Drying treatment, as a critical initial processing step, enables the transformation of industrial sewage sludge into green fuels, addressing dual environmental and energy challenges. A designed microwave drying thermogravimetric experimental system was developed to investigate the effects of sludge weight (20, 25, 30, 35, and 40 g) and microwave power (400, 450, 500, 550, and 600 W) on the drying performances through analysis of transient temperature and weight. Results identified three distinct drying stages: (I) rapid preheating dominated by sensible heat absorption of free water; (II) constant-temperature stage where microwave energy primarily converted to latent heat for free water removal; (III) slower bound-water removal stage. Crucially, drying performance peaked at 30 g sludge weight. Increasing microwave power significantly enhanced efficiency, reducing total drying time by 37.4% when power rose from 400 W to 600 W. Maximum drying efficiency (81.9 wt.% moisture removal) occurred at 500 W, demonstrating a non-linear power-efficiency relationship. These findings provide essential mechanistic insights and operational parameters to optimize industrial sludge to energy processes.
- Open Access
- Article
Understanding the Transient Microwave Drying Performances of Industrial Sewage Sludge Towards Green Fuel and Energy
- Kaihan Xie 1,
- Zhihong Liu 1,
- Man Zhang 2, *,
- Wenke Zhao 1,
- Yaning Zhang 1, *
Author Information
Received: 03 May 2025 | Revised: 28 Jun 2025 | Accepted: 02 Jul 2025 | Published: 08 Jul 2025
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
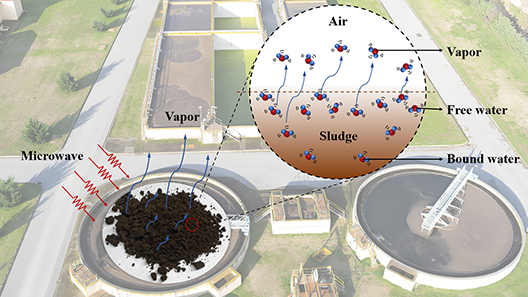
Keywords
microwave drying | industrial sewage sludge | transient thermogravimetry | weight | temperature
References
- 1.Guo. H.Y.; Tan, Z.W.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Dynamic characteristics analysis of metallurgical waste heat radiative drying of thin layers of sewage sludge. Processes 2023, 11, 2535.
- 2.Feng, J.I.; Burke, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Assessing metal contamination and speciation in sewage sludge: Implications for soil application and environmental risk. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio. 2023, 22, 1037–1058.
- 3.Wang, L.P.; Chang, Y.Z.; Li, A. Hydrothermal carbonization for energy-efficient processing of sewage sludge: A review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 108, 423–440.
- 4.Li, Y.D.; Yang, D.; Zhou, X.H.; et al. Heavy metal migration characteristics of co-combustion between sewage sludge and high alkaline coal on circulating fluidized bed. J. Therm. Sci. 2022, 31, 2178–2188.
- 5.Nwankwo, N.C.; Madougou, S.; Inoussa, M.M.; et al. Review of Nigeria’s renewable energy policies with focus on biogas technology penetration and adoption. Discov. Energy 2024, 4, 14.
- 6.Li, Q.; Zhong, Z.Q.; Du, H.R.; et al. Co-pyrolysis of municipal sludge and papermaking sludge: Pyrolysis behaviors and heavy metals immobilizations. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2024, 181, 106595.
- 7.Jiang, S.Y.; Du, Y.; Li, Y.J.; et al. Crystal facet effect of the support in Ni/La2O2CO3 catalysts for toluene steam reforming. Fuel 2025, 387, 134388.
- 8.Ji, X.L.; Yang, Q.Y.; Huang, X.Y.; et al. Combustion characteristics and NOx release of sludge combustion with coal in a 660 MW boiler. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 258C, 124749.
- 9.Cheng, D.M.; Xiong, J.S.; Chen, J.Y.; et al. Effect of biochar addition on antibiotic and heavy metal resistance genes during sewage sludge composting. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115732.
- 10.Jin, F.Y.; Lu, J.X.; Sun, F.; et al. Application and development of sludge-based materials for environmental pollution remediation: A bibliometric review from 2004 to 2024. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 8072–8087.
- 11.Mian, M.M.; Ao, W.Y.; Deng, S.B. Sludge-based biochar adsorbent: Pore tuning mechanisms, challenges, and role in carbon sequestration. Biochar 2023, 5, 83.
- 12.Laghari, A.A.; Leghari, A.; Kumar, A.; et al. A parametric study of particle size influence on sewage sludge-derived hydrochar and coal char co-gasification: Reactivity and carbon conversion analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 196, 107715.
- 13.Quan, L.M.; Kamyab, H.; Yuzir, A.; et al. Review of the application of gasification and combustion technology and waste-to-energy technologies in sewage sludge treatment. Fuel 2022, 316, 123199.
- 14.Jiang, Y.F.; Gao, F.Y.; Peng, G.D.; et al. Effect of carbon to nitrogen ratios of municipal sludge on its dehydration property. Energ. Source Part A 2023, 45, 2509–2522.
- 15.Zhang, K.B.; Yu, A.B.; He, X.H.; et al. Process simulation and techno-economic analysis of 400 t/d pilot plant for municipal sewage sludge drying and combustion. Process Saf. Environ. 2025, 196, 106833.
- 16.Mariusz, K.; Tomasz, K. Increase in efficiency of separating pollution from sewage sludge through the pressure filtration process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2023, 301, 181–189.
- 17.Wang, G.Y.; Wu, W.F.; Qiao, F.X.; et al. Research on an electric energy-saving grain drying system with internal circulation of the drying medium. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13476.
- 18.Papastefanakis, N.; Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Maragkaki, A.E.; et al. Application of solar drying as a pre-treatment method for storing wet feedstocks prior to use in anaerobic digesters: Effect on methane production and digestate composition. Fuel 2023, 348, 128477.
- 19.Yao, L.S.; Song, Z.L.; Sun, C.G.; et al. Study on the evolution of internal and external water of lignite during microwave drying and the moisture reabsorption characteristics of dried lignite. Energy Source Part A 2025, 47, 3284–3301.
- 20.Idris, A.; Khalid, K.; Omar, W. Drying of silica sludge using microwave heating. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2004, 24, 905–918.
- 21.Savvakis, N.; Tournaki, S.; Tarasi, D.; et al. Environmental effects from the use of traditional biomass for heating in rural areas: A case study of Anogeia, Crete. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 4, 5473–5495.
- 22.Savvakis, N.; Sifakis, N.; Kotakidis, X.; et al. Multiple energy resources integration in the food industry: A technoeconomic analysis. J. Clean Prod. 2023, 426, 139055.
- 23.Guo, X.J.; Hao, Q.D.; Qiao, X.G.; et al. An evaluation of different pretreatment methods of hot-air drying of garlic: Drying characteristics, energy consumption and quality properties. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 180, 114685.
- 24.Martynenko, A.; Bashkir, I.; Kudra, T. The energy efficiency of electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying of foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2021, 118A, 744–764.
- 25.Al Katsaprakakis, D.; Moschovos, T.; Michopoulos, A; et al. Feasibility for the introduction of decentralised combined heat and power plants in agricultural processes. A case study for the heating of algae cultivation ponds. Sustain. Energy Technol. 2022, 53, 102757.
- 26.Arnaoutakis, G.E.; Papadakis, N.; Al Katsaprakakis, D; et al. CombiCSP: A python routine for dynamic modeling of concentrating solar power plants. Softw. Impacts 2022, 13, 100367.
- 27.Arnaoutakis, G.E.; Katsaprakakis, D.A.; Christakis, D.G. Dynamic modeling of combined concentrating solar tower and parabolic trough for increased day-to-day performance. Appl. Energy 2022, 323, 119450.
- 28.Ahmad, F.Z.; Kashif, M.; Zhao, W.K.; et al. Microwave Heating Performances of Eucalyptus Camaldulensis Leaves with Silicon Carbide for Biofuel Upgrading. Green Energy Fuel Res. 2025, 2, 1–12.
- 29.Alfiya, P.V.; Jayashree, E.; Anees, K. Techno-economic, environmental impact and exergy analysis of microwave assisted drying of nutmeg mace. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2025, 44, e14550.
- 30.Wang, J.; Wen, M.Y.; Ren, J.R.; et al. Tailoring microwave frequencies for high-efficiency hydrogen production from biomass, Energy 2024, 297, 131337.
- 31.Ahmad, F.; Zhang, Y.N.; Fu, W.M.; et al. Microwave-assisted chemical looping gasification of sugarcane bagasse biomass using Fe3O4 as oxygen carrier for H2/CO-rich syngas production. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 501, 157675.
- 32.Ozdemir, M.; Sakine, K. Effects of microwave drying on physicochemical characteristics, microstructure, and antioxidant properties of propolis extract. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2023, 104, 2189–2197.
- 33.Carvalho, G.R.; Monteiro, R.L.; Laurindo, J.B.; et al. Microwave and microwave-vacuum drying as alternatives to convective drying in barley malt processing. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2021, 73, 102770.
- 34.Wang, G.Y.; Zhang, K.; Huang, B.C.; et al. Microwave Drying of Sewage Sludge: Process Performance and Energy Consumption. Processes 2024, 12, 432.
- 35.Slezak, M.; Migas, P.; Bernasowski, M. The use of microwave treatment as a sustainable technology for the drying of metallurgical sludge. Materials 2024, 17, 6207.
- 36.Wulyapash, W.; Phongphiphat, A.; Towprayoon, S. Comparative study of hot air drying and microwave drying for dewatered sludge. Clean Technol. Environ. 2022, 24, 423–436.
- 37.Liu, C.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, M.; et al. Drying of industrial sludge using microwave: Heating performance, mass loss, and energy analysis. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 197, 107794.
- 38.Kodom, P.; Aragón-Barroso, A.J.; Koledzi, E.K.; et al. Microwave Treatment of Three Different Types of Sewage Sludge Based on Their Solar Drying Exposure Time: Effect on Microorganisms, Water Content and Agronomic Aspects. Water 2024, 16, 321.
- 39.Kocbek, E.; Garcia, H.A.; Hooijmans, C.M.; et al. Effects of the sludge physical-chemical properties on its microwave drying performance, Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 828, 154142.
- 40.Li, L.Z.; Jiang, X.W.; Qin, X.M.; et al. Experimental study and energy analysis on microwave-assisted lignite drying. Dry Technol. 2019, 37, 962–975.
- 41.Guo, J.L.; Zheng, L.; Li, Z.F. Microwave drying behavior, energy consumption, and mathematical modeling of sewage sludge in a novel pilot-scale microwave drying system. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146109.
- 42.Jie, E.; Zhao, X.; Liu, G.; et al. Effects analysis on optimal microwave energy consumption in the heating process of composite regeneration for the diesel particulate filter. Appl. Energy 2019, 254, 113736.
- 43.Ke, C.F.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.N.; et al. Energy absorption performances of silicon carbide particles during microwave heating process. Chem. Eng. Process 2022, 172, 108796.
- 44.Gong, Z.Q.; Zhang, H.T.; Liu, C. et al. Co-Pyrolysis Characteristics and Kinetic Analysis of Oil Sludge with Different Additives. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 30, 1452–1467.
- 45.Liu, Q.W.; Liu, M.M.; Zhao, K.; et al. Microwave Application in Biomass Conversion: A Review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2024, 11, e202400020.
- 46.Ito, S.; Huang, H.Y.; Watanabe, F.J.; et al. Heat transfer during microwave-assisted desorption of water vapor from zeolite packed bed. Dry Technol. 2012, 30, 1707–1713.
- 47.Luo, R.; Tu, C.Z. Actual diffusivities and diffusion paths of water vapor in asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 207, 145–157.
- 48.Guan, B.W.; Cao, X.H.; Wang, A.P.; et al. Investigation on void connectivity characteristics of steel slag asphalt mixture subjected to dry-wet cycles and microwave heating utilizing computed tomography technology. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 47.
How to Cite
Xie, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Y. Understanding the Transient Microwave Drying Performances of Industrial Sewage Sludge Towards Green Fuel and Energy. Green Energy and Fuel Research 2025, 2 (3), 174–186. https://doi.org/10.53941/gefr.2025.100013.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2025 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


