Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i) are a new class of antidiabetic drugs that act by inhibiting the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal renal tubule, which results in lowering the level of blood and urinary glucose. Besides the glucose-lowing effect, some clinical trials found the benefits of SGLT2i in treating heart failure with or without diabetes. In 2021, SGLT2i were recommended by the European Society of Cardiology in treating of heart failure. Compared to heart failure, hypertension is a common cardiovascular disease with an increasing prevalence globally. There is also clinical evidence indicating that SGLT2i can lower blood pressure. Here we focused on addressing the role of SGLT-2i in treating hypertension and its possible mechanism in this review.
- Open Access
- Review
Role of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor in Hypertension
- Zhitong Zhou,
- Daowen Wang,
- Junfang Wu *
Author Information
Received: 17 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 15 Nov 2022 | Published: 21 Dec 2022
Abstract
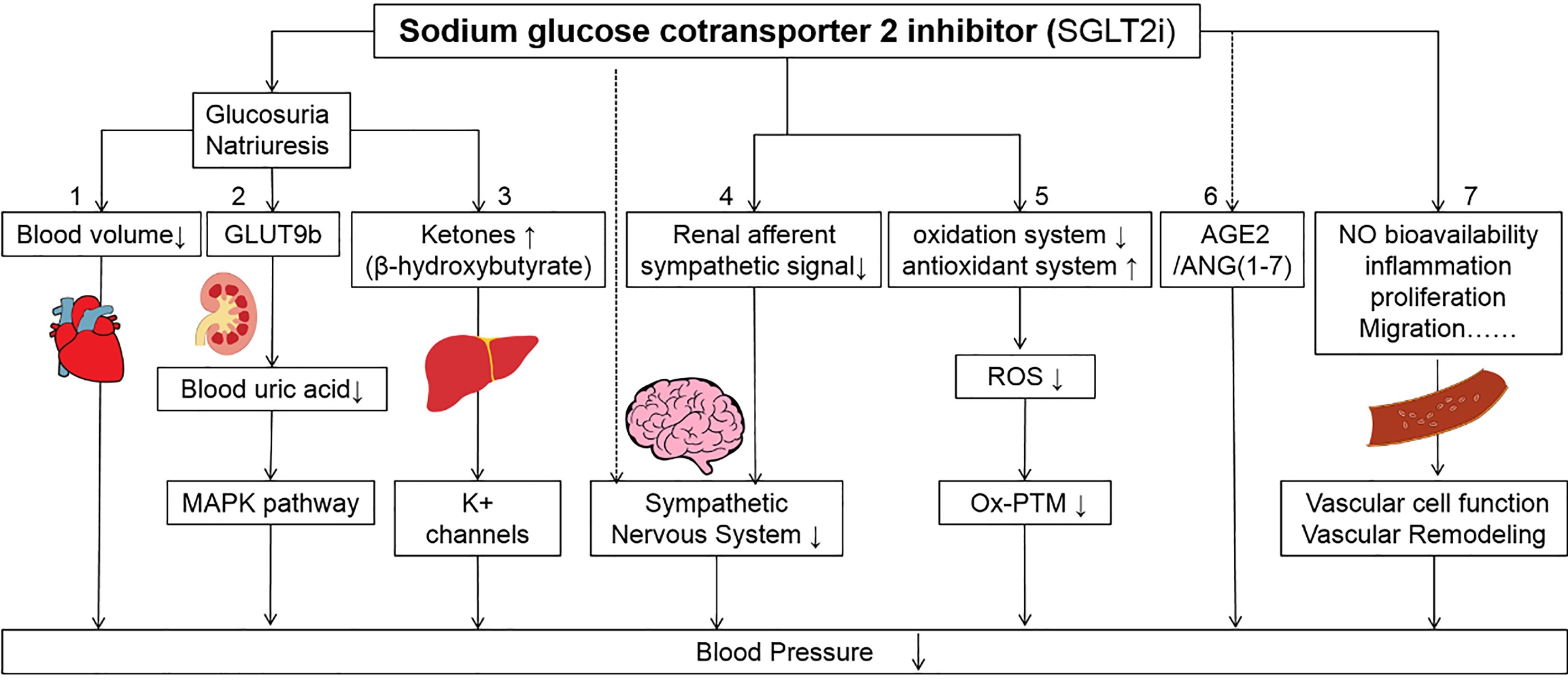
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1.Vallon V.; Verma S. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on kidney and cardiovascular function. Annu. Rev. Physiol., 2021, 83: 503-528.
- 2.Neal B.; Perkovic V.; Mahaffey K.W.; et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med., 2017, 377(7): 644-657.
- 3.Wanner C.; Inzucchi S.E.; Lachin J.M.; et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med., 2016, 375(4): 323-334.
- 4.Wiviott S.D.; Raz I.; Bonaca M.P.; et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med., 2019, 380(4): 347-357.
- 5.McMurray J.J.V.; Solomon S.D.; Inzucchi S.E.; et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med., 2019, 381(21): 1995-2008.
- 6.Anker S.D.; Butler J.; Filippatos G.; et al. Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N. Engl. J. Med., 2021, 385(16): 1451-1461.
- 7.Solomon S.D.; Vaduganathan M.; Claggett B.L.; et al. Baseline characteristics of patients with HF with mildly reduced and preserved ejection fraction: DELIVER trial. JACC: Heart Failure, 2022, 10(3): 184-197.
- 8.Kario K.; Okada K.; Kato M.; et al. 24-Hour blood pressure-lowering effect of an SGLT-2 inhibitor in patients with diabetes and uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension: results from the randomized, placebo-controlled SACRA study. Circulation, 2018, 139(18): 2089-2097.
- 9.Sternlicht H.; Bakris G.L. Blood pressure lowering and sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2is)inhibitors: more than osmotic diuresis. Curr. Hypertens. Rep., 2019, 21(2): 12.
- 10.Akbari A.; Rafiee M.; Sathyapalan T.; et al. Impacts of sodium/glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors on circulating uric acid concentrations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Res., 2022, 2022: 7520632.
- 11.Bailey C.J. Uric acid and the cardio-renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors. Diabetes, Obes. Metab., 2019, 21(6): 1291-1298.
- 12.Corry D.B.; Eslami P.; Yamamoto K.; et al. Uric acid stimulates vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and oxidative stress via the vascular renin-angiotensin system. J. Hypertens., 2008, 26(2): 269-275.
- 13.Kang D.H.; Park S.K.; Lee I.K.; et al. Uric acid-induced C-reactive protein expression: implication on cell proliferation and nitric oxide production of human vascular cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2005, 16(12): 3553-3562.
- 14.Herrington W.G.; Savarese G.; Haynes R.; et al. Cardiac, renal, and metabolic effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors: a position paper from the European Society of Cardiology ad-hoc task force on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors. Eur. J. Heart Failure, 2021, 23(8): 1260-1275.
- 15.Chakraborty S.; Galla S.; Cheng X.; et al. Salt-responsive metabolite, β-hydroxybutyrate, attenuates hypertension. Cell Rep., 2018, 25(3):677-689.e4.
- 16.McCarthy C.G.; Chakraborty S.; Singh G.; et al. Ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate is an autophagy-dependent vasodilator. JCI insight, 2021, 6(20): e149037.
- 17.Grassi G. The sympathetic nervous system in hypertension: roadmap update of a long journey. Am. J. Hypertens., 2021, 34(12): 1247-1254.
- 18.Chilton R.; Tikkanen I.; Cannon C.P.; et al. Effects of empagliflozin on blood pressure and markers of arterial stiffness and vascular resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obes. Metab., 2015, 17(12): 1180-1193.
- 19.Herat L.Y.; Magno A.L.; Rudnicka C.; et al. SGLT2 inhibitor-induced sympathoinhibition: a novel mechanism for cardiorenal protection. JACC: Basic to Translational Science, 2019, 5(2): 169-179.
- 20.Sano M. A new class of drugs for heart failure: SGLT2 inhibitors reduce sympathetic overactivity. J. Cardiol., 2017, 71(5): 471-476.
- 21.Nguyen T.; Wen S.; Gong M.; et al. Dapagliflozin activates neurons in the central nervous system and regulates cardiovascular activity by inhibiting SGLT-2 in mice. Diabetes, Metab. Syndr. Obes.: Targets Ther., 2020, 13: 2781-2799.
- 22.Yaribeygi H.; Atkin S.L.; Butler A.E.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors and oxidative stress: an update. J. Cell. Physiol., 2019, 234(4): 3231-3237.
- 23.Griendling K.K.; Camargo L.L.; Rios F.J.; et al. Oxidative stress and hypertension. Circ. Res., 2021, 128(7): 993-1020.
- 24.Viola A.; Monticone S.; Burrello J.; et al. Renin and aldosterone measurements in the management of arterial hypertension. Horm. Metab. Res., 2015, 47(6): 418-426.
- 25.Patel S.; Rauf A.; Khan H.; et al. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): the ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2017, 94: 317-325.
- 26.Puglisi S.; Rossini A.; Poli R.; et al. Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists on renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Front. Endocrinol., 2021, 12: 738848.
- 27.Hou Y.C.; Zheng C.M.; Yen T.H.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of SGLT2 inhibitor on cardiorenal protection. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(21): 7833.
- 28.Durante W.; Behnammanesh G.; Peyton K.J. Effects of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on vascular cell function and arterial remodeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(16): 8786.
- 29.Prado A.F.; Batista R.I.M.; Tanus-Santos J.E.;et al. Matrix metalloproteinases and arterial hypertension: role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in vascular functional and structural alterations. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(4): 585.
- 30.Endemann D.H.; Schiffrin E.L. Endothelial dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2004, 15(8): 1983-1992.
- 31.Touyz R.M.; Alves-Lopes R.; Rios F.J.; et al. Vascular smooth muscle contraction in hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res., 2018, 114(4): 529-539.
- 32.Reina-Couto M.; Afonso J.; Carvalho J.; et al. Interrelationship between renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and oxidative stress in chronic heart failure patients with or without renal impairment. Biomed. Pharmacother., 2021, 133: 110938.
- 33.Zhao Y.; Li L.; Lu Z.S.; et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor canagliflozin antagonizes salt-sensitive hypertension through modifying transient receptor potential channels 3 mediated vascular calcium handling. J. Am. Heart Assoc., 2022, 11(15): e025328.
- 34.Alqudsi M.; Velez J.C.Q.; Navarrete J. Medical management of resistant hypertension: the role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i). Current Opinion in Cardiology, 2021, 36(4): 420-428.
How to Cite
Zhou, Z.; Wang, D.; Wu, J. Role of Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor in Hypertension. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology 2022, 1 (1), 8. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.v1i1.175.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Zhitong Zhou, Dao Wen Wang, Junfang Wu
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


