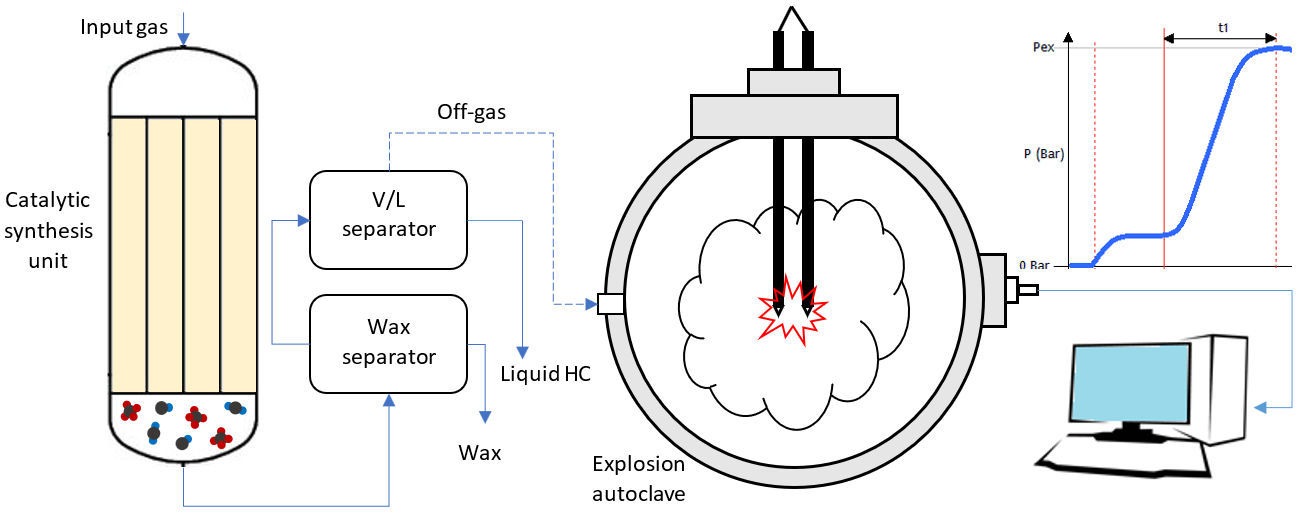
In this research evaluation, the catalytic synthesis off-gas was investigated through a safety assessment approach. Though operation safety measures are of utmost importance in the industrial processes, they are difficult to maintain when variable components are dealt with. Four different scenarios based on various process phases and off-gas compositions were experimentally evaluated. The results exhibited significant differences in explosion pressure values, revealing the most severe consequences during the start-up phase, when H2 is abundant, and during the advanced process (over 30 h of operation), when CO is abundant in the off-gas composition. The first case possessed 200 MPa/s explosion pressure change, while the latter was equal to 152 MPa/s. These findings have provided a significant guideline for progressive industrial applications with complex material mass balance.
- Open Access
- Article
Safety Evaluation of Catalytic Synthesis Off-Gases through Explosion Pressure Determination
- Jakub Čespiva 1, *,
- Jan Skřínský 1,
- Thangavel Sangeetha 2, 3,
- David Kupka 1
Author Information
Received: 24 Dec 2024 | Revised: 20 Feb 2025 | Accepted: 21 Feb 2025 | Published: 24 Feb 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
catalytic synthesis | off-gas | explosion pressure | explosion autoclave | safety assessment
References
- 1.Faramawy, S.; Zaki, T.; Sakr, A.A.-E. Natural gas origin, composition, and processing: A review. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 2016, 34, 34–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2016.06.030.
- 2.Čespiva, J.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Vereš, J.; et al. Evaluation of the performance of the cross/updraft type gasification technology with the sliding bed over a circular grate. Biomass Bioenergy 2022, 167, 106639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2022.106639.
- 3.Lubitz, W.; Tumas, W. Hydrogen: An Overview. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3900–3903. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050200z.
- 4.Cheng, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, F. Explosibility Safety Factor: An Approach to Assess Mine Gas Explosion Risk. Fire Technol. 2015, 51, 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10694-013-0324-y.
- 5.Spitzer, S.H.; Askar, E.; Benke, A.; et al. 1st international round robin test on safety characteristics of hybrid mixtures. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2023, 81, 104947. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2022.104947.
- 6.Helegda, M.; Pokorny, J.; Helegda, I.; et al. Parameters Affecting the Explosion Characteristics of Hybrid Mixtures Arising from the Use of Alternative Energy Sources. Fire 2024, 7, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7040139.
- 7.Frost, C.G.; Mutton, L. Heterogeneous catalytic synthesis using microreactor technology. Green. Chem. 2010, 12, 1687. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0gc00133c.
- 8.Jayakumar, M.; Karmegam, N.; Gundupalli, M.P.; et al. Heterogeneous base catalysts: Synthesis and application for biodiesel production—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 331, 125054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.125054.
- 9.Marakatti, V.S.; Gaigneaux, E.M. Recent Advances in Heterogeneous Catalysis for Ammonia Synthesis. ChemCatChem 2020, 12, 5838–5857. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.202001141.
- 10.Ding, L.; Shi, T.; Gu, J.; et al. CO2 Hydrogenation to Ethanol over Cu@Na-Beta. Chem 2020, 6, 2673–2689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chempr.2020.07.001.
- 11.Konnerth, H.; Matsagar, B.M.; Chen, S.S.; et al. Metal-organic framework (MOF)-derived catalysts for fine chemical production. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 416, 213319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213319.
- 12.Ye, W.; Guo, X.; Ma, T. A review on electrochemical synthesized copper-based catalysts for electrochemical reduction of CO2 to C2+ products. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 414, 128825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128825.
- 13.Jiao F, Zhang H, Li W, Zhao Y, Guo J, Zhang X; et al. Experimental and numerical study of the influence of initial temperature on explosion limits and explosion process of syngas-air mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 22261–22272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.05.017.
- 14.Pietraccini, M.; Glaude, P.-A.; Dufour, A.; et al. Making hybrid mixture explosions a common case. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2023, 83, 105048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2023.105048.
- 15.Anekwe, I.M.S.; Akpasi, S.O.; Enemuo, E.M.; et al. Innovations in catalytic understanding: A journey through advanced characterization. Mater. Today Catal. 2024, 7, 100061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcata.2024.100061.
- 16.Takeda, D.; Kim, W.K.; Wada, Y.; et al. Toward Risk Assessment of Explosion Hazard: Experimental Determination of Flame Fractal Dimension. Adv. Mat. Res. 2011, 320, 151–155. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.320.151.
- 17.Gavrilović, L.; Jørgensen, E.A.; Pandey, U.; et al. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis over an alumina-supported cobalt catalyst in a fixed bed reactor—Effect of process parameters. Catal. Today 2021, 369, 150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2020.07.055.
- 18.Gaseous Combustion at High Pressure. Nature 1932, 130, 769–769. https://doi.org/10.1038/130769b0.
- 19.Silva, R.S.F.; Tamanqueira, J.B.; Dias, J.C.M.; et al. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography with time of flight mass spectrometry applied to analysis of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis products obtained with and without carbon dioxide addition to feed gas. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 2121–2126. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532011001100015.
- 20.Hayakawa, H.; Tanaka, H.; Fujimoto, K. Studies on catalytic performance of precipitated iron/silica catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2007, 328, 117–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2007.05.035.
- 21.Amin, M.; Usman, M.; Kella, T.; et al. Issues and challenges of Fischer–Tropsch synthesis catalysts. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1462503. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2024.1462503.
- 22.Inaba, Y.; Nishihara, T.; Groethe, M.A.; et al. Study on explosion characteristics of natural gas and methane in semi-open space for the HTTR hydrogen production system. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2004, 232, 111–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucengdes.2004.04.007.
- 23.Han, H.; Ma, Q.; Qin, Z.; et al. Experimental study on combustion and explosion characteristics of hydrogen-air premixed gas in rectangular channels with large aspect ratio. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 57, 1041–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.01.125.
- 24.Zhao, E.; Liu, Z.; Lin, S.; et al. Experimental Study on Explosion Characteristics of LPG/Air Mixtures Suppressed by CO2 Synergistic Inert Powder. Fire 2024, 7, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire7080275.
- 25.Čespiva, J.; Wnukowski, M.; Skřínský, J.; et al. Production efficiency and safety assessment of the solid waste-derived liquid hydrocarbons. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2023.117915.
- 26.Makhura, E.; Rakereng, J.; Rapoo, O.; et al. Effect of the operation parameters on the Fischer Tropsch synthesis process using different reactors. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 35, 349–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.promfg.2019.05.051.
- 27.Elbashir, N.O.; Dutta, P.; Manivannan, A.; et al. Impact of cobalt-based catalyst characteristics on the performance of conventional gas-phase and supercritical-phase Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 285, 169–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2005.02.023.
- 28.Bukur, D.B.; Todic, B.; Elbashir, N. Role of water-gas-shift reaction in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis on iron catalysts: A review. Catal. Today 2016, 275, 66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.11.005.
- 29.Luo, Z.; Liu, L.; Cheng, F.; et al. Effects of a carbon monoxide-dominant gas mixture on the explosion and flame propagation behaviors of methane in air. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2019, 58, 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2019.01.004.
- 30.Deng, J.; Cheng, F.; Song, Y.; et al. Experimental and simulation studies on the influence of carbon monoxide on explosion characteristics of methane. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2015, 36, 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlp.2015.05.002.
How to Cite
Čespiva, J.; Skřínský, J.; Sangeetha, T.; Kupka, D. Safety Evaluation of Catalytic Synthesis Off-Gases through Explosion Pressure Determination. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (1), 26–33. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100003.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


