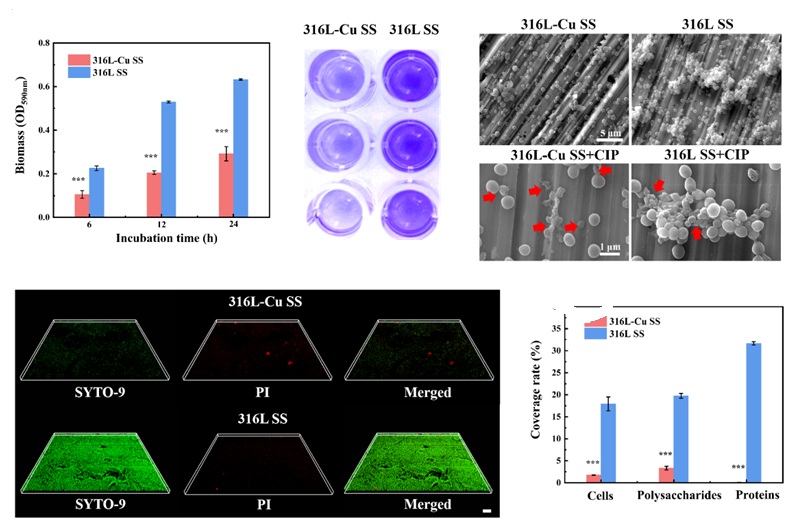
Treating biofilm formation-induced implant-associated infections is challenging, and they often lead to antimicrobial resistance, which significantly contributes to human mortality worldwide. Consequently, an increase in antibiotic resistance has warranted the development of more effective strategies to combat the drug-resistant bacterial infections. Hence, this study aimed to develop an antibacterial metal implant material (Cu-bearing 316L stainless steel) as a quorum-sensing inhibitor (QSI) for reversing drug resistance in resistant bacteria. Notably, RNA sequencing results revealed that 316L-Cu SS could interfere with the formation of multidrug resistance barriers of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), including biofilm development and metabolism, by inhibiting quorum-sensing signals. Furthermore, the resistance of MRSA to ciprofloxacin (CIP) was reversed, with up to a 67% decline in minimum bactericidal concentration. Subsequently, a QSI–CIP combination strategy was developed for synergistic action against MRSA, which achieved almost complete elimination of MRSA at low antibiotic dosage. Overall, the findings of this study present the novel antibacterial implant material as a lead QSI, highlighting the potential of adjunctive pathoblocker-mediated therapy against infections and providing a long-term activity to address the intractable challenge of drug-resistant bacteria with enhanced sustainability.
- Open Access
- Article
Cu-Bearing Antibacterial Stainless Steel Potentiates Antibiotic Sensitivity to Combat Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- Xinrui Zhang 1,
- Yingping Wang 2,
- Chunguang Yang 1,*,
- Ke Yang 1,3,*
Author Information
Received: 06 Sep 2025 | Revised: 15 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 19 Sep 2025 | Published: 30 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
drug-resistant bacterial | antibiotic | biofilm | Cu-bearing antibacterial stainless steel | quorum sensing
References
- 1.Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205.
- 2.Kumar, K.; Chopra, S. New drugs for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An update. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1465–1470.
- 3.Fisher, R.A.; Gollan, B.; Helaine, S. Persistent bacterial infections and persister cells. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 453–464.
- 4.Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An overview of basic and clinical research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218.
- 5.Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J. et al. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51.
- 6.Kurlenda, J.; Grinholc, M. Alternative therapies in Staphylococcus aureus diseases. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2012 59, 171–184.
- 7.Palser, S.; Smith, S.; Nash, E.F.; et al. Treatments for preventing recurrence of infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis (Protocol). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 12, CD012300.
- 8.Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The host-microbe interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18.
- 9.Cos, P.; Tote, K.; Horemans, T. Biofilms: An extra hurdle for effective antimicrobial therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 2279–2295.
- 10.Costerton, W.; Veeh, R.; Shirtliff, M.; et al. The application of biofilm science to the study and control of chronic bacterial infections. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1466–1477.
- 11.Petit, T.J.P.; Lebreton, A. Adaptations of intracellular bacteria to vacuolar or cytosolic niches. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 736–748.
- 12.Rumbaugh, K.P.; Sauer, K. Biofilm dispersion. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 571–586.
- 13.Schütz, C.; Empting, M.; Beilstein, J. Targeting the Pseudomonas quinolone signal quorum sensing system for the discovery of novel anti-infective pathoblockers. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2627–2645.
- 14.Guan, W.; Tan, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Ultrasonic interfacial engineering of red phosphorous-metal for eradicating mrsa infection effectively. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006047.
- 15.Chai, H.W.; Guo, L.; Wang, X.T.; et al. Antibacterial effect of 317L stainless steel contained copper in prevention of implant-related infection in vitro and in vivo. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2525–2535.
- 16.Zhao, J.; Cao, Z.Q.; Ren, L.; et al. A novel ureteral stent material with antibacterial and reducing encrustation properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 221–228.
- 17.Zhuang, Y.F.; Ren, L.; Zhang, S.Y.; et al. Antibacterial effect of a copper-containing titanium alloy against implant-associated infection induced by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 472–484.
- 18.Zhang, X.R.; Yang, C.G.; Xi, T.; et al. Cu-bearing stainless steel affects its contact-killing efficiency by mediating the interfacial interaction with bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 2303–2315.
- 19.Natan, M.; Edin, F.; Perkas, N.; et al. Two are better than one: Combining ZnO and MgF2 nanoparticles reduces Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation on cochlear implants. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2473–2481.
- 20.Xing, J.; Qi, S.; Wang, Z.; et al. Antimicrobial peptide functionalized conductive nanowire array electrode as a promising candidate for bacterial environment application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806353.1–1806353.9.
- 21.Wagner, S.; Sommer, R.; Hinsberger, S.; et al. Novel strategies for the treatment of pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5929–5969.
- 22.Christian, Schütz.; Ho, D.K.; Hamed, M.M.; et al. A new PqsR inverse agonist potentiates tobramycin efficacy to eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004369.
- 23.Liu, R.; Tang, Y.L.; Zeng, L.L.; et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of anti-bacterial copper-bearing titanium alloy for dental application. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 1112–1126.
- 24.Xiao, X.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Q.; et al. Impairment of biofilm formation by TiO2 photocatalysis through quorum quenching. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11895–11902.
- 25.Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. NorC, a new efflux pump regulated by MgrA of Staphylococcus aures. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2006, 50, 1104–1107.
- 26.Høiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Givskov, M.; et al. Antibiotic resistance of bacterial biofilms. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 322–332.
- 27.Prakash, B.; Veeregowda, B.; Krishnappa, G. Biofilms: A survival strategy of bacteria. Curr. Sci. 2003, 85, 1299–1307.
- 28.Costerton, J.W.; Lewandowski, Z.; Caldwell, D.E.; et al. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 711–745.
- 29.Xavier, K.; Bassler, B. Interference with AI-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature 2005, 437, 750.
- 30.Zhao, L.; Xue, T.; Shang, F.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus AI-2 quorum sensing associates with the KdpDE two-component system to regulate capsular polysaccharide synthesis and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3506–3515.
- 31.Li, M.; Villaruz, A.E.; Vadyvaloo, V.; et al. AI-2-dependent gene regulation in staphylococcus epidermidis. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 4.
- 32.Zhang, X.L.; Lee, K.; Yu, H.R.; et al. Photolytic quorum quenching: A new anti-biofouling strategy for membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 378, 12223–12232.
- 33.Zhang, X.R.; Yang, C.G.; Yang, K. Contact killing of Cu-bearing stainless steel based on charge transfer caused by the microdomain potential difference. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 361–372.
- 34.Crowe, M.; O’Sullivan, M.; Cassetti, O.; et al. Estimation and consumption pattern of free sugar intake in 3-year-old Irish preschool children. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2065–2074.
- 35.Orelle, C.; Mathieu, K.; Jault, J.M. Multidrug ABC transporters in bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 2019, 170, 381–391.
- 36.Barbosa, T.M.; Levy, S.B. The impact of antibiotic use on resistance development and persistence. Drug Resist. Updates 2000, 3, 303–311.
- 37.Huda, N.; Lee, E.W.; Chen, J.; et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of an ABC multidrug efflux pump, VcaM, in Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2413–2417.
- 38.Tiwari, S.; Van Tonder, A.J.; Vilchèze, C.; et al. Arginine-deprivation induced oxidative damage sterilizes mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9779–9784.
- 39.Suga, H.; Smith, K.M. Molecular mechanisms of bacterial quorum sensing as a new drug target. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 586–591.
How to Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yang, K. Cu-Bearing Antibacterial Stainless Steel Potentiates Antibiotic Sensitivity to Combat Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Advanced Antibacterial Materials 2026, 1 (1), 27–36. https://doi.org/10.53941/aam.2026.100003.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References