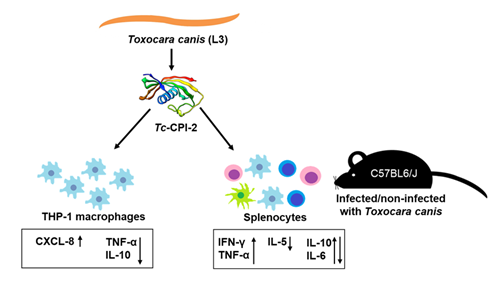
Parasites are known for their ability to escape from the immune system of their hosts. One of the strategies is the release of specific molecules with high immunomodulatory activity. Cysteine protease inhibitors (cystatins) have been shown to play an essential role in suppressing the host’s immune response. Cystatins have been found in many species of parasites from different taxa. Herein, we report cloning and expression of the cysteine protease inhibitor, Tc-CPI-2, from dog roundworm (Toxocara canis) infective L3 larvae, a causative agent of human toxocarosis. Sequence analysis revealed two specific cystatin-like domains, the Q-x-V-x-G motif and the S-N-D motif. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that Tc-CPI-2 belongs to type 2 cystatin subfamily. The recombinant cystatin was expressed in Escherichia coli, purified, and used to stimulate human THP-1 macrophages in vitro and mouse splenocytes ex vivo. Cell treatment with the recombinant molecule induced significant cytokine secretion changes, suggesting that it may be responsible for the Th2/Th1 immune response switch in T. canis-infected mice. Altogether, our results prove that Tc-CPI-2 is a molecule with promising immunoregulatory and therapeutic potential.
- Open Access
- Article
Cloning and Expression of a Molecule with Immunomodulatory Potential, a Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from Toxocara canis
- Justyna Karabowicz,
- Oliwia Śniadała,
- Julia Wiśniewska,
- Ewa Długosz *
Author Information
Received: 01 May 2025 | Revised: 04 Jun 2025 | Accepted: 25 Jun 2025 | Published: 26 Jun 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
cystatins | immunomodulation | toxocarosis | recombinant molecules
References
- 1.Zavasnik-Bergant, T. Cystatin protease inhibitors and immune functions. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 4625–4637.
- 2.Prunk, M.; Nanut, M.P.; Sabotič, J.; et al. Cystatins, cysteine peptidase inhibitors, as regulators of immune cell cytotoxicity. Period. Biol. 2016, 118, 353–362.
- 3.Rawlings, N.D.; Morton, F.R.; Kok, C.Y.; et al. MEROPS: The peptidase database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 320–325.
- 4.Abrahamson, M.; Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Nathanson, C.M. Cystatins. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 2003, 99, 179–199.
- 5.Klotz, C.; Ziegler, T.; Daniłowicz-Luebert, E.; et al. Cystatins of parasitic organisms. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 712, 208–221.
- 6.Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Barrett, A.J.; Gerhartz, B.; et al. Inhibition of mammalian legumain by some cystatins is due to a novel second reactive site. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19195–19203.
- 7.Lee, C.; Bongcam-Rudloff, E.; Sollner, C.; et al. Type 3 cystatins; fetuins, kininogen and histidine-rich glycoprotein. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2911–2922.
- 8.Lustigman, S.; Brotman, B.; Huima, T.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of onchocystatin, a cysteine proteinase inhibitor of Onchocerca volvulus. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17339–17346.
- 9.Liu, S.; Dong, J.; Mei, G.; et al. Crystallization and preliminary crystallographic studies of a cysteine protease inhibitor from the human nematode parasite Ascaris lumbricoides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2011, 67, 228–230.
- 10.Dong, X.; Xu, J.; Song, H.; et al. Molecular Characterization of a Dirofilaria immitis Cysteine Protease Inhibitor (Cystatin) and Its Possible Role in Filarial Immune Evasion. Genes 2019, 10, 300.
- 11.Liu, J.; Svärd, S.G.; Klotz, C. Giardia intestinalis cystatin is a potent inhibitor of papain, parasite cysteine proteases and, to a lesser extent, human cathepsin B. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 1313–1325.
- 12.Manoury, B.; Gregory, W.F.; Maizels, R.M.; et al. Bm-CPI-2, a cystatin homolog secreted by the filarial parasite Brugia malayi, inhibits class II MHC-restricted antigen processing. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 447–451.
- 13.He, B.; Cai, G.; Ni, Y.; et al. Characterization and expression of a novel cystatin gene from Schistosoma japonicum. Mol. Cell Probes 2011, 25, 186–193.
- 14.Chmelař, J.; Kotál, J.; Langhansová, H.; et al. Protease inhibitors in tick saliva: The role of serpins and cystatins in tick-host-pathogen interaction. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 216.
- 15.Gregory, W.F.; Maizels, R.M. Cystatins from filarial parasites: Evolution, adaptation and function in the host-parasite relationship. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 1389–1398.
- 16.Khatri, V.; Chauhan, N.; Kalyanasundaram, R. Parasite cystatin: Immunomodulatory molecule with therapeutic activity against immune mediated disorders. Pathogens 2020, 9, 431.
- 17.Hartmann, S.; Kyewski, B.; Sonnenburg, B.; et al. A filarial cysteine protease inhibitor down-regulates T cell proliferation and enhances interleukin-10 production. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 2253–2260.
- 18.Schönemeyer, A.; Lucius, R.; Sonnenburg, B.; et al. Modulation of Human T Cell Responses and Macrophage Functions by Onchocystatin, a Secreted Protein of the Filarial Nematode Onchocerca volvulus. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3207–3215.
- 19.Klotz, C.; Ziegler, T.; Figueiredo, A.S.; et al. A helminth immunomodulator exploits host signaling events to regulate cytokine production in macrophages. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001248.
- 20.Acevedo, N.; Lozano, A.; Zakzuk, J.; et al. Cystatin from the helminth Ascaris lumbricoides upregulates mevalonate and cholesterol biosynthesis pathways and immunomodulatory genes in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1328401.
- 21.Zhu, X.Q.; Korhonen, P.K.; Cai, H.; et al. Genetic blueprint of the zoonotic pathogen Toxocara canis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6145.
- 22.Rostami, A.; Riahi, S.M.; Holland, C.V.; et al. Seroprevalence estimates for toxocariasis in people worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007809.
- 23.Overgaauw, P.A.M.; van Knapen, F. Veterinary and public health aspects of Toxocara spp. Vet. Parasitol. 2013, 193, 398–403.
- 24.Ma, G.; Holland, C.V.; Wang, T.; et al. Human toxocariasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e14–e24.
- 25.Rostami, A.; Ma, G.; Wang, T.; et al. Human toxocariasis—A look at a neglected disease through an epidemiological ‘prism’. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 74, 104002.
- 26.Oaks, J.A.; Kayes, S.G. Artificial hatching and culture of Toxocara canis second stage larvae. J. Parasitol. 1979, 65, 969–970.
- 27.BLAST. Available online: https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- 28.Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; et al. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410.
- 29.Clustal Omega. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/jdispatcher/msa/clustalo (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- 30.Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539.
- 31.SignalP. Available online: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/SignalP-5.0/ (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- 32.Net-O-glyc. Available online: https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/NetOGlyc-4.0/ (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- 33.Steentoft, C.; Vakhrushev, S.Y.; Joshi, H.J.; et al. Precision mapping of the human O-GalNAc glycoproteome through SimpleCell technology. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1478–1488.
- 34.Phyre2. Available online: https://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index (accessed on 29 April 2025).
- 35.Powell, H.R.; Islam, S.A.; David, A.; et al. Phyre2.2: A Community Resource for Template-based Protein Structure Prediction. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 168960.
- 36.Teodorowicz, M.; Perdijk, O.; Verhoek, I.; et al. Optimized triton X-114 assisted lipopolysaccharide (LPS) removal method reveals the immunomodulatory effect of food proteins. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173778.
- 37.Zawistowska-Deniziak, A.; Basałaj, K.; Strojny, B.; et al. New Data on Human Macrophages Polarization by Hymenolepis diminuta Tapeworm–An In Vitro Study. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8,148.
- 38.Długosz, E.; Basałaj, K.; Zawistowska-Deniziak, A. Cytokine production and signalling in human THP-1 macrophages is dependent on Toxocara canis glycans. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 2925–2933.
- 39.Lekki-Jóźwiak, J.; Karabowicz, J.; Paschall, M.; et al. Characteristics of Toxocara canis Induced Lung Inflammation in C57BL/6 Mice; Institute of Veterinary Medicine, Department of Preclinical Sciences, Warsaw University of Life Sciences: Warsaw, Poland, in preparation.
- 40.Murray, J.; Manoury, B.; Balic, A.; et al. Bm-CPI-2, a cystatin from Brugia malayi nematode parasites, differs from Caenorhabditis elegans cystatins in a specific site mediating inhibition of the antigen-processing enzyme AEP. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2005, 139, 197–203.
- 41.Coronado, S.; Barrios, L.; Zakzuk, J.; et al. A recombinant cystatin from Ascaris lumbricoides attenuates inflammation of DSS-induced colitis. Parasite Immunol. 2017, 39, e12425.
- 42.Dainichi, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Ishii, K.; et al. Nippocystatin, a Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, Inhibits Antigen Processing and Modulates Antigen-Specific Immune Response. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 7380–7386.
- 43.Junginger, J.; Raue, K.; Wolf, K.; et al. Zoonotic intestinal helminths interact with the canine immune system by modulating T cell responses and preventing dendritic cell maturation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10310.
- 44.Chantree, P.; Tarasuk, M.; Prathaphan, P.; et al. Type I Cystatin Derived from Fasciola gigantica Suppresses Macrophage-Mediated Inflammatory Responses. Pathogens 2023, 12, 395.
- 45.Venugopal, G.; Mueller, M.; Hartmann, S.; et al. Differential immunomodulation in human monocytes versus macrophages by filarial cystatin. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188138.
- 46.Coronado, S.; Zakzuk, J.; Regino, R.; et al. Ascaris lumbricoides cystatin prevents development of allergic airway inflammation in a mouse model. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2280.
- 47.Yan, K.; Wang, B.; Zhou, H.; et al. Amelioration of type 1 diabetes by recombinant fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase and cystatin derived from Schistosoma japonicum in a murine model. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 203–214.
- 48.Schnoeller, C.; Rausch, S.; Pillai, S.; et al. A Helminth Immunomodulator Reduces Allergic and Inflammatory Responses by Induction of IL-10-Producing Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 4265–4272.
- 49.Daniłowicz-Luebert, E.; Steinfelder, S.; Kühl, A.A.; et al. A nematode immunomodulator suppresses grass pollen-specific allergic responses by controlling excessive Th2 inflammation. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 201–210.
- 50.Pfaff, A.W.; Schulz-Key, H.; Soboslay, P.T.; et al. Litomosoides sigmodontis cystatin acts as an immunomodulator during experimental filariasis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 171–178.
- 51.Chen, L.; He, B.; Hou, W.; et al. Cysteine protease inhibitor of Schistosoma japonicum–A parasite-derived negative immunoregulatory factor. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 901–908.
- 52.Kuroda, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Shan, B.E.; et al. Suppression of macrophage interleukin-12 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha production in mice infected with Toxocara canis. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 305–311.
- 53.Długosz, E.; Wasyl, K.; Klockiewicz, M.; et al. Toxocara canis mucins among other excretory-secretory antigens induce in vitro secretion of cytokines by mouse splenocytes. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3365–3371.
- 54.Ziegler, T.; Rausch, S.; Steinfelder, S.; et al. A Novel Regulatory Macrophage Induced by a Helminth Molecule Instructs IL-10 in CD4+ T Cells and Protects against Mucosal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1555–1564.
- 55.Pinelli, E.; Brandes, S.; Dormans, J.; et al. Infection with the roundworm Toxocara canis leads to exacerbation of experimental allergic airway inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2008, 38, 649–658.
- 56.Arumugam, S.; Zhan, B.; Abraham, D.; et al. Vaccination with recombinant Brugia malayi cystatin proteins alters worm migration, homing and final niche selection following a subcutaneous challenge of Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus) with B. malayi infective larvae. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 43.
Issue
Volume 1, Issue 1How to Cite
Karabowicz, J.; Śniadała, O.; Wiśniewska, J.; Długosz, E. Cloning and Expression of a Molecule with Immunomodulatory Potential, a Cysteine Protease Inhibitor from Toxocara canis. Parasitological Science 2025, 1 (1), 1.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


