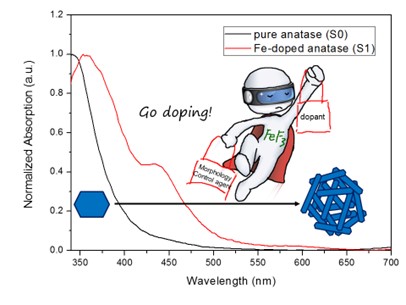
This work presents a facile hydrothermal method for synthesizing iron-doped anatase TiO2 hierarchical microspheres composed of embedded single crystals with exposed {001} facets. In this approach, ferric fluoride (FeF3) uniquely serves as both the iron source for doping and a morphology control agent. The influence of a wide range of Fe doping concentrations (from 2.23% to 20.13% atomic ratio) on the phase structure, morphology, optical properties, and photocatalytic activity was systematically investigated. The results show that at low doping levels (<15%), single-phase anatase microspheres are formed, with the constituent nanosheets becoming progressively thinner as the dopant amount increases. At higher concentrations, a phase transition occurs, yielding mixed phases of anatase and rutile (17.46% Fe) or rutile and an unidentified phase (20.13% Fe). Photocatalytic activity tests revealed that low Fe content (2.23% and 5.38%) enhanced the generation of hydroxyl radicals compared to undoped TiO2, while higher concentrations led to decreased activity. This non-monotonic trend is attributed to the “dual role” of the iron dopant: (1) morphology control by fluoride ions, which increases the exposure of active {001} facets; (2) Fe-induced charge separation at low concentrations, which enhances carrier lifetime, and Fe-induced recombination centers at high concentrations, which diminishes photocatalytic efficiency. This work provides a novel strategy for precisely tuning the morphology and electronic structure of TiO2 and offers insights into the complex role of dopants in photocatalysis.
- Open Access
- Article
Controlling Photocatalytic Activity via a “Dual Role” Dopant: A Systematic Study of Fe-Doped TiO2 Microspheres with Exposed {001} Facets
- Jingxuan Wang 1,
- Jinan Niu 1, *,
- Jinpen Bao 1,
- Liuyun Huang 1,
- Deyuan Wang 2,
- Yifan Li 3,
- Peizhong Feng 1, *
Author Information
Received: 23 Jun 2025 | Revised: 13 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 24 Sep 2025 | Published: 29 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
titanium dioxide | iron doping | photocatalysis | {001} facets | morphology control | ferric fluoride
References
- 1.Liu, G.; Yang, H.G.; Pan, J.; et al. Titanium dioxide crystals with tailored facets. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9559.
- 2.Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photoch. Photobio. C 2003, 4, 145.
- 3.Kubacka, A.; Fernández-García, M.; Colón, G. Advanced nanoarchitectures for solar photocatalytic applications. Chem. Rev. 2011, 112, 1555.
- 4.Niu, J.N.; Shen, S.S.; He, S.F.; et al. Synthesis and photoactivity of anatase porous single crystals with different pore sizes. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 11936.
- 5.
Zhou, W.; Du, G.; Hu, P.; et al. Nanoheterostructures on TiO2 nanobelts achieved by acid hydrothermal method with enhanced photocatalytic and gas sensitive performance. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 7937.
- 6.
Zhu, W.D.; Wang, C.W.; Chen, J.B.; et al. Enhanced field emission from hydrogenated TiO2 nanotube arrays. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 455204.
- 7.Fujishima, A.; Honda, K. Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode. Nature 1972, 238, 37.
- 8.Tong, H.; Ouyang, S.; Bi, Y.; et al. Nano‐photocatalytic materials: possibilities and challenges. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 229.
- 9.
Chen, R.Y.; Lai, D.X.; Wang, D.X.; et al. Enhanced photocatalytic activity of kaolinite-TiO2-graphene oxide composite with a porous stacking structure. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 889, 161682.
- 10.
Li, C.; Sun, L.; Niu, J.; et al. Core-shell Bi-containing spheres and TiO2 nanoparticles co-loaded on kaolinite as an efficient photocatalyst for methyl orange degradation. Catal. Commun. 2023, 175, 106609.
- 11.
Li, C.; Shen, S.; Niu, J.; et al. Mesoporous single-crystal-based TiO2 microspheres decorated by carbon nitride for obviously improved photocatalytic performance and recyclability. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 150, 110524.
- 12.Liu, L.; Chen, X. Titanium dioxide nanomaterials: self-structural modifications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9890.
- 13.Chen, D.H.; Caruso, R.A. Recent progress in the synthesis of spherical titania nanostructures and their applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1356.
- 14.
Berger, H.; Tang, H.; Levy, F. Growth and Raman spectroscopic characterization of TiO2 anatase single crystals. J. Cryst. Growth. 1993, 130, 108.
- 15.
Niu, J.N.; Shen, S.S.; Zhou, L.; et al. Synthesis and hydrogenation of anatase TiO2 microspheres composed of porous single crystals for significantly improved photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 62907.
- 16.
Yang, H.G.; Sun, C.H.; Qiao, S.Z.; et al. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with a large percentage of reactive facets. Nature 2008, 453, 638.
- 17.
Choi, W.; Termin, A.; Hoffmann, M.R. The role of metal ion dopants in quantum-sized TiO2: Correlation between photoreactivity and charge carrier recombination dynamics. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 13669.
- 18.Litter, M.I. Heterogeneous photocatalysis: transition metal ions in photocatalytic systems. Appl. Catal. B 1999, 23, 89.
- 19.
Shen, S.S.; Niu, J.N.; Shen, S.T.; et al. A method for adjusting nitrogen doping amount in anatase TiO2 single crystals with well-faceted shape and micron size. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 107, 75.
- 20.
Adán, C.; Bahamonde, A.; Fernández-García, M.; et al. Structure and activity of nanosized iron-doped anatase TiO2 catalysts for phenol photocatalytic degradation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2007, 72, 11.
- 21.
Delekar, S.D.; Yadav, H.M.; Achary, S.N.; et al. Structural refinement and photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 536.
- 22.
Reddy, J.K.; Lalitha, K.; Reddy, P.V.L.; et al. Fe/TiO2: A Visible Light Active Photocatalyst for the Continuous Production of Hydrogen from Water Splitting Under Solar Irradiation. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 340.
- 23.
Sun, T.; Liu, E.; Fan, J.; et al. High photocatalytic activity of hydrogen production from water over Fe doped and Ag deposited anatase TiO2 catalyst synthesized by solvothermal method. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 228, 896.
- 24.
Abdulla-Al-Mamun, M.; Kusumoto, Y.; Islam, M.S. Enhanced photocatalytic cytotoxic activity of Ag@ Fe-doped TiO2 nanocomposites against human epithelial carcinoma cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 5460.
- 25.
Wang, S.; Lian, J.S.; Zheng, W.T.; et al. Photocatalytic property of Fe doped anatase and rutile TiO2 nanocrystal particles prepared by sol–gel technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 260.
- 26.
Kim, T.H.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Gyawali, G.; et al. Synthesis of solar light responsive Fe, N co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst by sonochemical method. Catal. Today 2013, 212, 75.
- 27.Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; et al. Release of engineered nanomaterials from personal care products throughout their life cycle. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 1.
- 28.
Feilizadeh, M.; Mul, G.; Vossoughi, M. E. coli inactivation by visible light irradiation using a Fe–Cd/TiO2 photocatalyst: statistical analysis and optimization of operating parameters. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2015, 168, 441.
- 29.
Larumbe, S.; Monge, M.; Gómez-Polo, C. Comparative study of (N, Fe) doped TiO2 photocatalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 327, 490.
- 30.
Kaur, N.; Shahi, S.K.; Singh, V. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of magnetically separable γ-Fe2O3/N, Fe codoped TiO2 heterojunction for degradation of Reactive Blue 4 dye. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61623.
- 31.
Kuvarega, A.T.; Krause, R.W.; Mamba, B.B. Comparison between base metals and platinum group metals in nitrogen, M codoped TiO2 (M= Fe, Cu, Pd, Os) for photocatalytic removal of an organic dye in water. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 962102.
- 32.
Zhang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Lv, F.; et al. Photocatalytic treatment of 2, 4, 6-trinitotoluene in red water by multi-doped TiO2 with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 452, 103.
- 33.
Chen, B.; Haring, A.J.; Beach, J.A.; et al. Visible light induced photocatalytic activity of Fe3+/Ti3+ co-doped TiO2 nanostructures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 18033.
- 34.
Sun, T.; Liu, E.; Liang, X.; et al. Enhanced hydrogen evolution from water splitting using Fe-Ni codoped and Ag deposited anatase TiO2 synthesized by solvothermal method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 696.
- 35.
Liu, T.; Zhang, H. Novel Fe-doped anatase TiO2 nanosheet hierarchical spheres with 94%{001} facets for efficient visible light photodegradation of organic dye. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 16255.
- 36.Yu, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, W.; et al. Low-cost synthesis of robust anatase polyhedral structures with a preponderance of exposed {001} facets for enhanced photoactivities. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 434.
- 37.
Lazzeri, M.; Vittadini, A.; Selloni, A. Structure and energetics of stoichiometric TiO2 anatase surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 155409.
- 38.
Lazzeri, M.; Vittadini, A.; Selloni, A. Erratum: Structure and energetics of stoichiometric TiO2 anatase surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 119901.
- 39.
Li, H.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.; et al. Controlled synthesis of anatase TiO2 single crystals with dominant {001} facets from TiO2 powders. ChemPlusChem 2012, 77, 1017.
- 40.
Yang, H.G.; Liu, G.; Qiao, S.Z.; et al. Solvothermal synthesis and photoreactivity of anatase TiO2 nanosheets with dominant {001} facets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4078.
- 41.
Jo, W.K.; Natarajan, T.S. Influence of TiO2 morphology on the photocatalytic efficiency of direct Z-scheme g-C3N4/TiO2 photocatalysts for isoniazid degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 281, 549.
- 42.Cho, K.; Biswas, P.; Fraundorf, P. Characterization of nanostructured pristine and Fe-and V-doped titania synthesized by atomization and bubbling. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 558.
- 43.
Zhu, S.; Li, Y.; Fan, C.; et al. Structural studies of iron-doped TiO2 nano-composites by Mössbauer spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction and transmission microscopy. Phys. B 2005, 364, 199.
- 44.Fan, W.Q.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; et al. Titanium dioxide macroporous materials doped with iron: Synthesis and photo-catalytic properties. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 116.
- 45.Wang, Z.M.; Yang, G.; Biswas, P.; et al. Processing of iron-doped titania powders in flame aerosol reactors. Powder Technol. 2001, 114, 197.
- 46.Post, J.E.; Buchwald, V.F. Crystal structure refinement of akaganeite. Am. Mineral. 1991, 76, 272.
- 47.
Yu, Y.L.; Wang, X.L.; Sun, H.Y.; et al. 3D anatase TiO2 hollow microspheres assembled with high-energy {001} facets for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7901.
- 48.
Dai, G.P.; Liu, S.Q.; Liang, Y.; et al. A simple preparation of carbon and nitrogen co-doped nanoscaled TiO2 with exposed {001} facets for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2013, 368–369, 38.
- 49.Han, X.; Kuang, Q.; Jin, M.; et al. Synthesis of titania nanosheets with a high percentage of exposed (001) facets and related photocatalytic properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3152.
- 50.
Liu, M.; Piao, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with exposed {001} and {110} facets: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis. Chem. Comm. 2010, 46, 1664.
- 51.Song, X.; Boily, J.F. Competitive ligand exchange on akaganéite surfaces enriches bulk chloride loadings. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 331.
- 52.Morcillo, M.; Alcántara, J.; Díaz, I.; et al. Corrosión atmosférica marina de aceros al carbono. Rev. Metal. 2015, 51, e045.
- 53.
Li, J.; Zeng, H.C. Hollowing Sn-doped TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 15839.
- 54.
Xu, R.; Zeng, H.C. Self-generation of tiered surfactant superstructures for one-pot synthesis of Co3O4 nanocubes and their close-and non-close-packed organizations. Langmuir 2004, 20, 9780.
- 55.Chang, Y.; Lye, M.L.; Zeng, H.C. Large-scale synthesis of high-quality ultralong copper nanowires. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3746.
- 56.
Xu, M.; Da, P.; Wu, H.; et al. Controlled Sn-doping in TiO2 nanowire photoanodes with enhanced photoelectrochemical conversion. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 1503.
- 57.
Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Fe3+-TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by combining sol–gel method with hydrothermal treatment and their characterization. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A-Chem. 2006, 180, 196.
- 58.Teo, S.H.; Zeng, H.C. Surface and textural properties of network-modified silica as a function of transition metal dopant zirconium. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 9093.
- 59.
Tong, T.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B.; et al. Preparation of Fe3+-doped TiO2 catalysts by controlled hydrolysis of titanium alkoxide and study on their photocatalytic activity for methyl orange degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 155, 572.
- 60.
Wang, Y.M.; Liu, S.W.; Lü, M.K.; et al. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of Zr4+-doped TiO2 nanocrystals. J. Mol. Catal. A-Chem. 2004, 215, 137.
- 61.
Lukáč, J.; Klementova, M.; Bezdička, P.; et al. Influence of Zr as TiO2 doping ion on photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2007, 74, 83.
- 62.Burdett, J.K.; Hughbanks, T.; Miller, G.J., Jr.; et al. Structural-electronic relationships in inorganic solids: powder neutron diffraction studies of the rutile and anatase polymorphs of titanium dioxide at 15 and 295 K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 3639.
- 63.Fan, W.Q.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhang, G.H.; et al. Titanium dioxide macroporous materials doped with iron: Synthesis and photo-catalytic properties. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 116.
- 64.Wang, Z.M.; Yang, G.; Biswas, P.; et al. Processing of iron-doped titania powders in flame aerosol reactors. Powder Technol. 2001, 114, 197.
- 65.
Reddy, J.K.; Lalitha, K.; Reddy, P.V.L.; et al. Fe/TiO2: A visible light active photocatalyst for the continuous production of hydrogen from water splitting under solar irradiation. Catalysis Lett. 2014, 144, 340.
- 66.
Xu, Z.; Yu, J. Visible-light-induced photoelectrochemical behaviors of Fe-modified TiO2 nanotube arrays. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3138.
- 67.
Delekar, S.D.; Yadav, H.M.; Achary, S.N.; et al. Structural refinement and photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped anatase TiO2 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 263, 536.
- 68.
Xu, A.W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.Q. The preparation, characterization, and their photocatalytic activities of rare-earth-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Catal. 2002, 207, 151.
- 69.
Hsutomu, H.; Nosaka, Y. Properties of O2•− and OH• formed in TiO2 aqueous suspensions by photocatalytic reaction and the influence of H2O2 and some ions. Langmuir 2002, 18, 3247.
- 70.
Yu, J.C.; Yu, J.; Ho, W.; et al. Effects of F-doping on the photocatalytic activity and microstructures of nanocrystalline TiO2 powders. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3808.
- 71.
Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; et al. High activity TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by a modified sol–gel method: characterization and their photocatalytic activity for the degradation of XRG and X-GL. Topic. Catalysis 2005, 35, 261.
- 72.
Liu, M.; Piao, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. Anatase TiO2 single crystals with exposed {001} and {110} facets: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalysis. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1664.
- 73.Thimsen, E.; Biswas, S.; Lo, C.S.; Biswas, P. Predicting the band structure of mixed transition metal oxides: theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 2014.
- 74.
Wang, C.Y.; Böttcher, C.; Bahnemann, D.W.; et al. A comparative study of nanometer sized Fe(III)-doped TiO2 photocatalysts: synthesis, characterization and activity. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 2322.
- 75.
Niu, Y.; Xing, M.; Zhang, J.; Tian, B. Visible light activated sulfur and iron co-doped TiO2 photocatalyst for the photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Catal. Today 2013, 201, 159.
- 76.
Carneiro, J.O.; Azevedo, S.; Fernandes, F.; et al. Synthesis of iron-doped TiO2 nanoparticles by ball-milling process: the influence of process parameters on the structural, optical, magnetic, and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 7476.
- 77.
Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Zakaria, R.; Ying, J.Y. Role of particle size in nanocrystalline TiO2-based photocatalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 10871.
- 78.
Zhu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. Fe3+-TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by combining sol–gel method with hydrothermal treatment and their characterization. J. Photoch. Photobio. A 2006, 180, 196.
- 79.Liu, Z.; Ran, H.; Niu, J.; et al. One-pot synthesis of bismuth oxyhalide/oxygen-rich bismuth oxyhalide Heterojunction and its photocatalytic activity. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2014, 431, 187.
- 80.
He, D.; Chen, M.; Teng, F.; et al. Enhanced cyclability of CdS/TiO2 photocatalyst by stable interface structure. Superlattice. Microstruct. 2012, 51, 799.
- 81.
Liu, L.; Gu, X.; Sun, C.; et al. In situ loading of ultra-small Cu2O particles on TiO2 nanosheets to enhance the visible-light photoactivity. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6351.
- 82.
Hou, J.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; et al. Bi2O3 quantum dots decorated anatase TiO2 nanocrystals with exposed {001} facets on graphene sheets for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2013, 129, 333.
- 83.
Liu, Z.; Sun, D.D.; Guo, P.; Leckie, J.O. An efficient bicomponent TiO2/SnO2 nanofiber photocatalyst fabricated by electrospinning with a side-by-side dual spinneret method. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1081.
- 84.
Jiang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H. Photocatalytic degradation characteristics of different organic compounds at TiO2 nanoporous film electrodes with mixed anatase/rutile phases. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 303.
- 85.
Liu, B.; Khare, A.; Aydil, E.S. TiO2–B/anatase core–shell heterojunction nanowires for photocatalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2011, 3, 4444.
- 86.
Guo, E.; Yin, L. Tailored SrTiO3/TiO2 heterostructures for dye-sensitized solar cells with enhanced photoelectric conversion performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13390–13401.
- 87.
Scanlon, D.O.; Dunnill, C.W.; Buckeridge, J.; et al. Band alignment of rutile and anatase TiO2. Nat. Mater. 2013, 12, 798.
- 88.
Cao, Y.; He, T.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y. Fabrication of rutile TiO2-Sn/anatase TiO2-N heterostructure and its application in visible-light photocatalysis. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 3627.
- 89.
Hensel, J.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.Z. Synergistic effect of CdSe quantum dot sensitization and nitrogen doping of TiO2 nanostructures for photoelectrochemical solar hydrogen generation. Nano. Lett. 2010, 10, 478.
- 90.
Pian, X.; Lin, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Pillared nanocomposite TiO2/Bi-doped hexaniobate with visible-light photocatalytic activity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 6531.
- 91.Zhu, J.; Zach, M. Nanostructured materials for photocatalytic hydrogen production. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 260.
- 92.Leland, J.K.; Bard, A.J. Photochemistry of colloidal semiconducting iron oxide polymorphs. J. Phys. Chem. 1987, 91, 5076.
- 93.White, A.F. Rev. Heterogeneous electrochemical reactions associated with oxidation of ferrous oxide and silicate surfaces. Mineral. Geochem. 1990, 23, 467.
- 94.
Chowdhury, M.; Ntiribinyange, M.; Nyamayaro, K.; Fester, V. Photocatalytic activities of ultra-small β-FeOOH and TiO2 heterojunction structure under simulated solar irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2015, 68, 133.
- 95.Pradel, J.; Castillo, S.; Traverse, J.P.; et al. Ferric hydroxide oxide from the goethite process: characterization and potential use. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 1801.
- 96.
Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, S. Enhancement of visible-light photocatalysis by coupling with narrow-band-gap semiconductor: a case study on Bi2S3/Bi2WO6. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2012, 4, 593.
- 97.
Rawal, S.B.; Bera, S.; Lee, D.; et al. Design of visible-light photocatalysts by coupling of narrow bandgap semiconductors and TiO2: Effect of their relative energy band positions on the photocatalytic efficiency. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 1822.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


