With global water scarcity worsening, improving water treatment efficiency and sustainability has become a priority for governments worldwide. Ion exchange membranes (IEMs) in capacitive deionization (CDI) are regarded as a promising water treatment technology, capable of meeting the urgent demand for sustainable water resource utilization. In this mini-review, we have provided an overview of the research progress made in IEM-assisted CDI (MCDI), focusing on membrane materials, system configurations, patent analysis, and commercialization. Bibliometric and citation analyses reveal a surge in research and patent activity related to MCDI over the past five years, highlighting their growing global interest. The commercialization of MCDI is accelerating, driven by government funding in Europe, the U.S., Japan, and South Korea, alongside industry innovations improving efficiency and scalability. Patent analysis identifies dominant technical topics, patent strength, and the evolving patent numbers and expiration patterns of MCDI. Although challenges remain regarding cost, membrane durability, and scalability, MCDI is set to be a transformative technology in next-generation water purification and electrochemical separation systems. This review examines the current state of MCDI across various countries, offering insights into its role in advancing sustainable water resource management and enhancing water treatment technologies.
- Open Access
- Review
A Mini-Review of Ion Exchange Membranes for Capacitive Deionization: Research Progress, Commercialization, and Patent Trends
- Po-An Chen 1,
- Kuan-Ting Lee 2, *,
- Jie-Lun Chang 1
Author Information
Received: 24 Apr 2025 | Revised: 27 May 2025 | Accepted: 03 Jun 2025 | Published: 04 Jun 2025
Abstract
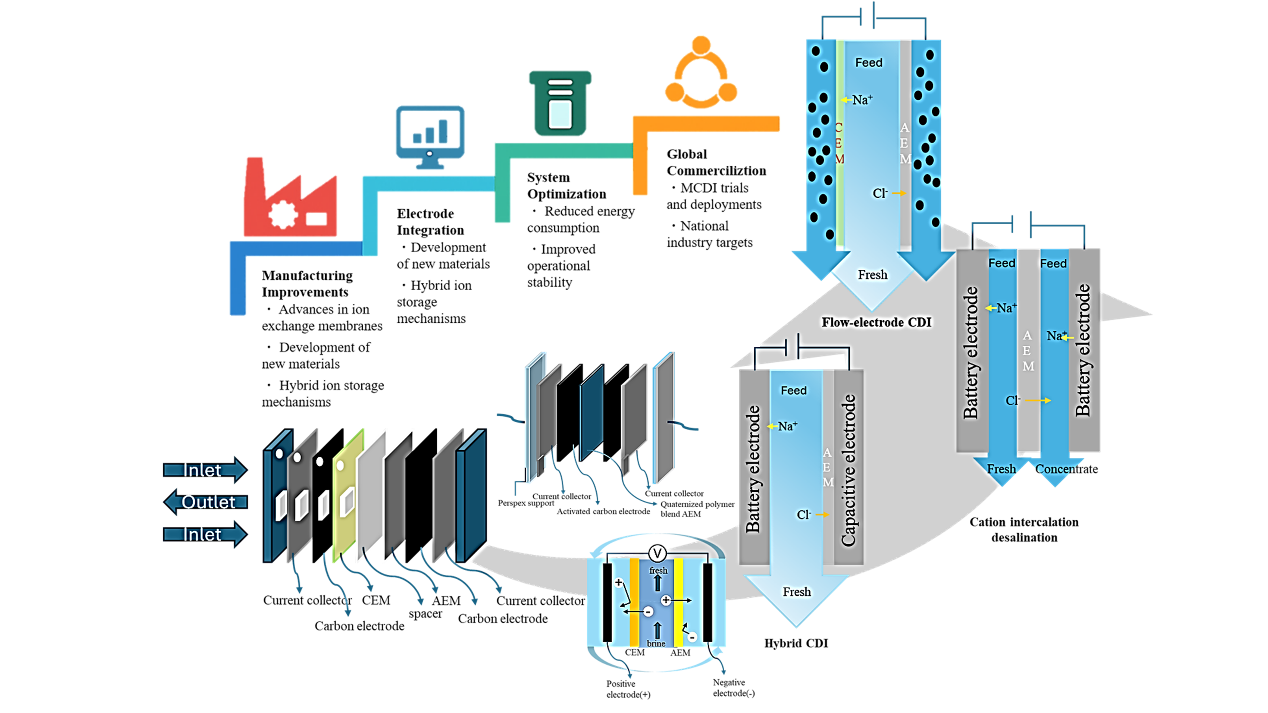
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
ion exchange membranes | capacitive deionization | water treatment | commercialization | patent analysis
References
- 1.Nandiyanto, A.B.D.; Al Husaeni, D.F. A bibliometric analysis of materials research in Indonesian journal using VOSviewer. J. Eng. Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.36909/jer.ASSEEE.16037.
- 2.Martins, J.; Gonçalves, R.; Branco, F. A bibliometric analysis and visualization of e-learning adoption using VOSviewer. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2024, 23, 1177–1191.
- 3.Lee, K.-T.; Cai, Y.-S.; Hou, Q.-Y.; et al. A Brief Overview of Green Hydrogen on Production, Regulations, and Commercialization. Green Energy Fuel Res. 2024, 1, 3–12.
- 4.Jiang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; et al. A comprehensive review on the synthesis and applications of ion exchange membranes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130817.
- 5.Alkhadra, M.A.; Su, X.; Suss, M.E.; et al. Electrochemical methods for water purification, ion separations, and energy conversion. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 13547–13635.
- 6.Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, G.; et al. Tailored Porous Ion Exchange Membrane for Separation of Charged Organic Compound. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=5147562 (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- 7.Zhang, S.; Tanioka, A.; Matsumoto, H. De novo ion-exchange membranes based on nanofibers. Membranes 2021, 11, 652.
- 8.Qian, H.; Xu, G.; Yang, S.; et al. Advancing lithium–magnesium separation: Pioneering swelling-embedded cation exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (ether ether ketone). ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 18019–18029.
- 9.Li, X.; Chen, G.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Sulfonated polyphenylene oxide-based artificial lung membrane with prominent selectivity of CO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130419.
- 10.Han, S.-Y.; Yu, D.M.; Mo, Y.-H.; et al. Ion exchange capacity controlled biphenol-based sulfonated poly (arylene ether sulfone) for polymer electrolyte membrane water electrolyzers: Comparison of random and multi-block copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 634, 119370.
- 11.Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Escorihuela, J.; Solorza-Feria, O.; et al. Proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs): Advances and challenges. Polymers 2021, 13, 3064.
- 12.Lv, S.; Li, X.; Lu, M.; et al. Recent advances in non-perfluorinated sulfonic acid proton exchange membranes in the energy field. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 9345–9370.
- 13.Porada, S.; Zhao, R.; van der Wal, A.; et al. Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 1388–1442.
- 14.Luo, J.; Li, M.; Heng, Y. Bio-inspired design of next-generation ultrapermeable membrane systems. NPJ Clean Water 2024, 7, 4.
- 15.Bernardes, A.F.; Meng, Z.; Campos, L.C.; et al. Bio-inspired anti-fouling strategies for membrane-based separations. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 5064–5071.
- 16.Giacalone, F.; Catrini, P.; Gurreri, L.; et al. Exergy analysis of electrodialysis for water desalination: Influence of irreversibility sources. Energy Convers. Manag. 2022, 258, 115314.
- 17.Butylskii, D.Y.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; et al. Selective recovery and re-utilization of lithium: Prospects for the use of membrane methods. Russ. Chem. Rev 2023, 92, 5074.
- 18.Mei, Y.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.-C.; et al. Reverse electrodialysis chemical cell for energy harvesting from controlled acid–base neutralization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 4640–4647.
- 19.Mubita, T.; Porada, S.; Biesheuvel, P.; et al. Strategies to increase ion selectivity in electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 292, 120944.
- 20.Honarparvar, S.; Reible, D. Modeling multicomponent ion transport to investigate selective ion removal in electrodialysis. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2020, 1, 100007.
- 21.Wang, C.; Park, M.J.; Yu, H.; et al. Recent advances of nanocomposite membranes using layer-by-layer assembly. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 661, 120926.
- 22.Lipton, J.; Weng, G.-M.; Rӧhr, J.A.; et al. Layer-by-layer assembly of two-dimensional materials: Meticulous control on the nanoscale. Matter 2020, 2, 1148–1165.
- 23.Schneider, R.; Facure, M.H.; Chagas, P.A.; et al. Tailoring the surface properties of micro/nanofibers using 0d, 1d, 2d, and 3d nanostructures: A review on post‐modification methods. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100430.
- 24.Yan, L.; Yang, X.; Zeng, H.; et al. Nanocomposite hydrogel engineered hierarchical membranes for efficient oil/water separation and heavy metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 668, 121243.
- 25.Yang, L.; Xiao, H.; Qian, Y.; et al. Bioinspired hierarchical porous membrane for efficient uranium extraction from seawater. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 71–80.
- 26.Reimonn, G.; Kamcev, J. Techno-economic perspective on the limitations and prospects of ion-exchange membrane technologies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2025, 47, 101077.
- 27.Xu, F.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, R.; et al. Selective Ion Separation by Capacitive Deionization: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2025, 18, 1107.
- 28.Schertzer, W.; Shukla, S.; Sose, A.; et al. AI-driven design of fluorine-free polymers for sustainable and high-performance anion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Inform. 2025, 5, 5.
- 29.Chang, W.-T.; Chen, P.-A.; Peng, C.-Y.; et al. Capacitive deionization and disinfection of saltwater using nanostructured (Cu–Ag)@ C/rGO composite electrodes. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 883–889.
- 30.Chen, P.-A.; Liu, S.-H.; Wang, H.P. Pseudocapacitive Deionization of Saltwater by Mn3O4@ C/Activated Carbon. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13315–13322.
- 31.Xiao, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, L.; et al. Membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI) for selective ion separation and recovery: Fundamentals, challenges, and opportunities. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 699, 122650.
- 32.Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Tactics for boosting the desalination stability of capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 153808.
- 33.Elewa, M.M.; El Batouti, M.; Al-Harby, N.F. A comparison of capacitive deionization and membrane capacitive deionization using novel fabricated ion exchange membranes. Materials 2023, 16, 4872.
- 34.Gamaethiralalage, J.; Singh, K.; Sahin, S.; et al. Recent advances in ion selectivity with capacitive deionization. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 1095–1120.
- 35.Shu, G.; Song, Z.; Wang, W.; et al. Review of emerging multiple ion-exchange membrane electrochemical systems for effective energy conversion and storage. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2024, 70, 103926.
- 36.Volfkovich, Y.M. The Effect of Structure of Porous Components of Electrochemical Devices on Their Characteristics (A Review). Russ. J. Electrochem. 2023, 59, 347–418.
- 37.Salmeron-Sanchez, I.; Asenjo-Pascual, J.; Avilés-Moreno, J.R.; et al. Microstructural description of ion exchange membranes: The effect of PPy-based modification. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120771.
- 38.Yu, H.; Hossain, S.M.; Wang, C.; et al. Selective lithium extraction from diluted binary solutions using metal-organic frameworks (MOF)-based membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI). Desalination 2023, 556, 116569.
- 39.Tsai, S.-W.; Hackl, L.; Kumar, A.; et al. Exploring the electrosorption selectivity of nitrate over chloride in capacitive deionization (CDI) and membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI). Desalination 2021, 497, 114764.
- 40.Asadipour, E.; Ramani, V. Morphology Control of Immiscible Polymer-Blended Anion-Exchange Membranes. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2025, 8, 4681–4687.
- 41.Hager, L.; Hegelheimer, M.; Stonawski, J.; et al. Novel side chain functionalized polystyrene/O-PBI blends with high alkaline stability for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE). J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 22347–22359.
- 42.Nagar, A.; Islam, M.R.; Pradeep, T. New technologies for drinking water. Technol. Solut. Water Sustain. Chall. Prospect. 2023, 123. https://doi.org/10.2166/9781789063714_0123.
- 43.Mohammed, N.; Lian, H.; Islam, M.S.; et al. Selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes using functionalized cellulose nanocrystals. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129237.
- 44.Chae, S.H.; Hong, S.W.; Son, M. Metadata and feature importance analyses of membrane capacitive deionization models: Is a water treatment artificial intelligence panacea possible? Desalination 2024, 585, 117784.
- 45.Rashid, R.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; et al. A state-of-the-art review on wastewater treatment techniques: The effectiveness of adsorption method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 9050–9066.
- 46.Muddemann, T.; Haupt, D.; Sievers, M.; et al. Electrochemical reactors for wastewater treatment. ChemBioEng Rev. 2019, 6, 142–156.
- 47.Lee, K.-T.; Ho, K.-Y.; Chen, W.-H.; et al. Construction and demolition waste as a high-efficiency advanced process for organic pollutant degradation in Fenton-like reaction to approach circular economy. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122246.
- 48.Lee, K.-T.; Chuah, X.-F.; Cheng, Y.-C.; et al. Pt coupled ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals as a breakthrough photocatalyst for Fenton-like processes–photodegradation treatments from hours to seconds. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18578–18585.
- 49.Narayanan, C.; Narayan, V. Biological wastewater treatment and bioreactor design: A review. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 1–17.
- 50.UN-Water. Water Scarcity; United Nations: New York City, NY, USA, 2021.
- 51.Khatoon, U.T.; Velidandi, A. An Overview on the Role of Government Initiatives in Nanotechnology Innovation for Sustainable Economic Development and Research Progress. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1250.
- 52.Suss, M.E.; Porada, S.; Sun, X.; et al. Water desalination via capacitive deionization: What is it and what can we expect from it? Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2296–2319.
- 53.Hassanvand, A.; Wei, K.; Talebi, S.; et al. The role of ion exchange membranes in membrane capacitive deionisation. Membranes 2017, 7, 54.
- 54.Pawlowski, S.; Huertas, R.M.; Galinha, C.F.; et al. On operation of reverse electrodialysis (RED) and membrane capacitive deionisation (MCDI) with natural saline streams: A critical review. Desalination 2020, 476, 114183.
- 55.Zhao, R.; Biesheuvel, P.; Van der Wal, A. Energy consumption and constant current operation in membrane capacitive deionization. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9520–9527.
- 56.State, P. Electricity-Driven Water Purification Method May Extend to Saltier Waters. 2022. Available online: https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/964214?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 24 April 2025).
- 57.McNair, R.; Szekely, G.; Dryfe, R.A. Ion-exchange materials for membrane capacitive deionization. ACS EST Water 2020, 1, 217–239.
- 58.Jeon, S.-i.; Kim, N.; Jo, K.; et al. Improvement in the desalination performance of membrane capacitive deionization with a bipolar electrode via an energy recovery process. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135603.
- 59.Kim, J.; Hong, S. Pilot study of emerging low-energy seawater reverse osmosis desalination technologies for high-salinity, high-temperature, and high-turbidity seawater. Desalination 2023, 565, 116871.
- 60.Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, B.; et al. Emerging frontiers in multichannel membrane capacitive deionization: Recent advances and future prospects. Langmuir 2024, 40, 4567–4578.
How to Cite
Chen, P.-A.; Lee, K.-T.; Chang, J.-L. A Mini-Review of Ion Exchange Membranes for Capacitive Deionization: Research Progress, Commercialization, and Patent Trends. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (2), 127–138. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100010.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


