Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the world. Myocardial infraction (MI) as one of the most harmful forms of ischaemic heart disease requires rigorous and tempestive approaches which are not met by current clinical interventions. Nanotechnology has developed promising clinical applications for imaging, diagnostic, gene delivery and tissue engineering, which makes this technology a potential candidate for novel therapeutic delivery approach. This review highlights several recent research reports regarding advances in drug delivery using nanoparticle-based (NP) strategies, as well as future challenges and opportunities.
- Open Access
- Review
Nanoparticle-based Drug Delivery System for Post Myocardial Infarction Management
- Minxuan Liu,
- Chiara Ramponi,
- Xiaoxue Fan,
- Xinzhuang Zhang,
- Liang Cao,
- Zhenzhong Wang,
- Wei Xiao *
Author Information
Received: 15 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 21 Nov 2022 | Published: 21 Dec 2022
Abstract
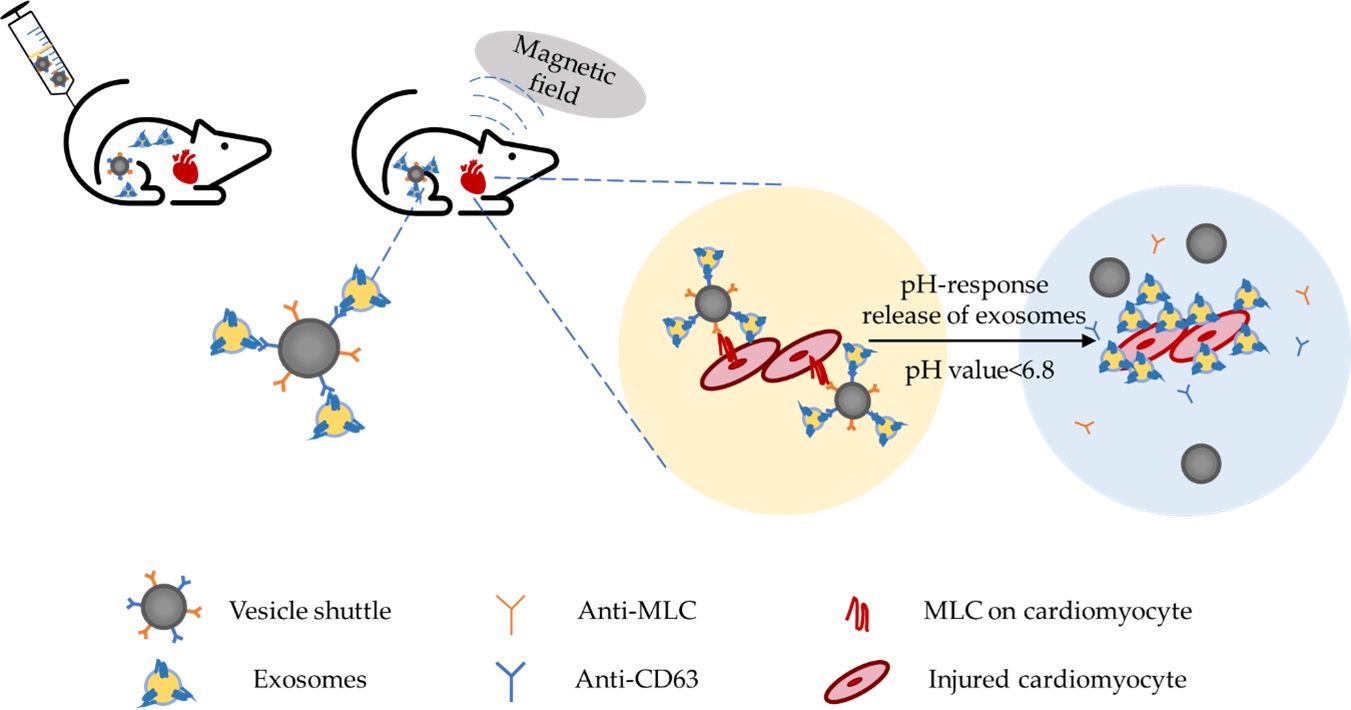
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
References
- 1.Nichols M.; Townsend N.; Scarborough P.; et al. Cardiovascular disease in Europe 2014: epidemiological update. Eur. Heart J., 2014, 35(42): 2950-2959.
- 2.Reed G.W.; Rossi J.E.; Cannon C.P. Acute myocardial infarction. Lancet, 2017, 389(10065): 197-210.
- 3.Marín-Juez R.; El-Sammak H.; Helker C.S.M.; et al. Coronary revascularization during heart regeneration is regulated by epicardial and endocardial cues and forms a scaffold for cardiomyocyte repopulation. Dev. Cell, 2019, 51(4): 503-515.e4.
- 4.Heusch G. Myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective. Nat. Rev. Cardiol., 2020, 17(12): 773-789.doi:10.1038/s41569-020-0403-y.
- 5.Yang L.Q.; Peng J.J.; Shi A.P.; et al. Myocardium-targeted micelle nanomedicine that salvages the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(34): 38562-38574.
- 6.Chen J.L.; Huang N.; Ma B.L.; et al. Guidance of stem cells to a target destination in vivo by magnetic nanoparticles in a magnetic field. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2013, 5(13): 5976-5985.
- 7.Bahadur S.; Sachan N.; Harwansh R.K.; et al. Nanoparticlized system: promising approach for the management of alzheimer’s disease through intranasal delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des., 2020, 26(12): 1331-1344.
- 8.Pala R.; Anju V.T.; Dyavaiah M.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Nanomed., 2020, 15: 3741-3769.
- 9.Pan Q.; Xu J.; Wen C.J.; et al. Nanoparticles: promising tools for the treatment and prevention of myocardial infarction. Int. J. Nanomed., 2021, 16: 6719-6747.
- 10.Saikia C.; Das M.K.; Ramteke A.; et al. Effect of crosslinker on drug delivery properties of curcumin loaded starch coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2016, 93(Pt A): 1121-1132.
- 11.Malekzadeh A.M.; Ramazani A.; Rezaei S.J.T.; et al. Design and construction of multifunctional hyperbranched polymers coated magnetite nanoparticles for both targeting magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 490: 64-73.
- 12.Prabhakar U.; Maeda H.; Jain R.K.; et al. Challenges and key considerations of the enhanced permeability and retention effect for nanomedicine drug delivery in oncology. Cancer Res., 2013, 73(8): 2412-2417.
- 13.Suarez S.; Almutairi A.; Christman K.L. Micro- and nanoparticles for treating cardiovascular disease. Biomater. Sci., 2015, 3(4): 564-580.
- 14.Nguyen M.M.; Carlini A.S.; Chien M.P.; et al. Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for targeted accumulation and prolonged retention in heart tissue after myocardial infarction. Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(37): 5547-5552.
- 15.Lu A.H.; Salabas E.L.; Schüth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2007, 46(8): 1222-1244.
- 16.Arias L.S.; Pessan J.P.; Vieira A.P.M.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications: a perspective on synthesis, drugs, antimicrobial activity, and toxicity. Antibiotics, 2018, 7(2): 46.
- 17.Cheng M.; Yang J.J.; Zhao X.Q.; et al. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1): 959.
- 18.Cheng K.; Shen D.L.; Hensley M.T.; et al. Magnetic antibody-linked nanomatchmakers for therapeutic cell targeting. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4880.
- 19.Liu S., Chen X. , Bao L.;et al., Treatment of infarcted heart tissue via the capture and local delivery of circulating exosomes through antibody-conjugated magnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2020 4(11) 1063-1075.
- 20.Théry C.; Zitvogel L.; Amigorena S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2002, 2(8): 569-579.
- 21.Kowal J., Arras G., Colombo M.; et al., Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 113 (2016) E968-77.
- 22.Han Z.; Liu S.Q.; Pei Y.G.; et al. Highly efficient magnetic labelling allows MRI tracking of the homing of stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles following systemic delivery. J. Extracell. Vesicles, 2021, 10(3): e12054.
- 23.Busato A.; Bonafede R.; Bontempi P.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled exosomes from stem cells: a new method to obtain labeled exosomes. Int. J. Nanomed., 2016, 11: 2481-2490.
- 24.Li H.; Zhu J.; Xu Y.W.; et al. Notoginsenoside R1-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles targeting the site of injury through inflammatory cells improves heart repair after myocardial infarction. Redox. Biol., 2022, 54: 102384.
- 25.Wu X.X.; Liu L.; Zheng Q.L.; et al. Protocatechuic aldehyde protects cardiomycoytes against ischemic injury via regulation of nuclear pyruvate kinase M2. Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 2021, 11(11): 3553-3566.
How to Cite
Liu, M.; Ramponi, C.; Fan, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. Nanoparticle-based Drug Delivery System for Post Myocardial Infarction Management. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology 2022, 1 (1), 11. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.v1i1.171.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Minxuan Liu, Chiara Ramponi, Xiaoxue Fan, Xinzhuang Zhang, Liang Cao, Zhenzhong Wang, Wei Xiao
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


