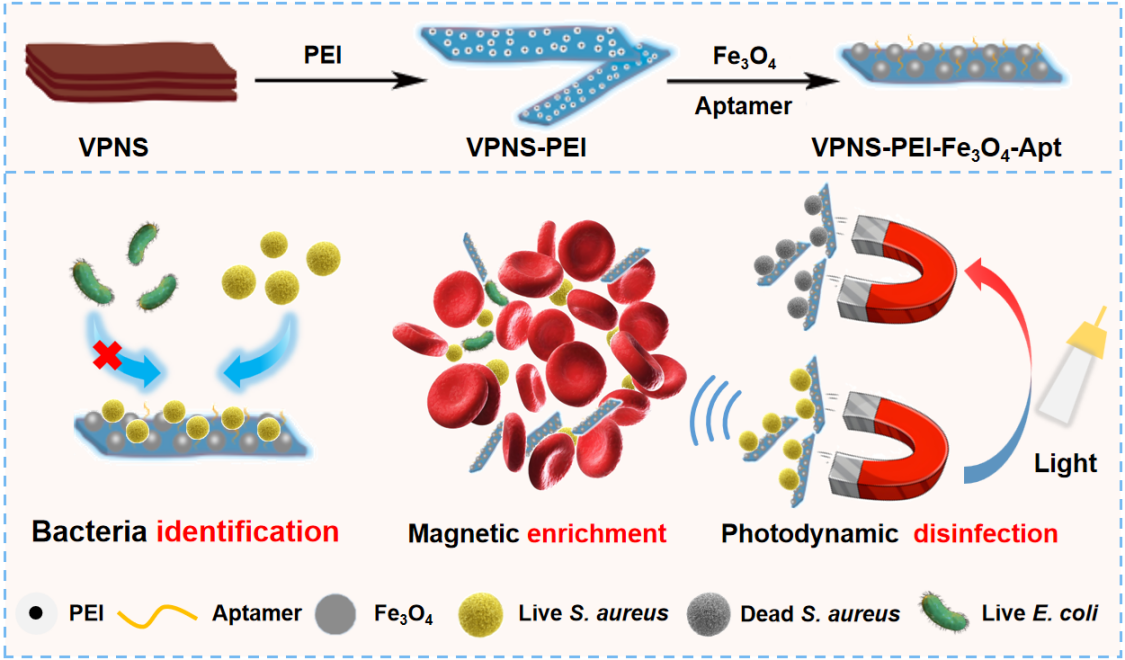
Despite the availability of various bacterial detection and elimination technologies, the sensitive diagnosis and treatment of sepsis caused by bloodstream infections remain significant challenges. Here, we report a magnetic nanosystem VPNS@PEI-Fe3O4-Apt based on functionalized two-dimensional violet phosphorus nanosheets (VPNS) by iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4), and bacteria-specific recognition aptamers (Apt) for early sepsis diagnosis and complete in vitro blood disinfection. We demonstrated that the VPNS@PEI-Fe3O4-Apt nanosystem can achieve the identification and enrichment of bacterial species in blood, resulting in the successful diagnosis of sepsis caused by a single bacterium (Staphylococcus aureus) or multiple bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli). The strategy of VPNS@PEI-Fe3O4-Apt nanosystem has high detection sensitivity (~10 colony-forming units), while significantly reducing diagnostic turnaround time to within 2 h, suggesting that it has great potential for diagnosing early sepsis in clinical therapy. Furthermore, owing to the antibacterial ability derived from the excellent photodynamic (PDT) effect of VPNS and its good biocompatibility, efficient and safe complete disinfection of blood in vitro is achieved. We believe that the VPNS@PEI-Fe3O4-Apt magnetic nanosystem provides a new strategy for bacterial detection and treatment of sepsis.
- Open Access
- Article
Bacteria-Identifiable 2D Violet Phosphorene-Based Nanosystems for Sepsis Diagnosis and Blood Disinfection
Author Information
Received: 16 Aug 2025 | Revised: 04 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 05 Sep 2025 | Published: 16 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
violet phosphorus nanosheets | specific identification | magnetic nanosystem | sepsis treatment
References
- 1.Cohen, J. The immunopathogenesis of sepsis. Nature 2002, 420, 885–891.
- 2.Burnouf, T.; Radosevich, M. Reducing the risk of infection from plasma products: Specific preventative strategies. Blood Rev. 2000, 14, 94–110.
- 3.Savelkoel, J.; Claushuis, T.A.M.; van Engelen, T.S.R.; et al. Global impact of world sepsis day on digital awareness of sepsis: An evaluation using google trends. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 61.
- 4.Prescott, H.C.; Angus, D.C. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: A review. JAMA 2018, 319, 62–75.
- 5.Zampieri, F.G.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Semler, M.W. Fluid therapy for critically ill adults with sepsis: A review. JAMA 2023, 329, 1967–1980.
- 6.Mancini, N.; Carletti, S.; Ghidoli, N.; et al. The era of molecular and other non-culture-based methods in diagnosis of sepsis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 235–251.
- 7.Meyer, T.; Franke, G.; Polywka, S.K.A.; et al. Improved detection of bacterial central nervous system infections by use of a broad-range pcr assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1751–1753.
- 8.Hsieh, K.; Ferguson, B.S.; Eisenstein, M.; et al. Integrated electrochemical microsystems for genetic detection of pathogens at the point of care. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 911–920.
- 9.Sunbul, M.; Jäschke, A. Contact-mediated quenching for RNA imaging in bacteria with a fluorophore-binding aptamer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13401–13404.
- 10.Zhang, L.; Dong, W.F.; Sun, H.B. Multifunctional superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Design, synthesis and biomedical photonic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 7664–7684.
- 11.Gu, H.; Ho, P.L.; Tsang, K.W.T.; et al. Using biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles to capture vancomycin-resistant enterococci and other gram-positive bacteria at ultralow concentration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 15702–15703.
- 12.Chen, J.; Duncan, B.; Wang, Z.; et al. Bacteriophage-based nanoprobes for rapid bacteria separation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16230–16236.
- 13.Ray, P.C.; Khan, S.A.; Singh, A.K.; et al. Nanomaterials for targeted detection and photothermal killing of bacteria. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3193–3209.
- 14.Zhou, R.; Wu, X.; Xue, S.; et al. Magnetic metal-organic frameworks-based ratiometric sers aptasensor for sensitive detection of patulin in apples. Food Chem. 2025, 466, 142200.
- 15.Kavruk, M.; Babaie, Z.; Kibar, G.; et al. Aptamer decorated PDA@magnetic silica microparticles for bacteria purification. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 285.
- 16.Didar, T.F.; Cartwright, M.J.; Rottman, M.; et al. Improved treatment of systemic blood infections using antibiotics with extracorporeal opsonin hemoadsorption. Biomaterials 2015, 67, 382–392.
- 17.Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. Aptamer-based detection of circulating targets for precision medicine. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 12035–12105.
- 18.Li, Z.; Luo, B.; Chen, Y.; et al. Nanomaterial-based encapsulation of biochemicals for targeted sepsis therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2025, 33, 102054.
- 19.Li, S.; Cui, S.; Yin, D.; et al. Dual antibacterial activities of a chitosan-modified upconversion photodynamic therapy system against drug-resistant bacteria in deep tissue. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3912–3924.
- 20.Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Structure and properties of violet phosphorus and its phosphorene exfoliation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1074–1080.
- 21.Zhao, C.; Han, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Violet phosphorus nanosheet: A biocompatible and stable platform for stimuli-responsive multimodal cancer phototherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2201995.
- 22.Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Violet phosphorene nanosheets coupled with CRISPR/Cas12a in a biosensor with a low background signal for onsite detection of tigecycline-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Sens. Actuators B: Chem. 2023, 395, 134509.
- 23.Shen, Q.; Kang, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. Bacterial elimination via cell membrane penetration by violet phosphorene peripheral sub-nanoneedles combined with oxidative stress. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 4926–4937.
How to Cite
Shen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Kang, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, A. Bacteria-Identifiable 2D Violet Phosphorene-Based Nanosystems for Sepsis Diagnosis and Blood Disinfection. Advanced Antibacterial Materials 2026, 1 (1), 16–26. https://doi.org/10.53941/aam.2026.100002.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References