Hyperlipidemia is one of the conditions that constitute metabolic disorder and it is a common public health problem. The condition is characterized by increased levels of cholesterol, triglycerides and/or lipoproteins; it is a recognized as a risk factor for the onset of many diseases such as type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and cardiovascular disease. Up to now, the primary drugs for treating hyperlipidemia are statins and monoclonal antibody drugs against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9). The main limitation of statins for long-term use is intolerable side effects. Evolocumab and Alirocumab, two monoclonal antibodies against PCSK9, can effectively decrease the level of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in patients with statin intolerance and familial hypercholesterolemia, while causing fewer side effects. However, due to its short half-life and high costs, these monoclonal antibody treatments might result in patients’ non-compliance with medication and considerable economic burden on patients. Given that RNA plays a key role in gene regulation, RNA-based therapeutics have become powerful blueprints for designing new anti-hyperlipidemia drugs. Here, we summarized RNA-based therapeutic strategies and the current clinical trials for RNA drugs in hyperlipidemia treatment.
- Open Access
- Review
From Bench to Bedside: Current Developments in RNA-Based Therapies for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia
- Yufei Zhou,
- Chen Chen *
Author Information
Received: 07 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 06 Nov 2022 | Published: 21 Dec 2022
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
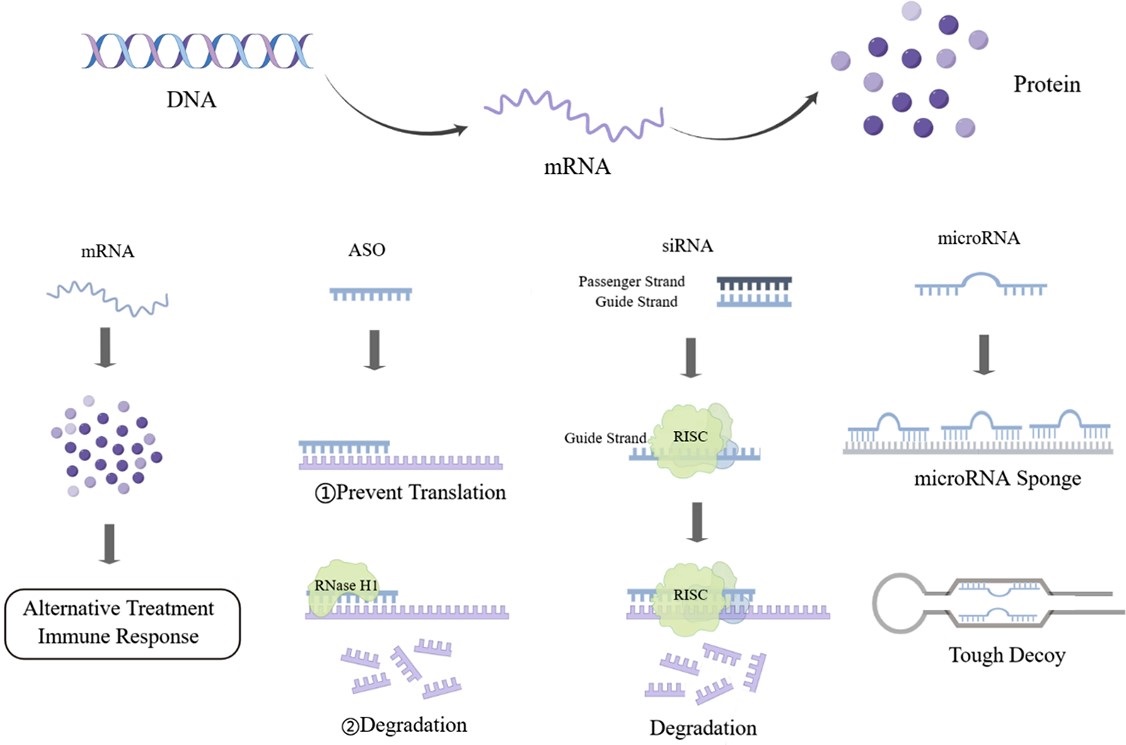
Keywords
hyperlipidemia | microRNA | therapeutic strategies | clinical trial
References
- 1.Rosenson R.S.; Najera S.D.; Hegele R.A. Heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia presenting as chylomicronemia syndrome. J. Clin. Lipidol., 2017, 11(1): 294-296.
- 2.Averbukh L.D.; Turshudzhyan A.; Wu D.C.; et al. Statin-induced liver injury patterns: a clinical review. J Clin Transl Hepatol, 2022, 10(3): 543-552.
- 3.Vinci P.; Panizon E.; Tosoni L.M.; et al. Statin-associated myopathy: emphasis on mechanisms and targeted therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(21): 11687.
- 4.Carmena R.; Betteridge D.J. Diabetogenic action of statins: mechanisms. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep., 2019, 21(6): 23.
- 5.Galicia-Garcia U.; Jebari S.; Larrea-Sebal A.; et al. Statin treatment-induced development of type 2 diabetes: from clinical evidence to mechanistic insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2020, 21(13): 4725.
- 6.Santos R.D.; Stein E.A.; Hovingh G.K.; et al. Long-term evolocumab in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2020, 75(6): 565-574.
- 7.Santos R.D.; Ruzza A.; Hovingh G.K.; et al. Evolocumab in pediatric heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. N. Engl. J. Med., 2020, 383(14): 1317-1327.
- 8.Blom D.J.; Harada-Shiba M.; Rubba P.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in adults with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia: the ODYSSEY HoFH trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2020, 76(2): 131-142.
- 9.Nissen S.E.; Stroes E.; Dent-Acosta R.E.; et al. Efficacy and tolerability of evolocumab vs ezetimibe in patients with muscle-related statin intolerance: the GAUSS-3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA, 2016, 315(15): 1580-1590.
- 10.Hu B.; Zhong L.P.; Weng Y.H.; et al. Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther., 2020, 5(1): 101.
- 11.Tsimikas S. RNA-targeted therapeutics for lipid disorders. Curr. Opin. Lipidol., 2018, 29(6): 459-466.
- 12.Kazi D.S.; Penko J.; Coxson P.G.; et al. Updated cost-effectiveness analysis of PCSK9 inhibitors based on the results of the FOURIER trial. JAMA, 2017, 318(8): 748-750.
- 13.Yu A.M.; Choi Y.H.; Tu M.J. RNA drugs and RNA targets for small molecules: principles, progress, and challenges. Pharmacol. Rev., 2020, 72(4): 862-898.
- 14.Qin S.G.; Tang X.S.; Chen Y.T.; et al. mRNA-based therapeutics: powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases. Signal Transduction Targeted Ther., 2022, 7(1): 166.
- 15.Katzmann J.L.; Packard C.J.; Chapman M.J.; et al. Targeting RNA with antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNA: JACC state-of-the-art review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2020, 76(5): 563-579.
- 16.Kulkarni J.A.; Witzigmann D.; Thomson S.B.; et al. The current landscape of nucleic acid therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16(6): 630-643.
- 17.Wada F.; Yamamoto T.; Ueda T.; et al. Cholesterol-GalNAc dual conjugation strategy for reducing renal distribution of antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acid Ther., 2018, 28(1): 50-57.
- 18.Kubczak M.; Michlewska S.; Bryszewska M.; et al. Nanoparticles for local delivery of siRNA in lung therapy. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2021, 179: 114038.
- 19.Weng Y.H.; Li C.H.; Yang T.R.; et al. The challenge and prospect of mRNA therapeutics landscape. Biotechnol. Adv., 2020, 40: 107534.
- 20.Hu B.; Li B.; Li K.; et al. Thermostable ionizable lipid-like nanoparticle (iLAND) for RNAi treatment of hyperlipidemia. Sci. Adv., 2022, 8(7): eabm1418.
- 21.Ammirati E.; Veronese G.; Brambatti M.; et al. Fulminant versus acute nonfulminant myocarditis in patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 2019, 74(3): 299-311.
- 22.Soh J.; Iqbal J.; Queiroz J.; et al. MicroRNA-30c reduces hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in mice by decreasing lipid synthesis and lipoprotein secretion. Nat. Med., 2013, 19(7): 892-900.
- 23.Zhang T.P.; Shi H.T.; Liu N.N.; et al. Activation of microRNA-378a-3p biogenesis promotes hepatic secretion of VLDL and hyperlipidemia by modulating ApoB100-Sortilin1 axis. Theranostics, 2020, 10(9): 3952-3966.
- 24.Ng R.; Wu H.; Xiao H.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-24 expression in liver prevents hepatic lipid accumulation and hyperlipidemia. Hepatology, 2014, 60(2): 554-564.
- 25.Bernardo B.C.; Gregorevic P.; Ritchie R.H.; et al. Generation of MicroRNA-34 sponges and tough decoys for the heart: developments and challenges. Front. Pharmacol., 2018, 9: 1090.
- 26.Li H.P.; Fan J.H.; Zhao Y.R.; et al. Nuclear miR-320 mediates diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction by activating transcription of fatty acid metabolic genes to cause lipotoxicity in the heart. Circ. Res., 2019, 125(12): 1106-1120.
- 27.Jeong D.; Yoo J.; Lee P.; et al. miR-25 tough decoy enhances cardiac function in heart failure. Mol. Ther., 2018, 26(3): 718-729.
- 28.Zheng C.Y.; Khoo C.; Furtado J.; et al. Apolipoprotein C-Ⅲ and the metabolic basis for hypertriglyceridemia and the dense low-density lipoprotein phenotype. Circulation, 2010, 121(15): 1722-1734.
- 29.Witztum J.L.; Gaudet D.; Freedman S.D.; et al. Volanesorsen and triglyceride levels in familial chylomicronemia syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med., 2019, 381(6): 531-542.
- 30.Hegele R.A. Apolipoprotein C-Ⅲ inhibition to lower triglycerides: one ring to rule them all?. Eur. Heart J., 2022, 43(14): 1413-1415.
- 31.Graham M.J.; Lee R.G.; Brandt T.A.; et al. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of ANGPTL3 antisense oligonucleotides. N. Engl. J. Med., 2017, 377(3): 222-232.
- 32.Horton J.D.; Cohen J.C.; Hobbs H.H. Molecular biology of PCSK9: its role in LDL metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci., 2007, 32(2): 71-77.
- 33.Collaboration NCDRF. Repositioning of the global epicentre of non-optimal cholesterol. Nature, 2020, 582(7810): 73-77.
- 34.Blanco-Domínguez R.; Sánchez-Díaz R.; De La Fuente H.; et al. A novel circulating MicroRNA for the detection of acute myocarditis. N. Engl. J. Med., 2021, 384(21): 2014-2027.
How to Cite
Zhou, Y.; Chen, C. From Bench to Bedside: Current Developments in RNA-Based Therapies for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology 2022, 1 (1), 7. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.v1i1.141.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Yufei Zhou, Chen Chen
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


