Background: Neuroinflammation plays a vital role in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease (PD). Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. (EL) has previously reported to exert anti-inflammation activity. Methods: In the present study, we examined the effects of the EL extract (ELE) on 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced mouse model of PD and potential molecular mechanisms. The anti-neuroinflammation effect of ELE was also determined in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced BV-2 cells in vitro. Moreover, the ELE-interacting target proteins were identified. And the bioinformatics analysis was performed based on the identified targets. Results: Our results showed that ELE significantly alleviated motor performance impairment and neuronal damage in MPTP-induced PD mice. In particular, ELE reversed MPTP-induced neuroinflammation via inhibiting microglial activation that was associated with progressive PD. Moreover, the anti-neuroinflammation effect of ELE was confirmed in LPS-induced BV-2 cells by detecting the release of pro-inflammatory factors such as nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (Il-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). Furthermore, the ELE- interacting target proteins were identified by affinity purification-mass spectrometry-based proteomics strategy. Then, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway was enriched by kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) analysis. We found that ELE markedly increased AMPK phosphorylation and inhibited nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signal in BV-2 cells. Conclusion: Collectively, these results indicate that ELE may exert significant neuroprotective effects against PD via targeting neuroinflammation.
- Open Access
- Article
Eupatorium Lindleyanum DC. Extract Protects against MPTP-induced Mouse of Parkinson’s Disease by Targeting Neuroinflammation
- Yichi Zhang 1,
- Lu Yao 1,
- Xiaowen Zhang 1,
- Zhuo Yang 1,
- Yang Chen 2,
- Lingli Zheng 1,
- Yongzhe Zheng 1,
- Wei Yu 2,
- Nilufar Z. Mamadalieva 3,
- Bo Han 2,
- Pengfei Tu 1,
- Rimma F. Mukhamatkhanova 3,
- Kewu Zeng 1, *
Author Information
Received: 10 May 2024 | Revised: 14 May 2024 | Accepted: 24 May 2024 | Published: 06 Jun 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
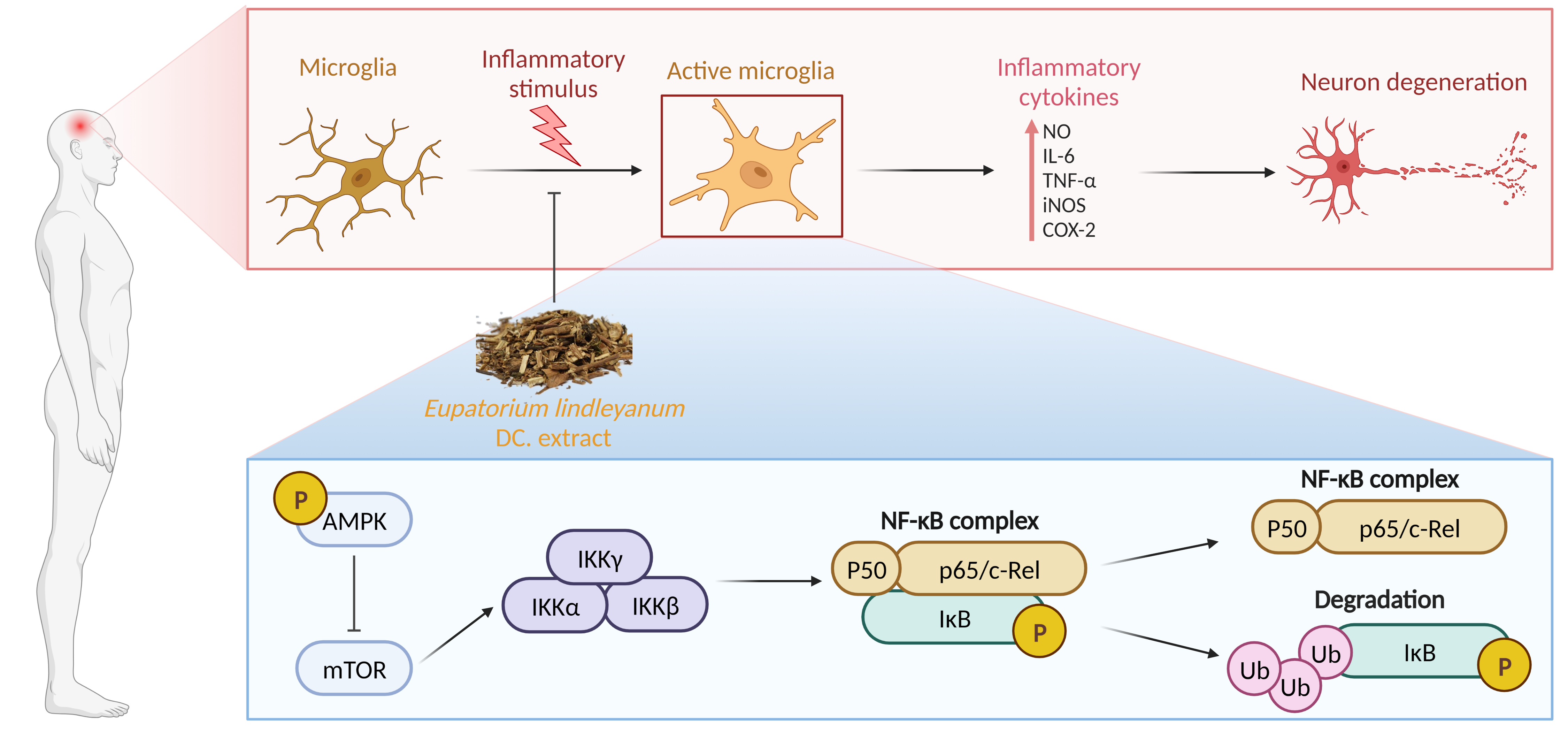
Keywords
Parkinson’s disease | Neuroinflammation | Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. | Target identification | AMPK pathway
References
- 1.Panicker, N.; Kam, T.I.; Wang, H.; et al. Neuronal NLRP3 is a parkin substrate that drives neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2022, 110, 2422–2437.
- 2.Gordon, R.; Albornoz, E.A.; Christie, D.C.; et al. Inflammasome inhibition prevents α-synuclein pathology and dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaah4066, https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aah4066.
- 3.Qian, H.; Kang, X.; Hu, J.; et al. Reversing a model of Parkinson’s disease with in situ converted nigral neurons. Nature 2020, 582, 550–556, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2388-4.
- 4.Bloem, B.R.; Okun, M.S.; Klein, C. Parkinson’s disease. The Lancet. 2021, 397, 2284–2303.
- 5.Qu, C.; Liu, L.; Xu, Q.Q. Neuroprotective effects of San-Jia-Fu-Mai decoction: Studies on the in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2021, 7, 192–200.
- 6.Raza, C.; Anjum, R.; Shakeel, N.U.A. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms, translational models and management strategies. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 77–90, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.03.057.
- 7.Hirsch, E.C.; Hunot, S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 382–397.
- 8.Pajares, M.; Rojo, A.I.; Manda, G.; et al. Inflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2020, 9, 1687, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071687.
- 9.Zhou, Q.; Le, M.L.; Yang, Y.Y. Discovery of novel phosphodiesterase-1 inhibitors for curing vascular dementia: Suppression of neuroinflammation by blocking NF-kappaB transcription regulation and activating cAMP/CREB axis. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2023, 13, 1180–1191.
- 10.Kim, B.-W.; Koppula, S.; Park, S.-Y.; et al. Attenuation of neuroinflammatory responses and behavioral deficits by Ligusticum officinale (Makino) Kitag in stimulated microglia and MPTP-induced mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 388–397, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2014.11.004.
- 11.Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; et al. Novel Microglia-based Therapeutic Approaches to Neurodegenerative Disorders. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 491–502, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-022-01013-6.
- 12.Huang, B.X.; Liu, J.X.; Meng, T.Y. Polydatin prevents lipopolysaccharide (LPS)- induced Parkinson’s disease via regulation of the AKT/GSK3β-Nrf2/NF-κB signaling axis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2527.
- 13.Chu, C.J.; Ren, H.L.; Xu, N.Y. Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. sesquiterpenes fraction attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 185, 263–271.
- 14.Huang, L.; Xu, D.Q.; Chen, Y.Y. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of chemical components in Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry integrated with anti-inflammatory activity research. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 3174–3187.
- 15.Chu, C.; Yao, S.; Chen, J.; et al. Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. flavonoids fraction attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 39, 23–33, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.06.032.
- 16.Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Lai, F.; et al. Traditional Applications, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Eupatorium lindleyanum DC.: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 8, 577124 https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.577124.
- 17.Zheng, S.Z.; Zhang, X.W.; Song, X.M.; et al. Epoxymicheliolide directly targets histone H2B to inhibit neuroinflammation via recruiting E3 ligase RNF20. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 177, 106093, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106093.
- 18.Kong, X.; Ai, G.; Wang, D.; et al. PDE4 and Epac1 Synergistically Promote Rectal Carcinoma via the cAMP Pathway. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2019, 2019, 1–5, https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7145198.
- 19.Zhao, M.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Global identification of the cellular targets for a multi-molecule system by a photochemically-induced coupling reaction. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 3449–3452, https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc00392e.
- 20.Zhang, X.W.; Feng, N.; Liu, Y.C.; et al. Neuroinflammation inhibition by small-molecule targeting USP7 noncatalytic domain for neurodegenerative disease therapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo0789, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abo0789.
- 21.Zheng, Z.V.; Cheung, C.Y.; Lyu, H.; et al. Baicalein enhances the effect of low dose Levodopa on the gait deficits and protects dopaminergic neurons in experimental Parkinsonism. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 64, 242–251, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2019.02.005.
- 22.Wang, X.H.; Lu, G.; Hu, X.; et al. Quantitative assessment of gait and neurochemical correlation in a classical murine model of Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 142–142, https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-13-142.
- 23.Li, Y.N.; Xia, Y.; Yin, S.J. Targeting microglial α-synuclein/TLRs/NF- kappaB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719807.
- 24.Yao, L.; Liao, M.; Wang, J.K.; et al. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Photo-Cross-Linking Strategy for Cellular Target Identification of Supercomplex Molecular Systems. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3180–3187, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04652.
- 25.Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; et al. Betaine in inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01070.
- 26.Hernandez-Baixauli, J.; Abasolo, N.; Palacios-Jordan, H.; et al. Imbalances in TCA, Short Fatty Acids and One-Carbon Metabolisms as Important Features of Homeostatic Disruption Evidenced by a Multi-Omics Integrative Approach of LPS-Induced Chronic Inflammation in Male Wistar Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2563, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23052563.
- 27.Behl, T.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.; et al. Reviving the mutual impact of SARS-COV-2 and obesity on patients: From morbidity to mortality. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113178–113178, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113178.
- 28.Hardie, D.G.; Schaffer, B.E.; Brunet, A. AMPK: An Energy-Sensing Pathway with Multiple Inputs and Outputs. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 26, 190–201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.013.
- 29.Chen, Y.H.; Li, Y.P.; Li, C.X. Dexmedetomidine alleviates pain in MPTP-treated mice by activating the AMPK/mTOR/NF-kappaB pathways in astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 791, 136933.
- 30.Kim, D.Y.; Leem, Y.H.; Park, J.S.; et al. RIPK1 Regulates Microglial Activation in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation and MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Models. Cells 2023, 12, 417, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12030417.
- 31.Han, C.J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Sun, L. The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits microglial activation via the AMPK/mTOR/NF-kappaB pathway. Acta. Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 1292–1302.
- 32.Yu, Q.; Zeng, K.W.; Ma, X.L.; et al. Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses pro-inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2017, 15, 751–757, https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(17)30106-1.
- 33.Herrero, M.T.; Estrada, C.; Maatouk, L. Inflammation in Parkinson’s disease: role of glucocorticoids. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 32.
- 34.Gan, P.; Xia, Q.F.; Hang, G.H. Knockdown of cathepsin D protects dopaminergic neurons against neuroinflammation-mediated neurotoxicity through inhibition of NF-κB signalling pathway in Parkinson’s disease model. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 46, 337–349.
- 35.Chen, Y.H.; Jiang, M.J.; Li, L. DL-3-n-butylphthalide reduces microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson’s disease model mice. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3884–3890.
- 36.Zhang, Y.; Dong, F.; Cao, Z.; et al. Eupalinolide A induces autophagy via the ROS/ERK signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 61, 1–16, https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2022.5421.
- 37.Wang, F.; Zhong, H.H.; Fang, S.Q. Potential anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactones from Eupatorium lindleyanum. Planta. Med. 2018, 84, 123–128.
- 38.Lv, H.N.; Wen, R.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Nitrogen Oxide Inhibitory Trimeric and Dimeric Carbazole Alkaloids from Murraya tetramera. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2432–2439, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00527.
- 39.Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, K.W.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Prenylated Phenylpropenols and Coumarin Derivatives from Murraya exotica. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 22–33, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.7b00518.
- 40.Zhang, J.; Hu, K.; Di, L.; et al. Traditional herbal medicine and nanomedicine: Converging disciplines to improve therapeutic efficacy and human health. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113964, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2021.113964.
- 41.Peng, X.; Tang, F.; Yang, Y.; et al. Bidirectional effects and mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 298, 115578, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2022.115578.
- 42.Yang, Y.; Wu, C. The linkage of gut microbiota and the property theory of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): Cold-natured and sweet-flavored TCMs as an example. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116167, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.116167.
- 43.Steinberg, G.R.; Hardie, D.G. New insights into activation and function of the AMPK. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 255–272, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x.
- 44.Mao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; et al. Overview of Research into mTOR Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 5295, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27165295.
- 45.Ding, Y.J.; Peng, Y.M.; Wu, H.L. The protective roles of liraglutide on Kawasaki disease via AMPK/mTOR/NF-kappaB pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 110028.
- 46.Fu, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Herbal Compounds Play a Role in Neuroprotection through the Inhibition of Microglial Activation. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9348046.
- 47.Qiao, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Herbal/Natural Compounds Resist Hallmarks of Brain Aging: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 920, https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox12040920.
How to Cite
Zhang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, W.; Mamadalieva, N. Z.; Han, B.; Tu, P.; Mukhamatkhanova, R. F.; Zeng, K. Eupatorium Lindleyanum DC. Extract Protects against MPTP-induced Mouse of Parkinson’s Disease by Targeting Neuroinflammation. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology 2024, 3 (2), 100009. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.2024.100009.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


