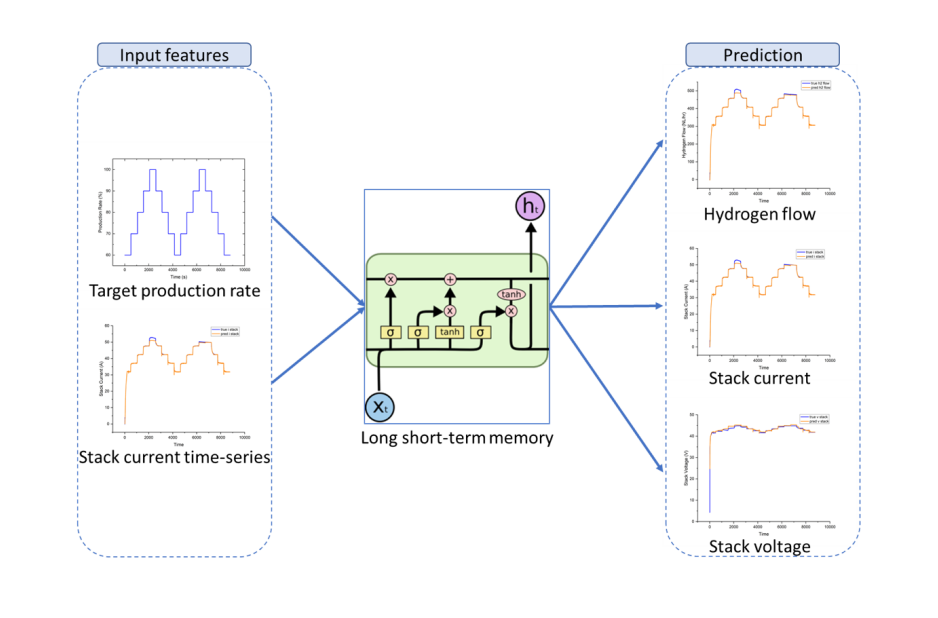
Commercial anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers (AEMWE) typically do not provide detailed information about internal system parameters or stack characteristics, making physics-based modeling difficult and limiting their integration into customized digital simulation environments. Moreover, electrochemical and multiphysics models often require extensive computational resources, and parameter optimization can be prohibitively expensive. This study investigates the use of a long short-term memory (LSTM) network to predict the dynamic response of a commercial AEMWE under varying hydrogen production rates. The goal is to establish a data-driven model that replicates the operational logic of the real system, enabling the prediction of stack current, stack voltage, and hydrogen flow rate directly from the target production rate with significantly lower computational cost while preserving the transient behavior of the device. Model validation shows that the proposed LSTM achieves RMSE values of 0.48 for stack current, 0.92 for stack voltage, and 5.22 for hydrogen flow rate. The model successfully captures the overall dynamic trends and demonstrates that hydrogen flow rate and stack voltage can be inferred from the target production rate and stack current. Training is computationally efficient, allowing rapid model development. Although undershoot occurs during rapid decreases in production rate due to the smoothing characteristics of LSTM, the overall prediction error remains within acceptable bounds. The results highlight the potential of data-driven modeling for fast and practical AEMWE system representation, supporting future development of digital twins and accelerating applications in green hydrogen technologies.
- Open Access
- Article
LSTM-Based Prediction of System Dynamics in a Commercial AEM Water Electrolyzer Under Target Hydrogen Production Rates
Author Information
Received: 19 Dec 2025 | Revised: 27 Jan 2026 | Accepted: 29 Jan 2026 | Published: 03 Feb 2026
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
anion exchange membrane water electrolysis | long short-term memory | deep learning | digital twin | dynamic modeling
References
- 1.
Gevaert, S.; Pause, L.; Cezne, E.; et al. Green Hydrogen in the Global South: A Literature Review. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Eric-Cezne/publication/366809109_Green_Hydrogen_in_the_Global_South_A_literature_review/links/63b2fb56097c7832ca84c636/Green-Hydrogen-in-the-Global-South-A-literature-review.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- 2.
Huang, P.H.; Kuo, J.K.; Wu, Z.D. Applying Small Wind Turbines and a Photovoltaic System to Facilitate Electrolysis Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 8514–8524.
- 3.
Kumar, S.S.; Himabindu, V. Hydrogen Production by PEM Water Electrolysis—A Review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 442–454.
- 4.
Smolinka, T.; Bergmann, H.; Garche, J.; et al. Chapter 4—The History of Water Electrolysis from Its Beginnings to the Present. In Electrochemical Power Sources: Fundamentals, Systems, and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2022; pp. 83–164.
- 5.
Blasi, A.; Fiorenza, G.; Freda, C.; et al. 6-Steam Reforming of Biofuels for the Production of Hydrogen-Rich Gas. In Membranes for Clean and Renewable Power Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014; pp. 145–181.
- 6.
Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-Storage Materials for Mobile Applications. Nature 2001, 414, 353–358.
- 7.
Khan, M.A.; Zhao, H.; Zou, W.; et al. Recent Progresses in Electrocatalysts for Water Electrolysis. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2018, 1, 483–530.
- 8.
Altinisik, H.; Celebi, C.; Özden, A.; et al. A Review on Membranes for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2026, 226, 114530.
- 9.
Khan, A.M.; Nielsen, M.R.; Golsorkhi, M.S.; et al. Multiphysics Modeling of Electrolyzers under Dynamic Converter Operation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 176, 105–116.
- 10.
Narayanan, A.; Jensen, K.J.; Bisgaard, T.; et al. Multiscale and Multiphysics Simulation Framework for Alkaline Electrolyzer Stacks. In Proceedings of the European Electrolyser & Fuel Cell Forum (EFCF 2025); Lucerne, Switzerland, 1–4 July 2025; p. A0506.
- 11.
Chen, K.; Hu, K.; Yang, J.; et al. Multiphysics Modeling and Parameter Analysis of Industrial Power-to-Hydrogen Electrolyzers. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Energy, Electrical and Power Engineering (CEEPE), Guangzhou, China, 12–14 May 2023.
- 12.
Wang, Y.; Lin, H.-W.; An, W.; et al. Comparison and General Law Research of Multiple Machine-Learning Models for Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolytic Cell Parameters Prediction. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 546.
- 13.
Xu, B.; Ma, W.; Wu, W.; et al. Degradation Prediction of PEM Water Electrolyzer under Constant and Start-Stop Loads Based on CNN-LSTM. Energy AI 2024, 18, 100407.
- 14.
Chen, K.; Laghrouche, S.; Djerdir, A. Prognosis of Fuel Cell Degradation under Different Applications Using Wavelet Analysis and Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Neural Network. Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 802–814.
- 15.
Cheng, Y.; Huang, C.N.; Kuo, J.K.; et al. Optimization of Alkaline Water Electrolyzers through Taguchi Statistical Screening and Grey Wolf Metaheuristics. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 192, 130–142.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


