carbide foam supported MCM41 composite catalyst. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 19729–19739.
- 32.Tuci, G.; Liu, Y.; Rossin, A.; et al. Porous silicon carbide (SiC): A chance for improving catalysts or just another active-phase carrier? Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 10559–10665.
- 33.Seehar, T.H.; Toor, S.S.; Sharma, K.; et al. Influence of process conditions on hydrothermal liquefaction of eucalyptus biomass for biocrude production and investigation of the inorganics distribution. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2021, 5, 1477–1487.
- 34.Cui, L.; Qin, N.; Li, H.; et al. Heating performances of corn straw particles in a microwave chamber. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 7186–7197.
- 35.Santhosh, B.; Ionescu, E.; Andreolli, F.; et al. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the microstructure and thermal conductivity of polymer-derived monolithic and porous SiC ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 1151–1162.
- 36.Zhang, Z.; Huang, K.; Mao, C.; et al. Microwave assisted catalytic pyrolysis of bagasse to produce hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 35626–35634.
- 37.Fan, Y.; Jin, L.; Ji, W.; et al. Microwave-induced carbonization of rapeseed shell for bio-oil and bio-char: Multi-variable optimization and microwave absorber effect. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 191, 23–38.
- 38.Reddy, B.R.; Malhotra, A.; Najmi, S.; et al. Microwave assisted heating of plastic waste: Effect of plastic/susceptor (SiC) contacting patterns. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 182, 109202.
- 39.Fan, L.; Song, H.; Lu, Q.; et al. Screening microwave susceptors for microwave-assisted pyrolysis of lignin: Comparison of product yield and chemical profile. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 142, 104623.
How to Cite
Ahmad, F.; Kashif, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Microwave Heating Performances of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Leaves with Silicon Carbide for Biofuel Upgrading. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100001.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


