Modern downdraft gasifiers used commercially are predominantly tailored for efficiently converting woody biomass, such as wood chips. However, substantial value also lies in the utilization of wood residues and Municipal Solid Waste (MSW), which are often underexploited. For gasifiers to serve a wider range of applications effectively, they must be capable of handling diverse waste inputs and adjusting their operation in real-time to suit varying material characteristics. This study centers on the advancement of a tar-free gasification system capable of processing MSW with high flexibility. The investigation outlines the systematic approach taken in designing, developing, and assessing the performance of this innovative gasifier. The core focus of the technology is to convert MSW into usable thermal energy through gasification. The prototype developed in this work features a square-shaped stratified fixed-bed downdraft gasifier, engineered to process up to 10 kg of feedstock per hour. It accommodates both pelletized and non-pelletized forms of MSW, offering versatility in input types. During experimental trials, the highest volume of producer gas 38 m3/h. was recorded in the third trial phase, which utilized a balanced mixture of wood and MSW in equal proportions. This setup also yielded the highest calorific value of gas, calculated at 1250 kcal/Nm3. By integrating advanced thermal flare systems that efficiently combust the produced gas, the developed gasifier significantly reduces thermal energy production costs. Furthermore, analyses of the mass and energy distribution confirmed an efficient and consistent relationship between the fuel input and the energy output, validating the system’s operational effectiveness.
- Open Access
- Article
Analysis of Thermal Properties in Co-Gasification of Municipal Solid Waste and Woody Biomass
- Crossline Ajona 1, 2,
- Ayyadurai Saravanakumar 1, *
Author Information
Received: 08 May 2025 | Revised: 29 May 2025 | Accepted: 11 Jun 2025 | Published: 16 Jun 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
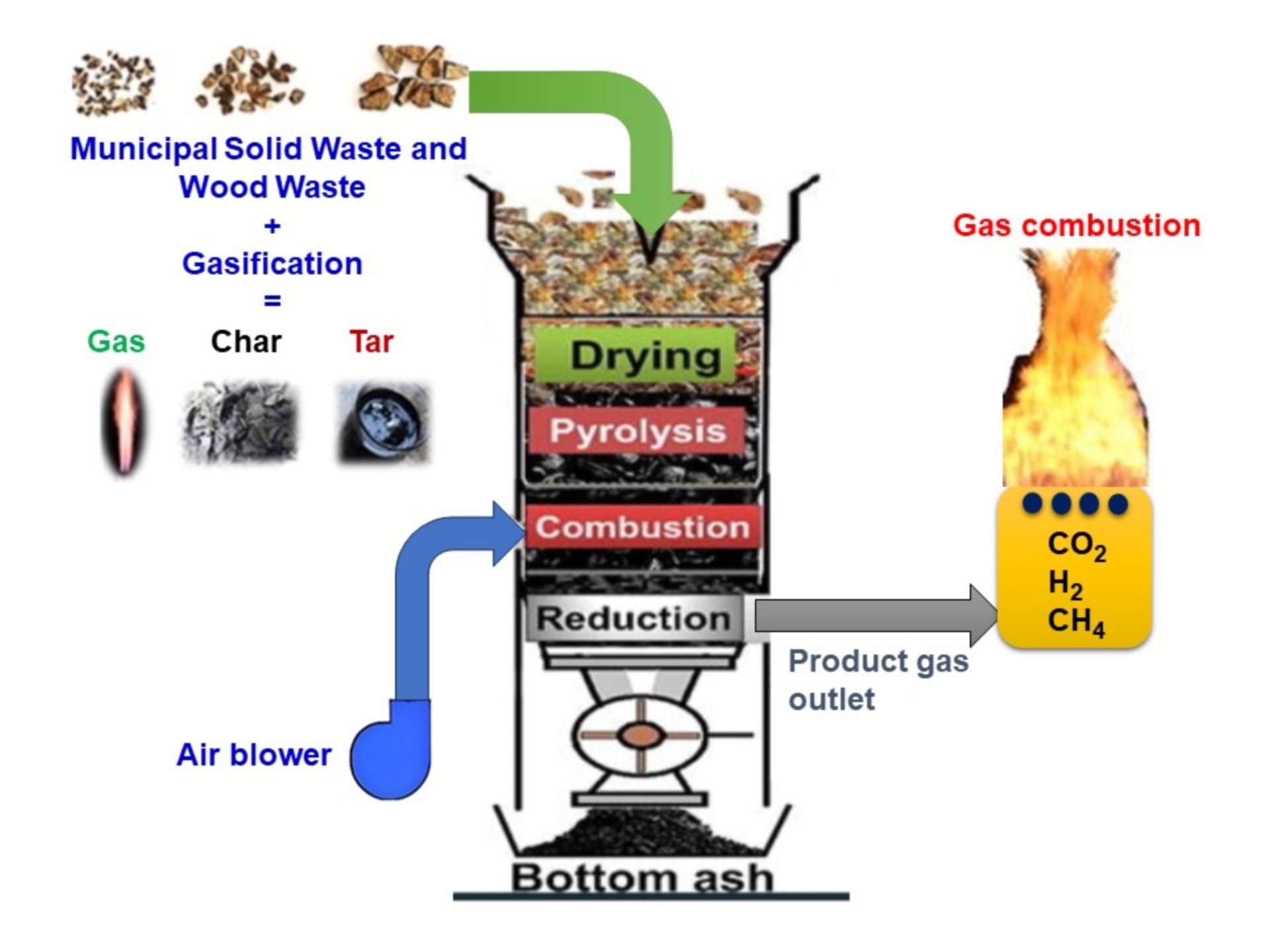
References
- 1.Nimita Jebaranjitham, J.; Selvan Christyraj, J.D.; Prasannan, A.; et al. Current Scenario of Solid Waste Management Techniques and Challenges in COVID-19—A Review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09855. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HELIYON.2022.E09855.
- 2.Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; et al. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12717. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH191912717.
- 3.Report of the Task Force on Waste to Energy (Volume I) (In the Context of Integrated MSW Management). 2014. Available online: https://sbmurban.org/storage/app/media/pdf/Task_force_report_on_WTE.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- 4.Annual Report, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change. New Delhi, 2015. Available online: https://moef.gov.in/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/MinistryofEnvirormentAnnualReport2015-16English.pdf (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- 5.Guo, M.; Lin, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Configuration Optimization of a Biomass Chemical Looping Gasification (CLG) System Combined with CO2 Absorption. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121459. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RENENE.2024.121459.
- 6.Li, J.; Fu, W.; Bai, X.; et al. Oxidative Pyrolysis Characteristics and Exothermic Heat Release Effects of Cellulose, Hemicellulose, and Lignin. Fuel 2025, 386, 134212. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2024.134212.
- 7.Racero-Galaraga, D.; Rhenals-Julio, J.D.; Sofan-German, S.; et al. Proximate Analysis in Biomass: Standards, Applications and Key Characteristics. Results Chem. 2024, 12, 101886. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RECHEM.2024.101886.
- 8.Puri, L.; Hu, Y.; Naterer, G. Critical Review of the Role of Ash Content and Composition in Biomass Pyrolysis. Front. Fuels 2024, 2, 1378361. https://doi.org/10.3389/FFUEL.2024.1378361.
- 9.Liu, Y.; Yin, K.; Wu, J.; et al. Ash Chemistry in Chemical Looping Process for Biomass Valorization: A Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147429. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2023.147429.
- 10.Ranzi, E.; Faravelli, T.; Manenti, F. Pyrolysis, Gasification, and Combustion of Solid Fuels. In Advances in Chemical Engineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Volume 49, pp 1–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/BS.ACHE.2016.09.001.
- 11.Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Raheem, A.; et al. Syngas Production from Biomass Gasification: Influences of Feedstock Properties, Reactor Type, and Reaction Parameters. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31620–31631. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.3C03050.
- 12.Jayanarasimhan, A.; Pathak, R.M.; Shivapuji, A.M.; et al. Tar Formation in Gasification Systems: A Holistic Review of Remediation Approaches and Removal Methods. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 2060–2079. https://doi.org/10.1021/ACSOMEGA.3C04425.
- 13.Chen, D.; Yin, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Pyrolysis Technologies for Municipal Solid Waste: A Review. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2466–2486. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2014.08.004.
- 14.Al-Rumaihi, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Mckay, G.; et al. A Review of Pyrolysis Technologies and Feedstock: A Blending Approach for Plastic and Biomass towards Optimum Biochar Yield. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112715. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2022.112715.
- 15.Kumar, A.; Thakur, A.K.; Gaurav, G.K.; et al. A Critical Review on Sustainable Hazardous Waste Management Strategies: A Step towards a Circular Economy. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023 3048 2023, 30, 105030–105055. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11356-023-29511-8.
- 16.Brunner, P.H.; Morf, L.S. Waste to Energy, Indispensable Cornerstone for Circular Economy: A Mini-Review. Waste Manag. Res. 2025, 43, 26–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734242X241227376.
- 17.Farooq, A.; Haputta, P.; Silalertruksa, T.; et al. A Framework for the Selection of Suitable Waste to Energy Technologies for a Sustainable Municipal Solid Waste Management System. Front. Sustain. 2021, 2, 681690. https://doi.org/10.3389/FRSUS.2021.681690.
- 18.Materazzi, M.; Lettieri, P.; Taylor, R.; et al. Performance Analysis of RDF Gasification in a Two Stage Fluidized Bed–Plasma Process. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 256–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WASMAN.2015.06.016.
- 19.Dong, J.; Tang, Y.; Nzihou, A.; et al. Comparison of Waste-to-Energy Technologies of Gasification and Incineration Using Life Cycle Assessment: Case Studies in Finland, France and China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 203, 287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.08.139.
- 20.Achinas, S.; Gramsbergen, M.; Achinas, V.; et al. Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Industrial Progress for Boosting the Circular Economy; Springer: Singapore, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-7525-9_106-1.
- 21.Seo, Y.-C.; Alam, M.T.; Yang, W.-S.; et al. Gasification of Municipal Solid Waste. In Gasification for Low-grade Feedstock; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. https://doi.org/10.5772/INTECHOPEN.73685.
- 22.Tauqir, W.; Zubair, M.; Nazir, H. Parametric Analysis of a Steady State Equilibrium-Based Biomass Gasification Model for Syngas and Biochar Production and Heat Generation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 199, 111954. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2019.111954.
- 23.Su, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Tar Destruction under Partial Oxidation Environment. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1513–1524. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUPROC.2011.03.013.
- 24.Valderrama Rios, M.L.; González, A. M.; Lora, E.E.S.; et al. Reduction of Tar Generated during Biomass Gasification: A Review. Biomass Bioenergy 2018, 108, 345–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOMBIOE.2017.12.002.
- 25.Lan, W.; Chen, G.; Zhu, X.; et al. Progress in Techniques of Biomass Conversion into Syngas. J. Energy Inst. 2015, 88, 151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JOEI.2014.05.003.
- 26.Sher, F.; Hameed, S.; Smječanin Omerbegović, N.; et al. Cutting-Edge Biomass Gasification Technologies for Renewable Energy Generation and Achieving Net Zero Emissions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 323, 119213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENCONMAN.2024.119213.
- 27.Sikarwar, V.S.; Zhao, M.; Clough, P.; et al. An Overview of Advances in Biomass Gasification. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2939–2977. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6EE00935B.
- 28.Thakare, S.; Nandi, S. Study on Potential of Gasification Technology for Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) in Pune City. Energy Procedia 2016, 90, 509–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYPRO.2016.11.218.
- 29.Saravanakumar, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; Hoang, A. T.; et al. Thermochemical Conversion of Large-Size Woody Biomass for Carbon Neutrality: Principles, Applications, and Issues. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128562. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2022.128562.
How to Cite
Ajona, C.; Saravanakumar, A. Analysis of Thermal Properties in Co-Gasification of Municipal Solid Waste and Woody Biomass. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (2), 139–151. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100011.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


