Anion exchange membrane water electrolysis (AEMWE) holds promise for low-cost hydrogen production, thereby addressing the energy crisis humanity faces. Of the two half-reactions, the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and the oxygen evolution reaction (OER), the latter, with sluggish dynamics, is the crucial one toward electrocatalytic water splitting, which requires a non-noble metal catalyst possessing high performance to make the reaction process efficient and economical. Such a condition requires a proper understanding of the reaction mechanism, careful design and optimization of catalyst materials, and maintenance of catalyst durability under AEMWE conditions during long-term operation. NiFe layered double hydroxide (NiFe-LDH), with its unique chemistry and electronic structure that facilitates moderate intermediate adsorption energies and offers tolerance to site deactivation, is of considerable interest as an electrocatalyst. In this review, we systematically discuss the OER catalytic mechanism in alkaline water electrolysis and provide evaluative criteria of the catalytic performance. Also, we summarize the corresponding synthesis strategies and characterization methods for NiFe-LDH catalysts, including morphology control, elemental doping, interfacial engineering, and defect construction. Furthermore, we address the recent bottleneck in developing NiFe-LDH catalysts for the OER under alkaline conditions and their application in AEMWE. Unlike previous reviews that separately discussed OER electrocatalysts or AEMWE operation, this work uniquely bridges the fundamental design of NiFe-LDH catalysts with their integration and performance in practical anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer systems. Finally, we share our thoughts regarding future development directions of NiFe-LDH catalysts toward alkaline OER, a critical step towards the commercialization of water electrolysis technology for green hydrogen production.
- Open Access
- Review
Progress and Perspectives on NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Catalysts for the Alkaline Oxygen Evolution Reaction
Author Information
Received: 17 Sep 2025 | Revised: 16 Oct 2025 | Accepted: 16 Oct 2025 | Published: 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
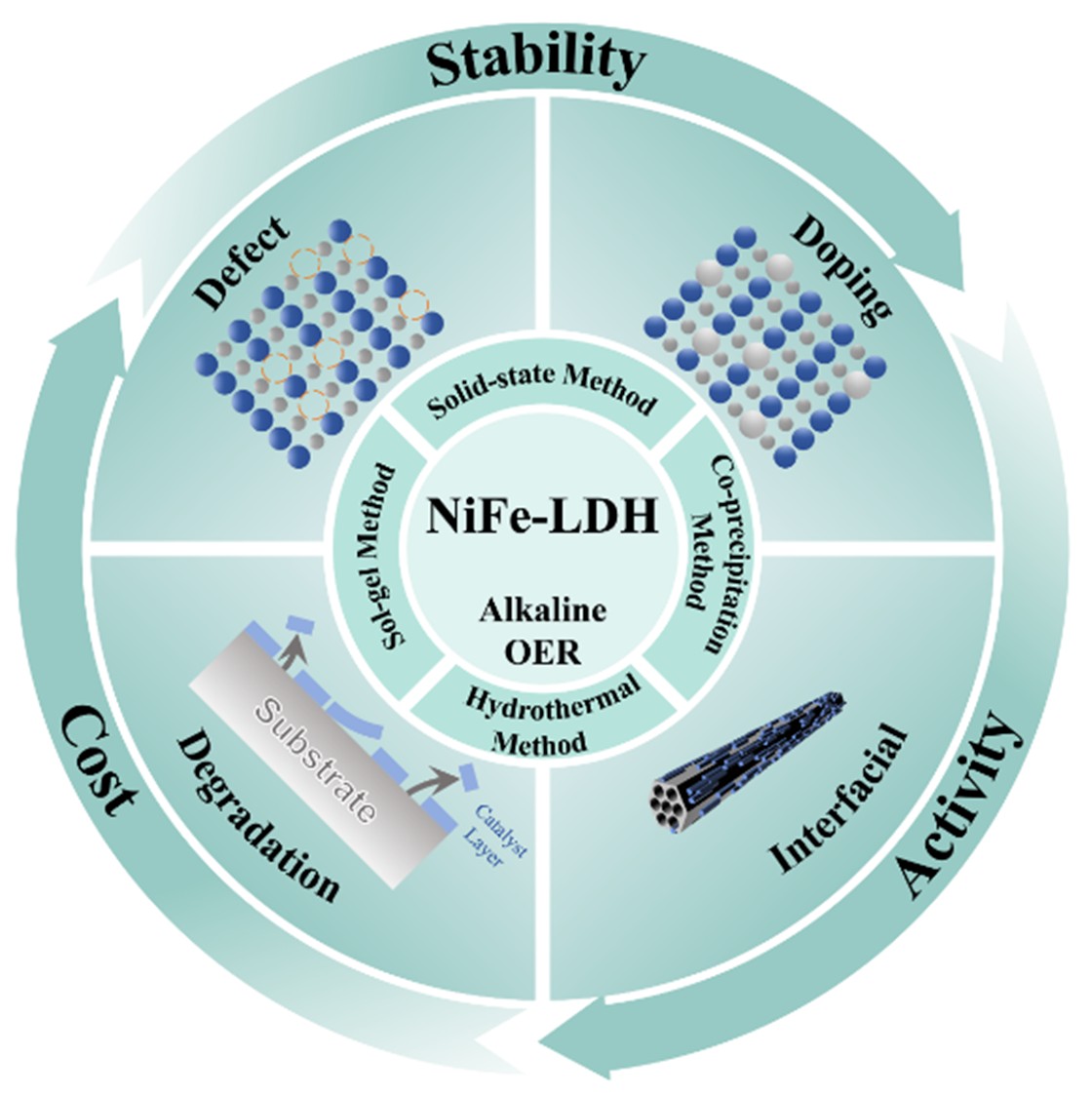
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
NiFe layered double hydroxide | electrocatalysis | water splitting | oxygen evolution reaction | anion exchange membrane water electrolyzer
References
- 1.Du, N.; Roy, C.; Peach, R.; et al. Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11830–11895.
- 2.Zhang, R.; Hanaoka, T. Cross-Cutting Scenarios and Strategies for Designing Decarbonization Pathways in the Transport Sector toward Carbon Neutrality. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3629.
- 3.Zou, C.; Xiong, B.; Xue, H.; et al. The Role of New Energy in Carbon Neutral. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2021, 48, 480–491.
- 4.Kanan, M.W.; Surendranath, Y.; Nocera, D.G. Cobalt–Phosphate Oxygen-Evolving Compound. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 38, 109–114.
- 5.Suntivich, J.; May, K.J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; et al. Perovskite Oxide Optimized for Oxygen Evolution Catalysis from Molecular Orbital Principles. Science 2011, 334, 1383–1385.
- 6.David, M.; Ocampo-Martínez, C.; Sánchez-Peña, R. Advances in Alkaline Water Electrolyzers: A Review. J. Energy Storage 2019, 23, 392–403.
- 7.Sebbahi, S.; Assila, A.; Alaoui Belghiti, A.; et al. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Alkaline Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 82, 583–599.
- 8.Xu, Y.; Cai, S.; Chi, B.; et al. Technological Limitations and Recent Developments in a Solid Oxide Electrolyzer Cell: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 548–591.
- 9.Lin, C.; Li, J.-L.; Li, X.; et al. In-Situ Reconstructed Ru Atom Array on α-MnO2 with Enhanced Performance for Acidic Water Oxidation. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 1012–1023.
- 10.Wu, Z.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Li, B.; et al. Non-Iridium-Based Electrocatalyst for Durable Acidic Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Nat. Mater. 2023, 22, 100–108.
- 11.King, L.A.; Hubert, M.A.; Capuano, C.; et al. A Non-Precious Metal Hydrogen Catalyst in a Commercial Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Electrolyser. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1071–1074.
- 12.Li, G.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Core-Shell Structured V-Doped CoPx@FeOOH for Efficient Seawater Electrolysis. ChemCatChem 2025, 17, e00850.
- 13.Henkensmeier, D.; Cho, W.C.; Jannasch, P.; et al. Separators and Membranes for Advanced Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6393–6443.
- 14.Niether, C.; Faure, S.; Bordet, A.; et al. Improved Water Electrolysis Using Magnetic Heating of FeC–Ni Core–Shell Nanoparticles. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 476–483.
- 15.Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Kong, H.; et al. Non-Precious-Metal Catalysts for Alkaline Water Electrolysis: Operando Characterizations, Theoretical Calculations, and Recent Advances. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 9154–9196.
- 16.Tang, Z.; Wu, B.; Yan, K.; et al. Long-Term Stability for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis: Recent Development and Future Perspectives. Future Batter. 2025, 5, 100024.
- 17.Li, W.; Li, F.; Yang, H.; et al. A Bio-Inspired Coordination Polymer as Outstanding Water Oxidation Catalyst via Second Coordination Sphere Engineering. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5074.
- 18.Park, S.; Liu, L.; Demirkır, Ç.; et al. Solutal Marangoni Effect Determines Bubble Dynamics during Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution. Nat. Chem. 2023, 15, 1532–1540.
- 19.Zheng, W.; He, L.; Tang, T.; et al. Poly(Dibenzothiophene-Terphenyl Piperidinium) for High-Performance Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Angew. Chem. 2024, 63, e202405738.
- 20.Kumar, R.; Singh, R.; Dutta, S. Review and Outlook of Hydrogen Production through Catalytic Processes. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 2601–2629.
- 21.Vincent, I.; Bessarabov, D. Low Cost Hydrogen Production by Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1690–1704.
- 22.Niu, H.J.; Ran, N.; Zhou, W.; et al. Synergistic Atomic Environment Optimization of Nickel-Iron Dual Sites by Co Doping and Cr Vacancy for Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 2607–2615.
- 23.Gong, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; et al. An Advanced Ni-Fe Layered Double Hydroxide Electrocatalyst for Water Oxidation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8452–8455.
- 24.Abellán, G.; Carrasco, J.A.; Coronado, E.; et al. Alkoxide-Intercalated CoFe-Layered Double Hydroxides as Precursors of Colloidal Nanosheet Suspensions: Structural, Magnetic and Electrochemical Properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 3723–3731.
- 25.Carrasco, J.A.; Sanchis-Gual, R.; Silva, A.S.-D.; et al. Influence of the Interlayer Space on the Water Oxidation Performance in a Family of Surfactant-Intercalated NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxides. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 6798–6807.
- 26.Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.; et al. Sub-3 nm Ultrafine Monolayer Layered Double Hydroxide Nanosheets for Electrochemical Water Oxidation. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1703585.
- 27.Song, F.; Hu, X. Exfoliation of Layered Double Hydroxides for Enhanced Oxygen Evolution Catalysis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4477.
- 28.Tang, J.; Xu, X.; Tang, T.; et al. Perovskite-Based Electrocatalysts for Cost-Effective Ultrahigh-Current-Density Water Splitting in Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer Cell. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2201099.
- 29.Dekel, D.R. Review of Cell Performance in Anion Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 158–169.
- 30.Couture, G.; Alaaeddine, A.; Boschet, F.; et al. Polymeric Materials as Anion-Exchange Membranes for Alkaline Fuel Cells. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1521–1557.
- 31.Villagra, A.; Millet, P. An Analysis of PEM Water Electrolysis Cells Operating at Elevated Current Densities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 9708–9717.
- 32.Park, Y.S.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Jang Myeong, M.J.; et al. Ternary Layered Double Hydroxide Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrocatalyst for Anion Exchange Membrane Alkaline Seawater Electrolysis. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 75, 127–134.
- 33.Vincent, I.; Kruger, A.; Bessarabov, D. Development of Efficient Membrane Electrode Assembly for Low Cost Hydrogen Production by Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 10752–10761.
- 34.Li, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Zwitterion-Modified NiFe OER Catalyst Achieving Ultrastable Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis via Dynamic Alkaline Microenvironment Engineering. Angew. Chem. 2025, 64, e202505924.
- 35.Koper, M.T.M. Thermodynamic Theory of Multi-Electron Transfer Reactions: Implications for Electrocatalysis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 660, 254–260.
- 36.Lin, G.; Dong, A.; Li, Z.; et al. An Interlayer Anchored NiMo/MoO2 Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis at High Current Density. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2507525.
- 37.Vincent, I.; Lee, E.-C.; Kim, H.-M. Highly Cost-Effective Platinum-Free Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis for Large Scale Energy Storage and Hydrogen Production. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 37429–37438.
- 38.Grigoriev, S.A.; Fateev, V.N.; Bessarabov, D.G.; et al. Current Status, Research Trends, and Challenges in Water Electrolysis Science and Technology. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 26036–26058.
- 39.Du, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Anion Exchange Membrane Seawater Electrolysis at 1.0 A cm−2 With an Anode Catalyst Stable for 9000 H. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2416661.
- 40.Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Z.; et al. POM-Intercalated NiFe-LDH as Enhanced OER Catalyst for Highly Efficient and Durable Water Electrolysis at Ampere-Scale Current Densities. ACS Catal. 2025, 15, 6486–6496.
- 41.Cui, X.; Ding, Y.; Tang, T.; et al. Hierarchical NiFeMoO4 Precatalyst Reconstructed NiFeOOH Anodes for Efficient and Durable Anion-Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 17, 29659–29668.
- 42.Mirabella, F.; Müllner, M.; Touzalin, T.; et al. Ni-Modified Fe3O4(001) Surface as a Simple Model System for Understanding the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 389, 138638.
- 43.Oener, S.Z.; Foster, M.J.; Boettcher, S.W. Accelerating Water Dissociation in Bipolar Membranes and for Electrocatalysis. Science 2020, 369, 1099–1103.
- 44.Zeng, K.; Zhang, D. Recent Progress in Alkaline Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production and Applications. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 307–326.
- 45.Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Shou, D.; et al. A Highly-Flexible and Breathable Photo-Thermo-Electric Membrane for Energy Harvesting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2470067.
- 46.Jiang, T.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, C.; et al. Novel Fe-Modulating Raney-Ni Electrodes toward High-Efficient and Durable AEM Water Electrolyzer. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2501634.
- 47.Trasatti, S. Electrocatalysis in the Anodic Evolution of Oxygen and Chlorine. Electrochim. Acta 1984, 29, 1503–1512.
- 48.Seh, Z.W.; Kibsgaard, J.; Dickens, C.F.; et al. Combining Theory and Experiment in Electrocatalysis: Insights into Materials Design. Science 2017, 355, 4998.
- 49.McCrory, C.C.L.; Jung, S.; Peters, J.C.; et al. Benchmarking Heterogeneous Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16977–16987.
- 50.Lamy, C.; Millet, P. A Critical Review on the Definitions Used to Calculate the Energy Efficiency Coefficients of Water Electrolysis Cells Working under Near Ambient Temperature Conditions. J. Power Sources 2020, 447, 227350.
- 51.Wang, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, M.; et al. Precious Metal-Free Approach to Hydrogen Electrocatalysis for Energy Conversion: From Mechanism Understanding to Catalyst Design. Nano. Energy 2017, 42, 69–89.
- 52.Wang, M.; Yan, C.; Liu, T.; et al. Enhancing Built-In Electric Field via Balancing Interfacial Atom Orbit Hybridization at Boride@Sulfide Heterostructure for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202425657.
- 53.Li, J.; Zheng, G. One-Dimensional Earth-Abundant Nanomaterials for Water-Splitting Electrocatalysts. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600380.
- 54.Lei, C.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; et al. Efficient Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution on Atomically Dispersed Ni–Nx Species Anchored Porous Carbon with Embedded Ni Nanoparticles by Accelerating Water Dissociation Kinetics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 149–156.
- 55.Zhu, J.; Hu, L.; Zhao, P.; et al. Recent Advances in Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Using Nanoparticles. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 851–918.
- 56.Shi, Y.; Zhang, B. Recent Advances in Transition Metal Phosphide Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications in Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1529–1541.
- 57.Li, Y.; Pei, W.; He, J.; et al. Hybrids of PtRu Nanoclusters and Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for Highly Efficient Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10870–10875.
- 58.Nsanzimana, J.M.V.; Cai, L.; Djire, A.; et al. Tailoring Chemical Microenvironment of Iron-Triad Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Production by Water Electrolysis. Adv. Energy Mater. 2025, 15, 2501686.
- 59.Park, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, T.K.; et al. N3-butyl Imidazolium-Based Anion Exchange Membranes Blended with Poly (vinyl alcohol) for Alkaline Water Electrolysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 611, 118355.
- 60.Ursua, A.; Gandia, L.M.; Sanchis, P. Hydrogen Production from Water Electrolysis: Current Status and Future Trends. Proc. IEEE 2012, 100, 410–426.
- 61.Naughton, M.S.; Brushett, F.R.; Kenis, P.J.A. Carbonate Resilience of Flowing Electrolyte-Based Alkaline Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 1762–1768.
- 62.Miller, H.A.; Bouzek, K.; Hnat, J.; et al. Green Hydrogen from Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis: A Review of Recent Developments in Critical Materials and Operating Conditions. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2020, 4, 2114–2133.
- 63.Pushkareva, I.V.; Pushkarev, A.S.; Grigoriev, S.A.; et al. Comparative Study of Anion Exchange Membranes for Low-Cost Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 26070–26079.
- 64.Ham, K.; Bae, S.; Lee, J. Classification and Technical Target of Water Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 95, 554–576.
- 65.Felgenhauer, M.; Hamacher, T. State-of-the-Art of Commercial Electrolyzers and on-Site Hydrogen Generation for Logistic Vehicles in South Carolina. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 2084–2090.
- 66.Navarro, R.M.; Guil, R.; Fierro, J.L.G. Introduction to Hydrogen Production. In Compendium of Hydrogen Energy; Subramani, V., Basile, A., Veziroğlu, T.N., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 21–61.
- 67.Motealleh, B.; Liu, Z.; Masel, R.I.; et al. Next-Generation Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers Operating for Commercially Relevant Lifetimes. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 3379–3386.
- 68.Dau, H.; Limberg, C.; Reier, T.; et al. The Mechanism of Water Oxidation: From Electrolysis via Homogeneous to Biological Catalysis. ChemCatChem 2010, 2, 724–761.
- 69.Li, J. Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Energy Conversion and Storage: Design Strategies Under and Beyond the Energy Scaling Relationship. Nano Micro Lett. 2022, 14, 112.
- 70.Cui, X.; Ren, P.; Deng, D.; et al. Single Layer Graphene Encapsulating Non-Precious Metals as High-Performance Electrocatalysts for Water Oxidation. Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 123–129.
- 71.Craig, M.J.; Coulter, G.; Dolan, E.; et al. Universal Scaling Relations for the Rational Design of Molecular Water Oxidation Catalysts with Near-Zero Overpotential. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4993.
- 72.Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Hao, J.; et al. Integrating the Cationic Engineering and Hollow Structure Engineering into Perovskites Oxides for Efficient and Stable Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 327, 135033.
- 73.Liu, H.J.; Chiang, C.Y.; Wu, Y.S.; et al. Breaking the Relation between Activity and Stability of the Oxygen-Evolution Reaction by Highly Doping Ru in Wide-Band-Gap SrTiO3 as Electrocatalyst. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 6132–6142.
- 74.Qi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; et al. Strain Modified Oxygen Evolution Reaction Performance in Epitaxial, Freestanding, and Van Der Waals Manganite Thin Films. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7066–7072.
- 75.Song, J.; Wei, C.; Huang, Z.F.; et al. A Review on Fundamentals for Designing Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 2196–2214.
- 76.Grimaud, A.; Diaz-Morales, O.; Han, B.; et al. Activating Lattice Oxygen Redox Reactions in Metal Oxides to Catalyse Oxygen Evolution. Nat. Chem. 2017, 9, 457–465.
- 77.Hwang, J.; Rao, R.R.; Giordano, L.; et al. Perovskites in Catalysis and Electrocatalysis. Science 2017, 358, 751–756.
- 78.Hardin, W.G.; Mefford, J.T.; Slanac, D.A.; et al. Tuning the Electrocatalytic Activity of Perovskites through Active Site Variation and Support Interactions. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 3368–3376.
- 79.Huang, Z.-F.; Song, J.; Du, Y.; et al. Chemical and Structural Origin of Lattice Oxygen Oxidation in Co–Zn Oxyhydroxide Oxygen Evolution Electrocatalysts. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 329–338.
- 80.Siahrostami, S.; Villegas, S.J.; Bagherzadeh Mostaghimi, A.H.; et al. A Review on Challenges and Successes in Atomic-Scale Design of Catalysts for Electrochemical Synthesis of Hydrogen Peroxide. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 7495–7511.
- 81.Ling, T.; Yan, D.Y.; Jiao, Y.; et al. Engineering Surface Atomic Structure of Single-Crystal Cobalt (II) Oxide Nanorods for Superior Electrocatalysis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12876.
- 82.Zhuang, L.; Ge, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Ultrathin Iron-Cobalt Oxide Nanosheets with Abundant Oxygen Vacancies for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606793.
- 83.Petrie, J.R.; Cooper, V.R.; Freeland, J.W.; et al. Enhanced Bifunctional Oxygen Catalysis in Strained LaNiO3 Perovskites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2488–2491.
- 84.Kuai, C.; Liu, L.; Hu, A.; et al. Dissolved Fe Species Enable a Cooperative Solid–Molecular Mechanism for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction on NiFe-Based Catalysts. Nat. Catal. 2025, 8, 523–535.
- 85.Shi, G.; Li, J.; Lu, T.; et al. Lattice O–O Ligands in Fe-Incorporated Hydroxides Enhance Water Oxidation Electrocatalysis. Nat. Chem. 2025, 17, 1607–1614.
- 86.Pan, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. Direct Evidence of Boosted Oxygen Evolution over Perovskite by Enhanced Lattice Oxygen Participation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2002.
- 87.Xu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhong, Y.; et al. New Undisputed Evidence and Strategy for Enhanced Lattice-Oxygen Participation of Perovskite Electrocatalyst through Cation Deficiency Manipulation. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200530.
- 88.Seijas-Da Silva, A.; Hartert, A.; Oestreicher, V.; et al. Scalable Synthesis of NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxide for Efficient Anion Exchange Membrane Electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6138.
- 89.Abellán, G.; Coronado, E.; Martí-Gastaldo, C.; et al. Hexagonal Nanosheets from the Exfoliation of Ni2+-Fe3+ LDHs: A Route towards Layered Multifunctional Materials. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7451–7455.
- 90.Carrasco, J.A.; Romero, J.; Varela, M.; et al. Alkoxide-Intercalated NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxides Magnetic Nanosheets as Efficient Water Oxidation Electrocatalysts. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 478–487.
- 91.Jaramillo-Hernández, C.; Seijas-Da Silva, A.; Abellán, G. Crystallographic Phase-Dependent Electrochemical Properties of Layered Hydroxides for Energy Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 28, e202400754.
- 92.Zhang, D.; Ou, S.; Chang, X. Synergistic Effect of Defect Engineering and Crystalline/Amorphous Interfaces in NiFe Layered Double Hydroxides for Efficient Oxygen Evolution. J. Alloy Compd. 2025, 1036, 182010.
- 93.Guo, D.; Yu, H.; Chi, J.; et al. Cu2S@NiFe Layered Double Hydroxides Nanosheets Hollow Nanorod Arrays Self-Supported Oxygen Evolution Reaction Electrode for Efficient Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17743–17757.
- 94.Wei, Z.; Guo, M.; Zhang, Q. Scalable Electrodeposition of NiFe-Based Electrocatalysts with Self-Evolving Multi-Vacancies for High-Performance Industrial Water Electrolysis. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 322, 122101.
- 95.He, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Z.; et al. Activating Lattice Oxygen in NiFe-Based (oxy)Hydroxide for Water Electrolysis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2191.
- 96.Wang, X.; Pi, W.; Hu, S.; et al. Boosting Oxygen Evolution Reaction Performance on NiFe-Based Catalysts Through d-Orbital Hybridization. Nano Micro Lett. 2025, 17, 11.
- 97.Wu, L.; Ning, M.; Xing, X.; et al. Boosting Oxygen Evolution Reaction of (Fe,Ni)OOH via Defect Engineering for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Under Industrial Conditions. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2306097.
- 98.Wu, F.; Tian, F.; Li, M.; et al. Engineering Lattice Oxygen Regeneration of NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Enhances Oxygen Evolution Catalysis Durability. Angew. Chem. 2025, 64, e202413250.
- 99.Zhang, R.; Ji, X.; Fan, Y.; et al. Local Coordination Engineering of NiFe-LDH Catalyst with Carboxylate and Sodium for Durable Seawater Oxygen Evolution. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2026, 381, 125850.
- 100.Luo, J.; Im, J.-H.; Mayer, M.T.; et al. Water Photolysis at 12.3% Efficiency via Perovskite Photovoltaics and Earth-Abundant Catalysts. Science 2014, 345, 1593–1596.
- 101.Anderson, G.C.; Pivovar, B.S.; Alia, S.M. Establishing Performance Baselines for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 044503.
- 102.Anantharaj, S.; Kundu, S. Do the Evaluation Parameters Reflect Intrinsic Activity of Electrocatalysts in Electrochemical Water Splitting? ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1260–1264.
- 103.Anantharaj, S.; Karthik, P.E.; Noda, S. The Significance of Properly Reporting Turnover Frequency in Electrocatalysis Research. Angew. Chem. 2021, 60, 23051–23067.
- 104.Tsotridis, G.; Pilenga, A. EU Harmonized Protocols for Testing of Low Temperature Water Electrolysis; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2021.
- 105.Fang, Y.-H.; Liu, Z.-P. Tafel Kinetics of Electrocatalytic Reactions: From Experiment to First-Principles. ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 4364–4376.
- 106.Anantharaj, S.; Noda, S.; Driess, M.; et al. The Pitfalls of Using Potentiodynamic Polarization Curves for Tafel Analysis in Electrocatalytic Water Splitting. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1607–1611.
- 107.Lyons, M.E.G.; Floquet, S. Mechanism of Oxygen Reactions at Porous Oxide Electrodes. Part 2—Oxygen Evolution at RuO2, IrO2 and IrxRu1−xO2 Electrodes in Aqueous Acid and Alkaline Solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5314–5335.
- 108.Chen, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, X.; et al. Well-defined Nanostructures of High Entropy Alloys for Electrocatalysis. Exploration 2025, 5, 20230036.
- 109.Geiger, S.; Kasian, O.; Ledendecker, M.; et al. The Stability Number as a Metric for Electrocatalyst Stability Benchmarking. Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 508–515.
- 110.Trotochaud, L.; Young, S.L.; Ranney, J.K.; et al. Nickel–Iron Oxyhydroxide Oxygen-Evolution Electrocatalysts: The Role of Intentional and Incidental Iron Incorporation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6744–6753.
- 111.Corrigan, D.A. The Catalysis of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction by Iron Impurities in Thin Film Nickel Oxide Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1987, 134, 377.
- 112.Wu, D.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; et al. Time-Resolved Spectroscopy Uncovers Deprotonation-Induced Reconstruction in Oxygen-Evolution NiFe-Based (Oxy)Hydroxides. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 726.
- 113.Friebel, D.; Louie, M.W.; Bajdich, M.; et al. Identification of Highly Active Fe Sites in (Ni,Fe)OOH for Electrocatalytic Water Splitting. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1305–1313.
- 114.Wang, F.; Zou, P.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Activating Lattice Oxygen in High-Entropy LDH for Robust and Durable Water Oxidation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6019.
- 115.Zhao, S.; Tan, C.; He, C.T.; et al. Structural Transformation of Highly Active Metal–Organic Framework Electrocatalysts during the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 881–890.
- 116.Wu, T.; Sun, S.; Song, J.; et al. Iron-Facilitated Dynamic Active-Site Generation on Spinel CoAl2O4 with Self-Termination of Surface Reconstruction for Water Oxidation. Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 763–772.
- 117.Xiao, H.; Shin, H.; Goddard, W.A. Synergy between Fe and Ni in the Optimal Performance of (Ni,Fe)OOH Catalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5872–5877.
- 118.Zheng, X.; Zhang, B.; De Luna, P.; et al. Theory-Driven Design of High-Valence Metal Sites for Water Oxidation Confirmed Using in Situ Soft X-Ray Absorption. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 149–154.
- 119.Li, Y.F.; Li, J.L.; Liu, Z.P. Structure and Catalysis of NiOOH: Recent Advances on Atomic Simulation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2021, 125, 27033–27045.
- 120.Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Cheng, S.; et al. Recent Progress and Perspective on Lithium Metal Battery with Nickel-Rich Layered Oxide Cathode. eScience, 2024, 4, 100265.
- 121.Molina-Muriel, M.; Campagna Zignani, S.; Goberna-Ferrón, S.; et al. Efficient NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxide Electrocatalyst Synthesized via a Solvent-Free Mechanochemical Method for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 22671–22678.
- 122.Jin, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. One-Step Synthesis of Layered Double Hydroxides by a Solvent-Free Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 12955–12961.
- 123.Li, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; et al. Enhance the Proportion of Fe3+ in NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxides by Utilizing Citric Acid to Improve the Efficiency and Durability of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202401582.
- 124.Hayes, D.; Alia, S.; Pivovar, B.; et al. Targeted Synthesis, Characterization, and Electrochemical Analysis of Transition-Metal-Oxide Catalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Chem Catal. 2024, 4, 100905.
- 125.Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H.; et al. NiFe Layered-Double-Hydroxide Nanosheet Arrays Grown in situ on Ni Foam for Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 87, 130–137.
- 126.Liu, Z.Y.; Wang, Q.Y.; Hu, J.M. Introducing Carbon Dots to NiFe-LDH via a Mild Coprecipitation–Aging Method to Construct a Heterojunction for Effective Oxygen Evolution. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 110–118.
- 127.Li, Z.; Wei, P.; Wang, G. Recent Advances on Perovskite Electrocatalysts for Water Oxidation in Alkaline Medium. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 11724–11744.
- 128.Chen, M.; Kitiphatpiboon, N.; Feng, C.; et al. Recent Progress in Transition-Metal-Oxide-Based Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Natural Seawater Splitting: A Critical Review. eScience, 2023, 3, 100111.
- 129.Wang, X.; Yu, M.; Feng, X. Electronic structure regulation of noble metal-free materials toward alkaline oxygen electrocatalysis. eScience, 2023, 3, 100141.
- 130.Li, D.; Park, E.J.; Zhu, W.; et al. Highly Quaternized Polystyrene Ionomers for High Performance Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysers. Nat. Energy 2020, 5, 378–385.
- 131.Li, H.; Kraglund, M.R.; Reumert, A.K.; et al. Poly(Vinyl Benzyl Methylpyrrolidinium) Hydroxide Derived Anion Exchange Membranes for Water Electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 17914–17922.
- 132.Sankar, S.; Roby, S.; Kuroki, H.; et al. High-Performing Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis Using Self-Supported Metal Phosphide Anode Catalysts and an Ether-Free Aromatic Polyelectrolyte. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 854–865.
- 133.Park, Y.S.; Lee, J.; Jang, M.J.; et al. High-Performance Anion Exchange Membrane Alkaline Seawater Electrolysis. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 9586–9592.
- 134.Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Sulfidation of CoCuOx Supported on Nickel Foam to Form a Heterostructure and Oxygen Vacancies for a High-Performance Anion-Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 45756–45763.
- 135.Lee, J.; Jung, H.; Park, Y.S.; et al. High-Efficiency Anion-Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer Enabled by Ternary Layered Double Hydroxide Anode. Small 2021, 17, 2100639.
- 136.Choi, W.-S.; Jang, M.J.; Park, Y.S.; et al. Three-Dimensional Honeycomb-Like Cu0.81Co2.19O4 Nanosheet Arrays Supported by Ni Foam and Their High Efficiency as Oxygen Evolution Electrodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 38663–38668.
- 137.Woo, J.; Han, S.; Yoon, J. Mn-Doped Sequentially Electrodeposited Co-Based Oxygen Evolution Catalyst for Efficient Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23288–23295.
- 138.Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Cao, S.; et al. Amorphous-Crystalline Interface Coupling Induced Highly Active Ultrathin NiFe Oxy-Hydroxide Design towards Accelerated Alkaline Oxygen Evolution. J. Catal. 2024, 430, 115354.
- 139.Park, Y.S.; Yang, J.; Lee, J.; et al. Superior Performance of Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzer: Ensemble of Producing Oxygen Vacancies and Controlling Mass Transfer Resistance. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 278, 119276.
- 140.Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; et al. Constructing Ru-O-TM Bridge in NiFe-LDH Enables High Current Hydrazine-assisted H2 Production. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2401694.
- 141.Li, Z.; Chen, G.; Gou, S.; et al. NiFe-LDH and PPy-Reinforced PVA Conductive Hydrogels for All-in-One High-Performance Supercapacitors. J. Alloy Compd. 2024, 1009, 176850.
- 142.Guo, L.; Xie, J.; Chen, S.; et al. Self-Supported Crystalline-Amorphous Composites of Metal Phosphate and NiS for High-Performance Water Electrolysis under Industrial Conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 340, 123252.
- 143.Hu, Y.; Shen, T.; Wu, Z.; et al. Coordination Stabilization of Fe by Porphyrin-Intercalated NiFe-LDH Under Industrial-Level Alkaline Conditions for Long-Term Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2413533.
- 144.Inamdar, A.I.; Chavan, H.S.; Seok, J.H.; et al. Optimal Rule-of-Thumb Design of NiFeMo Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoflakes for Highly Efficient and Durable Overall Water-Splitting at Large Currents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 20497–20508.
- 145.Yang, Y.; Lie, W.H.; Unocic, R.R.; et al. Defect-Promoted Ni-Based Layer Double Hydroxides with Enhanced Deprotonation Capability for Efficient Biomass Electrooxidation. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2305573.
- 146.Guo, W.; Yan, X.; Lu, Q.; et al. Mo-Modified NiFe LDH Nanoflower Anode Catalyst Synthesized via a Top-down Etching Method for Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 145, 237–249.
- 147.Ha, J.S.; Park, Y.; Jeong, J.-Y.; et al. Solar-Powered AEM Electrolyzer via PGM-Free (Oxy)Hydroxide Anode with Solar to Hydrogen Conversion Efficiency of 12.44%. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2401782.
- 148.Zhao, T.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Heterostructured V-Doped Ni2P/Ni12P5 Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution in Anion Exchange Membrane Water Electrolyzers. Small 2022, 18, 2204758.
- 149.Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Stability Challenges and Opportunities of NiFe-Based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Media. Carbon Neutraliz. 2024, 3, 172–198.
- 150.He, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Recent Progress on Stability of Layered Double Hydroxide-Based Catalysts for Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Nanomaterials 2024, 14,1533.
- 151.Iqbal, S.; Ehlers, J.C.; Hussain, I.; et al. Trends and Industrial Prospects of NiFe-Layered Double Hydroxide for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 499, 156219.
- 152.Xu, H.; Yao, B. Industrial Applications of Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) Catalysts in High-Current Density Water Electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 162, 150714.
How to Cite
Zheng, Z.; Deng, L.; Xing, G.; Peng, S.; Chen, S.; Lv, C. Progress and Perspectives on NiFe Layered Double Hydroxide Catalysts for the Alkaline Oxygen Evolution Reaction. eChem 2025, 1 (1), 3. https://doi.org/10.53941/echem.2025.100003.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


