The increasing global concern about global warming has spurred researchers and industries to actively explore low-carbon energy alternatives to reduce carbon emissions and lessen dependence on traditional energy sources. Waste-to-energy (WTE) conversion has emerged as a promising solution in this pursuit. However, the prevalence of flame retardants (FRs) in various household materials poses a challenge to WTE processes. FRs, commonly added to prevent fire hazards, include chlorine-, phosphorus-, and nitrogen-based variants, each with specific applications and fire suppression mechanisms. Thermal treatment technologies, such as incineration, pyrolysis, gasification, and hydrothermal treatment, are currently employed for energy conversion. While effective in reducing waste volume and degrading most FRs, these processes can generate secondary pollutants, including polychlorinated dioxins, with complex reaction pathways that are difficult to control. This necessitates stringent management measures to mitigate the associated environmental risks. In contrast, non-thermal degradation techniques, such as chemical degradation, photocatalysis, biodegradation, and electrochemical methods, offer more environmentally friendly alternatives. However, current technological limitations constrain their application scope and efficiency. This review aims to comprehensively examine the pollutant emission behaviors of FRs during thermal treatment processes for energy conversion, highlight the associated environmental risks, and assess the potential of non-thermal degradation techniques. By analyzing these aspects, the review seeks to provide scientific insights and technological support for achieving waste valorization and low-carbon sustainability.
- Open Access
- Review
Thermal Reactions and Byproducts from the Waste-to-Energy Process of Flame Retardant-Containing Wastes—A Review
- Chun-Yun Hsiao,
- Sheng-Lun Lin *
Author Information
Received: 14 Feb 2025 | Revised: 27 Apr 2025 | Accepted: 28 Apr 2025 | Published: 08 May 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
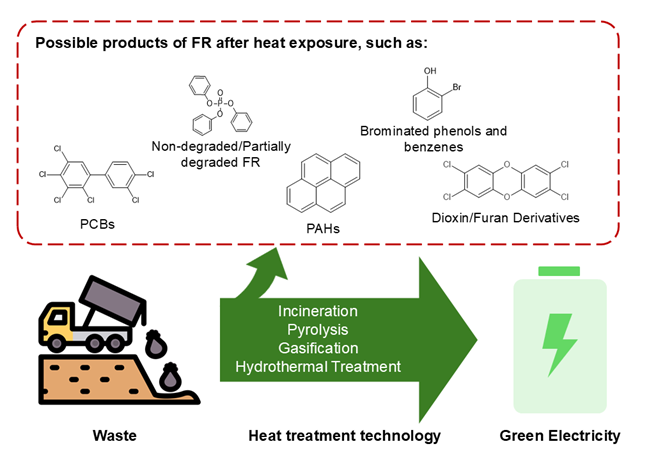
Keywords
waste-to-energy | persistent organic pollutants | flame retardant | thermal treatment | non-thermal degradation
References
- 1.Van der Schyff, V.; Kalina, J.; Abballe, A.; et al. Has Regulatory Action Reduced Human Exposure to Flame Retardants? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19106–19124.
- 2.Feiteiro, J.; Rocha, S.M.; Mariana, M.; et al. Pathways involved in the human vascular Tetrabromobisphenol A response: Calcium and potassium channels and nitric oxide donors. Toxicology 2022, 470, 153158.
- 3.Xu, P.; Tao, B.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Occurrence, composition, source, and regional distribution of halogenated flame retardants and polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxin/dibenzofuran in the soils of Guiyu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 61–71.
- 4.Hendriks, H.S.; Westerink, R.H. Neurotoxicity and risk assessment of brominated and alternative flame retardants. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2015, 52, 248–269.
- 5.Alaee, M.; Arias, P.; Sjödin, A.; et al. An overview of commercially used brominated flame retardants, their applications, their use patterns in different countries/regions and possible modes of release. Environ. Int. 2003, 29, 683–689.
- 6.Sharkey, M.; Harrad, S.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; et al. Phasing-out of legacy brominated flame retardants: The UNEP Stockholm Convention and other legislative action worldwide. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106041.
- 7.Yao, C.; Yang, H.; Li, Y. A review on organophosphate flame retardants in the environment: Occurrence, accumulation, metabolism and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148837.
- 8.Van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153.
- 9.Li, Q.; Guo, M.; Song, H.; et al. Size distribution and inhalation exposure of airborne particle-bound polybrominated diphenyl ethers, new brominated flame retardants, organophosphate esters, and chlorinated paraffins at urban open consumption place. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148695.
- 10.Levchik, S.; Weil, E. Developments in phosphorus flame retardants. In Advances in Fire Retardant Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 41–66.
- 11.Kung, H.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Huang, B.-W.; et al. An overview: Organophosphate flame retardants in the atmosphere. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 220148.
- 12.Miranda, R.G.; Sampaio, C.F.; Leite, F.G.; et al. Flame Retardants: New and Old Environmental Contaminants. In The Toxicity of Environmental Pollutants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022.
- 13.Kajiwara, N.; Desborough, J.; Harrad, S.; et al. Photolysis of brominated flame retardants in textiles exposed to natural sunlight. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2013, 15, 653–660.
- 14.Chokwe, T.B.; Abafe, O.A.; Mbelu, S.P.; et al. A review of sources, fate, levels, toxicity, exposure and transformations of organophosphorus flame-retardants and plasticizers in the environment. Emerg. Contam. 2020, 6, 345–366.
- 15.Bergman, Å.; Rydén, A.; Law, R.J.; et al. A novel abbreviation standard for organobromine, organochlorine and organophosphorus flame retardants and some characteristics of the chemicals. Environ. Int. 2012, 49, 57–82.
- 16.Mack, A.G. Flame retardants, halogenated. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000.
- 17.Abbasi, G.; Li, L.; Breivik, K. Global historical stocks and emissions of PBDEs. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6330–6340.
- 18.McGrath, T.J.; Morrison, P.D.; Ball, A.S.; et al. Detection of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in the urban soils of Melbourne, Australia. Emerg. Contam. 2017, 3, 23–31.
- 19.Al-Omran, L.S. Physiochemical properties and environmental levels of legacy and novel brominated flame retardants. In Flame Retardants; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018.
- 20.Gao, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhang, H.; et al. Analysis of emerging halogenated flame retardants in environment. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 41–70.
- 21.van Mourik, L.M.; Gaus, C.; Leonards, P.E.; et al. Chlorinated paraffins in the environment: A review on their production, fate, levels and trends between 2010 and 2015. Chemosphere 2016, 155, 415–428.
- 22.Horacek, H.; Grabner, R. Advantages of flame retardants based on nitrogen compounds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1996, 54, 205–215.
- 23.Morgan, A.B. Non-Halogenated Flame Retardant Handbook; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021.
- 24.Lu, S.-Y.; Hamerton, I. Recent developments in the chemistry of halogen-free flame retardant polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 1661–1712.
- 25.Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D. Combustion and Fire Retardancy of Aliphatic Nylons; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000.
- 26.Geschwindner, C.; Goedderz, D.; Li, T.; et al. The effects of various flame retardants on the combustion of polypropylene: Combining optical diagnostics and pyrolysis fragment analysis. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2023, 211, 110321.
- 27.Zhang, M.; Buekens, A.; Li, X. Brominated flame retardants and the formation of dioxins and furans in fires and combustion. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 304, 26–39.
- 28.Altarawneh, M.; Saeed, A.; Al-Harahsheh, M.; et al. Thermal decomposition of brominated flame retardants (BFRs): Products and mechanisms. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 70, 212–259.
- 29.Huo, S.; Song, P.; Yu, B.; et al. Phosphorus-containing flame retardant epoxy thermosets: Recent advances and future perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 114, 101366.
- 30.Yang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y. Synthesis of a novel flame retardant containing phosphorus, nitrogen and boron and its application in flame-retardant epoxy resin. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 133, 358–366.
- 31.Kundu, C.K.; Li, Z.; Song, L.; et al. An overview of fire retardant treatments for synthetic textiles: From traditional approaches to recent applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 137, 109911.
- 32.Samani, P.; van der Meer, Y. Life cycle assessment (LCA) studies on flame retardants: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123259.
- 33.Lu, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, L.; et al. Molecules Featuring the Azaheterocycle Moiety toward the Application of Flame-Retardant Polymers. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2023, 30, 343–361.
- 34.Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Char structure and charring mechanism of phosphazene-based epoxy resin during combustion. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 200, 109927.
- 35.Wang, Q.; Shi, W. Kinetics study of thermal decomposition of epoxy resins containing flame retardant components. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 1747–1754.
- 36.Vojta, S.; Melymuk, L.; Klánová, J. Changes in flame retardant and legacy contaminant concentrations in indoor air during building construction, furnishing, and use. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11891–11899.
- 37.Vojta, Š.; Bečanová, J.; Melymuk, L.; et al. Screening for halogenated flame retardants in European consumer products, building materials and wastes. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 457–466.
- 38.Kajiwara, N.; Noma, Y.; Takigami, H. Brominated and organophosphate flame retardants in selected consumer products on the Japanese market in 2008. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1250–1259.
- 39.Rauert, C.; Lazarov, B.; Harrad, S.; et al. A review of chamber experiments for determining specific emission rates and investigating migration pathways of flame retardants. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 44–55.
- 40.Ni, Y.; Kumagai, K.; Yanagisawa, Y. Measuring emissions of organophosphate flame retardants using a passive flux sampler. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3235–3240.
- 41.Kemmlein, S.; Hahn, O.; Jann, O. Emissions of organophosphate and brominated flame retardants from selected consumer products and building materials. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 5485–5493.
- 42.Carlsson, H.; Nilsson, U.; Östman, C. Video display units: An emission source of the contact allergenic flame retardant triphenyl phosphate in the indoor environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3885–3889.
- 43.Takigami, H.; Suzuki, G.; Hirai, Y.; et al. Flame retardants in indoor dust and air of a hotel in Japan. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 688–693.
- 44.Zhu, H.; Kannan, K. Melamine and cyanuric acid in foodstuffs from the United States and their implications for human exposure. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104950.
- 45.Zhu, H.; Kannan, K. Distribution profiles of melamine and its derivatives in indoor dust from 12 countries and the implications for human exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12801–12808.
- 46.Antoš, K.; Sedlář, J. Influence of brominated flame retardant thermal decomposition products on HALS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 188–194.
- 47.Luda, M.; Balabanovich, A.; Hornung, A.; et al. Thermal degradation of a brominated bisphenol a derivative. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2003, 14, 741–748.
- 48.Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. Sources and environmental behaviors of Dechlorane Plus and related compounds—A review. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 206–220.
- 49.Nguyen, C.; Kim, J. Thermal stabilities and flame retardancies of nitrogen–phosphorus flame retardants based on bisphosphoramidates. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2008, 93, 1037–1043.
- 50.Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Jiao, C.; et al. Preparation and thermal properties of a novel flame-retardant coating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1141–1150.
- 51.Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Di Cortemiglia, M.L. Overview of fire retardant mechanisms. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1991, 33, 131–154.
- 52.Thirumal, M.; Khastgir, D.; Nando, G.; et al. Halogen-free flame retardant PUF: Effect of melamine compounds on mechanical, thermal and flame retardant properties. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1138–1145.
- 53.Balabanovich, A.; Hornung, A.; Merz, D.; et al. The effect of a curing agent on the thermal degradation of fire retardant brominated epoxy resins. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 85, 713–723.
- 54.Wang, X.; He, S.; Wang, G.; et al. Characterization of PBDD/F emissions from simulated polystyrene insulation foam via lab-scale programmed thermal treatment testing. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 926–933.
- 55.Wan, J.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X.-L.; et al. Emission of brominated pollutants from waste printed circuit boards during thermal treatment: A review. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 230135.
- 56.Liang, J.; Lu, G.; Wang, R.; et al. The formation pathways of polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans (PBDD/Fs) from pyrolysis of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs): Effects of bromination arrangement and level. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123004.
- 57.Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Long, Y.; et al. Influence of bromination arrangement and level on the formation of polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans from pyrolysis and combustion of polybrominated diphenyl ethers: Mechanisms and kinetics. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140543.
- 58.Hart, J.R. Insights of potential by-product emissions from halogenated flame-retardant combustion by chemical equilibrium calculations. Int. J. Chem. Model. 2016, 8, 341–351.
- 59.Purser, D. Fire safety performance of flame retardants compared with toxic and environmental hazards. In Polymer Green Flame Retardants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 45–86.
- 60.Saeed, A. Studies on the Decomposition of Selected Brominated Flame Retardants (BFRs) and Formation of Polybrominated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans (PBDD/Fs) and Mixed Halogenated Dibenzo-p-dioxins and Dibenzofurans (PXDD/Fs). Ph.D. Thesis, Murdoch University, Perth, WA, Australia, 2016.
- 61.Xin, S.; Gao, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Identification of the released and transformed products during the thermal decomposition of a highly chlorinated paraffin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10153–10162.
- 62.Lombardi, L.; Carnevale, E.; Corti, A. A review of technologies and performances of thermal treatment systems for energy recovery from waste. Waste Manag. 2015, 37, 26–44.
- 63.Sakai, S.; Watanabe, J.; Honda, Y.; et al. Combustion of brominated flame retardants and behavior of its byproducts. Chemosphere 2001, 42, 519–531.
- 64.Matsukami, H.; Kose, T.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Pilot-scale incineration of wastes with high content of chlorinated and non-halogenated organophosphorus flame retardants used as alternatives for PBDEs. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 672–681.
- 65.Kwon, E.-H.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Jeon, T.-W.; et al. Study on Thermal Treatment of Chlorinated Flame Retardant in Waste Containing Halogen Flame Retardant. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2018, 18, 655–663.
- 66.Liang, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, P.; et al. Municipal sewage sludge incineration and its air pollution control. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126456.
- 67.Yang, H.-H.; Cheruiyot, N.K.; Lin, C.; et al. Control of extreme brominated persistent organic pollutant emissions from start-ups of waste-to-energy incinerators. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131108.
- 68.Wang, R.; Xu, Z. Recycling of non-metallic fractions from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE): A review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 1455–1469.
- 69.Hu, X.; Gholizadeh, M. Biomass pyrolysis: A review of the process development and challenges from initial researches up to the commercialisation stage. J. Energy Chem. 2019, 39, 109–143.
- 70.Tange, L.; Drohmann, D. Waste electrical and electronic equipment plastics with brominated flame retardants–from legislation to separate treatment–thermal processes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 88, 35–40.
- 71.Grause, G.; Furusawa, M.; Okuwaki, A.; et al. Pyrolysis of tetrabromobisphenol-A containing paper laminated printed circuit boards. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 872–878.
- 72.Ye, Z.; Yang, F.; Lin, W.; et al. Improvement of pyrolysis oil obtained from co-pyrolysis of WPCBs and compound additive during two stage pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 135, 415–421.
- 73.Zhu, P.; Sui, S.; Wang, B.; et al. A study of pyrolysis and pyrolysis products of flame-retardant cotton fabrics by DSC, TGA, and PY–GC–MS. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2004, 71, 645–655.
- 74.Eschenbacher, A.; Varghese, R.J.; Weng, J.; et al. Fast pyrolysis of polyurethanes and polyisocyanurate with and without flame retardant: Compounds of interest for chemical recycling. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2021, 160, 105374.
- 75.Chen, G.; Liu, T.; Luan, P.; et al. Distribution, migration, and removal of N-containing products during polyurethane pyrolysis: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131406.
- 76.Cho, S.-H.; Park, J.; Jung, S.; et al. Syngas Production via CO2-Mediated Melamine Pyrolysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 2476–2483.
- 77.Kumagai, S.; Grause, G.; Kameda, T.; et al. Thermal decomposition of tetrabromobisphenol-A containing printed circuit boards in the presence of calcium hydroxide. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 282–293.
- 78.Charitopoulou, M.A.; Stefanidis, S.D.; Lappas, A.A.; et al. Catalytic pyrolysis of polymers with brominated flame-retardants originating in waste electric and electronic equipment (WEEE) using various catalysts. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 26, 100612.
- 79.Chen, Y.; Ke, Y.; Liang, S.; et al. Enhanced bromine fixation and tar lightweighting in co-pyrolysis of non-metallic fractions of waste printed circuit boards with Bayer red mud. Waste Manag. 2023, 162, 72–82.
- 80.Zhan, H.; Zhuang, X.; Song, Y.; et al. Formation and regulatory mechanisms of N-containing gaseous pollutants during stage-pyrolysis of agricultural biowastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117706.
- 81.Sajid, M.; Raheem, A.; Ullah, N.; et al. Gasification of municipal solid waste: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112815.
- 82.Lidman Olsson, E.O.; Glarborg, P.; et al. Release of P from pyrolysis, combustion, and gasification of biomass—A model compound study. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 15817–15830.
- 83.Yamawaki, T. The gasification recycling technology of plastics WEEE containing brominated flame retardants. Fire Mater. 2003, 27, 315–319.
- 84.Lo, Y.-P.; Prabu, S.; Chang, M.-B.; et al. Hydrogen production and pollutants emission characteristics by co-gasified of paper-mill sludge and automobile shredder residues in a commercial scale fluidized bed gasifier. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52, 46–57.
- 85.Ciuffi, B.; Chiaramonti, D.; Rizzo, A.M.; et al. A critical review of SCWG in the context of available gasification technologies for plastic waste. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6307.
- 86.Alvarez, J.; Kumagai, S.; Wu, C.; et al. Hydrogen production from biomass and plastic mixtures by pyrolysis-gasification. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 10883–10891.
- 87.Pinto, F.; Franco, C.; André, R.; et al. Co-gasification study of biomass mixed with plastic wastes. Fuel 2002, 81, 291–297.
- 88.Weiland, F.; Lundin, L.; Celebi, M.; et al. Aspects of chemical recycling of complex plastic waste via the gasification route. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 65–77.
- 89.Lachos-Perez, D.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Abaide, E.R.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonization and Liquefaction: Differences, progress, challenges, and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126084.
- 90.Uddin, M.A.; Bhaskar, T.; Kusaba, T.; et al. Debromination of flame retardant high impact polystyrene (HIPS-Br) by hydrothermal treatment and recovery of bromine free plastics. Green Chem. 2003, 5, 260–263.
- 91.Nose, K.; Hashimoto, S.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Degradation pathways of decabromodiphenyl ether during hydrothermal treatment. Chemosphere 2007, 68, 120–125.
- 92.Yin, J.; Li, G.; He, W.; et al. Hydrothermal decomposition of brominated epoxy resin in waste printed circuit boards. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2011, 92, 131–136.
- 93.Zhan, L.; Zhao, X.; Ahmad, Z.; et al. Leaching behavior of Sb and Br from E-waste flame retardant plastics. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125684.
- 94.Xue, Y.; Bai, L.; Chi, M.; et al. Co-hydrothermal carbonization of lignocellulose biomass and polyvinyl chloride: The migration and transformation of chlorine. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137155.
- 95.Xiu, F.-R.; Bai, Q.; Qi, Y.; et al. An alkali-enhanced subcritical water treatment strategy of short-chain chlorinated paraffins: Dechlorination and hydrocarbons recovery. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166574.
- 96.Tangredi, A.; Barca, C.; Ferrasse, J.-H.; et al. Effect of process parameters on phosphorus conversion pathways during hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142342.
- 97.Li, J.; Jin, J.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Enhancing phosphorus bioavailability in sewage sludge through co-hydrothermal treatment with biomass. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 51, 103448.
- 98.Huang, R.; Tang, Y. Speciation dynamics of phosphorus during (hydro) thermal treatments of sewage sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14466–14474.
- 99.Aragón-Briceño, C.; Pozarlik, A.; Bramer, E.; et al. Hydrothermal carbonization of wet biomass from nitrogen and phosphorus approach: A review. Renew. Energy 2021, 171, 401–415.
- 100.Tang, L.; Hu, Z.; Gao, P.; et al. Transformation characteristics of nitrogen, sulfur and chlorine during microwave-assisted hydrothermal treatment of excavated waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135638.
- 101.Song, Q.; Feng, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Degradation of the flame retardant triphenyl phosphate by ferrous ion-activated hydrogen peroxide and persulfate: Kinetics, pathways, and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 929–936.
- 102.Yang, P.; Liu, J.; Korshin, G.V.; et al. New insights into the role of nitrite in the degradation of tetrabromobisphenol S by sulfate radical oxidation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17743–17752.
- 103.Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; et al. Efficient heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by modified CuFe2O4 for degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124345.
- 104.Han, Q.; Dong, W.; Wang, H.; et al. Degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A by ferrate (VI) oxidation: Performance, inorganic and organic products, pathway and toxicity control. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 92–102.
- 105.Ma, C.; Guo, Z.; Fang, Z.; et al. Flame retardancy and chemical degradation of epoxy containing phenylphosphonate group under mild conditions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 239, 109967.
- 106.Dang, Y.; Tang, K.; Wang, Z.; et al. Organophosphate esters (OPEs) flame retardants in water: A review of photocatalysis, adsorption, and biological degradation. Molecules 2023, 28, 2983.
- 107.Rani, M.; Sillanpää, M.; Shanker, U. An updated review on environmental occurrence, scientific assessment and removal of brominated flame retardants by engineered nanomaterials. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115998.
- 108.Yuan, X.; Lacorte, S.; Cristale, J.; et al. Removal of organophosphate esters from municipal secondary effluent by ozone and UV/H2O2 treatments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 1028–1034.
- 109.Antonopoulou, M.; Giannakas, A.; Bairamis, F.; et al. Degradation of organophosphorus flame retardant tris (1-chloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TCPP) by visible light N, S-codoped TiO2 photocatalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 318, 231–239.
- 110.Ling, S.; Huang, K.; Tariq, M.; et al. Photodegradation of novel brominated flame retardants (NBFRs) in a liquid system: Kinetics and photoproducts. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 938–946.
- 111.Hou, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; et al. Aerobic degradation of nonhalogenated organophosphate flame esters (OPEs) by enriched cultures from sludge: Kinetics, pathways, bacterial community evolution, and toxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143385.
- 112.Cámara, B.; Herrera, C.; González, M.; et al. From PCBs to highly toxic metabolites by the biphenyl pathway. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 842–850.
- 113.Segev, O.; Kushmaro, A.; Brenner, A. Environmental impact of flame retardants (persistence and biodegradability). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 478–491.
- 114.Zhang, M.; Shi, Q.; Song, X.; et al. Recent electrochemical methods in electrochemical degradation of halogenated organics: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 10457–10486.
- 115.Huang, Z.; Deng, D.; Qiao, J.; et al. New insight into the cosolvent effect on the degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) over millimeter-scale palladised sponge iron (Pd-s-Fe0) particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 1423–1436.
- 116.Oturan, N.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Zhang, H.; et al. Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants in landfill leachates treated by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12187–12196.
- 117.Tang, S.; Luo, Z.; Liao, J.; et al. Degradation and detoxification mechanisms of organophosphorus flame retardant tris (1, 3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate (TDCPP) during electrochemical oxidation process. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108090.
- 118.Dong, J.; Li, G.; Gao, J.; et al. Catalytic degradation of brominated flame retardants in the environment: New techniques and research highlights. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 848, 157695.
- 119.Ishii, A.; Amagai, K.; Furuhata, T.; et al. Thermal gasification behavior of plastics with flame retardant. Fuel 2007, 86, 2475–2484.
- 120.Boro, B.; Tiwari, P. Effect of metals and brominated flame retardants on thermal degradation kinetics of waste printed circuit board. Thermochim. Acta 2024, 736, 179747.
- 121.Bifulco, A.; Chen, J.; Sekar, A.; et al. Recycling of flame retardant polymers: Current technologies and future perspectives. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 199, 156–183.
- 122.Tang, W.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-L.; et al. Mitigation of PBDE net discharge in hazardous waste thermal treatment system through reintroducion of sludge and fly ash into GASMILD operations. Chemosphere 2024, 364, 143026.
- 123.Wang, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, Q.; et al. Low chlorine oil production through fast pyrolysis of mixed plastics combined with hydrothermal dechlorination pretreatment. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 149, 105–114.
How to Cite
Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, S.-L. Thermal Reactions and Byproducts from the Waste-to-Energy Process of Flame Retardant-Containing Wastes—A Review. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (2), 109–126. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100009.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


