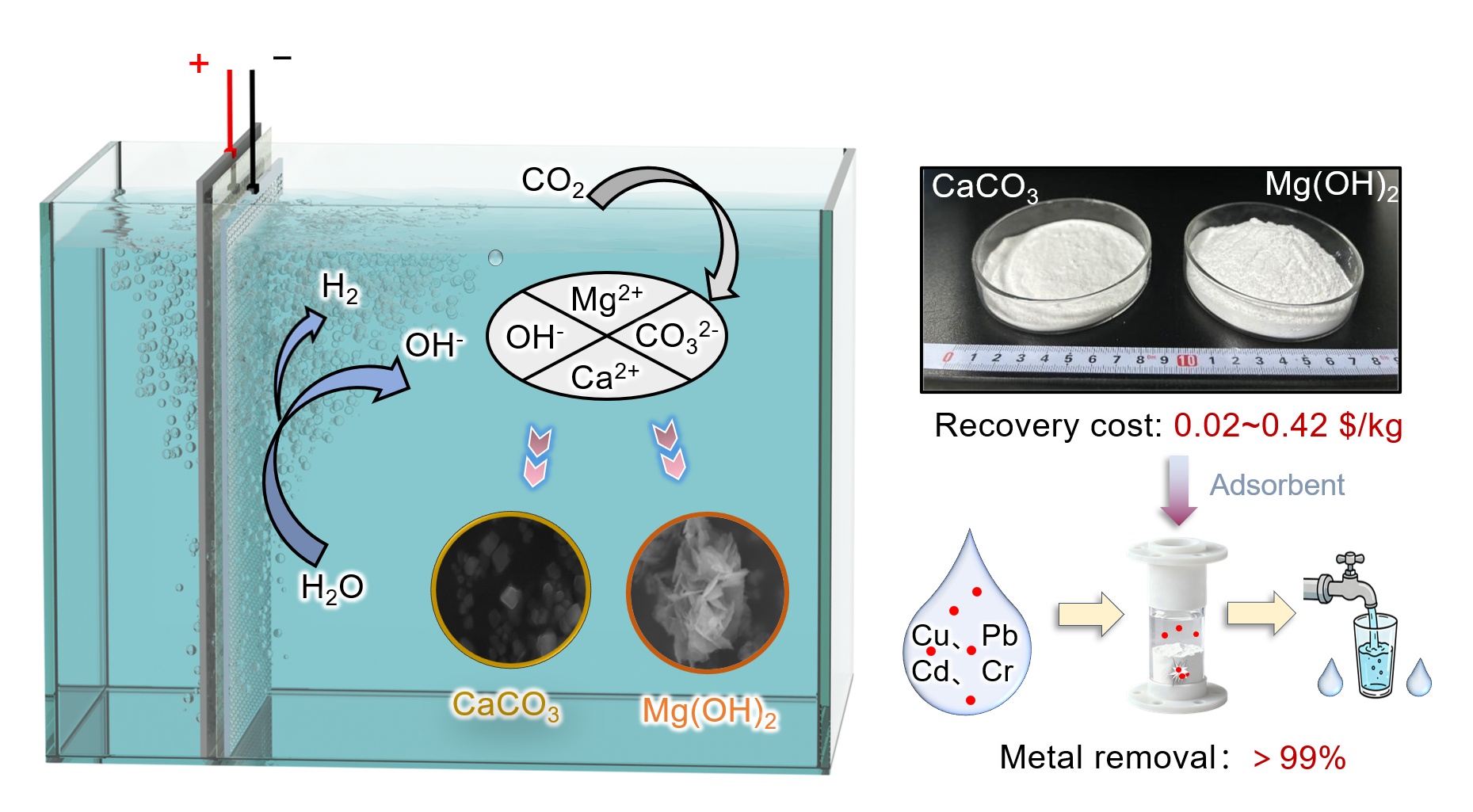
Rapid industrialization posed a serious threat to water safety due to heavy metal pollution, creating an urgent need for a green and efficient remediation solution. This research, leveraging electrocatalytic technology, innovatively proposes an electrochemical homogeneous nucleation strategy for the selective recovery of Ca2+ and Mg2+ from seawater. Through employing pH-controlled sequential precipitation, this strategy enables the synthesis of nano-CaCO3 (BET surface area: 50.4 m2/g) and nano-Mg(OH)2 (109.8 m2/g), which serve as high-performance adsorbents for efficient heavy metal removal. Both adsorbents demonstrated adsorption behaviors well-fitted to the Langmuir model, exhibiting exceptional maximum adsorption capacities for Cu(II) (838.2–1331.0 mg/g), Pb(II) (2180.5–3696.8 mg/g), Cd(II) (1065.3–1997.4 mg/g), and Cr(III) (424.1–637.5 mg/g). When configured as fixed-bed columns, the adsorbents reduced effluent concentrations of Cu(II), Pb(II), Cd(II), and Cr(III) to below 0.7 μg/L, meeting World Health Organization drinking water standards. Life cycle assessment revealed the electrochemical strategy reduced carbon emissions by 50–80% compared to conventional methods, achieving net-negative emissions (−10.428 kg CO2eq per ton of water) when incorporating resource recovery benefits. This approach represents a synergistic solution for both resource utilization and environmental remediation, demonstrating significant potential for sustainable water treatment and circular economy development.
- Open Access
- Article
Green Valorization of Seawater via Homogeneous Nucleation Electrochemistry: Synthesis of Nano-CaCO3 and Mg(OH)2 Adsorbents for Heavy Metal Removal
- Yuchen Zhao 1,
- Wenda Kang 1, 2, *,
- Shuixiang Xie 3, 4,
- Yidong Ruan 1,
- Xiang Zhou 1,
- Weilong Wang 1,
- Yongqian Zhang 5,
- Hongtao Yu 1,
- Gong Zhang 2
Author Information
Received: 18 Oct 2025 | Revised: 07 Nov 2025 | Accepted: 14 Nov 2025 | Published: 21 Nov 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1.Liu, S.; Sun, Q.; Xu, N.; et al. Recent advances in the treatment of heavy/precious metal pollution, resource recovery and reutilization: Progress and perspective. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 523, 216268.
- 2.Maierdan, Y.; Gu, K.; Chen, B.; et al. Recycling of heavy-metal-contaminated river sludge into unfired green bricks: Strength, water resistance, and heavy-metals leaching behavior-A laboratory simulation study. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130882.
- 3.Bielski, A.; Zielina, M.; Młyńska, A. Analysis of heavy metals leaching from internal pipe cement coating into potable water. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121425.
- 4.Shrestha, R.; Ban, S.; Devkota, S.; et al. Technological trends in heavy metals removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105688.
- 5.Yang, L.; Hu, W.; Chang, Z.; et al. Electrochemical recovery and high value-added reutilization of heavy metal ions from wastewater: Recent advances and future trends. Environ. Int. 2021, 152, 106512.
- 6.Zhao, X.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Preparation of porous calcium carbonate biochar and its beryllium adsorption performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110102.
- 7.Jiang, D.; Yang, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Removal of the heavy metal ion nickel(II) via an adsorption method using flower globular magnesium hydroxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 131–140.
- 8.Falyouna, O.; Bensaida, K.; Maamoun, I.; et al. Synthesis of hybrid magnesium hydroxide/magnesium oxide nanorods [Mg(OH)2/MgO] for prompt and efficient adsorption of ciprofloxacin from aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130949.
- 9.Feng, Y.; Liu, W.; Mu, C.; et al. Highly effective Pb(II) adsorption using physical-chemical double crosslinked polyvinyl alcohol-coated nano-calcium carbonate aerogel beads. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2025, 861, 141832.
- 10.Zhu, H.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; et al. Controllable synthesis of coral-like hierarchical porous magnesium hydroxide with various surface area and pore volume for lead and cadmium ion adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125922.
- 11.
Rolfe, A.; Huang, Y.; Haaf, M.; et al. Technical and environmental study of calcium carbonate looping versus oxy-fuel options for low CO2 emission cement plants. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2018, 75, 85–97.
- 12.Yam, B.J.Y.; Le, D.K.; Do, N.H.; et al. Recycling of magnesium waste into magnesium hydroxide aerogels. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104101.
- 13.Gude, V.G. Geothermal source potential for water desalination-Current status and future perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 1038–1065.
- 14.Khodadousti, S.; Kolliopoulos, G. Batteries in desalination: A review of emerging electrochemical desalination technologies. Desalination 2024, 573, 117202.
- 15.Meng, G.; Xu, J.; Cheng, R.; et al. Controllable synthesis and characterization of high-purity calcium carbonate whisker-like fibers by electrochemical cathodic reduction method. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130923.
- 16.Lei, Y.; Hidayat, I.; Saakes, M.; et al. Fate of calcium, magnesium and inorganic carbon in electrochemical phosphorus recovery from domestic wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 453–459.
- 17.
Liao, Z.; Wu, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. Removal of aqueous Cu2+ by amorphous calcium carbonate: Efficiency and mechanism. Minerals 2022, 12, 362.
- 18.Rouff, A.A.; Elzinga, E.J.; Reeder, R.J.; et al. X-ray absorption spectroscopic evidence for the formation of Pb(II) inner-sphere adsorption complexes and precipitates at the calcite-water interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1700–1707.
- 19.Brown, G.E., Jr.; Foster, A.L.; Ostergren, J.D. Mineral surfaces and bioavailability of heavy metals: A molecular-scale perspective. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3388–3395.
- 20.Henrist, C.; Mathieu, J.P.; Vogels, C.; et al. Morphological study of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles precipitated in dilute aqueous solution. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 252, 176–187.
- 21.Yan, H.; Zhang, X.H.; Wu, J.M.; et al. The use of CTAB to improve the crystallinity and dispersibility of ultrafine magnesium hydroxide by hydrothermal route. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 2483–2486.
- 22.HG/T 3249-2001; Industrial Heavy Calcium Carbonate (in Chinese). Chemical Industry Standard of PRC: Beijing, China, 2001.
- 23.HG/T 3607-2007; Magnesium Hydroxide for Industrial Use (in Chinese). Chemical Industry Standard of PRC: Beijing, China, 2007.
- 24.Tang, X.-J.; Du, Z.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-M.; et al. Correlation between microstructure and dissolution property of magnesium hydroxide synthesized via magnesia hydroxylation: Effect of hydration agents. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119371.
- 25.Murphy, O.P.; Vashishtha, M.; Palanisamy, P.; et al. A review on the adsorption isotherms and design calculations for the optimization of adsorbent mass and contact time. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 17407–17430.
- 26.Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Chen, Q.; et al. One-pot synthesis of magnetic Ni@Mg(OH)2 core-shell nanocomposites as a recyclable removal agent for heavy metals. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 1533–1540.
- 27.Huang, D.; Li, B.; Wu, M.; et al. Graphene oxide-based Fe-Mg(hydr)oxide nanocomposite as heavy-metals adsorbent. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 63, 2097–2105.
- 28.Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. Mg(OH)2-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron enhancing the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 7961–7969.
- 29.Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; et al. Removal of cadmium(II) from aqueous solution by granular activated carbon supported magnesium hydroxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 61, 287–291.
- 30.Wang, P.; Ye, Y.; Liang, D.; et al. Layered mesoporous Mg(OH)2/GO nanosheet composite for efficient removal of water contaminants. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26977–26983.
- 31.
Zhang, R.; Richardson, J.J.; Masters, A.F.; et al. Effective removal of toxic heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by CaCO3 microparticles. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 136.
- 32.Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Biogenic calcium carbonate with hierarchical organic–inorganic composite structure enhancing the removal of Pb(II) from wastewater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 35785–35793.
- 33.Merrikhpour, H.; Jalali, M. Waste calcite sludge as an adsorbent for the removal of cadmium, copper, lead, and zinc from aqueous solutions. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2012, 14, 845–855.
- 34.
Mohammadifard, H.; Amiri, M.C. Evaluating Cu(II) removal from aqueous solutions with response surface methodology by using novel synthesized CaCO3 nanoparticles prepared in a colloidal gas aphron system. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2017, 204, 476–484.
- 35.Lin, P.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Hsieh, S.L.; et al. Preparation of vaterite calcium carbonate granules from discarded oyster shells as an adsorbent for heavy-metal-ions removal. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126903.
- 36.
Zhang, M.; Shen, H.; Qian, Z.; et al. Dual-purpose applications of magnetic phase-change microcapsules with crystalline-phase-tunable CaCO3 shell for waste heat recovery and heavy-metal-ion removal. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105672.
- 37.Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Fly-ash-derived calcium silicate hydrate as a highly efficient and fast adsorbent for Cu(II) ions: Role of copolymer functionalization. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 22843–22852.
- 38.Wang, P.; Shen, T.; Li, X.; et al. Magnetic mesoporous calcium carbonate-based nanocomposites for the removal of toxic Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 1272–1281.
- 39.Velarde, L.; Nabavi, M.S.; Escalera, E.; et al. Adsorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 328, 138508.
- 40.Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. The sorption of single- and multi-heavy metals in aqueous solution using enhanced nano-hydroxyapatite assisted with ultrasonic. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105240.
- 41.Zheng, T.; Fan, H.; Zhao, J.; et al. Tuning electron configuration of metal sites for the diesel adsorptive desulfurization over ion-exchanged zeolite Y. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113751.
- 42.Zhao, F.; Cai, H.; Song, Z.; et al. Structural confinement for Cr3+ activators toward efficient near-infrared phosphors with suppressed concentration quenching. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3621–3630.
- 43.Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Anang, E.; et al. Effects of electronegativity and hydration energy on the selective adsorption of heavy metal ions by synthetic NaX zeolite. Materials 2021, 14, 4066.
- 44.Strawn, D.G. Sorption mechanisms of chemicals in soils. Soil Syst. 2021, 5, 13.
- 45.Moreno-Castilla, C.; Álvarez-Merino, M.A.; Pastrana-Martínez, L.M.; et al. Adsorption mechanisms of metal cations from water on an oxidized carbon surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 345, 461–466.
- 46.Majigsuren, E.; Byambasuren, U.; Bat-Amgalan, M.; et al. Adsorption of chromium(III) and chromium(VI) ions from aqueous solution using chitosan-clay composite materials. Polymers 2024, 16, 1399.
- 47.Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Activated carbons and low-cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811.
- 48.
Jin, B.; Wang, S.; Lei, Y.; et al. Green and effective remediation of heavy-metals-contaminated water using CaCO3 vaterite synthesized through biomineralization. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 353, 120136.
- 49.Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, R.; et al. Efficient flocculation of multiple heavy metals by iron-based modified-carbonate biochar: Adsorption mechanism and practical application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115120.
- 50.Zeng, H.; Jin, B.; Xu, S.; et al. Removal of copper, lead and cadmium from water through enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation by soybean urease. Environ. Res. 2025, 277, 121610.
- 51.Ashokan, A.; Sampath Kumar, T.S.; Jayaraman, G. Process optimization for the rapid conversion of calcite into hydroxyapatite microspheres for chromatographic applications. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12164.
- 52.Hassan, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; et al. Mesoporous biopolymer architecture enhanced the adsorption and selectivity of aqueous heavy-metal ions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15316–15331.
- 53.Sphera Solutions GmbH. GaBi LCA Databases & Software: Database Documentation and Electricity Grid Mix Datasets; Sphera Solutions GmbH: Leinfelden-Echterdingen, Germany, 2024.
- 54.Luong, V.-T.; Amal, R.; Scott, J.A.; et al. A comparison of carbon footprints of magnesium oxide and magnesium hydroxide produced from conventional processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 1035–1044.
- 55.Sphera. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Database: Updated, Reliable and Consistent Environmental Data. 2022. Available online: https://sphera.com/life-cycle-assessment-lca-database (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- 56.Goedkoop, M.; Oele, M.; Leijting, J.; et al. ReCiPe 2008: A Life Cycle Impact Assessment Method which Comprises Harmonised Category Indicators at the Midpoint and the Endpoint Level. Report I: Characterisation; Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment (VROM): The Hague, Netherlands, 2009.
- 57.Huijbregts, M. A. J.; Steinmann, Z. J. N.; Elshout, P. M. F.; et al. ReCiPe2016: A harmonised life cycle impact assessment method at midpoint and endpoint level. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 138–147.
- 58.Wernet, G.; Bauer, C.; Steubing, B.; et al. The ecoinvent database version 3 (part I): Overview and methodology. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 1218–1230.



