Electrospinning is a widely used technique for creating nano- to microscale fibers that resembles the fibrous structure of the extracellular matrix (ECM) environment, crucial for tissue engineering and disease modelling. Directly incorporating living cells into the electrospinning process, ‘cell electrospinning’, has evolved in the last two decades as a new biofabrication method combining homogenous cell loading with the potential of single cell resolution. However, keeping cells viable and functional during the electrohydrodynamic process is an ongoing challenge. In this review, key parameters in electrospinning affecting mammalian cell viability and functionality are assessed with the goal of identifying the most critical ones in the successful production of living cell-embedded fibers. The review further outlooks the potential mechanobiological and electrophysiological effects on the cells exposed under the electrohydrodynamic condition to layout a couple unexplored applications.
- Open Access
- Review
Cell Electrospinning: Electrohydrodynamic Effects on Cell Viability and Beyond
- Anne-Kathrine Kure Larsen,
- Menglin Chen *
Author Information
Received: 09 Jun 2025 | Revised: 09 Aug 2025 | Accepted: 13 Aug 2025 | Published: 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
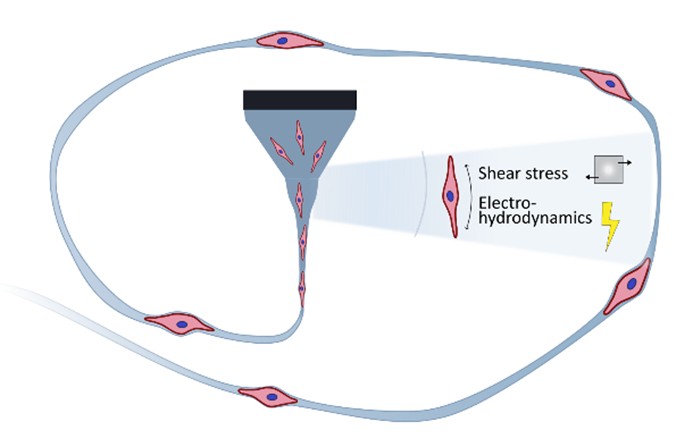
Keywords
cell electrospinning | biofabrication | tissue engineering | viability | mechanobiology | electrical stimulation
References
- 1.Luraghi, A.; Peri, F.; Moroni, L. Electrospinning for drug delivery applications: A review. J. Control. Release 2021, 334, 463–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.033.
- 2.Kishan, A.P.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E.M. Recent advancements in electrospinning design for tissue engineering applications: A review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 2892–2905. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36124.
- 3.Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Qu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, R.; Ma, W.; Huang, C. Multistructured Electrospun Nanofibers for Air Filtration: A Review. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 23293–23313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c06520.
- 4.Mercante, L.A.; Scagion, V.P.; Migliorini, F.L.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Correa, D.S. Electrospinning-based (bio)sensors for food and agricultural applications: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.04.004.
- 5.Taylor, S.G. Disintegration of water drops in an electric field. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1964, 280, 383–397. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1964.0151.
- 6.Baumgarten, P.K. Electrostatic spinning of acrylic microfibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1971, 36, 71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9797(71)90241-4.
- 7.Boda, S.K.; Li, X.; Xie, J. Electrospraying an enabling technology for pharmaceutical and biomedical applications: A review. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2018, 125, 164–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2018.04.002.
- 8.Jansen, K.A.; Donato, D.M.; Balcioglu, H.E.; Schmidt, T.; Danen, E.H.; Koenderink, G.H. A guide to mechanobiology: Where biology and physics meet. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 3043–3052. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.05.007.
- 9.Maurmann, N.; França, F.S.; Girón, J.; Pranke, P. Cell Electrospinning: A Review of Materials and Methodologies for Biofabrication. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300058. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202300058.
- 10.Nosoudi, N.; Hasanzadeh, A.; Hart, M.; Weaver, B. Advancements and Future Perspectives in Cell Electrospinning and Bio-Electrospraying. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300213. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202300213.
- 11.Elveren, B.; Kurečič, M.; Maver, T.; Maver, U. Cell Electrospinning: A Mini-Review of the Critical Processing Parameters and Its Use in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300057. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202300057.
- 12.Karvinen, J.; Kellomäki, M. Design aspects and characterization of hydrogel-based bioinks for extrusion-based bioprinting. Bioprinting 2023, 32, e00274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2023.e00274.
- 13.He, C.-F.; Qiao, T.-H.; Wang, G.-H.; Sun, Y.; He, Y. High-resolution projection-based 3D bioprinting. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2025, 3, 143–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44222-024-00218-w.
- 14.Lee, M.; Rizzo, R.; Surman, F.; Zenobi-Wong, M. Guiding Lights: Tissue Bioprinting Using Photoactivated Materials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10950–11027. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00077.
- 15.Zandrini, T.; Florczak, S.; Levato, R.; Ovsianikov, A. Breaking the resolution limits of 3D bioprinting: Future opportunities and present challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 604–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.10.009.
- 16.Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Method for the Preparation of Ultrathin Fibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200604646.
- 17.Boularaoui, S.; Al Hussein, G.; Khan, K.A.; Christoforou, N.; Stefanini, C. An overview of extrusion-based bioprinting with a focus on induced shear stress and its effect on cell viability. Bioprinting 2020, 20, e00093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2020.e00093.
- 18.Canbolat, M.F.; Tang, C.; Bernacki, S.H.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Khan, S. Mammalian Cell Viability in Electrospun Composite Nanofiber Structures. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1346–1356. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.201100108.
- 19.Yeo, M.; Yoon, J.W.; Park, G.T.; Shin, S.-C.; Song, Y.-C.; Cheon, Y.-I.; Lee, B.-J.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, J.H. Esophageal wound healing by aligned smooth muscle cell-laden nanofibrous patch. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 19, 100564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100564.
- 20.Nosoudi, N.; Oommen, A.J.; Stultz, S.; Jordan, M.; Aldabel, S.; Hohne, C.; Mosser, J.; Archacki, B.; Turner, A.; Turner, P. Electrospinning Live Cells Using Gelatin and Pullulan. Bioengineering 2020, 7, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering7010021.
- 21.Diep, E.; Schiffman, J.D. Electrospinning Living Bacteria: A Review of Applications from Agriculture to Health Care. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 951–964. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.2c01055.
- 22.Schulte-Hermann, J.; Riessland, H.; MacKinnon, N.; Korvink, J.G.; Islam, M. Biomineralization of Electrospun Bacteria-Encapsulated Fibers: A Relevant Step toward Living Ceramic Fibers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 7936–7943. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.4c00715.
- 23.Zussman, E. Encapsulation of cells within electrospun fibers. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2010, 22, 366–371. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.1812.
- 24.Zhang, Y.-Q.; Wang, P.; Shi, Q.-F.; Ning, X.; Chen, Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Zheng, J.; Long, Y.-Z. Advances in Wet Electrospinning: Rich Morphology and Promising Applications. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2025, 7, 374–413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-024-00493-7.
- 25.Townsend-Nicholson, A.; Jayasinghe, S.N. Cell Electrospinning: a Unique Biotechnique for Encapsulating Living Organisms for Generating Active Biological Microthreads/Scaffolds. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3364–3369.
- 26.Shih, Y.-H.; Yang, J.-C.; Li, S.-H.; Yang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-C. Bio-electrospinning of poly(l-lactic acid) hollow fibrous membrane. Text. Res. J. 2012, 82, 602–612. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517511420756.
- 27.Zanatta, G.; Steffens, D.; Braghirolli, D.I.; Fernandes, R.A.; Netto, C.A.; Pranke, P. Viability of mesenchymal stem cells during electrospinning. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 125–130. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x2011007500163.
- 28.Ang, H.Y.; Irvine, S.A.; Avrahami, R.; Sarig, U.; Bronshtein, T.; Zussman, E.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Machluf, M.; Venkatraman, S.S. Characterization of a bioactive fiber scaffold with entrapped HUVECs in coaxial electrospun core-shell fiber. Biomatter 2014, 4, e28238. https://doi.org/10.4161/biom.28238.
- 29.Ehler, E.; Jayasinghe, S.N. Cell electrospinning cardiac patches for tissue engineering the heart. Analyst 2014, 139, 4449–4452. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4an00766b.
- 30.Yeo, M.; Kim, G. Fabrication of cell-laden electrospun hybrid scaffolds of alginate-based bioink and PCL microstructures for tissue regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 275, 27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.04.038.
- 31.Braghirolli, D.; Pranke, P.; Zamboni, F.; Acasigua, G.A.X. Association of electrospinning with electrospraying: A strategy to produce 3D scaffolds with incorporated stem cells for use in tissue engineering. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 5159-5170. https://doi.org/10.2147/ijn.s84312.
- 32.Yeo, M.; Kim, G.H. Anisotropically Aligned Cell-Laden Nanofibrous Bundle Fabricated via Cell Electrospinning to Regenerate Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Small 2018, 14, 1803491. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201803491.
- 33.Wu, Y.; Ranjan, V.D.; Zhang, Y. A Living 3D In Vitro Neuronal Network Cultured inside Hollow Electrospun Microfibers. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1700218. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.201700218.
- 34.Guo, Y.; Gilbert-Honick, J.; Somers, S.M.; Mao, H.Q.; Grayson, W.L. Modified cell-electrospinning for 3D myogenesis of C2C12s in aligned fibrin microfiber bundles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 558–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.06.082.
- 35.Ranjan, V.D.; Zeng, P.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. In vitro cell culture in hollow microfibers with porous structures. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2175–2188. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9bm01986c.
- 36.Yeo, M.; Kim, G. Micro/nano-hierarchical scaffold fabricated using a cell electrospinning/3D printing process for co-culturing myoblasts and HUVECs to induce myoblast alignment and differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 102–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.042.
- 37.Das, P.; Hore, A.; Ghosh, A.; Datta, P. Bone tissue engineering construct fabricated using a cell electrospinning technique with polyglutamic acid biopolymer. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-021-02612-z.
- 38.Yang, I.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Liang, Y.-J.; Lin, T.-C.; Jakfar, S.; Thacker, M.; Wu, S.-C.; Lin, F.-H. The development of laminin-alginate microspheres encapsulated with Ginsenoside Rg1 and ADSCs for breast reconstruction after lumpectomy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1699–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.11.029.
- 39.Nosoudi, N.; Hart, C.; Mcknight, I.; Esmaeilpour, M.; Ghomian, T.; Zadeh, A.; Raines, R.; Ramirez Vick, J.E. Differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells to chondrocytes using electrospraying. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24301. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-03824-5.
- 40.Semitela, Â.; Ramalho, G.; Capitão, A.; Sousa, C.; Mendes, A.F.; Aap Marques, P.; Completo, A. Bio-electrospraying assessment toward in situ chondrocyte-laden electrospun scaffold fabrication. J. Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 204173142110693. https://doi.org/10.1177/20417314211069342.
- 41.Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liao, P.; Wang, F.; Zeng, W.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, N.; Moroni, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. In Situ Precision Cell Electrospinning as an Efficient Stem Cell Delivery Approach for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300970. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202300970.
- 42.Xu, F.; Dawson, C.; Hoare, T. Multicellular Layered Nanofibrous Poly(Oligo Ethylene Glycol Methacrylate) (POEGMA)-Based Hydrogel Scaffolds via Reactive Cell Electrospinning. Adv. Biol. 2023, 7, 2300052. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202300052.
- 43.Dawson, C.; Xu, F.; Hoare, T. Reactive Cell Electrospinning of Anisotropically Aligned and Bilayer Hydrogel Nanofiber Networks. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 6490–6503. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01013.
- 44.Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.E.; Ye, C. Immediate implantation of ultrafine fiber slow-release system based on cell electrospinning to induce osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Regen. Biomater. 2024, 11, rbad113. https://doi.org/10.1093/rb/rbad113.
- 45.Al-Abduljabbar, A.; Farooq, I. Electrospun Polymer Nanofibers: Processing, Properties, and Applications. Polymers 2022, 15, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010065.
- 46.Lasprilla-Botero, J.; Álvarez-Láinez, M.; Lagaron, J.M. The influence of electrospinning parameters and solvent selection on the morphology and diameter of polyimide nanofibers. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2017.12.003.
- 47.Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00593.
- 48.Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Garg, K.; Mccool, J.M.; Rodriguez, I.A.; Bowlin, G.L. The Use of Natural Polymers in Tissue Engineering: A Focus on Electrospun Extracellular Matrix Analogues. Polymers 2010, 2, 522–553. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym2040522.
- 49.Yang, J.M.; Yang, J.H.; Tsou, S.C.; Ding, C.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Yang, K.C.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, K.S.; Chen, S.W.; Wang, J.S. Cell proliferation on PVA/sodium alginate and PVA/poly(gamma-glutamic acid) electrospun fiber. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 66, 170–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2016.04.068.
- 50.Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, L.; Wang, Y.; Ye, F. Study on the Electrospinning of Gelatin/Pullulan Composite Nanofibers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091424.
- 51.Seon-Lutz, M.; Couffin, A.C.; Vignoud, S.; Schlatter, G.; Hebraud, A. Electrospinning in water and in situ crosslinking of hyaluronic acid/cyclodextrin nanofibers: Towards wound dressing with controlled drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 276–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.11.085.
- 52.Nie, H.; He, A.; Wu, W.; Zheng, J.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Han, C.C. Effect of poly(ethylene oxide) with different molecular weights on the electrospinnability of sodium alginate. Polymer 2009, 50, 4926–4934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2009.07.043.
- 53.Saquing, C.D.; Tang, C.; Monian, B.; Bonino, C.A.; Manasco, J.L.; Alsberg, E.; Khan, S.A. Alginate–Polyethylene Oxide Blend Nanofibers and the Role of the Carrier Polymer in Electrospinning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 8692–8704. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie302385b.
- 54.Kim, M.W. Surface activity and property of polyethyleneoxide (PEO) in water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 128, 145 154.
- 55.Bt Ibrahim, S.F.; Mohd Azam, N.A.N.; Mat Amin, K.A. Sodium alginate film: The effect of crosslinker on physical and mechanical properties. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 509, 012063. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/509/1/012063.
- 56.Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, S.; Guan, F.; Yu, Y.; Feng, S.; Song, X.; Bao, D.; Zhang, X. Development of cell adhesive and inherently antibacterial polyvinyl alcohol/polyethylene oxide nanofiber scaffolds via incorporating chitosan for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 124004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124004.
- 57.Huang, C.-Y.; Hu, K.-H.; Wei, Z.-H. Comparison of cell behavior on pva/pva-gelatin electrospun nanofibers with random and aligned configuration. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37960. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep37960.
- 58.Kwak, H.W.; Shin, M.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, H.; Song, D.W.; Yang, Y.; Shin, B.S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Fabrication of an ultrafine fish gelatin nanofibrous web from an aqueous solution by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1092–1103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.087.
- 59.Young, A.T.; White, O.C.; Daniele, M.A. Rheological Properties of Coordinated Physical Gelation and Chemical Crosslinking in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 2000183. https://doi.org/10.1002/mabi.202000183.
- 60.Xiao, S.; Guo, S.; Nesin, V.; Heller, R.; Schoenbach, K.H. Subnanosecond electric pulses cause membrane permeabilization and cell death. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2011.2112360.
- 61.Kotnik, T.; Rems, L.; Tarek, M.; Miklavcic, D. Membrane Electroporation and Electropermeabilization: Mechanisms and Models. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 63–91. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-052118-115451.
- 62.Zu, Y.; Huang, S.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, S. Size Specific Transfection to Mammalian Cells by Micropillar Array Electroporation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38661. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38661.
- 63.Harris, E.; Elmer, J.J. Optimization of electroporation and other non-viral gene delivery strategies for T cells. Biotechnol. Prog. 2021, 37, e3066. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.3066.
- 64.Yang, I.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Li, J.-J.; Liang, Y.-J.; Lin, T.-C.; Jakfar, S.; Thacker, M.; Wu, S.-C.; Lin, F.-H. The development of laminin-alginate microspheres encapsulated with Ginsenoside Rg1 and ADSCs for breast reconstruction after lumpectomy. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 1699–1710. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.11.029.
- 65.Jayasinghe, S.N.; Eagles, P.A.M.; Qureshi, A.N. Electric field driven jetting: An emerging approach for processing living cells. Biotechnol. J. 2006, 1, 86–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.200500025.
- 66.O’Hare, M.J.; Ormerod, M.G.; Imrie, P.R.; Peacock, J.H.; Asche, W. Electropermeabilization and Electrosensitivity of Different Types of Mammalian Cells. In Electroporation and Electrofusion in Cell Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 319–330.
- 67.ĈemazˆR, M.; Jarm, T.; Miklavĉiĉ, D.; Lebar, A.M.; Ihan, A.; Kopitar, N.A.; Serŝa, G. Effect of Electric-Field Intensity on Electropermeabilization and Electrosensitmty of Various Tumor-Cell Lines In Vitro. Electro Magnetobiol. 1998, 17, 263–272. https://doi.org/10.3109/15368379809022571.
- 68.Lang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lei, L.; Jiang, H. AC Electrothermal Circulatory Pumping Chip for Cell Culture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26792–26801. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b08863.
- 69.Pucihar, G.; Kotnik, T.; Kanduser, M.; Miklavcic, D. The influence of medium conductivity on electropermeabilization and survival of cells in vitro. Bioelectrochemistry 2001, 54, 107–115.
- 70.Kucernak, A.R.; Wang, H.; Lin, X. Avoid Using Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) as an Electrolyte for Accurate OER Studies. ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 3939–3946. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.4c01589.
- 71.Ageev, I.M.; Rybin, Y.M. Features of Measuring the Electrical Conductivity of Distilled Water in Contact with Air. Meas. Tech. 2020, 62, 923–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11018-020-01714-2.
- 72.Sun, Z.; Deitzel, J.M.; Knopf, J.; Chen, X.; Gillespie, J.W. The effect of solvent dielectric properties on the collection of oriented electrospun fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 2585–2594. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.35454.
- 73.Wendorff, J.H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Electrospinning: Materials, Processing and Applications; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012.
- 74.Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. Analysis of the Effects of Solution Conductivity on Electrospinning Process and Fiber Morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1109–1117. https://doi.org/10.1109/tia.2011.2127431.
- 75.Nezarati, R.M.; Eifert, M.B.; Cosgriff-Hernandez, E. Effects of humidity and solution viscosity on electrospun fiber morphology. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2013, 19, 810–819. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEC.2012.0671.
- 76.Kim, Y.B.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.H. Strategy to Achieve Highly Porous/Biocompatible Macroscale Cell Blocks, Using a Collagen/Genipin-bioink and an Optimal 3D Printing Process. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32230–32240. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11669.
- 77.Blaeser, A.; Duarte Campos, D.F.; Puster, U.; Richtering, W.; Stevens, M.M.; Fischer, H. Controlling Shear Stress in 3D Bioprinting is a Key Factor to Balance Printing Resolution and Stem Cell Integrity. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 326–333. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201500677.
- 78.Yoon, J.; Yang, H.S.; Lee, B.S.; Yu, W.R. Recent Progress in Coaxial Electrospinning: New Parameters, Various Structures, and Wide Applications. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1704765. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704765.
- 79.Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and their Applications. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201900281.
- 80.Lu, Y.; Huang, J.; Yu, G.; Cardenas, R.; Wei, S.; Wujcik, E.K.; Guo, Z. Coaxial electrospun fibers: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 654–677. https://doi.org/10.1002/wnan.1391.
- 81.Saudi, A.; Amini, S.; Amirpour, N.; Kazemi, M.; Zargar Kharazi, A.; Salehi, H.; Rafienia, M. Promoting neural cell proliferation and differentiation by incorporating lignin into electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(glycerol sebacate) fibers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 104, 110005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110005.
- 82.Liu, J.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Ruan, H.J.; Fan, C.Y. Peripheral nerve regeneration using composite poly(lactic acid-caprolactone)/nerve growth factor conduits prepared by coaxial electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2011, 96A, 13–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.32946.
- 83.Xu, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Jia, S.; Hao, D.; Zhu, L. Electrospun PCL Nerve Conduit Filled with GelMA Gel for CNTF and IGF-1 Delivery in Promoting Sciatic Nerve Regeneration in Rat. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 6309–6321. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c01048.
- 84.Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, M. 3D myotube guidance on hierarchically organized anisotropic and conductive fibers for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2020, 116, 111070. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.111070.
- 85.Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. Cell-laden microfibers for bottom-up tissue engineering. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 236–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2014.10.018.
- 86.Jana, S.; Levengood, S.K.L.; Zhang, M. Anisotropic Materials for Skeletal-Muscle-Tissue Engineering. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 10588–10612. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201600240.
- 87.Batalov, I.; Jallerat, Q.; Kim, S.; Bliley, J.; Feinberg, A.W. Engineering aligned human cardiac muscle using developmentally inspired fibronectin micropatterns. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11502. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-87550-y.
- 88.Kobayashi, M.; Lei, N.Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, B.M.; Dunn, J.C. Orthogonally oriented scaffolds with aligned fibers for engineering intestinal smooth muscle. Biomaterials 2015, 61, 75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.05.023.
- 89.Nardone, G.; Oliver-De La Cruz, J.; Vrbsky, J.; Martini, C.; Pribyl, J.; Skládal, P.; Pešl, M.; Caluori, G.; Pagliari, S.; Martino, F.; et al. YAP regulates cell mechanics by controlling focal adhesion assembly. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15321. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15321.
- 90.Teo, B.K.K.; Wong, S.T.; Lim, C.K.; Kung, T.Y.S.; Yap, C.H.; Ramagopal, Y.; Romer, L.H.; Yim, E.K.F. Nanotopography Modulates Mechanotransduction of Stem Cells and Induces Differentiation through Focal Adhesion Kinase. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 4785–4798. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn304966.
- 91.Von Erlach, T.C.; Bertazzo, S.; Wozniak, M.A.; Horejs, C.-M.; Maynard, S.A.; Attwood, S.; Robinson, B.K.; Autefage, H.; Kallepitis, C.; Del Río Hernández, A.; et al. Cell-geometry-dependent changes in plasma membrane order direct stem cell signalling and fate. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 237–242. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-017-0014-0.
- 92.Iranshahi, K.; Defraeye, T.; Rossi, R.M.; Müller, U.C. Electrohydrodynamics and its applications: Recent advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 232, 125895. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2024.125895.
- 93.Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, Z.; Kang, Y.; Xie, S.; Cai, Z.; Shan, X.; Li, Q. Pulsed electromagnetic field-assisted reduced graphene oxide composite 3D printed nerve scaffold promotes sciatic nerve regeneration in rats. Biofabrication 2024, 16, 035013. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5090/ad3d8a.
- 94.Jensen, B.N.; Wang, Y.; Le Friec, A.; Nabavi, S.; Dong, M.; Seliktar, D.; Chen, M. Wireless electromagnetic neural stimulation patch with anisotropic guidance. NPJ Flex. Electron. 2023, 7, 34. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41528-023-00270-3.
- 95.Liu, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Wan, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, L. Cell-Traction-Triggered On-Demand Electrical Stimulation for Neuron-Like Differentiation. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2106317. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202106317.
- 96.Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; Qiu, J.; Tang, W.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z.L. Self-Powered Electrical Stimulation for Enhancing Neural Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Graphene-Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Hybrid Microfibers. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5086–5095. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b00200.
- 97.Hu, W.; Wei, X.; Zhu, L.; Yin, D.; Wei, A.; Bi, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, G.; Qiang, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Enhancing proliferation and migration of fibroblast cells by electric stimulation based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 600–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2018.12.077.
- 98.Choe, G.; Han, U.G.; Ye, S.; Kang, S.; Yoo, J.; Cho, Y.S.; Jung, Y. Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Nerve-Guided Facial Nerve Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 9, 3512–3521. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.3c00222.
- 99.He, L.; Xiao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Reddy, S.; Shi, X.; Su, X.; Chiu, K.; Ramakrishna, S. Engineering an Injectable Electroactive Nanohybrid Hydrogel for Boosting Peripheral Nerve Growth and Myelination in Combination with Electrical Stimulation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 53150–53163. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c16885.
- 100.Huang, J.; Xue, S.; Buchmann, P.; Teixeira, A.P.; Fussenegger, M.; Huang, J.; Xue, S.; Buchmann, P.; Teixeira, A.P.; Fussenegger, M. An electrogenetic interface to program mammalian gene expression by direct current. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1395–1407. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-023-00850-7.
- 101.Argentati, C.; Morena, F.; Tortorella, I.; Bazzucchi, M.; Porcellati, S.; Emiliani, C.; Martino, S. Insight into Mechanobiology: How Stem Cells Feel Mechanical Forces and Orchestrate Biological Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5337 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215337.
- 102.Elosegui-Artola, A.; Andreu, I.; Beedle, A.E.M.; Lezamiz, A.; Uroz, M.; Kosmalska, A.J.; Oria, R.; Kechagia, J.Z.; Rico-Lastres, P.; Le Roux, A.L.; et al. Force Triggers YAP Nuclear Entry by Regulating Transport across Nuclear Pores. Cell 2017, 171, 1397–1410.e1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.008.
How to Cite
Larsen, A.-K. K.; Chen, M. Cell Electrospinning: Electrohydrodynamic Effects on Cell Viability and Beyond. Materials and Interfaces 2025, 2 (3), 332–347. https://doi.org/10.53941/mi.2025.100025.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


