Pharmaceuticals are contaminants of emerging concern due to their ineffective removal in wastewater treatment plants and largely unknown effects on the ecosystem. Specifically, statins are a class of blood-lipid lowering agents that are the most prescribed drug class in the United States. High concentrations of statins have been reported in water systems ranging from fresh water to wastewater. Exposure studies are frequently conducted on aquatic organisms; however, terrestrial organisms must also be assessed for accumulation of pharmaceuticals as treated wastewater is frequently used to irrigate farm fields, introducing contaminants to a greater number of species. Earthworms, specifically Eisenia hortensis, are frequently used as bioindicators of soil contamination. However, they have not been assessed as a bioindicator of pharmaceuticals in the environment, which this work seeks to address. Benchtop matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry imaging (MSI) was optimized and employed to visualize statin localization in longitudinal sections of Eisenia hortensis following an exposure period to atorvastatin, lovastatin, or simvastatin. All three statins were detected successfully by MSI. Lovastatin and simvastatin were ubiquitously distributed, providing evidence for both dermal absorption and ingestion of contaminated soil. Atorvastatin localized to the intestinal wall, differing from the other two analytes likely due to differences in logP values. This work suggests that Eisenia hortensis is a suitable bioindicator of statins in the environment.
- Open Access
- Article
Benchtop Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Eisenia Hortensis Exposed to Statins
- Kendra G. Selby †,
- Claire E. Korte †,
- Lauren H. Phan,
- Gabriel A. Bressendorff,
- Ashley R. Chirchirillo,
- Kevin R. Tucker *
Author Information
Received: 26 Sep 2025 | Revised: 01 Dec 2025 | Accepted: 03 Dec 2025 | Published: 09 Dec 2025
Abstract
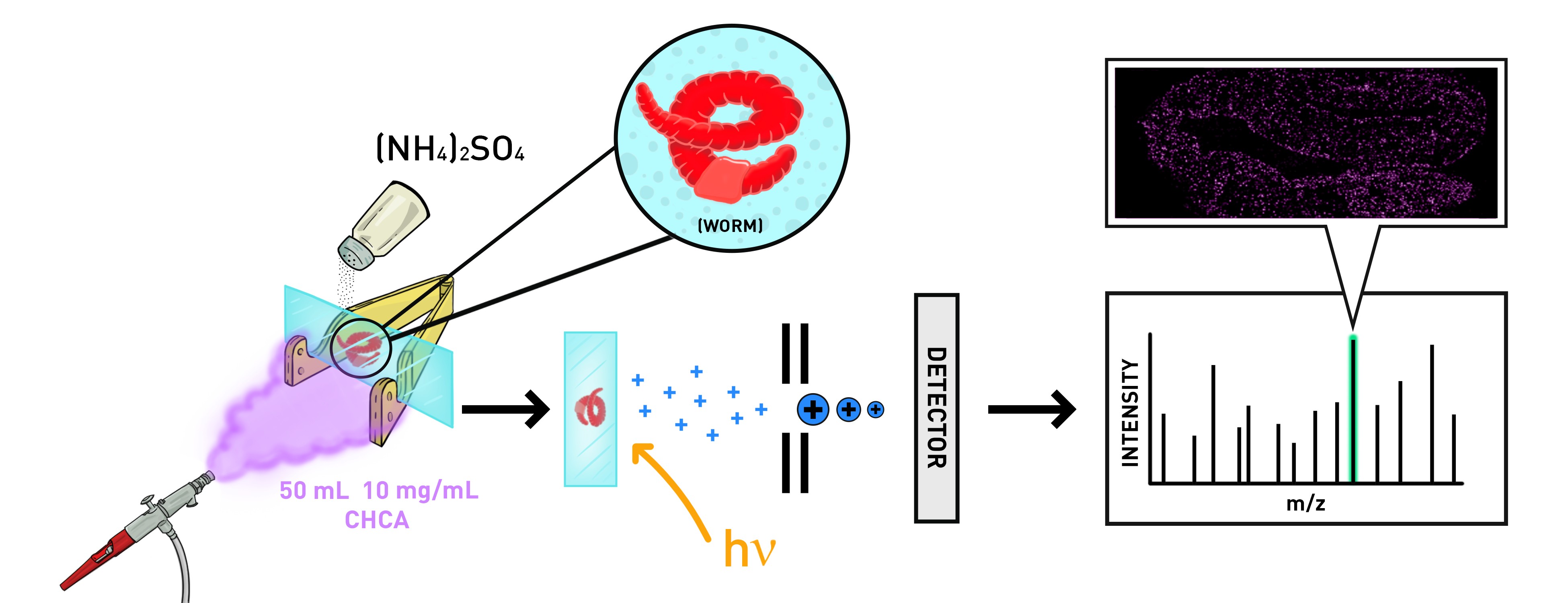
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization | linear time-of-flight | earthworm | toxicology | statins | pharmaceuticals
References
- 1.
Matesun, J.; Petrik, L.; Musvoto, E.; et al. Limitations of Wastewater Treatment Plants in Removing Trace Anthropogenic Biomarkers and Future Directions: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 281, 116610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116610.
- 2.
Belete, B.; Desye, B.; Ambelu, A.; et al. Micropollutant Removal Efficiency of Advanced Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Systematic Review. Env. Health Insights 2023, 17, 11786302231195158. https://doi.org/10.1177/11786302231195158.
- 3.
Daughton, C.G.; Ternes, T.A. Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in the Environment: Agents of Subtle Change? Env. Health Perspect. 1999, 107, 907–938. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107s6907.
- 4.
Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence Patterns of Pharmaceuticals in Water and Wastewater Environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-1035-8.
- 5.
Ben Chabchoubi, I.; Lam, S.S.; Pane, S.E.; et al. Hazard and Health Risk Assessment of Exposure to Pharmaceutical Active Compounds via Toxicological Evaluation by Zebrafish. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 120698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120698.
- 6.
Maron, D.J.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F. Current Perspectives on Statins. Circulation 2000, 101, 207–213. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.2.207.
- 7.
Kantor, E.D.; Rehm, C.D.; Haas, J.S.; et al. Trends in Prescription Drug Use Among Adults in the United States From 1999-2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1818–1830. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.13766.
- 8.
Ottmar, K.J.; Colosi, L.M.; Smith, J.A. Fate and Transport of Atorvastatin and Simvastatin Drugs during Conventional Wastewater Treatment. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1184–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.03.066.
- 9.
Conley, J.M.; Symes, S.J.; Schorr, M.S.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Pharmaceutical Concentrations in the Upper Tennessee River Basin. Chemosphere 2008, 73, 1178–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.062.
- 10.
Barros, S.; Coimbra, A.M.; Alves, N.; et al. Chronic Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Levels of Simvastatin Disrupts Zebrafish Brain Gene Signaling Involved in Energy Metabolism. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2020, 83, 113–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2020.1733722.
- 11.
Pino, M.R.; Val, J.; Mainar, A.M.; et al. Acute Toxicological Effects on the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida of 18 Common Pharmaceuticals in Artificial Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 225–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.02.080.
- 12.
IndraKumar Singh, S.; Singh, W.R.; Bhat, S.A.; et al. Vermiremediation of Allopathic Pharmaceutical Industry Sludge Amended with Cattle Dung Employing Eisenia Fetida. Env. Res. 2022, 214, 113766. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113766.
- 13.
Singh, D.; Suthar, S. Vermicomposting of Herbal Pharmaceutical Industry Waste: Earthworm Growth, Plant-Available Nutrient and Microbial Quality of End Materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 112, 179–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.02.101.
- 14.
McKelvie, J.R.; Wolfe, D.M.; Celejewski, M.A.; et al. Metabolic Responses of Eisenia fetida after Sub-Lethal Exposure to Organic Contaminants with Different Toxic Modes of Action. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3620–3626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.08.002.
- 15.
Vergara-Luis, I.; Rutkoski, C.F.; Urionabarrenetxea, E.; et al. Antimicrobials in Eisenia Fetida Earthworms: A Comprehensive Study from Method Development to the Assessment of Uptake and Degradation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171214.
- 16.
Carter, L.J.; Ryan, J.J.; Boxall, A.B.A. Effects of Soil Properties on the Uptake of Pharmaceuticals into Earthworms. Env. Pollut. 2016, 213, 922–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.03.044.
- 17.
Carter, L.J.; Garman, C.D.; Ryan, J.; et al. Fate and Uptake of Pharmaceuticals in Soil-Earthworm Systems. Env. Sci Technol. 2014, 48, 5955–5963. https://doi.org/10.1021/es500567w.
- 18.
Selby, K.G.; Korte, C.E.; Phan, L.H.; et al. Method Optimization for Benchtop Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Lipids in Eisenia Hortensis. Front. Environ. Chem. 2024, 5, 1334207. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvc.2024.1334207.
- 19.
Wu, X.; Conkle, J.L.; Ernst, F.; et al. Treated Wastewater Irrigation: Uptake of Pharmaceutical and Personal Care Products by Common Vegetables under Field Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11286–11293. https://doi.org/10.1021/es502868k.
- 20.
Dovletyarova, E.A.; Tapia-Pizarro, F.; Ermakov, A.I.; et al. Copper Toxicity Thresholds for Earthworm Dendrobaena Veneta: Insights from a Site with Unique Monometallic Soil Contamination. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2025, 44, 2707–2715. https://doi.org/10.1093/etojnl/vgaf155.
- 21.
OuYang, C.; Chen, B.; Li, L. High Throughput In Situ DDA Analysis of Neuropeptides by Coupling Novel Multiplex Mass Spectrometric Imaging (MSI) with Gas-Phase Fractionation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 1992–2001. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-015-1265-0.
- 22.
Davis, R.B.; Hoang, J.A.; Rizzo, S.M.; et al. Quantitation and Localization of Beta-Blockers and SSRIs Accumulation in Fathead Minnows by Complementary Mass Spectrometry Analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140331.
- 23.
Selby, K.G.; Hubecky, E.M.; Zerda-Pinto, V.; et al. Mass Spectrometry Imaging for Environmental Sciences: A Review of Current and Future Applications. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 42, e00232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teac.2024.e00232.
- 24.
Körber, A.; Anthony, I.G.M.; Heeren, R.M.A. Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 15517–15549. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.4c05249.
- 25.
Germershausen, J.I.; Hunt, V.M.; Bostedor, R.G.; et al. Tissue Selectivity of the Cholesterol-Lowering Agents Lovastatin, Simvastatin and Pravastatin in Rats In Vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 158, 667–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291X(89)92773-3.
- 26.
van Agthoven, M.A.; Barrow, M.P.; Chiron, L.; et al. Differentiating Fragmentation Pathways of Cholesterol by Two-Dimensional Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass. Spectrom. 2015, 26, 2105–2114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13361-015-1226-7.
- 27.
Goncalves, I.L.; Tal, S.; Barki-Harrington, L.; et al. Conserved Statin-Mediated Activation of the P38-MAPK Pathway Protects Caenorhabditis Elegans from the Cholesterol-Independent Effects of Statins. Mol. Metab. 2020, 39, 101003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101003.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


