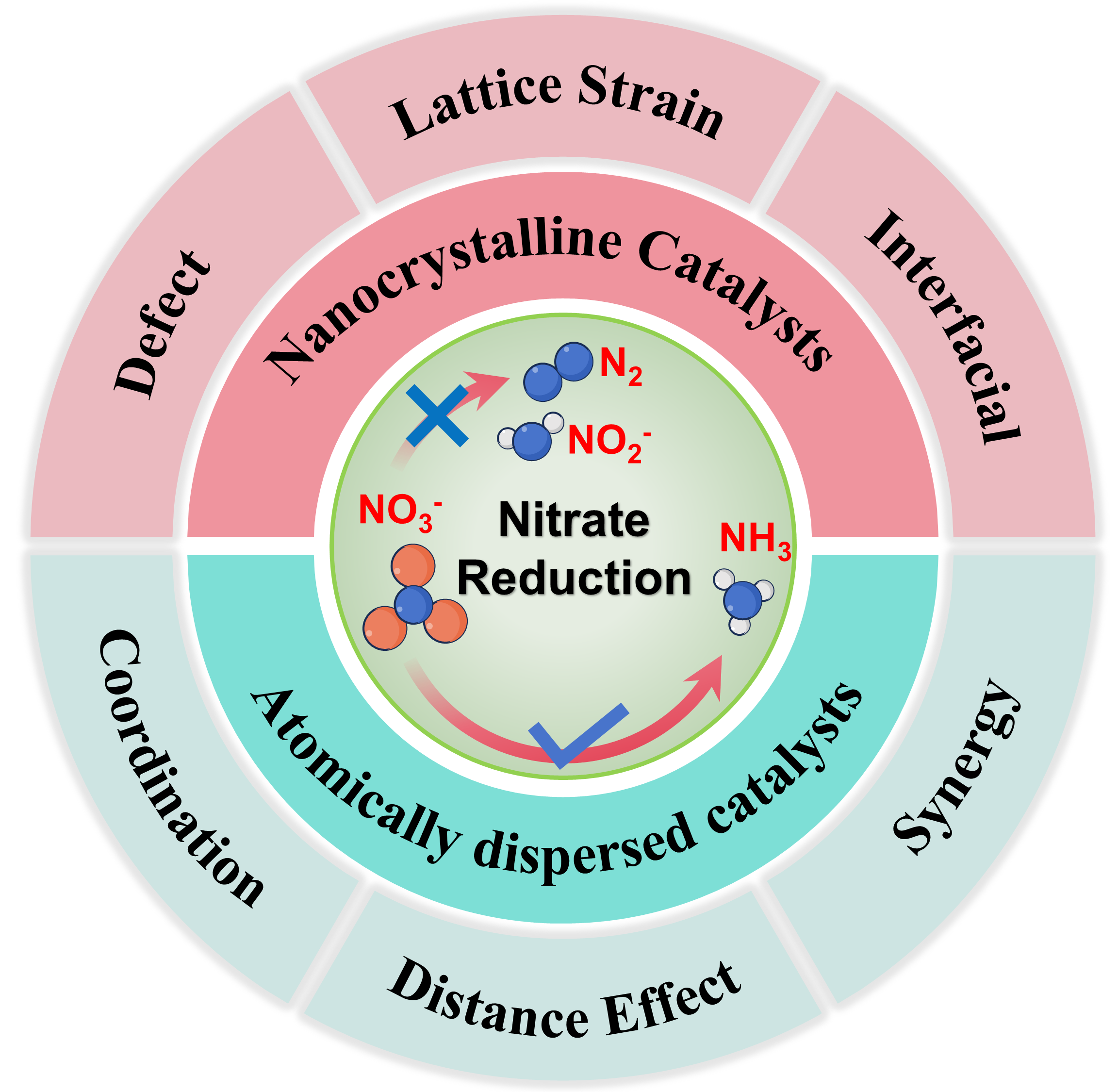
Ammonia is a vital industrial feedstock and a carbon-free hydrogen carrier, yet the conventional Haber–Bosch process requires extreme temperatures and pressures and produces substantial CO2 emissions, rendering its large-scale operation energy-intensive and environmentally unsustainable. Electrochemical nitrate reduction (NO3RR) has emerged as a promising alternative, benefiting from the relatively low N=O bond dissociation energy and the high solubility of nitrate ions in aqueous media. This approach not only enables ammonia production under ambient conditions but also provides a sustainable pathway for nitrate wastewater remediation, thereby addressing two pressing global challenges simultaneously. In this review, we present a comprehensive overview of recent advances in NO3RR catalyst development, with particular emphasis on two major classes: nanocrystalline catalysts and atomically dispersed catalysts. Nanocrystalline systems leverage tunable parameters such as crystal facet exposure, lattice strain, defect density, and heteroatom doping to regulate adsorption energies, enhance intermediate activation, and reconcile competing reaction pathways. Atomically dispersed catalysts—including single-atom, dual-atom, and sub-nanometer cluster architectures—achieve nearly complete atomic utilization while offering precisely defined active sites that serve as model platforms for probing structure–activity relationships. Together, these two categories represent complementary strategies: nanocrystals emphasize mesoscale control of morphology and electronic structure, whereas atomic-level catalysts advance the frontier of precision design and mechanistic understanding. We highlight the critical role of in situ and operando characterization in capturing dynamic transformations. Finally, this review discusses the challenges and opportunities that remain for translating these fundamental advances into scalable, efficient, and sustainable electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis.
- Open Access
- Review
Rational Design of Nano and Atomically Dispersed Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Ammonia Synthesis from Nitrate
- Ziteng Zhang †,
- Zhiyi Sun †,
- Zihao Wei *,
- Zhuo Chen *,
- Qi Sun,
- Ziheng Zhan,
- Xuecong Li,
- Aoxue Huang,
- Shenghua Li *,
- Wenxing Chen *,
- Siping Pang *
Author Information
Received: 17 Aug 2025 | Revised: 12 Sep 2025 | Accepted: 25 Sep 2025 | Published: 28 Sep 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
nanocrystalline catalysts | atomically dispersed catalysts | electrocatalytic nitrate reduction | in situ characterization
References
- 1.Kitano, M.; Inoue, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.; et al. Ammonia synthesis using a stable electride as an electron donor and reversible hydrogen store. Nat. Chem. 2012, 4, 934–940.
- 2.Ham, C.; Koper, M.; Hetterscheid, D. Challenges in reduction of dinitrogen by proton and electron transfer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5183–5191.
- 3.Fryzuk, M. Ammonia transformed. Nature 2004, 427, 498–499.
- 4.Guo, J.; Chen, P. Catalyst: NH3 as an Energy Carrier. Chem 2017, 3, 709–712.
- 5.Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Shi, Y.; et al. Ammonia recovery from nitrate-rich wastewater using a membrane-free electrochemical system. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 1251–1263.
- 6.Kandemir, T.; Schuster, M.; Senyshyn, A.; et al. The Haber–Bosch process revisited: On the real structure and stability of “ammonia iron” under working condition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12723–12726.
- 7.Talib, S.H.; Ali, B.; Dar, A.H.; et al. Catalytic reduction of N2O by CO molecules using transition metal-phosphomolybdic acid (TM1/PMA) single-atom catalysts: A theoretical perspective. Nano Res. Energy 2025, 4, e9120158.
- 8.Licht, S.; Cui, B.; Wang, B.; et al. Retracted: Ammonia synthesis by N2 and steam electrolysis in molten hydroxide suspensions of nanoscale Fe2O3. Science 2014, 345, 637–640.
- 9.Chen, S.; Perathoner, S.; Ampelli, C.; et al. Electrocatalytic synthesis of ammonia at room temperature and atmospheric pressure from water and nitrogen on a carbon-nanotube-based electrocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 129, 2743–2747.
- 10.Yu, X.; Han, P.; Wei, Z.; et al. Boron-doped graphene for electrocatalytic N2 reduction. Joule 2018, 2, 1610–1622.
- 11.Qin, S.; Li, K.; Cao, M.; et al. Fe-Co-Ni ternary single-atom electrocatalyst and stable quasi-solid-electrolyte enabling high-efficiency zinc-air batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2024, 3, e9120122.
- 12.Chen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, H.; et al. Electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia via direct eight-electron transfer using a copper–molecular solid catalyst. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 605–613.
- 13.Yang, J.; Qi, H.; Li, A.; et al. Potential-driven restructuring of Cu single atoms to nanoparticles for boosting the electrochemical reduction of nitrate to ammonia. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 12062–12071.
- 14.Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; et al. Molecular electrocatalysts for rapid and selective reduction of nitrogenous waste to ammonia. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2239–2246.
- 15.Wang, Y.-R.; Ding, H.-M.; Yue, M.; et al. Subtle tuning of micro-environment in COFs nanoribbons actuates low electricity-consumption photo-assisted Co-electrolysis of methanol and CO2. Nano Res. Energy 2025, 4, e9120146.
- 16.Feng, C.; Bo, K.; Wan, J.; et al. Triple synergy engineering via metal-free dual-atom incorporation for self-sustaining acidic ammonia electrosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202505211.
- 17.Gu, X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; et al. Tiara Ni Clusters for Electrocatalytic Nitrate Reduction to Ammonia with 97% Faradaic Efficiency. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 22785–22795.
- 18.Foster, S.; Bakovic, S.; Duda, R.; et al. Catalysts for nitrogen reduction to ammonia. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 490–500.
- 19.Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; et al. Present and future of functionalized Cu current collectors for stabilizing lithium metal anodes. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120048.
- 20.Zhao, Q.; Gan, R.; Ran, Y.-L.; et al. Single-atom catalysts: Controlled synthesis and dynamic mechanism in electrochemical oxygen evolution substitution reactions. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 4903–4920.
- 21.Legare, M.; Belanger-Chabot, G.; Dewhurst, R.; et al. Nitrogen fixation and reduction at boron. Science 2018, 359, 896–900.
- 22.Suryanto, B.; Du, H.; Wang, D.; et al. Challenges and prospects in the catalysis of electroreduction of nitrogen to ammonia. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 290–296.
- 23.Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Peng, L.-M. Recent progress of photodetector based on carbon nanotube film and application in optoelectronic integration. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120058.
- 24.Yan, J.; Ye, F.; Dai, Q.; et al. Recent progress in carbon-based electrochemical catalysts: From structure design to potential applications. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120047.
- 25.Sun, R.; Xu, F.; Wang, C.-H.; et al. Rational design of metal selenides nanomaterials for alkali metal ion (Li+/Na+/K+) batteries: Current status and perspectives. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 1906–1931.
- 26.Pham, H.Q.; Pham, H.T.Q.; Huynh, Q.; et al. Single-Atom Iridium-Based Catalysts: Synthesis Strategies and Electro(Photo)-Catalytic Applications for Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215143.
- 27.Langevelde, P.; Katsounaros, I.; Koper, M. Electrocatalytic nitrate reduction for sustainable ammonia production. Joule 2021, 5, 290–294.
- 28.Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. A review of emerging adsorbents for nitrate removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 493–504.
- 29.Pham, H.Q.; Huynh, T.T. Applications of doped-MXene-based materials for electrochemical energy storage. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 517, 216039.
- 30.Gruber, N.; Galloway, J. An earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 2008, 451, 293–296.
- 31.Zhao, R.; Yan, Q.; Yu, L.; et al. A Bi‐Co corridor construction effectively improving the selectivity of electrocatalytic nitrate reduction toward ammonia by nearly 100%. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2306633.
- 32.Rosca, V.; Duca, M.; Groot, M.; et al. Nitrogen cycle electrocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2209–2244.
- 33.Li, J.; Zhan, G.; Yang, J.; et al. Efficient ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate on strained ruthenium nanoclusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15, 7036–7046.
- 34.Aslam, M.K.; Hussain, I.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; et al. Advances in covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic CO2 reduction: Strategies and future perspectives. Nano Res. Energy 2025, 4, e9120149.
- 35.Liu, X.; Liu, C.; He, X.; et al. Fe-doped Co3O4 nanowire strutted 3D pinewood-derived carbon: A highly selective electrocatalyst for ammonia production via nitrate reduction. Nano Res. 2024, 17, 2276–2282.
- 36.Zhou, X.; Yang, T.; Li, T.; et al. In-situ fabrication of carbon compound NiFeMo-P anchored on nickel foam as bi-functional catalyst for boosting overall water splitting. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120086.
- 37.Pham, H.Q.; Dao, T.-B.-N.; Nguyen, A.Q.K.; et al. Nitrogen-doped, properties and applications for electrochemical hydrogen production. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 341, 103493.
- 38.Li, N.-P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Synergistic effect between Er-doped MoS2 nanosheets and interfacial Mo–N coupling phases for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 1301–1308.
- 39.Zhang, W.-T.; Wang, X.-Q.; Zhang, F.-Q.; et al. Frontiers in high entropy alloys and high entropy functional materials. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 4639–4776.
- 40.Qiao, B.; Wang, A.; Yang, X.; et al. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 634–641.
- 41.Zhang, Y.-Z.; Ao, H.-S.; Dong, Q.; et al. Electrolytes additives for Zn metal anodes: Regulation mechanism and current perspectives. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 4162–4197.
- 42.Fan, Y.; Yan, Y.; Nwokonkwo, O.; et al. Tuning nitrate reduction reaction selectivity via selective adsorption in electrified membranes. Nat. Chem. Eng. 2025, 2, 379–390.
- 43.Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Amination strategy to boost the CO2 electroreduction current density of M–N/C single-atom catalysts to the industrial application level. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2349–2356.
- 44.Liu, L.-L.; Ma, S.-S.; Li, R.-P.; et al. Engineering 4f-2p-3d orbital hybridization on cerium-doped nickel–molybdenum phosphates for energy-saving hydrogen evolution. Rare Met. 2025, 44, 1883–1894.
- 45.Zheng, X.; Li, P.; Dou, S.; et al. Non-carbon-supported single-atom site catalysts for electrocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 2809–2858.
- 46.Chen, F.; Wu, Z.; Gupta, S.; et al. Efficient conversion of low-concentration nitrate sources into ammonia on a Ru-dispersed Cu nanowire electrocatalyst. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 759–767.
- 47.Zhou, B.; Yu, L.; Zhang, W.; et al. Cu1−Fe Dual Sites for Superior Neutral Ammonia Electrosynthesis from Nitrate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202406046.
- 48.Wang, Q.; Wei, H.; Liu, P.; et al. Recent advances in copper-based catalysts for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction toward multi-carbon products. Nano Res. Energy 2024, 3, e9120112.
- 49.Guo, H.; Guo, Z.; Xue, G.; et al. Entropy‐driven stabilization of noble metal single atoms: Advancing ammonia synthesis and energy output in zinc‐nitrate batteries. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2500224.
- 50.Cai, Y.-M.; Li, Y.-H.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Synergistic rare-earth yttrium single atoms and copper phosphide nanoparticles for high-selectivity ammonia electrosynthesis. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 5792–5801.
- 51.Wang, Y.; Hao, F.; Xu, H.; et al. Interfacial water structure modulation on unconventional phase non-precious metal alloy nanostructures for efficient nitrate electroreduction to ammonia in neutral media. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202508617.
- 52.Han, S.; Li, H.; Li, T.; et al. Ultralow overpotential nitrate reduction to ammonia via a three-step relay mechanism. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 402–414.
- 53.Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Dai, H.; et al. Photoelectrochemical nitrate denitrification towards acidic ammonia synthesis on copper-decorated black silicon. Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 9233–9243.
- 54.Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Xu, Z.; et al. Modulating the nitrate reduction pathway on unconventional phase ultrathin nanoalloys for selective ammonia electrosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 26, 23226–23238.
- 55.You, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, J.; et al. Structure reconstruction driven by oxygen vacancies forming P-CoMoO4/Co (OH)2 heterostructure boosting electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 363, 124837.
- 56.Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Chen, K.; et al. Unlocking the coupling potential of built-in electric field and pulsed electroreduction for efficient nitrate to ammonia at low concentrations. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 374, 125387.
- 57.Xu, M.; Dong, S.; Guo, H.; et al. Defective perovskite supported palladium-nickel nanocatalyst for effective electrochemical nitrate reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 375, 125433.
- 58.Wang, R.; Jia, S.; Wu, L.; et al. Tuning the acid hardness nature of Cu catalyst for selective nitrate‐to‐ammonia electroreduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 15, e202425262.
- 59.Chao, G.; Zong, W.; Zhu, J.; et al. Selective mass accumulation at the metal–polymer bridging interface for efficient nitrate electroreduction to ammonia and Zn-nitrate batteries. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 25, 21432–21442.
- 60.Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhong, L.; et al. Boosting ammonia electrosynthesis via interfacial tandem nitrate reduction enabled by an amorphous@ crystalline electrocatalyst. Mater. Today 2025, 85, 49–59.
- 61.Zhu, G.; Bao, W.; Xie, M.; et al. Accelerating tandem electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia via multi‐site synergy in mesoporous carbon‐supported high‐entropy intermetallics. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 5, 2413560.
- 62.Wu, T.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; et al. Three-dimensional Cu3P/Cu heterostructure as robust tandem electrocatalyst for selective electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 358, 124408.
- 63.Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Wang, Z.; et al. Enhanced nitrate-to-ammonia activity on copper–nickel alloys via tuning of intermediate adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12, 5702–5708.
- 64.Guo, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; et al. Pd doping-weakened intermediate adsorption to promote electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on TiO2 nanoarrays for ammonia production and energy supply with zinc–nitrate batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 3938–3944.
- 65.Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Cao, X.; et al. Unveiling cutting‐edge developments in electrocatalytic nitrate‐to‐ammonia conversion. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 16, 2312746.
- 66.Cao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Meng, L.; et al. Recent advances in electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia: Mechanism insight and catalyst design. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 21, 7965–7985.
- 67.Min, B.; Gao, Q.; Yan, Z.; et al. Powering the remediation of the nitrogen cycle: Progress and perspectives of electrochemical nitrate reduction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 41, 14635–14650.
- 68.Vooys, A.; Santen, R.; Veen, J. Electrocatalytic reduction of NO3− on palladium/copper electrodes. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 154, 203–215.
- 69.Dima, G.; Vooys, A.; Koper, M. Electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate at low concentration on coinage and transition-metal electrodes in acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 554, 15–23.
- 70.Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Song, H.; et al. Design strategies towards transition metal single atom catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction–A review. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120082.
- 71.Carvalho, O.; Marks, R.; Nguyen, H.; et al. Role of electronic structure on nitrate reduction to ammonium: A periodic journey. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 32, 14809–14818.
- 72.Guo, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, S.; et al. Achilles’ heel of single atom catalysts towards practical PEMFC application: Degradation mechanisms and regulatory strategies. Nano Res. Energy 2025, 4, e9120144.
- 73.Wu, B.; Wang, T.; Liu, B.; et al. Stable solar water splitting with wettable organic-layer-protected silicon photocathodes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4460.
- 74.Jin, W.; Lee, Y.; Shin, C.; et al. Crystalline silicon photocathode with tapered microwire arrays achieving a high current density of 41.7 mA cm⁻2. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2400178.
- 75.Tayyebi, A.; Mehrotra, R.; Mubarok, M.A.; et al. Bias-free solar NH3 production by perovskite-based photocathode coupled to valorization of glycerol. Nat. Catal. 2024, 7, 510.
- 76.Chiang, C.-H.; Kao, Y.-T.; Wu, P.-H.; et al. Efficient ammonia photosynthesis from nitrate by graphene/Si Schottky junction integrated with Ni–Fe LDH catalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 11179.
- 77.Zhou, J.; Wen, M.; Huang, R.; et al. Regulating active hydrogen adsorbed on grain boundary defects of nano-nickel for boosting ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 2611.
- 78.Ballif, C.; Haug, F.-J.; Boccard, M.; et al. Status and perspectives of crystalline silicon photovoltaics in research and industry. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 597.
- 79.Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Fan, G.; et al. In situ electrochemical reconstruction of cation‐vacancy‐enriched Ni@Ni2P particles in hollow N‐doped carbon nanofibers for efficient nitrate reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202505948.
- 80.Sui, C.; Jiang, Z.; Higueros, G.; et al. Designing electrodes and electrolytes for batteries by leveraging deep learning. Nano Res. Energy 2024, 3, e9120102.
- 81.Wu, Q.; Han, Y.; Wu, L.; et al. Constructing asymmetric Sn‐Cu‐C interface via defective carbon trapped atomic clusters for efficient neutral nitrate reduction. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2505743.
- 82.Yin, H.; He, J.; Xiao, B.; et al. Advances and prospects of g-C3N4 in lithium-sulfur batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2024, 3, e9120138.
- 83.Jang, D.; Maeng, J.; Kim, J.; et al. Boosting electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction for ammonia synthesis by plasma-induced oxygen vacancies over MnCuOx. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 610, 155521.
- 84.Messias, I.; Winkler, M.E.G.; Costa, G.F.; et al. Role of structural and compositional changes of Cu2O nanocubes in nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 9034–9044.
- 85.Liu, D.; Qiao, L.; Peng, S.; et al. Recent advances in electrocatalysts for efficient nitrate reduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2303480.
- 86.Zhang, B.; Dai, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. Defect-induced triple synergistic modulation in copper for superior electrochemical ammonia production across broad nitrate concentrations. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2816.
- 87.Sun, Y.; Shi, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Electroreduction of nitrate into ammonia on Co3O4: Mechanistic insights into Co2+-promoted NO3RR performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 512, 162506.
- 88.Maeng, J.; Jang, D.; Ha, J.; et al. Oxygen Vacancy‐Controlled CuOx/N, Se Co‐Doped Porous Carbon via Plasma‐Treatment for Enhanced Electro‐Reduction of Nitrate to Green Ammonia. Small 2024, 20, 2403253.
- 89.Mei, W.; Chang, C.-W.; Li, Z.; et al. Robust oxygen-vacancy-engineered Co(OH)2/Cu heterostructures boost nitrate electroreduction to ammonia beyond 2 A cm−2. Adv. Mater. 2025, 2507363.
- 90.Song, M.; Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Fe and Cu double-doped Co3O4 nanorod with abundant oxygen vacancies: A high-rate electrocatalyst for tandem electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 16641–16651.
- 91.Bui, T.S.; Lovell, E.C.; Daiyan, R.; et al. Defective metal oxides: Lessons from CO2RR and applications in NOxRR. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2205814.
- 92.Gu, L.; Cong, Y.; Wu, Z.; et al. Multiscopic microenvironment engineering in nitrate electrocatalytic reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2500316.
- 93.Li, H.; Ma, N.; Long, Y.; et al. The electrocatalytic role of oxygen vacancy in nitrate reduction reactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2024, 16, 46312–46322.
- 94.Jeong, Y.J.; Tan, R.; You, T.H.; et al. Boosting nitrate-to-ammonia electrosynthesis via hierarchically branched TiO2 nanorods. J. Mater. Chem. A 2025, 13, 28295–28304.
- 95.Lv, Y.; Ren, J.; Jiang, M.; et al. A-site deficiency-mediated creation of oxygen vacancies in LaMnO3-δ nanofibers for efficient nitrate reduction. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 8094–8102.
- 96.Deng, Z.-W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, J.; et al. Rational design and energy catalytic application of high-loading single-atom catalysts. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 4844–4866.
- 97.Yang, L.-H.; Lin, Z.-Q.; Yu, C.-H.; et al. Polarity-inverted perovskite LaFeO3 promotes nitrate electroreduction by intensifying the adsorption effect. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2026, 245, 164–174.
- 98.Wu, Q.; Fan, X.; Shan, B.; et al. Insights into lattice oxygen and strains of oxide-derived copper for ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3479.
- 99.Yoon, A.; Bai, L.; Yang, F.; et al. Revealing catalyst restructuring and composition during nitrate electroreduction through correlated operando microscopy and spectroscopy. Nat. Mater. 2025, 24, 762–769.
- 100.Fu, W.; Yin, Y.; He, S.; et al. Electrocatalytic conversion of nitrate to ammonia on the oxygen vacancy engineering of zinc oxide for nitrogen recovery from nitrate-polluted surface water. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120279.
- 101.Li, P.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; et al. Pulsed nitrate-to-ammonia electroreduction facilitated by tandem catalysis of nitrite intermediates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6471.
- 102.Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Li, J.; et al. High-ammonia selective metal–organic framework–derived Co-doped Fe/Fe2O3 catalysts for electrochemical nitrate reduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, 2115504119.
- 103.Li, J.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Subnanometric alkaline-earth oxide clusters for sustainable nitrate to ammonia photosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1098.
- 104.Wei, Q.; He, Y.; Ding, G.; et al. Pd orbital hybridization and lattice strain induced by B, Co-co-doped Cu promote the electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 161014.
- 105.Xu, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Lattice-strain and Lewis acid sites synergistically promoted nitrate electroreduction to ammonia over PdBP nanothorn arrays. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 16290–16296.
- 106.Gao, Q.; Yao, B.; Liu, Y.; et al. Strain relaxation enhances ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate on Cu/CuAu core/shell nanocrystals with ordered intermetallic layers. Chem. Catal. 2025, 5, 101328.
- 107.Wang, Y.; Hao, F.; Sun, M.; et al. Crystal phase engineering of ultrathin alloy nanostructures for highly efficient electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313548.
- 108.Liu, S.; Miao, W.; Ma, K.; et al. Defect-rich AuCu@Ag nanowires with exclusive strain effect accelerate nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2024, 350, 123919.
- 109.Fu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Enhancing electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia over Cu nanosheets via facet tandem catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303327.
- 110.Liu, H.; Jia, S.; Wu, L.; et al. Circumventing scaling relations via gradient orbital coupling promotes ammonia electrosynthesis on Cobalt catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202510478.
- 111.Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Duan, R.; et al. Reaction-driven formation of anisotropic strains in FeTeSe nanosheets boosts low-concentration nitrate reduction to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3595.
- 112.Liu, Z.; Li, Y.-Q.; Tan, Y.-F.; et al. Sulfur-modulated charge-asymmetry Cu–Zn bimetallic nanoclusters for efficient CO2 electroreduction. Rare Met. 2025, 44, 6211–6222.
- 113.Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, G.; et al. Electronic structure tuning in Cu–Co dual single atom catalysts for enhanced COOH* spillover and electrocalytic CO2 reduction activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 23, e202504423.
- 114.Gao, Q.; Pillai, H.S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Breaking adsorption-energy scaling limitations of electrocatalytic nitrate reduction on intermetallic CuPd nanocubes by machine-learned insights. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2338.
- 115.Lu, Y.; Yue, F.; Liu, T.; et al. Size-effect induced controllable Cu0-Cu+ sites for ampere-level nitrate electroreduction coupled with biomass upgrading. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2392.
- 116.Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Self-reducing Cu2O/Cu nanosheet interface for efficient electrocatalytic production of ammonium from nitrate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 371, 125254.
- 117.Li, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Nanoflower-Like CuPd/CuO heterostructure for an energy-output electrocatalytic system coupling ammonia electrosynthesis and zinc-nitrate battery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2501527.
- 118.Zheng, S.; Yang, X.; Shi, Z.-Z.; et al. The loss of interfacial water-adsorbate hydrogen bond connectivity position surface-active hydrogen as a crucial intermediate to enhance nitrate reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 26965–26974.
- 119.Li, X.; Rong, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Modulating the local coordination environment of single-atom catalysts for enhanced catalytic performance. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 7, 1842–1855.
- 120.Fei, H.; Dong, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Single atom electrocatalysts supported on graphene or graphene-like carbons. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 20, 5207–5241.
- 121.Gong, Y.; Jiao, L.; Qian, Y.; et al. Regulating the coordination environment of MOF‐templated single‐atom nickel electrocatalysts for boosting CO2 reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7, 2705–2709.
- 122.Liang, J.; Yu, Q.; Yang, X.; et al. A systematic theoretical study on FeOx-supported single-atom catalysts: M1/FeOx for CO oxidation. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 3, 1599–1611.
- 123.Zhang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, W.; et al. Coordination environment manipulation of single atom catalysts: Regulation strategies, characterization techniques and applications. Coordin. Chem. Rev. 2024, 515, 215952.
- 124.Zhu, Y.; Sokolowski, J.; Song, X.; et al. Engineering local coordination environments of atomically dispersed and heteroatom‐coordinated single metal site electrocatalysts for clean energy‐conversion. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 11, 1902844.
- 125.Gao, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, D. Microenvironment engineering of single/dual‐atom catalysts for electrocatalytic application. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 31, 2209654.
- 126.Wu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, S.; et al. Engineering the coordination sphere of isolated active sites to explore the intrinsic activity in single-atom catalysts. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 136.
- 127.Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Discriminating catalytically active FeNx species of atomically dispersed Fe–N–C catalyst for selective oxidation of the C–H bond. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 31, 10790–10798.
- 128.Du, J., Lin, Q.Y., Zhang, J.Q.; et al. N-doped core–shell mesoporous carbon spheres embedded by Ni nanoparticles for CO2 electroreduction. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 2284–2293.
- 129.Jakub, Z.; Hulva, J.; Meier, M.; et al. Local structure and coordination define adsorption in a model Ir1/Fe3O4 single‐atom catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 39, 13961–13968.
- 130.Chen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Da, Y.; et al. Mechanistic insights and advances in electrode/electrolyte interfaces for efficient electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to C2 products. SmartMat 2025, 6, e1324.
- 131.Wang, Z.; Hao, X.; Jiang, Z.; et al. C and N hybrid coordination derived Co–C–N complex as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 48, 15070–15073.
- 132.Yang, Q.; Jia, Y.; Wei, F.; et al. Understanding the activity of Co‐N4−xCx in atomic metal catalysts for oxygen reduction catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15, 6122–6127.
- 133.Chen, W.; Pei, J.; He, C.; et al. Single tungsten atoms supported on MOF‐derived N‐doped carbon for robust electrochemical hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 30, 1800396.
- 134.Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wen, W.; et al. Atomically dispersed unsaturated Cu-N3 sites on high-curvature hierarchically porous carbon nanotube for synergetic enhanced nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302651.
- 135.Liu, K.; Sun, Z.; Peng, X.; et al. Tailoring asymmetric RuCu dual-atom electrocatalyst toward ammonia synthesis from nitrate. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2167.
- 136.Talib, S.H.; Jiang, X.; Feng, S.; et al. Theoretical catalytic performance of single-atom catalysts M1/PW12O40 for alkyne hydrogenation materials. Nano Res. Energy 2024, 3, e9120128.
- 137.Yin, L.; Zhang, S.; Sun, M.; et al. Heteroatom‐driven coordination fields altering single cerium atom sites for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 28, 2302485.
- 138.Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Gao, S.; et al. Proton driving mechanism revealed in sulfur-doped single-atom FeN2O2 carbon dots for superior peroxidase activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 30, e202504575.
- 139.Ci, H.; Shi, Z.; Wang, M.; et al. A review in rational design of graphene toward advanced Li–S batteries. Nano Res. Energy 2023, 2, e9120054.
- 140.Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; et al. Breaking local charge symmetry of iron single atoms for efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, 39, e202308044.
- 141.Ajmal, S.; Kumar, A.; Mushtaq, M.; et al. Uniting synergistic effect of single‐Ni site and electric field of B‐Bridged‐N for boosted electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Small 2024, 20, 32, 2310082.
- 142.Jin, H.-L.; Li, Q.-N.; Tian, Y.-Y.; et al. Machine-learning-aided Au-based single-atom alloy catalysts discovery for electrochemical NO reduction reaction to NH3. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 5813–5822.
- 143.Wu, Q.; Fan, X.; Liu, K.; et al. Efficient and selective electroreduction of nitrate to ammonia via interfacial engineering of B-doped Cu nanoneedles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 361, 124597.
- 144.Wang, Z.; Lian, X.; Yang, R.; et al. Planar chlorination engineering enhances the polarity of the Fe–N4 site for boosting nitrate electroreduction. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 8230–8238.
- 145.Xiang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, P.; et al. Inter‐site distance effect in electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202500644.
- 146.Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, A.; et al. Near‐and long‐range electronic modulation of single metal sites to boost CO2 electrocatalytic reduction. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209298.
- 147.Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Zheng, M.; et al. Fe/Cu diatomic catalysts for electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3634.
- 148.Chen, Z.; Sang, K.; Ye, L.; et al. Tandem switch‐triggered on‐demand synthesis of aromatic amines in high yields. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 18, e202424847.
- 149.Luo, W.; Liu, K.; Luo, T.; et al. Promoting C–F bond activation for perfluorinated compounds decomposition via atomically synergistic Lewis and Brønsted acid sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 9, 7391–7399.
- 150.Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; et al. Nitrate electroreduction: Mechanism insight, in situ characterization, performance evaluation, and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 6720–6733.
- 151.Jia, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Boosting selective nitrate electroreduction to ammonium by constructing oxygen vacancies in TiO2. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 3533–3540.
- 152.Yan, K.; Ge, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Pd ensemble sites tuned local environment of Cu catalysts for matching propyne semi‐hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 19, e202503263.
- 153.Wang, L.; Gui, W.-K.; Jiang, S.; et al. Bi2S3 nanofiber bunch for highly efficient CO2 electroreduction to formate at low overpotential. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 3391–3399.
- 154.Morales, C.; Cave, E.; Nitopi, S.; et al. Improved CO2 reduction activity towards C2+ alcohols on a tandem gold on copper electrocatalyst. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 764–771.
- 155.Lou, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, S.; et al. Phase-dependent electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia on Janus Cu@ Ni tandem catalyst. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7, 5098–5108.
- 156.Li, X.; Shen, P.; Li, X.; et al. Sub-nm RuOx clusters on Pd metallene for synergistically enhanced nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2, 1081–1090.
- 157.Li, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. A fundamental viewpoint on the hydrogen spillover phenomenon of electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3502.
- 158.Feng, J.; Hu, Q.; Yue, X.; et al. Bimetallic phthalocyanine catalyst for ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate reduction across all pH ranges. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2025, 366, 125027.
- 159.Zhu, J.; Hu, L.; Zhao, P.; et al. Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 2, 851–918.
- 160.Xiao, H.; Lv, Y.; Hua, W.; et al. Atomically dispersed dual frustrated Lewis pairs for efficient relay conversion of nitrate into ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 377, 125501.
- 161.Wan, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Synergy between Fe and Mo single atom catalysts for ammonia electrosynthesis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 347, 123816.
- 162.Shen, F.; He, S.; Tang, X.; et al. Breaking linear scaling relation limitations on a dual‐driven single‐atom copper‐tungsten oxide catalyst for ammonia synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 21, e202423154.
- 163.Chen, H.; Qi, K.; Dong, X.; et al. Ligand-mediated activity of Cu4 clusters boosts electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202510429. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202510429.
- 164.Zhang, L.; Cai, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Unlocking high-current-density nitrate reduction and formaldehyde oxidation synergy for scalable ammonia production and fixation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 6, 2804–2816.
- 165.Wan, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, N.; et al. Axial chlorine-induced symmetry-breaking iron single-atom catalyst for electrochemical ammonia synthesis. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 6, 4507–4518.
- 166.Guan, J.; Cai, L.; Li, W.; et al. Boosting nitrate electroreduction to ammonia on atomic Ru-Co pair sites in hollow spinels. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 358, 124387.
- 167.Xia, J.; Xu, J.; Yu, B.; et al. A metal–sulfur–carbon catalyst mimicking the two‐component architecture of nitrogenase. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 45, e202412740.
- 168.Wang, B.; Ma, J.; Yang, R.; et al. Bridging nickel‐MOF and copper single atoms/clusters with H‐substituted graphdiyne for the tandem catalysis of nitrate to ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 30, e202404819.
- 169.Liu, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Shear‐strained Pd single‐atom electrocatalysts for nitrate reduction to ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 43, e202411396.
- 170.Zhao, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; et al. Isolated rhodium atoms activate porous TiO2 for enhanced electrocatalytic conversion of nitrate to ammonia. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2, 2411705.
- 171.Park, J.; Theerthagiri, J.; Yodsin, N.; et al. CO2 laser‐stabilized Ni‐Co dual single‐atomic sites for energy generation and ammonia harvesting. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 30, 2506137.
- 172.Zhong, W.; Hong, Q.; Ai, X.; et al. RhNi bimetallenes with lattice-compressed Rh skin towards ultrastable acidic nitrate electroreduction. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 23, 2314351.
- 173.Messe, A.; Napier, C.; Kim, D.; et al. Underpotential deposition of 3D transition metals: Versatile electrosynthesis of single-atom catalysts on oxidized carbon supports. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 19, 2311341.
- 174.Zhang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, K.; et al. Conjugated coordination polymer as a new platform for efficient and selective electroreduction of nitrate into ammonia. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 10, 2209855.
- 175.Ni, J.; Yan, J.; Li, F.; et al. Atomic Co-P catalytic pair drives efficient electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 28, 2400065.
- 176.Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. Concurrently selective electrosynthesis of ammonia and glycolic acid over cathodic single‐atom cobalt and anodic PdNi alloying catalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 6, 2415046.
- 177.Song, J.; Qian, S.; Yang, W.; et al. Nano-single-atom heterointerface engineering for pH-universal electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 49, 2409089.
- 178.Lin, H.; Wei, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Bi1‐CuCo2O4 hollow carbon nanofibers boosts NH3 production from electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 51, 2409696.
- 179.Zhang, N.; Zhang, G.; Shen, P.; et al. Lewis acid Fe‐V pairs promote nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 13, 2211537.
- 180.Zhang, G.; Wang, F.; Chen, K.; et al. Atomically dispersed Sn confined in FeS2 for nitrate‐to‐ammonia electroreduction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 1, 2305372.
- 181.Liu, L.; Xiao, T.; Fu, H.; et al. Construction and identification of highly active single-atom Fe1-NC catalytic site for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2023, 323, 122181.
- 182.Yu, J.; Gao, R.; Guo, X.; et al. Electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia on AuCu single-atom alloy aerogels under wide potential window. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 4, e202415975.
- 183.Xie, M.; Tang, S.; Li, Z.; et al. Intermetallic single-atom alloy In–Pd bimetallene for neutral electrosynthesis of ammonia from nitrate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 25, 13957–13967.
- 184.Ji, X.; Sun, K.; Liu, Z.; et al. Identification of dynamic active sites among Cu species derived from MOFs@ CuPc for electrocatalytic nitrate reduction reaction to ammonia. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 1, 110.
- 185.Xiang, T.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Boosting active hydrogen generation via ruthenium single atoms for efficient electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 365, 124943.
- 186.Li, Q.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Coupling ZnN4 atomic sites with graphitic nitrogen for enhanced ammonium production via electrocatalytic nitrate reduction. Small 2025, 21, 6, 2409925.
- 187.Wei, J.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Cobalt-copper dual-atom catalyst boosts electrocatalytic nitrate reduction from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 493, 138264.
- 188.Liu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wang, P.; et al. Pyridine-N-rich Cu single-atom catalyst boosts nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. App. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 340, 123228.
- 189.Weng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Active sites of copper-complex catalytic materials for electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 415.
- 190.Ren, Y.; Tian, F.; Jin, L.; et al. Fluidic MXene electrode functionalized with iron single atoms for selective electrocatalytic nitrate transformation to ammonia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 28, 10458–10466.
- 191.Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; et al. Single-atom Cu and Zn vacancy synergy in NiFe-LDH boosts metal–support interaction for high-efficiency nitrate-to-ammonia electroreduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 22, 11414–11425.
- 192.Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; et al. Atomically dispersed iron & iron clusters synergistically accelerate electrocatalytic ammonia synthesis. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158785.
- 193.Hao, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, R.; et al. Integrating few-atom layer metal on high-entropy alloys to catalyze nitrate reduction in tandem. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9020.
- 194.Yan, Z.; Gao, W.; Zhong, C.; et al. Regulating spin state of Fe (III) by the Mo single atom anchored in the (001) crystal face of α-Fe2O3 to achieve efficient electrocatalytic nitrate to synthesize ammonia. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 366, 125008.
- 195.Chen, K.; Ma, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Single‐atom Bi alloyed Pd metallene for nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 12, 2209890.
- 196.Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Dong, F.; et al. N‐coordinated Cu–Ni dual‐single‐atom catalyst for highly selective electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia. Small 2023, 19, 20, 2207695.
- 197.Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; et al. Gram‐scale ammonia synthesis via electrochemical nitrate reduction using enzyme‐inspired dual‐atomic Cu catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202510139.
- 198.Zhao, X.; Geng, Q.; Dong, F.; et al. Boosting the selectivity and efficiency of nitrate reduction to ammonia with a single-atom Cu electrocatalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143314.
- 199.Duan, W.; Chen; Zhu, Y.; et al. Synergistic effects of Co single atoms and Co nanoparticles for electrocatalytic nitrate-to-ammonium conversion in strongly acidic wastewater. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2025, 363, 124812.
- 200.Du, C.; Lu, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Selectively reducing nitrate into NH3 in neutral media by PdCu single-atom alloy electrocatalysis. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 16, 10560–10569.
- 201.Gu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; et al. Coordination desymmetrization of copper single‐atom catalyst for efficient nitrate reduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 38, e202409125.
- 202.Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Rational ligand design of conjugated coordination polymers for efficient and selective nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 27, 2418681.
- 203.Wang, Z.; Yi, Z.; Wong, L.; et al. Oxygen doping cooperated with Co‐N‐Fe dual‐catalytic sites: Synergistic mechanism for catalytic water purification within nanoconfined membrane. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 30, 2404278.
- 204.Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Frustrated Lewis pairs on Zr single atoms supported N‐doped TiO2‐x catalysts for electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 36, 2401094.
- 205.Zhao, T.; Chen, K.; Xu, X.; et al. Homonuclear dual-atom catalysts embedded on N-doped graphene for highly efficient nitrate reduction to ammonia: From theoretical prediction to experimental validation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2023, 339, 123156.
- 206.Shen, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; et al. N, O trans-coordinating silver single-atom catalyst for robust and efficient ammonia electrosynthesis from nitrate. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 331, 122687.
- 207.Zhang, A.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Doping regulation in transition metal compounds for electrocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 17, 9817–9844.
- 208.Wang, K.; Mao, R.; Liu, R.; et al. Intentional corrosion-induced reconstruction of defective NiFe layered double hydroxide boosts electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia. Nat. Water. 2023, 1, 1068–1078.
- 209.Wang, T.; Tao, L.; Zhu, X.; et al. Combined anodic and cathodic hydrogen production from aldehyde oxidation and hydrogen evolution reaction. Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 66–73.
- 210.Zhong, D.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Dinuclear metal synergistic catalysis for energy conversion. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 9, 3170–3214.
- 211.Cai, Z.; Zhou, D.; Wang, M.; et al. Introducing Fe2+ into nickel–iron layered double hydroxide: Local structure modulated water oxidation activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 30, 9392–9396.
- 212.Wei, C.; Feng, Z.; Baisariyev, M.; et al. Valence change ability and geometrical occupation of substitution cations determine the pseudocapacitance of spinel ferrite XFe2O4 (X = Mn, Co, Ni, Fe). Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 12, 4129–4133.
- 213.Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. In Situ X-ray absorption near-edge structure study of advanced NiFe(OH)x electrocatalyst on carbon paper for water oxidation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 34, 19573–19583.
- 214.Tylus, U.; Jia, Q.; Strickland, K.; et al. Elucidating oxygen reduction active sites in pyrolyzed metal–nitrogen coordinated non-precious-metal electrocatalyst systems. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 17, 8999–9008.
- 215.Wang, X.; Cullen, D.; Pan, Y.; et al. Nitrogen‐coordinated single cobalt atom catalysts for oxygen reduction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 11, 1706758.
- 216.Wan, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zuo, Y.; et al. Interfacial hydrogen-bond modulation of dynamic catalysts for nitrate electroreduction to ammonia. Energy Environ. Sci. 2025, 18, 7460–7469.
- 217.Zhong, J.; Duan, H.; Cai, M.; et al. Cascade electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate to ammonia using bimetallic covalent organic frameworks with tandem active sites. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 137, e202507956.
- 218.Li, X.; Xia, S.; Yang, S.; et al. Asymmetric manganese sites in covalent organic frameworks for efficient nitrate‐to‐ammonia electrocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 29, e202507479.
- 219.Pan, F.; Fang, L.; Li, B.; et al. N and OH-immobilized Cu3 clusters in situ reconstructed from single-metal sites for efficient CO2 electromethanation in bicontinuous mesochannels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 2, 1423–1434.
- 220.Ding, Z.; Pang, Y.; Ma, A.; et al. Single-atom catalysts based on two-dimensional metalloporphyrin monolayers for electrochemical nitrate reduction to ammonia by first-principles calculations and interpretable machine learning. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 80, 586–598.
- 221.Lv, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, M.; et al. High-throughput screening for efficient dual-atom catalysts in electrocatalytic nitrate reduction to ammonia via dissociation–association mechanism. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 6733–6746.
How to Cite
Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, A.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Pang, S. Rational Design of Nano and Atomically Dispersed Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Ammonia Synthesis from Nitrate. eChem 2025, 1 (1), 2. https://doi.org/10.53941/echem.2025.100002.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


