As an emerging desalination technology, capacitive deionization (CDI) has garnered significant attention due to its superior energy efficiency and performance metrics compared to conventional distillation and reverse osmosis (RO) techniques. Over the past decade, substantial advances have been achieved across multiple technical dimensions of CDI systems. This review focuses on two representative CDI architectures-hybrid capacitive deionization (HCDI) and flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI)-highlighting their core innovation mechanisms: the ion storage behavior in HCDI and the continuous operation characteristics of flow electrodes in FCDI. We systematically examine recent research progress in critical areas including innovative electrode materials, optimized cell configurations, and expanded contaminant removal targets (e.g., heavy metals/organic pollutants), while delving into machine learning (ML)-driven strategies for operational parameter optimization and system performance prediction. Ultimately, by synthesizing these technological breakthroughs and aligning them with current engineering requirements, this review aims to facilitate the scalable implementation and industrial adoption of CDI technology within sustainable water treatment frameworks.
- Open Access
- Review
Hybrid and Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization: Materials Design, Multispecies Removal, and Smart Regulation
- Yuan Gao,
- Chengan Ye,
- Rui Wang,
- Wenting Li *,
- Huan Pang *
Author Information
Received: 22 Sep 2025 | Revised: 14 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 04 Dec 2025 | Published: 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
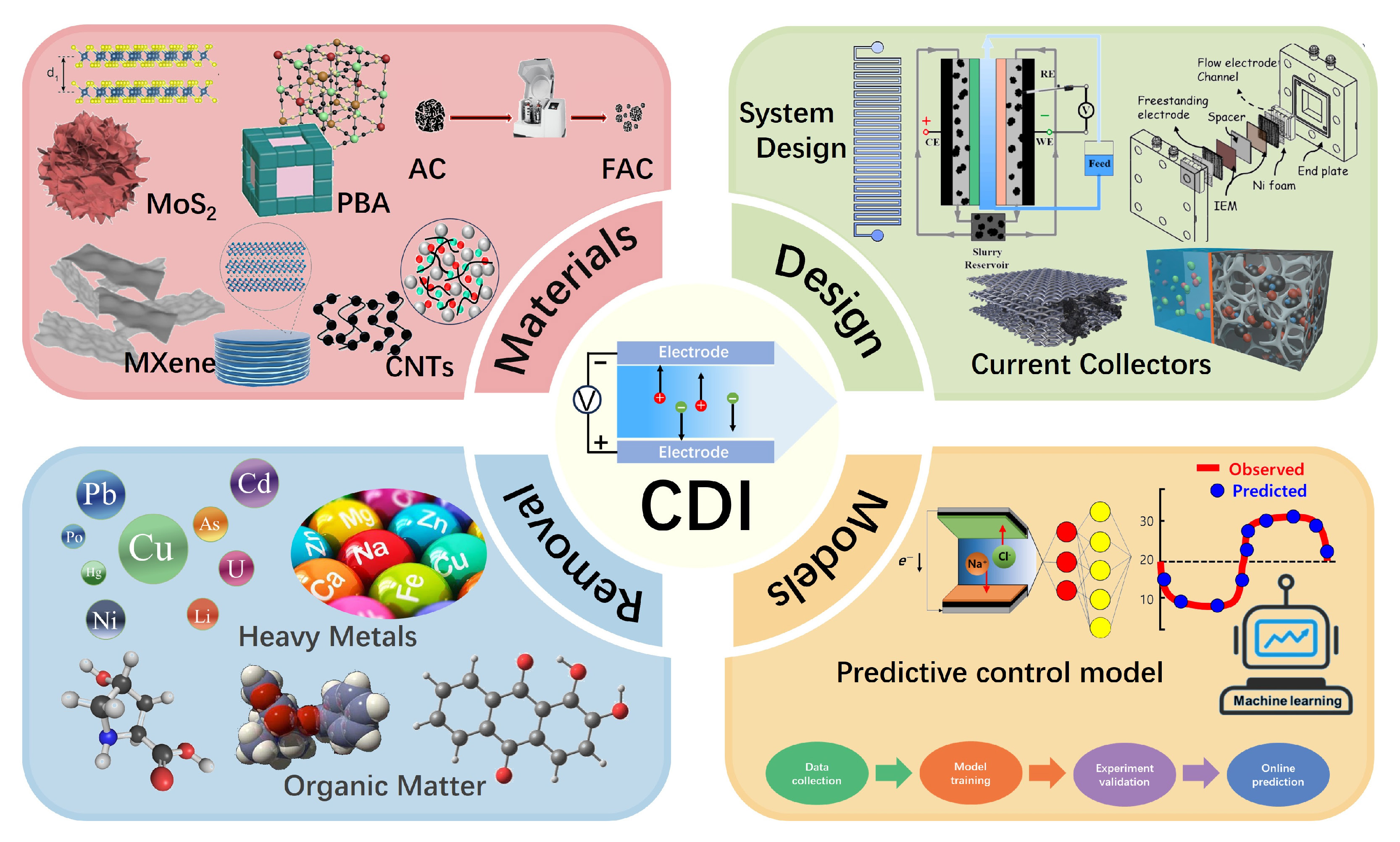
Keywords
capacitive deionization | electrode materials | cell design | ion removal | modeling
References
- 1.
Shahid, M.U.; Najam, T.; Islam, M.; et al. Engineering of metal organic framework (MOF) membrane for waste water treatment: Synthesis, applications and future challenges. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 57, 104676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.104676.
- 2.
Sun, K.; Tebyetekerwa, M.; Wang, C.; et al. Electrocapacitive Deionization: Mechanisms, Electrodes, and Cell Designs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213578. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202213578.
- 3.
Musie, W.; Gonfa, G. Fresh water resource, scarcity, water salinity challenges and possible remedies: A review. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18685.
- 4.
Chen, Z.; Ding, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Three-dimensional charge transfer pathway in close-packed nickel hexacyanoferrate−on−MXene nano-stacking for high-performance capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.139451.
- 5.
Meng, F.; Ding, Z.; Xu, X.; et al. Metal organic framework-derived nitrogen-doped porous carbon sustained Prussian blue analogues for efficient and fast hybrid capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 317, 123899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123899.
- 6.
Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Z.; et al. Chloride pre-intercalated CoFe-layered double hydroxide as chloride ion capturing electrode for capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133578.
- 7.
Cao, S.; Feng, W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Fabrication of CoTi-ZIF-9-derived carbon/MXene heterostructures for enhanced capacitive deionization in simulated seawater desalination. Desalination 2025, 613, 119059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2025.119059.
- 8.
Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. Space-Confined Metal Ion Strategy for Carbon Materials Derived from Cobalt Benzimidazole Frameworks with High Desalination Performance in Simulated Seawater. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301011. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202301011.
- 9.
Liu, H.; Chen, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Bioinspired Self-Standing, Self-Floating 3D Solar Evaporators Breaking the Trade-Off between Salt Cycle and Heat Localization for Continuous Seawater Desalination. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301596. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202301596.
- 10.
Tang, Y.; Cao, S.; Feng, W.; et al. Spatial confinement effect on hollow mesoporous carbon spheres/MOF-derived nanosheets superstructures for improved capacitive deionization performance. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 94907194. https://doi.org/10.26599/nr.2025.94907194.
- 11.
Tang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Su, Y.; et al. Enhanced Capacitive Deionization of Hollow Mesoporous Carbon Spheres/MOFs Derived Nanocomposites by Interface-Coating and Space-Encapsulating Design. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2403802. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202403802.
- 12.
Wu, X.; Lu, Y.; Ren, X.; et al. Interfacial Solar Evaporation: From Fundamental Research to Applications. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313090. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202313090.
- 13.
Lawal, D.U.; Antar, M.A.; Ismaila, K.G.; et al. Hybrid multi-stage flash (MSF) and membrane distillation (MD) desalination system for energy saving and brine minimization. Desalination 2023, 548, 116231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116231.
- 14.
Fritzmann, C.; Löwenberg, J.; Wintgens, T.; et al. State-of-the-art of reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 216, 1–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.12.009.
- 15.
Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Kurihara, M.; et al. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: Current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119292.
- 16.
Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Yang, B.; et al. Separation, anti-fouling, and chlorine resistance of the polyamide reverse osmosis membrane: From mechanisms to mitigation strategies. Water Res. 2021, 195, 116976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.116976.
- 17.
Li, J.; Peng, H.; Liu, K.; et al. Polyester Nanofiltration Membranes for Efficient Cations Separation. Adv. Mater. 2023, 36, 2309406. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202309406.
- 18.
Luo, J.; Wan, Y. Mix-charged nanofiltration membrane: Engineering charge spatial distribution for highly selective separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.142689.
- 19.
Yadav, D.; Karki, S.; Ingole, P.G. Current advances and opportunities in the development of nanofiltration (NF) membranes in the area of wastewater treatment, water desalination, biotechnological and pharmaceutical applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108109.
- 20.
Zhao, R.; Jin, P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Amino acid-based loose polyamide nanofiltration membrane with ultrahigh water permeance for efficient dye/salt separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 673, 121477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2023.121477.
- 21.
Arana Juve, J.-M.; Christensen, F.M.S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Electrodialysis for metal removal and recovery: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134857.
- 22.
Sedighi, M.; Behvand Usefi, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.; et al. Environmental sustainability and ions removal through electrodialysis desalination: Operating conditions and process parameters. Desalination 2023, 549, 116319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116319.
- 23.
Kumar, S.; Aldaqqa, N.M.; Alhseinat, E.; et al. Electrode Materials for Desalination of Water via Capacitive Deionization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302180. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202302180.
- 24.
Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Heterointerface optimization in a covalent organic framework-on-MXene for high-performance capacitive deionization of oxygenated saline water. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 1708–1716. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1mh01882e.
- 25.
Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. MOF-on-MOF nanoarchitectures for selectively functionalized nitrogen-doped carbon-graphitic carbon/carbon nanotubes heterostructure with high capacitive deionization performance. Nano Energy 2022, 97, 107146. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107146.
- 26.
Zhao, J.; Wu, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Efficient and Durable Sodium, Chloride-doped Iron Oxide-Hydroxide Nanohybrid-Promoted Capacitive Deionization of Saline Water via Synergetic Pseudocapacitive Process. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2201678. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202201678.
- 27.
He, Z.; Miller, C.J.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI): A flexible and tunable technology for customized water softening. Water Res. 2024, 259, 121871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121871.
- 28.
Xiao, Q.; Ma, J.; Xu, L.; et al. Membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI) for selective ion separation and recovery: Fundamentals, challenges, and opportunities. J. Membr. Sci. 2024, 699, 122650. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2024.122650.
- 29.
Zhu, Y.; Miller, C.; Lian, B.; et al. Brackish groundwater desalination by constant current membrane capacitive deionization (MCDI): Results of a long-term field trial in Central Australia. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121413.
- 30.
Jeon, S.-I.; Park, H.-R.; Yeo, J.-G.; et al. Desalination via a new membrane capacitive deionization process utilizing flow-electrodes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1471. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ee24443a.
- 31.
Yang, F.; He, Y.; Rosentsvit, L.; et al. Flow-electrode capacitive deionization: A review and new perspectives. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117222.
- 32.
Zhang, C.; Ma, J.; Wu, L.; et al. Flow Electrode Capacitive Deionization (FCDI): Recent Developments, Environmental Applications, and Future Perspectives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4243–4267. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c06552.
- 33.
Gao, M.; Yang, Z.; Liang, W.; et al. Recent advanced freestanding pseudocapacitive electrodes for efficient capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 324, 124577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124577.
- 34.
Wei, B.; Liu, Z. Pseudo-capacitive behaviors induced dual-ion selective deionization system based on MoS2/PPy//Ag@PANI/AC. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.131906.
- 35.
Zhou, X.; Shu, S.; Ye, X.; et al. Engineering Faradaic Electrode Materials for High-Efficiency Water Desalination. Small 2024, 20, 2400047. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202400047.
- 36.
Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Controlled synthesis of bismuth oxychloride-carbon nanofiber hybrid materials as highly efficient electrodes for rocking-chair capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126326.
- 37.
Tu, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; et al. Ternary-metal Prussian blue analogues as high-quality sodium ion capturing electrodes for rocking-chair capacitive deionization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 642, 680–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2023.04.007.
- 38.
Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Tailoring the electrode material and structure of rocking-chair capacitive deionization for high-performance desalination. Mater. Horiz. 2024, 11, 5209–5219. https://doi.org/10.1039/d4mh00773e.
- 39.
Liu, R.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Y.; et al. Optimization of flow field distribution to improve desalination performance of battery electrode deionization by designing flow channel structure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125661.
- 40.
Wei, W.; Feng, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Electrochemical Driven Phase Segregation Enabled Dual-Ion Removal Battery Deionization Electrode. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 4830–4837. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c01487.
- 41.
Wei, W.; Gu, X.; Wang, R.; et al. Wood-Based Self-Supporting Nanoporous Three-Dimensional Electrode for High-Efficiency Battery Deionization. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7572–7578. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.2c02583.
- 42.
Gao, L.; Dong, Q.; Hu, C.; et al. Surfactant-assisted self-assembly of flower-like ultrathin vanadium disulfide nanosheets for enhanced hybrid capacitive deionization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 627, 1011–1020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.07.111.
- 43.
Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Wang, K.; et al. Hybrid of pyrazine based π-conjugated organic molecule and MXene for hybrid capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123628.
- 44.
Gong, S.; Liu, H.; Zhao, F.; et al. Vertically Aligned Bismuthene Nanosheets on MXene for High-Performance Capacitive Deionization. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 4843–4853. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.2c11430.
- 45.
Lei, J.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, F.; et al. Flexible self-supporting CoFe-LDH/MXene film as a chloride ions storage electrode in capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135381.
- 46.
Guo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, D.; et al. Evolution of CuCoFe Prussian blue analogues with open nanoframe architectures for enhanced capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.153714.
- 47.
Lei, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; et al. Entropy Engineering Constrain Phase Transitions Enable Ultralong-life Prussian Blue Analogs Cathodes. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2402340. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402340.
- 48.
Sun, T.; Jia, M.; Zhang, H.; et al. Particle size reduction of manganese-doped Prussian blue analogues enhanced hybrid capacitive deionization performance. Desalination 2025, 606, 118787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2025.118787.
- 49.
Tran, N.A.T.; Khoi, T.M.; Phuoc, N.M.; et al. A review of recent advances in electrode materials and applications for flow-electrode desalination systems. Desalination 2022, 541, 116037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116037.
- 50.
Hatzell, K.B.; Hatzell, M.C.; Cook, K.M.; et al. Effect of Oxidation of Carbon Material on Suspension Electrodes for Flow Electrode Capacitive Deionization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2368–2377. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5055989.
- 51.
Aldaqqa, N.M.; Kumar, S.; Martínez, J.I.; et al. Surface Engineered 2D-β-ketoenamine Covalent Organic Framework for Superior Dechlorination via Hybrid Capacitive Deionization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202510345. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202510345.
- 52.
Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.; et al. Hybrid capacitive deionization to enhance the desalination performance of capacitive techniques. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 3683–3689. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ee02378a.
- 53.
Li, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Electrospun sodium titanate-MXene/carbon nanofibers as binder-free electrode for enhanced hybrid capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 511, 162040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.162040.
- 54.
Yao, S.; Wang, D.; Fu, W.; et al. Unveiling the role of Atomic-Level “Pump-Driven” effect in MoS2/MnO2 for facilitating directional charge transfer in hybrid capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 490, 151608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.151608.
- 55.
Shin, Y.-U.; Lim, J.; Boo, C.; et al. Improving the feasibility and applicability of flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI): Review of process optimization and energy efficiency. Desalination 2021, 502, 114930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.114930.
- 56.
Shi, C.; Wang, H.; Li, A.; et al. Process model for flow-electrode capacitive deionization for energy consumption estimation and system optimization. Water Res. 2023, 230, 119517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.119517.
- 57.
Wang, H.; Shi, C.; Zhu, G.; et al. Two-Phase flow model-driven optimization of charge percolation in flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123283.
- 58.
Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; He, C.; et al. Equivalent film-electrode model for flow-electrode capacitive deionization: Experimental validation and performance analysis. Water Res. 2020, 181, 115917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115917.
- 59.
Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Q.; et al. Achieving enhanced structural stability and electrical conductivity of MnHCF through Ni doping and CNT composite for efficient hybrid capacitive deionization. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2026, 257, 233–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2025.08.049.
- 60.
Li, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, F.; et al. Orbital-Level Electronic Modulation of MnO2 via Interfacial Built-In Electric Fields: Breaking the Jahn–Teller Distortion Cycle for Ultra-Durable Hybrid Capacitive Deionization. Small 2025, 21, 2505300. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202505300.
- 61.
Zhuang, Z.; Sun, L.; Tao, Y.; et al. Highly Efficient and Stable Capacitive Deionization Based on a Flower-Like Conjugated Polymer with Double Active-Sites. Energy Environ. Mater. 2024, 8, e12852. https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12852.
- 62.
Wei, H.; Wang, T.; Hu, R.; et al. Sulfur Vacancies Enriched Copper Sulfide Nanotubes Boost Desalination Efficiency of Hybrid Capacitive Deionization. Small 2025, 21, 2411810. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202411810.
- 63.
Rommerskirchen, A.; Linnartz, C.J.; Egidi, F.; et al. Flow-electrode capacitive deionization enables continuous and energy-efficient brine concentration. Desalination 2020, 490, 114453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114453.
- 64.
Yang, S.; Choi, J.; Yeo, J.-G.; et al. Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization Using an Aqueous Electrolyte with a High Salt Concentration. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 5892–5899. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04640.
- 65.
Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Xuan, X.; et al. Unlocking Enhanced Capacitive Deionization of NaTi2(PO4)3/Carbon Materials by the Yolk–Shell Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 9242–9253. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c01755.
- 66.
Chen, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Ultra-durable and highly-efficient hybrid capacitive deionization by MXene confined MoS2 heterostructure. Desalination 2022, 528, 115616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.115616.
- 67.
Du, J.; Xing, W.; Yu, J.; et al. Synergistic effect of intercalation and EDLC electrosorption of 2D/3D interconnected architectures to boost capacitive deionization for water desalination via MoSe2/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2023.119831.
- 68.
Buczek, S.; Barsoum, M.L.; Uzun, S.; et al. Rational Design of Titanium Carbide MXene Electrode Architectures for Hybrid Capacitive Deionization. Energy Environ. Mater. 2020, 3, 398–404. https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12110.
- 69.
Shi, X.-Y.; Gao, M.-H.; Hu, W.-W.; et al. Largely enhanced adsorption performance and stability of MXene through in-situ depositing polypyrrole nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.120596.
- 70.
Xi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. In-situ growth of Ni, Co-Prussian blue nanocubes on molten salt etched lamellar Ti3C2Tx/Ni for enhanced hybrid capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 155941. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.155941.
- 71.
Alfahel, R.; Tong, Y.; Pasha, M.; et al. A lamellar chitosan-lignosulfonate/MXene nanocomposite as binder-free electrode for high-performance capacitive deionization. Desalination 2024, 573, 117187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.117187.
- 72.
Zhang, T.; Chang, L.; Xiao, X. Surface and Interface Regulation of MXenes: Methods and Properties. Small Methods 2023, 7, 2201530. https://doi.org/10.1002/smtd.202201530.
- 73.
Jiang, M.; Li, M.; Cui, C.; et al. Molecular-Level Interfacial Chemistry Regulation of MXene Enables Energy Storage beyond Theoretical Limit. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7532–7545. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c12329.
- 74.
Wang, Q.; Su, X.; Jia, Y.; et al. Regulation of Microstructure and Absorption Properties of MXene Materials: Theoretical and Experimental. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e09994. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202509994.
- 75.
Kong, W.; Lu, X.; Tan, K.; et al. Controlling electrode-potential distribution to enable oxidation stability of MXene-based CDI desalination cells. Water Res. 2025, 284, 123948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123948.
- 76.
Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liang, S.; et al. Exploring MXene’s role in capacitive deionization: Advances, challenges, and future directions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.154130.
- 77.
Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, K.; et al. Preparation of fully coated PEDOT: PSS film on MXene for high reliability capacitive deionization. Desalination 2025, 594, 118306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2024.118306.
- 78.
Gao, M.; Xiao, W.; Miao, L.; et al. Prussian blue and its analogs: A robust platform for efficient capacitive deionization. Desalination 2024, 574, 117278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.117278.
- 79.
Singh, K.; Li, G.; Lee, J.; et al. Divalent Ion Selectivity in Capacitive Deionization with Vanadium Hexacyanoferrate: Experiments and Quantum-Chemical Computations. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105203. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202105203.
- 80.
Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; et al. Freestanding Ti3C2Tx MXene/Prussian Blue Analogues Films with Superior Ion Uptake for Efficient Capacitive Deionization by a Dual Pseudocapacitance Effect. ACS Nano 2021, 16, 1239–1249. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c09036.
- 81.
Zhao, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Rational design of Core-Shell heterostructured CoFe@NiFe Prussian blue analogues for efficient capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.150437.
- 82.
Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. Co-doped Ni-PBA anchored on optimized ZIF-67-derived Co/N-doped hollow carbon framework for high-performance hybrid capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 358, 130257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.130257.
- 83.
Zhou, W.; Huang, T.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Ternary-metal Prussian blue analog hollow spheres/MXene electrode based on self-assembly enabling highly stable capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 161124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.161124.
- 84.
Xing, W.; Luo, K.; Liang, J.; et al. Urchin-like core–shell tungsten oxide@carbon composite electrode for highly efficient and stable water desalination via hybrid capacitive deionization (HCDI). Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147268.
- 85.
Bu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; et al. Enhanced hybrid capacitive deionization performance by the mass balance of electrodes. Desalination 2023, 567, 116982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.116982.
- 86.
Tang, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W.; et al. Design of Uniform Hollow Carbon Nanoarchitectures: Different Capacitive Deionization between the Hollow Shell Thickness and Cavity Size. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206960. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202206960.
- 87.
Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, F.; et al. Selective removal of chloride ions by bismuth electrode in capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116600.
- 88.
Yoon, H.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; et al. Hybrid capacitive deionization with Ag coated carbon composite electrode. Desalination 2017, 422, 42–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2017.08.010.
- 89.
Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Shen, J.; et al. Ag-doped hollow ZIFs-derived nanoporous carbon for efficient hybrid capacitive deionization. Desalination 2020, 473, 114173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2019.114173.
- 90.
Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Promoting the uptake of chloride ions by ZnCo–Cl layered double hydroxide electrodes for enhanced capacitive deionization. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 1886–1895. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1en00350j.
- 91.
Xu, M.; Tan, Z.; Tian, Y.; et al. Binder-free Bi@MXene film with 3D sandwich structure for highly hybrid capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363, 132263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.132263.
- 92.
Kim, N.; Park, J.; Cho, Y.; et al. Comprehensive Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Study of Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization Cells. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8808–8817. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c01619.
- 93.
Ma, J.; Chen, L.; Yu, F. Environmental applications and perspectives of flow electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.126095.
- 94.
Tan, Z.; Song, W.; Mao, X.; et al. Efficient capacitive deionization with hierarchical porous carbon flow electrodes. Desalination 2024, 591, 118051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2024.118051.
- 95.
Folaranmi, G.; Tauk, M.; Bechelany, M.; et al. Investigation of fine activated carbon as a viable flow electrode in capacitive deionization. Desalination 2022, 525, 115500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.115500.
- 96.
Tauk, M.; Bechelany, M.; Lagerge, S.; et al. Influence of particle size distribution on carbon-based flowable electrode viscosity and desalination efficiency in flow electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122666.
- 97.
Zhang, W.; Xue, W.; Xiao, K.; et al. Selection and optimization of carbon-based electrode materials for flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123649.
- 98.
Han, M.; Tang, L.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Enhanced continuous desalination performance with iron-complexed malonate redox couples. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2023, 9, 2368–2377. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ew00400g.
- 99.
Qi, F.; Wang, X.; Zhu, P.; et al. Asymmetric Fe2+/Fe3+-Mediated Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization for the Removal of Chloride Ions in Reclaimed Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 8609–8619. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.4c00071.
- 100.
Lwin, T.T.A.; Chen, X.; Zaw, M.; et al. Enhanced desalination performance of flow capacitive deionization with the addition of conductive polymer in redox couples and activated carbon. Carbon 2025, 231, 119703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119703.
- 101.
Wei, Q.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Low energy consumption flow capacitive deionization with a combination of redox couples and carbon slurry. Carbon 2020, 170, 487–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.044.
- 102.
Wei, Q.; Tang, L.; Ramalingam, K.; et al. Redox-catalysis flow electrode desalination in an organic solvent. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 22254–22261. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ta05350g.
- 103.
Luo, L.; He, Q.; Yi, D.; et al. Indirect charging of carbon by aqueous redox mediators contributes to the enhanced desalination performance in flow-electrode CDI. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118688.
- 104.
Mani, S.; Thangapandi, B.; Elangovan, P.; et al. New insights into the performance analysis of flow-electrode capacitive deionization using ferri/ferrocyanide redox couples for continuous water desalination. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 147887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.147887.
- 105.
Freire, N.H.J.; Linnartz, C.J.; Montoro, L.A.; et al. Flow electrode capacitive deionization with iron-based redox electrolyte. Desalination 2024, 578, 117313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2024.117313.
- 106.
Alawad, S.M.; Mansour, R.B.; Al-Sulaiman, F.A.; et al. Renewable energy systems for water desalination applications: A comprehensive review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 286, 117035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2023.117035.
- 107.
Luo, K.; Chen, M.; Xing, W.; et al. Significantly enhanced desalination performance of flow-electrode capacitive deionization via cathodic iodide redox couple and its great potential in treatment of iodide-containing saline wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 129905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.129905.
- 108.
Wei, Q.; Cui, C.; Wang, Z.; et al. Enhanced phosphate removal and recovery from wastewater by flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI): Role of [Fe(CN)6]3–/4– redox couple. Water Res. 2025, 277, 123304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123304.
- 109.
Wu, L.; Garg, S.; Waite, T.D. Progress and challenges in the use of electrochemical oxidation and reduction processes for heavy metals removal and recovery from wastewaters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 479, 135581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.135581.
- 110.
Yang, J.; Peng, J.; Zhang, P.; et al. A redox-mediated polymer with extended π-delocalization for efficient Cr3+ elimination via capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 368, 133039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2025.133039.
- 111.
Xiong, L.; Tang, J. Strategies and Challenges on Selectivity of Photocatalytic Oxidation of Organic Substances. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003216. https://doi.org/10.1002/aenm.202003216.
- 112.
Chen, R.; Deng, X.; Wang, C.; et al. Enhanced desalination performances by using porous polyaniline-activated carbon composite flow-electrodes in capacitive deionization system. Desalination 2023, 557, 116568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.116568.
- 113.
Chen, K.-Y.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Wang, D.-M.; et al. Carbon nanotubes/activated carbon hybrid as a high-performance suspension electrode for the electrochemical desalination of wastewater. Desalination 2022, 522, 115440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2021.115440.
- 114.
Minh Phuoc, N.; Anh Thu Tran, N.; Minh Khoi, T.; et al. ZIF-67 metal-organic frameworks and CNTs-derived nanoporous carbon structures as novel electrodes for flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119466.
- 115.
Rauer, S.B.; Wang, S.; Köller, N.; et al. PEDOT:PSS-CNT Composite Particles Overcome Contact Resistances in Slurry Electrodes for Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303606. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202303606.
- 116.
Yan, L.; Issaka Alhassan, S.; Gang, H.; et al. Enhancing charge transfer utilizing ternary composite slurry for high-efficient flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143413.
- 117.
Cai, Y.; Zhao, F.; Zhao, J.; et al. Flexible construction of three-dimensional continuous conductive structure by hollow carbon sphere and CNT for promoted ions transport in flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126405.
- 118.
Alsultan, A.; Alkhaldi, A.; Alsaikhan, K.; et al. Surface-treated carbon black for durable, efficient, continuous flow electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 313, 123444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.123444.
- 119.
Wang, C.; Wu, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Pine-derived porous carbon for efficient capacitive deionization and the role of its hierarchical pore structure. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 126865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126865.
- 120.
Yang, R.; Xu, X.; Teng, J.; et al. Porous carbon flow-electrode derived from modified MOF-5 for capacitive deionization. Desalination 2024, 569, 117077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.117077.
- 121.
Xu, Y.; Duan, F.; Cao, R.; et al. Enhanced salt removal performance using nickel hexacyanoferrate/carbon nanotubes as flow cathode in asymmetric flow electrode capacitive deionization. Desalination 2023, 566, 116929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.116929.
- 122.
Xu, L.; Peng, S.; Mao, Y.; et al. Enhancing Brackish Water Desalination using Magnetic Flow-electrode Capacitive Deionization. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118290.
- 123.
Xu, L.; Tang, L.; Peng, S.; et al. Magnetic array for efficient and stable Flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.137415.
- 124.
Xu, L.; Peng, S.; Wu, K.; et al. Precise manipulation of the charge percolation networks of flow-electrode capacitive deionization using a pulsed magnetic field. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118963. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118963.
- 125.
Chen, R.; Deng, X.; Wang, C.; et al. A newly designed graphite-polyaniline composite current collector to enhance the performance of flow electrode capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134845.
- 126.
Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; He, Z.; et al. Flow-electrode capacitive deionization utilizing three-dimensional foam current collector for real seawater desalination. Water Res. 2022, 220, 118642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2022.118642.
- 127.
Zhang, X.; Pang, M.; Wei, Y.; et al. Three-dimensional titanium mesh-based flow electrode capacitive deionization for salt separation and enrichment in high salinity water. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.121147.
- 128.
Zhai, C.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Rectorite in flow-electrode capacitive deionization with three-dimensional current collector to achieve cost-effective desalination. Desalination 2024, 573, 117217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.117217.
- 129.
Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, H.; et al. Enhanced Desalination Performance by a Novel Archimedes Spiral Flow Channel for Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 1250–1259. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.1c00445.
- 130.
He, X.; Chen, W.; Sun, F.; et al. Enhanced NH4+ Removal and Recovery from Wastewater Using Na-Zeolite-based Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization: Insight from Ion Transport Flux. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8828–8838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.3c02286.
- 131.
Ma, J.; Wang, X.; Bian, Y.; et al. Novel Current Collector with Mosquito-Repellent Incense-Shaped Channel of Flow Electrode Capacitive Deionization. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 4818–4821. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c00442.
- 132.
Yan, L.; Annor Asare, J.; Wu, B.; et al. A Hexagonal Honeycomb-Shaped Flow Channel for High-Efficient Desalination and Flowability in Flow-Electrode Capacitive Deionization. ACS EST Water 2023, 3, 2753–2764. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.3c00242.
- 133.
Saif, H.M.; Gebregeorgis, T.H.; Crespo, J.G.; et al. The influence of flow electrode channel design on flow capacitive deionization performance: Experimental and CFD modelling insights. Desalination 2024, 578, 117452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2024.117452.
- 134.
Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; et al. Influence of ion exchange membrane arrangement on dual-channel flow electrode capacitive deionization: Theoretical analysis and experimentations. Desalination 2023, 548, 116288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116288.
- 135.
Xie, B.; Liu, Q.; Tan, G.; et al. A novel four-chamber flow electrode capacitive deionization system for continuous recovery of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 319, 124055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124055.
- 136.
Liu, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. A novel cell structure for high performance electrosorption process. Desalination 2025, 601, 118603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2025.118603.
- 137.
Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; et al. A novel two-stage continuous capacitive deionization system with connected flow electrode and freestanding electrode. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 152133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.152133.
- 138.
Hossain, S.M.; Yu, H.; Choo, Y.; et al. ZiF-8 induced carbon electrodes for selective lithium recovery from aqueous feed water by employing capacitive deionization system. Desalination 2023, 546, 116201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116201.
- 139.
Si, J.; Xue, C.; Li, S.; et al. Selective membrane capacitive deionization for superior lithium recovery. Desalination 2024, 572, 117154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.117154.
- 140.
Hong, S.P.; Yoon, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Selective phosphate removal using layered double hydroxide/reduced graphene oxide (LDH/rGO) composite electrode in capacitive deionization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 564, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.068.
- 141.
Bao, Y.; Miao, S.; Yin, P.; et al. Optimization of NiHCF/MnO2 composite electrodes for lithium extraction via capacitive deionization: A case of core-shell construction strategy. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 525, 170471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.170471.
- 142.
Dhanushkotti, R.; Mohammed, A.K.; Ranjeesh, K.C.; et al. Inherited Nitrogen Distribution Control in Covalent Organic Framework Cathodes for Efficient Electrochemical Lithium Recovery via Capacitive Deionization. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2417140. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202417140.
- 143.
Ma, G.; Zhang, X.; Cai, A.; et al. Lithium extraction from salt lake brine by four-stage ion-distillation of flow electrode capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.152519.
- 144.
Bae, S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; et al. Enhanced sulfate ion adsorption selectivity in capacitive deionization with ball-milled activated carbon. Desalination 2022, 540, 116014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.116014.
- 145.
Zhang, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Efficient phosphorus removal from ultra-low concentration wastewater by flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126973. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126973.
- 146.
Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Electric double layer capacitive adsorption and faradaic pseudo-capacitance behavior of ZnFe-PANI/CNT electrode for phosphate removal in capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 333, 125913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125913.
- 147.
Wang, H.; You, H.; Wu, G.; et al. Co/Fe co-doped ZIF-8 derived hierarchically porous composites as high-performance electrode materials for Cu2+ ions capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.141621.
- 148.
Wang, S.; Zhuang, H.; Shen, X.; et al. Copper removal and recovery from electroplating effluent with wide pH ranges through hybrid capacitive deionization using CuSe electrode. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131785.
- 149.
Shen, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; et al. Simultaneous Cu(II)-EDTA decomplexation and Cu(II) recovery using integrated contact-electro-catalysis and capacitive deionization from electroplating wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 472, 134548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134548.
- 150.
Gao, Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; et al. Selective single-atom adsorption for precision separation of lead ions in tap water via capacitive deionization. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2024.122665.
- 151.
Wang, R.; Xu, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Electro-enhanced adsorption of lead ions from slightly-polluted water by capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120122.
- 152.
Datar, S.D.; Mane, R.S.; Kumar, N.; et al. Effective removal of heavy metal-lead and inorganic salts by microporous carbon derived from Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 electrode using capacitive deionization. Desalination 2023, 558, 116619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2023.116619.
- 153.
Mao, M.; Yan, T.; Chen, G.; et al. Selective Capacitive Removal of Pb2+ from Wastewater over Redox-Active Electrodes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 730–737. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c06562.
- 154.
Tang, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; et al. Selective capacitive removal of Pb(II) ions from industrial wastewater using NF/Mn2CoO4@MoO2 electrodes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.153196.
- 155.
Liu, D.; Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; et al. A coupling technology of capacitive deionization and carbon-supported petal-like VS2 composite for effective and selective adsorption of lead (II) ions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 910, 116152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116152.
- 156.
Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiang, S.; et al. Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube encapsulated Fe7S8 nanoparticles for the high-efficiency and selective removal of Pb2+ by pseudocapacitive coupling. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 2051–2060. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2en00044j.
- 157.
Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, C.; et al. Enhanced selective electrosorption of Pb2+ from complex water on covalent organic framework-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122147.
- 158.
Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, X.; et al. Enhanced removal of lead ions from wastewaters by electrochemical adsorption using nitrogen-doped Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2024.155463.
- 159.
Yang, D.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Capacitive deionization of high concentrations of hexavalent chromium using nickel–ferric-layered double hydroxide/molybdenum disulfide asymmetric electrode. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 634, 793–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.12.100.
- 160.
Nguyen, T.K.A.; Huynh, T.V.; Doong, R.-A. Enhanced capacitive deionization of Cr(VI) using functionalized metal carbide 2D framework and badam tree leaf-derived carbon as the asymmetric electrode materials. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.146439.
- 161.
Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Pseudocapacitive deionization of high concentrations of hexavalent chromium using NiFe-layered double hydroxide/polypyrrole asymmetric electrode. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 328, 125004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125004.
- 162.
Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, X. Confinement-induced Ni-based MOF formed on Ti3C2Tx MXene support for enhanced capacitive deionization of chromium(VI). Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3727. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-87642-z.
- 163.
Wu, P.-C.; Viet Cuong, D.; Wu, J.-C.; et al. Harnessing in-situ electrocatalytic oxidation with a cobalt oxide decorated nanocomposite electrode for efficient arsenic removal in capacitive deionization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.145887.
- 164.
Cai, L.; Xu, B.; Gan, Y.; et al. Effective removal of trace arsenic from groundwater by capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125419.
- 165.
Garzón-Pérez, A.; Vilasó-Cadre, J.; Balderas, P.; et al. Capacitive deionization with Mg/Al mixed oxides for arsenic removal from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2025.116578.
- 166.
Gong, W.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H.; et al. Evaluating the performance of flow-electrode capacitive deionization for cadmium removal from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.102595.
- 167.
Mai, S.; Huang, H.; Long, J.; et al. Enhanced simultaneous removal of thallium and cadmium using flow-electrode capacitive deionization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2025.116938.
- 168.
Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Effective inspissation of uranium(VI) from radioactive wastewater using flow electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120172.
- 169.
Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. Efficient remediation and synchronous recovery of uranium by phosphate-functionalized magnetic carbon-based flow electrode capacitive deionization. Water Res. 2025, 281, 123707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2025.123707.
- 170.
Wang, Z.; Kou, J.; Li, M.; et al. Enhancement and sustained uranium removal of 2D transition metal sulfide-graphene oxide composite/carbon cloth cathodes in capacitive deionization system. Desalination 2025, 605, 118745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2025.118745.
- 171.
Li, W.; Kang, W.; Ye, C.; et al. Zirconium-based MOF/MXene aerogel composite for highly stable and selective capture of uranium from aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 702, 163323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.163323.
- 172.
Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Meng, N.; et al. Simultaneously-efficient electro-sorption of Pb(Ⅱ), Cu(Ⅱ) and Cd(Ⅱ) by Cu2+ modified superactive carbons. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 338, 126604. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.126604.
- 173.
Zhang, B.; Yi, Q.; Qu, W.; et al. Titanium Carbon Oxide Flakes with Tunable Interlayer Spacing for Efficient Capacitive Deionization. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401332. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202401332.
- 174.
Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, W.; et al. Cooperative reinforcement of photocatalysis-coupled capacitive deionization in fructose intercalated MoS2 for removal of tetracycline. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 331, 125583. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.125583.
- 175.
Lim, J.; Shin, Y.-U.; Son, A.; et al. TiO2 nanotube electrode for organic degradation coupled with flow-electrode capacitive deionization for brackish water desalination. NPJ Clean Water 2022, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-022-00150-9.
- 176.
Ge, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Simultaneous removal of sulfamethazine and sulfate via electrochemical oxidation and capacitive Deionization: Mechanisms of in-situ activation and strategies of the hybrid system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 344, 127202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.127202.
- 177.
Dahiya, S.; Mishra, B.K. Enhancing understandability and performance of flow electrode capacitive deionisation by optimizing configurational and operational parameters: A review on recent progress. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116660.
- 178.
Tang, K.; Yiacoumi, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Optimal conditions for efficient flow-electrode capacitive deionization. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116626.
- 179.
Mao, Y.; Long, S.; Kuai, X.; et al. Statistical uncertainty quantification to augment CDI electrode design and operation optimization. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2023.143825.
- 180.
Wang, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, G.; et al. Machine Learning-Guided Prediction of Desalination Capacity and Rate of Porous Carbons for Capacitive Deionization. Small 2024, 20, 2401214. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202401214.
- 181.
Salari, K.; Zarafshan, P.; Khashehchi, M.; et al. Modeling and predicting of water production by capacitive deionization method using artificial neural networks. Desalination 2022, 540, 115992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2022.115992.
- 182.
Lee, S.; Shim, J.; Kim, H.H.; et al. Optimizing capacitive deionization operation using dynamic modeling and reinforcement learning. Desalination 2025, 602, 118626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2025.118626.
- 183.
Qin, H.; Fang, F.; Mao, Y.; et al. Insights on CDI parametric controls and dependencies using gloabal sensitivity analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2024.129424.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


