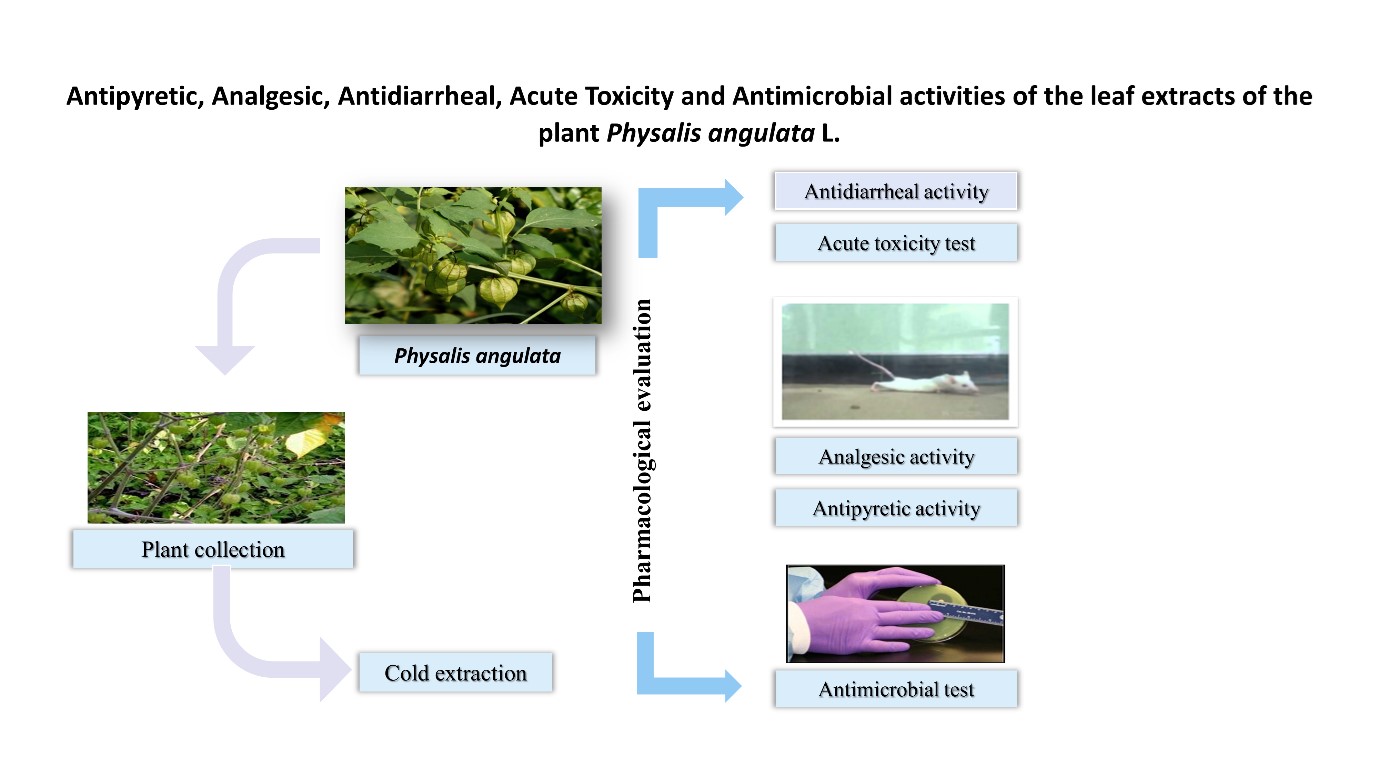
Physalis angulata L. family Solanaceae, commonly known as ground cherry, cape gooseberry, or bladder cherry, has a long history of traditional use in various regions around the world. The primary goal of this study is to investigate the different pharmacological effects produced by the ethanolic leaf extracts of Physalis angulata. The leaf extract was prepared in two different dosages: 250 mg/kg body weight and 500 mg/kg body weight, which were administered according to the body weight of the mice. In yeast-induced pyrexia in mice, after 4 h, positive control (Paracetamol 150 mg/kg), Physalis angulata 250 mg/kg, Physalis angulata 500 mg/kg expressed temperature were 98.78 ± 0.051 °F, 97.4 ± 0.213 °F and 96.56 ± 0.177 °F respectively. In the evaluation of acetic acid-induced peripheral analgesic activity, P. angulata extract exhibited 43% and 63% inhibition of writhing at 250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg body weight, respectively. Whereas the standard Diclofenac-Na inhibited 76% at a dose of 25 mg/kg body weight. In castor oil-induced diarrhea, plant extract inhibited defecation by 59.65% at 250 mg/kg body weight and 72.45% at 500 mg/kg b.w., whereas standard loperamide at a dose of 3 mg/kg b.w. inhibited 83.50% of defecation. Ethanolic extract of Physalis angulata at the dose of 300 mg/kg, 2000 mg/kg and 5000 mg/kg showed average weight 21.2 ± 1.56 gm, 21.8 ± 0.82 gm and 24.45 ± 1.51 gm respectively at 2nd day. The disc diffusion method has been adopted for the evaluation of antimicrobial activity. The ethanolic extracts of Physalis angulata leaf exhibited inhibitory activity against fourteen strains, including Bacillus megaterium, Salmonella paratyphi, Candida aibicans, Vibrio mimicus, and Staphylococcus aureus.
- Open Access
- Article
Evaluation of Therapeutic Activity of Physalis angulata (In Vitro Studies)
- Md. Shahlal 1,
- As-Sazzad Mahmud 1, 2, *,
- Rahul Dev Bairagi 2,
- Dipa Debnath 2,
- Barsha Sarker Nipa 3,
- Raiyan Rahman Reon 2,
- Rony Ahmed 4,
- Tawhidur Rahman 5,
- Shankar Sharma 6,
- Amit Kumar Acharzo 2
Author Information
Received: 19 Sep 2024 | Revised: 14 Oct 2024 | Accepted: 25 Oct 2024 | Published: 27 Nov 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Physalis angulata | analgesic | antipyretic | antidiarrheal | acute toxicity | antimicrobial
References
- 1.Akerele, O. WHO’s Traditional Medicine Programme: Progress and Perspectives. WHO Chron. 1984, 38, 76–81.
- 2.Ahvazi, M.; Khalighi-Sigaroodi, F.; Charkhchiyan, M.M.; et al. Introduction of Medicinal Plants Species with the Most Traditional Usage in Alamut Region. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2012, 11, 185–194.
- 3.Rivera, D.E.; Ocampo, Y.C.; Castro, J.P.; et al. Antibacterial Activity of Physalis angulata L., Merremia umbellata L., and Cryptostegia grandiflora Roxb. Ex R.Br.—Medicinal Plants of the Colombian Northern Coast. Orient. Pharm. Exp. Med. 2015, 15, 95–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-014-0176-0.
- 4.Medina-Medrano, J.R.; Almaraz-Abarca, N.; González-Elizondo, M.S.; et al. Phenolic Constituents and Antioxidant Properties of Five Wild Species of Physalis (Solanaceae). Bot. Stud. 2015, 56, 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40529-015-0101-y.
- 5.Ramakrishna Pillai, J.; Wali, A.F.; Menezes, G.A.; et al. Chemical Composition Analysis, Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Physalis angulata L.: A Comparative Study of Leaves and Fruit. Molecules 2022, 27, 1480. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051480.
- 6.Rivera, D.E.; Ocampo, Y.C.; Castro, J.P.; et al. A Screening of Plants Used in Colombian Traditional Medicine Revealed the Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Physalis angulata Calyces. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 1758–1766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.05.030.
- 7.Sun, C.-P.; Qiu, C.-Y.; Zhao, F.; et al. Physalins V-IX, 16,24-Cyclo-13,14-Seco Withanolides from Physalis angulata and Their Antiproliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4057. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-03849-9.
- 8.Mazumder, K.; Biswas, B.; Raja, I.M.; et al. A Review of Cytotoxic Plants of the Indian Subcontinent and a Broad-Spectrum Analysis of Their Bioactive Compounds. Molecules 2020, 25, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25081904.
- 9.Kindscher, K.; Long, Q.; Corbett, S.; et al. The Ethnobotany and Ethnopharmacology of Wild Tomatillos, Physalis Longifolia Nutt., and Related Physalis Species: A Review. Econ. Bot. 2012, 66, 298–310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12231-012-9210-7.
- 10.Petrovska, B.B. Historical Review of Medicinal Plants’ Usage. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2012, 6, 1–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.95849.
- 11.Haddad, M.H.F.; Mahbodfar, H.; Zamani, Z.; et al. Antimalarial Evaluation of Selected Medicinal Plant Extracts Used in Iranian Traditional Medicine. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2017, 20, 415–422. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2017.8583.
- 12.Gao, C.-Y.; Ma, T.; Luo, J.; et al. Three New Cytotoxic Withanolides from the Chinese Folk Medicine Physalis angulata. Nat. Product. Commun. 2015, 10, 2059–2062. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1501001211.
- 13.Mahklouf, M.H. A New Record Physalis angulata L. (Solanaceae) for the Flora of Syria. Am. J. Life Sci. Res. 2016, 2, 9–11.
- 14.Kamagaju, L.; Bizuru, E.; Minani, V.; et al. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Medicinal Plants Used in Rwanda for Voluntary Depigmentation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 708–717.
- 15.Lestiariani, L.; Djabir, Y.Y.; Rahim, A. Subacute Toxicity Effects of Physalis angulata Leaf Extract on Kidneys and Liver of Female Wistar Rats. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2023, 17, 19–26.
- 16.Ayodhyareddy, P.; Rupa, P. Ethno Medicinal, Phyto Chemical and Therapeutic Importance of Physalis angulata L.: A Review. Inter J Sci Res (IJSR) 2016, 5, 2122–2127.
- 17.Tiwari, P.; Kumar, B.; Kaur, M.; et al. Phytochemical Screening and Extraction: A Review. Int. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 98–106.
- 18.Eloff, J.N. Which Extractant Should Be Used for the Screening and Isolation of Antimicrobial Components from Plants? J. Ethnopharmacol. 1998, 60, 1–8.
- 19.Ncube, N.S.; Afolayan, A.J.; Okoh, A.I. Assessment Techniques of Antimicrobial Properties of Natural Compounds of Plant Origin: Current Methods and Future Trends. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 1797–1806.
- 20.Al-Ghamdi, M.S. The Anti-Inflammatory, Analgesic and Antipyretic Activity of Nigella Sativa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 76, 45–48.
- 21.Anderson, B.J. Paracetamol (Acetaminophen): Mechanisms of Action. Pediatr. Anesth. 2008, 18, 915–921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9592.2008.02764.x.
- 22.Ahmed, F.; Selim, M.S.T.; Das, A.K.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Antinociceptive Activities of Lippia nodiflora Linn. Die Pharm. An. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 59, 329–330.
- 23.Debnath, S.L.; Kundu, P.; Ahad, M.F.; et al. Investigation of Phytochemical and Pharmacological Assessment of Ethanol Extract of Stenochlaena palustris—An Edible Fern of Sundarbans. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2021, 9, 226–232.
- 24.Yimer, T.; Birru, E.M.; Adugna, M.; et al. Evaluation of Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of 80% Methanol Root Extract of Echinops kebericho M. (Asteraceae). JIR 2020, 13, 647–658. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S267154.
- 25.Junior, O.D.; Andreucci, V.C.; da Silva Cunha, I.B.; et al. Investigation of the Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Activities of a Sample of Brazilian Propolis. Acta Farm. Bonaer. 2004, 23, 285–291.
- 26.Jahan, T.; Kundu, P.; Sultana, T.; et al. Phytochemical Investigation and Assessment of Pharmacological Properties of Leaves of Duabanga grandiflora. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2021, 9, 25–32. https://doi.org/10.22271/plants.2021.v9.i6a.1348.
- 27.Kola-Mustapha, A.T.; Ghazali, Y.O.; Ayotunde, H.T.; et al. Evaluation of the Antidiarrheal Activity of the Leaf Extract of Parquetina nigrescens and Formulation into Oral Suspensions. JEP 2019, 11, 65–72. https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S214417.
- 28.Kifayatullah, M.; Mustafa, M.S.; Sengupta, P.; et al. Evaluation of the Acute and Sub-Acute Toxicity of the Ethanolic Extract of Pericampylus glaucus (Lam.) Merr. in BALB/c Mice. J. Acute Dis. 2015, 4, 309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.06.010.
- 29.Raju, G.S.; RahmanMoghal, M.M.; Hossain, M.S.; et al. Assessment of Pharmacological Activities of Two Medicinal Plant of Bangladesh: Launaea sarmentosa and Aegialitis rotundifolia Roxb in the Management of Pain, Pyrexia and Inflammation. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 55. https://doi.org/10.1186/0717-6287-47-55.
- 30.Manaharan, T.; Chakravarthi, S.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; et al. In Vivo Toxicity Evaluation of a Standardized Extract of Syzygium aqueum Leaf. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 718–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.09.006.
- 31.Tseha, S.T.; Mekonnen, Y.; Desalegn, A.; et al. Toxicity Study and Antibacterial Effects of the Leaves Extracts of Boscia coriacea and Uvaria leptocladon. Ethiop. J. Health Sci. 2022, 32, 823–832.
- 32.Airin, S.; Bairagi, R.D.; Noshin, S.; et al. Comparative Pharmacological Evaluation of Mangrove Plant Xylocarpus mekongensis Pierre and Associated Fungus. Eur. J. Pharm. Res. 2023, 3, 11–15. https://doi.org/10.24018/ejpharma.2023.3.5.73.
- 33.Sofowora, A.; Ogunbodede, E.; Onayade, A. The Role and Place of Medicinal Plants in the Strategies for Disease Prevention. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 10, 210–229.
- 34.Botting, R.M. Vane’s Discovery of the Mechanism of Action of Aspirin Changed Our Understanding of Its Clinical Pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rep. 2010, 62, 518–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(10)70308-X.
- 35.Zarghi, A.; Arfaei, S. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 655–683.
- 36.Ferrer, M.D.; Busquets-Cortés, C.; Capó, X.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 3225–3241.
- 37.Milani, D.A.Q.; Davis, D.D. Pain Management Medications. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023.
- 38.Nitbani, F.O.; Tjitda, P.J.P.; Wogo, H.E.; et al. Preparation of Ricinoleic Acid from Castor Oil: A Review. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 781–793. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess21226.
- 39.Mein, E.A.; Richards, D.G.; McMillin, D.L.; et al. Transdermal Absorption of Castor Oil. Evid-Based-Integr. Med. 2005, 2, 239–244. https://doi.org/10.2165/01197065-200502040-00006.
- 40.Sini, K.R.; Sinha, B.N.; Rajasekaran, A. Antidiarrheal Activity of Capparis zeylanica Leaf Extracts. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2011, 2, 39. https://doi.org/10.4103/2231-4040.79803.
- 41.Ushie, O.A.; Neji, P.A.; Abeng, F.E.; et al. Phytochemical Screening and Antimicrobial Activities of Chloroform and Ethyl Acetate Extracts of Physalis angulata. J. Chem. Soc. Niger. 2019, 44, 1062–1069.
How to Cite
Shahlal, Md.; Mahmud, A.-S.; Bairagi, R. D.; Debnath, D.; Nipa, B. S.; Reon, R. R.; Ahmed, R.; Rahman, T.; Sharma, S.; Acharzo, A. K. Evaluation of Therapeutic Activity of Physalis angulata (In Vitro Studies). Journal of Medicinal Natural Products 2024, 1 (1), 100007. https://doi.org/10.53941/jmnp.2024.100007.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


