Janus kinase (JAK) is a family of intracellular non-receptor tyrosine kinases with four members (JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and Tyk2). The JAK-STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway is an evolutionary conserved mechanism of transmembrane signal transduction relaying over 50 cytokines signals to regulate the proliferation, immune response, inflammation, and malignancy. The dysfunction of JAK-STAT signaling pathway is directly associated with the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, as well as tumor progression. Studies have shown that targeting the JAK family with small-molecule inhibitors can treat inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and myeloproliferative neoplasms. In this review, we discuss the current understanding of the JAK-STAT signaling and approved JAK inhibitors.
- Open Access
- Review
Janus Kinases and Autoimmunity: Bridging Pathways to Therapy
- Yazi Wei,
- Tiantai Zhang *
Author Information
Received: 07 Feb 2024 | Revised: 01 Mar 2024 | Accepted: 01 Mar 2024 | Published: 05 Jun 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
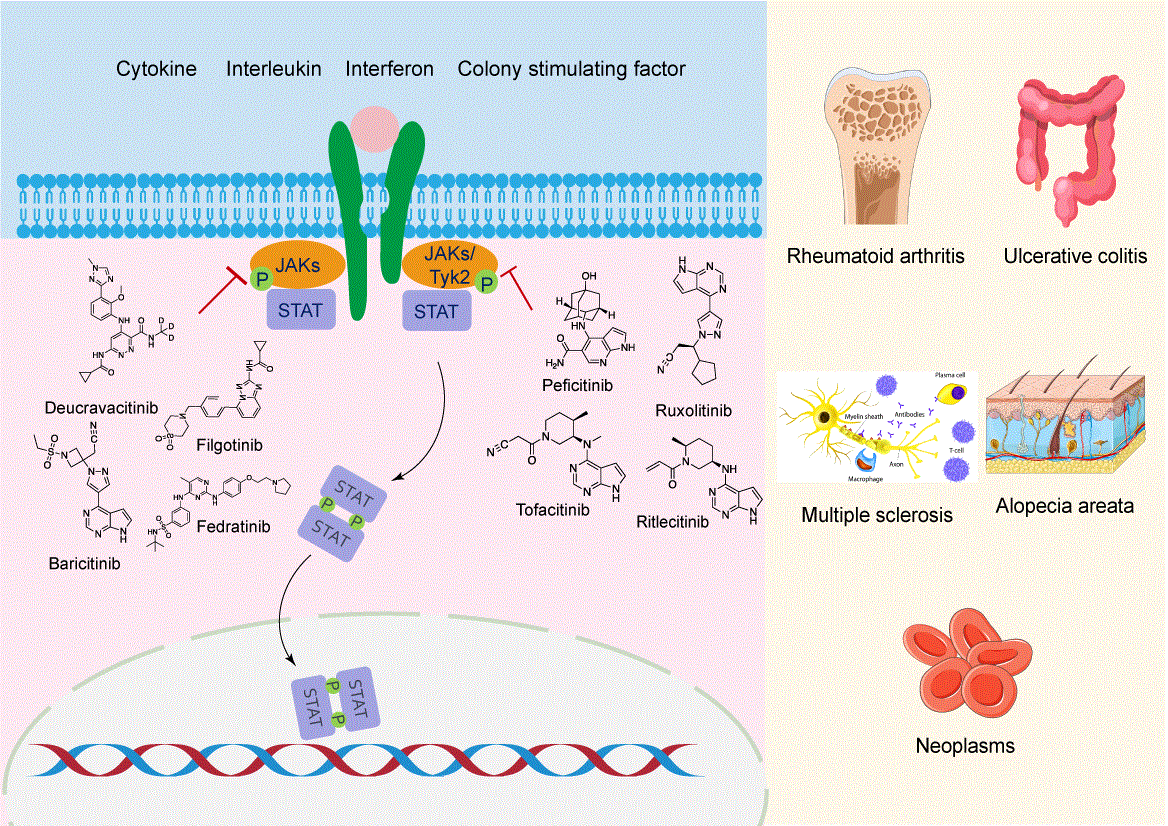
Keywords
Janus kinase | JAK-STAT pathway | autoimmune disease | JAK inhibitor
References
- 1.Banerjee, S.; Biehl, A.; Gadina, M. S.; et al. JAK-STAT signaling as a target for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: Current and future prospects. Drugs 2017, 77, 521–546.
- 2.Hu, X.; Li, J.; Fu, M.; et al. The JAK/STAT signaling oathway: From bench to clinic. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 402.
- 3.O’Shea, J.J.; Holland, S.M.L.; Staudt, M. JAKs and STATs in immunity, immunodeficiency, and cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 161–170.
- 4.Alunno, A.; Padjen, I.; Fanouriakis, A.; et al. Pathogenic and therapeutic relevance of JAK/STAT signaling in systemic lupus erythematosus: Integration of distinct inflammatory pathways and the prospect of their inhibition with an oral agent. Cell 2019, 8, 898.
- 5.Ihle, J.N.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Quelle, F.W.; et al. Signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily: JAKs and STATs. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1994, 19, 222–227.
- 6.Goll, G.L.; Kvien, T.K. New-generation JAK inhibitors: How selective can they be? Lancet 2018, 391, 2477–2478.
- 7.Schwartz, D.M.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; et al. JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 843–862.
- 8.Phillips, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Cheon, H.; et al. The JAK-STAT pathway at 30: Much learned, much more to do. Cell 2022, 185, 3857–3876.
- 9.Gadina, M.; Johnson, C.; Schwartz, D.; et al. Translational and clinical adences in JAK-STAT biology: The present and future of jakinib. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 499‒514.
- 10.Krolewaki, J.J.; Lee, R.; Eddy, R.; et al. Identification and chromosomal mapping of new human tyrosine kinease genes. Oncogene 1990, 5, 277‒282.
- 11.Wilks, A.F.; Harpur, A.G.; Kurban, R.R.; et al. Two novel protein-tyrosine kinases, each with a second phaophatransferase-related catalytic domain, define a new class of protein kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 2057–65.
- 12.Harpur, A.G.; Andres, A.C.; Zimiecki, A.; et al. JAK2, a third menber of the JAK family of protein tyrosine kinases. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1347‒1353.
- 13.Rane, S.G.; Reddy, E.P. JAK3, a novel JAK kinase associated with terminal differentiation of hematopoietic cells. Oncogene 1994, 9, 2415–23.
- 14.Yamaoka, K.; Saharinen, P.; Pesu, M.; et al. The Janus kinases (Jaks). Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 253.
- 15.RoskoskiJr. , R. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the treatment of neoplastic and inflammatory disorders. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 183, 106362.
- 16.Liosi, M.E.; Looplito, J.A.; Henry, S.P.; et al. Insights on JAK2 modulation by potent, selective, and cellpermeable pseudokinase-domain ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8380–8400.
- 17.Xue, C.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; et al. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Autoimmune disorders and cancer. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 204.
- 18.Castelo-Soccio, L.; Kim, H.; Gadina, M.; et al. Protein kinases: Drug targets for immunological disorders. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 787‒806.
- 19.Basquiera, A.L.; Soria, N.W.; Ryser, R.; et al. Clinical significance of V617F mutation of the JAK2 gene in patients with chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Hematology 2009, 14, 323‒330.
- 20.Shao, S.; Chen, C.J.; Shi, G.N.; et al. JAK inhibition ameliorated EAE by blocking GM-CSF-driven inflammatory signature of monocytes. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4185‒4201.
- 21.RoskoskiJr. , R. Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in the treatment of inflammatory and neoplastic diseases, Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 784‒803.
- 22.Chen, C.; Lu, D.; Sun, T.; et al. JAK3 inhibitors for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: A patent review (2016-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2022, 32, 225‒242.
- 23.Chen, C.; Yin, Y.; Shi, G.N.; et al. A highly selective JAK3 inhibitor is developed for treating rheumatoid arthritis by suppressing γc cytokines related JAK-STAT signal. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo4363.
- 24.Schindler, C.; Levy, D.E.; Decker, T. JAK-STAT signaling: From interferons to cytokines, J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20059‒20063.
- 25.He, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Selective Tyk2 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents: A patent review (2015‒2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 137‒149.
- 26.Wrobleski, S.T.; Moslin, R.; Lin, S.; et al. Highly selective inhibition of tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) for the treatment of autoimmune diseases: Discovery of the allosteric inhibitor BMS-986165. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8973–8995.
- 27.O’Shea, J.J.; Gadina, M.; Schreiber, R.D. Cytokine signaling in 2002: New surprises in the Jak/Stat pathway. Cell 2002, 109, S121–S131.
- 28.Ihle, J.N.; Kerr, I.M. Jaks and Stats in signaling by the cytokine receptor superfamily. Trends Genet. 1995, 11, 69–74.
- 29.Yoshimura, A.; Ohkubo, T.; Kiguchi, T.; et al. A novel cytokine-inducible gene CIS encodes an SH2-containing protein that binds to tyrosine-phosphorylated interleukin 3 and erythropoietin receptors. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 2816–2826.
- 30.Irie-Sasaki, J.; Sasaki, T.; Matsumoto, W.; et al. CD45 is a JAK phosphatase and negatively regulates cytokine receptor signalling. Nature 2001, 409, 349–354.
- 31.Ghoreschi, K.; Laurence, A.; O’Shea, J.J. Janus kinases in immune cell signaling. Immunol Rev. 2009, 228, 273–287.
- 32.Tefferi, A. Novel mutations and their functional and clinical relevance in myeloproliferative neoplasms: JAK2, MPL, TET2, ASXL1, CBL, and IKZFIDH1. Leukemia 2010, 24, 1128–1138
- 33.Allen Reish, H.E.; Standaert, D.G. Role of α-synuclein in inducing innate and adaptive immunity in Parkinson disease. J. Parkinson’s Dis. 2015, 5, 1–19.
- 34.Harel, S.; Higgins, C.A.; Cerise, J.E.; et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of JAK-STAT signaling promotes hair growth. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500973.
- 35.Legrand, J.M.D.; Roy, E.; Ellis, J.J.; et al. STAT5 activation in the dermal papilla is important for hair follicle growth phase induction. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1781–1791.
- 36.Angelini, J.; Talotta, R.; Roncato, R.; et al. JAK-Inhibitors for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A focus on the present and an outlook on the future. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1002.
- 37.Leroy, E.; Constantinescu, S.N. Rethinking JAK2 inhibition: Towards novel strategies of more specific and versatile Janus kinase inhibition. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1023–1038.
- 38.Vainchenker, W.; Leroy, E.; Gilles, L.; et al. JAK inhibitors for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms and other disorders. F1000Research 2018, 7, 82.
- 39.Quintás-Cardama, A.; Vaddi, K.; Liu, P.; et al. Preclinical characterization of the selective JAK1/2 inhibitor INCB018424: Therapeutic implications for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2010, 115, 3109–3117.
- 40.Raedler, L.A. Jakafi (Ruxolitinib): First FDA-approved medication for the treatment of patients with polycythemia vera. Am. Health Drug Benefits 2015, 8, 75–79.
- 41.Fogelman, D.; Cubillo, A.; García-Alfonso, P.; et al. Randomized, double-blind, phase two study of ruxolitinib plus regorafenib in patients with relapsed/refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5382–5393.
- 42.Jagasia, M.; Perale, M.A.; Schroeder, M.A.; et al. Ruxolitinib for the treatment of steroid-refractory acute GVHD (REACH1): A multicenter, open-label phase 2 trial. Blood 2020, 135, 1739–1749.
- 43.Cervantes, F.; Pereira, A. Does ruxolitinib prolong the survival of patients with myelofibrosis? Blood 2017, 129, 832–837.
- 44.Verstovsek, S.; Mesa, R.A.; Gotlib, J.; et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 799–807.
- 45.Papp, K.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Kircik, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: Results from 2 phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 863–872.
- 46.Rosmarin, D.; Passeron, T.; Pandya, A.G.; et al. Two Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trials of Ruxolitinib Cream for Vitiligo. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1445–1455.
- 47.Flanagan, M.E.; Blumenkopf, T.A.; Brissette, W.H.; et al. Discovery of CP-690,550: A potent and selective janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and organ transplant rejection, J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 8468–8484.
- 48.Fleischmann, R.; Kremer, J.; Cush, J.; et al. Placebo-controlled trial of tofacitinib monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 495–507.
- 49.Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.; Cohen, S.; et al. Tofacitinib or Adalimumab versus Placebo in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 508–519.
- 50.Gladman, D.; Rigby, W.; Azevedo, V.F.; et al. Tofacitinib for psoriatic arthritis in patients with an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1525–1536.
- 51.Mease, P.; Hall, S.; FitzGerald, O.; et al. Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo for psoriatic arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1537–1550.
- 52.Sandborn, W.J.; Ghosh, S.; Panes, J.; et al. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in active ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 616–624.
- 53.Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; et al. A Comprehensive overview of globally approved JAK inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001.
- 54.Markham, A. Baricitinib: First global approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 697–704.
- 55.Coricello, A.; Mesiti, F.; Lupia, A.; et al. Inside perspective of the synthetic and computational toolbox of JAK inhibitors: Recent updates. Molecules 2020, 25, 3321.
- 56.Fridman, J.S.; Scherle, P.A.; Collins, R.; et al. Selective inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 is efficacious in rodent models of arthritis: Preclinical characterization of INCB028050. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 5298–5307.
- 57.Melo, A.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Torres, T. Baricitinib for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 35, 2404–2413.
- 58.King, B.; Ko, J.; Forman, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the oral Janus kinase inhibitor baricitinib in the treatment of adults with alopecia areata: Phase 2 results from a randomized controlled study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 85, 847–853.
- 59.Bretz, F.; Posch, M.; Glimm, E.; et al. Graphical approaches for multiple comparison procedures using weighted Bonferroni, Simes, or parametric tests. Biometrical J. 2011, 53, 894–8913.
- 60.Freitas, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Torres, T. Barcitinib for the treatment for alopecia areata. Drugs 2023, 83, 761–770.
- 61.Markham, A.; Keam, S.J. Peficitinib: First global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 887–891.
- 62.Hamaguchi, H.; Amano, Y.; Moritomo, A.; et al. Discovery and structural characterization of peficitinib (ASP015K) as a novel and potent JAK inhibitor, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 4971–4983.
- 63.Dhillon, S. Delgocitinib: First approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 609–615.
- 64.Tanimoto, Y.; Ogawa, C.; Oki, Y.; et al. Pharmacological properties of JTE-052: A novel potent JAK inhibitor that suppresses various inflammatory responses in vitro and in vivo. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 41–51.
- 65.Lamb, Y.N. Pacritinib: First approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 831–838.
- 66.Keam, S.J. Momelotinib: First approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 1709–1715.
- 67.Parmentier, J.M.; Voss, J.; Graff, C.; et al. In vitro and in vivo characterization of the JAK1 selectivity of upadacitinib (ABT-494). BMC Rheumatol. 2018, 2, 23.
- 68.Dhillon, S.; Keam, S.J. Filgotinib: First approval. Drugs 2020, 80, 1987–1997.
- 69.Van Rompaey, L.; Galien, R.; van der Aar, E.M.; et al. Preclinical characterization of GLPG0634, a selective inhibitor of JAK1, for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3568–3577.
- 70.Deeks, E.D.; Duggan, S. Abrocitinib: First approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 2149–2157.
- 71.Vazquez, M.L.; Kaila, N.; Strohbach, J.W.; et al. Identification of N-{cis-3-[Methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino]cyclobutyl}propane-1-sulfonamide (PF-04965842): A selective JAK1 clinical candidate for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. J. Med. Chem, 2018, 61, 1130–1152.
- 72.Blair, H.A. Fedratinib: First approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1719–1725.
- 73.Wernig, G.; Kharas, M.G.; Okabe, R.; et al. Efficacy of TG101348, a selective JAK2 inhibitor, in treatment of a murine model of JAK2V617F-induced polycythemia vera. Cancer Cell. 2008, 13, 311–320.
- 74.Blair, H.A. Ritlecitinib: First approval. Drugs 2023, 83, 1315–1321.
- 75.Xu, H.; Jesson, M.I.; Seneviratne, U.I.; et al. PF-06651600, a Dual JAK3/TEC Family Kinase Inhibitor. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1235–1242.
- 76.Hoy, S.M. Deucravacitinib: First approval. Drugs 2022, 82, 1671–1679.
- 77.Le, A.M.; Puig, L.; Torres, T. Deucravacitinib for the treatment of psoriatic disease. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 813–822.
- 78.Jensen, L.T.; Attfield, K.E.; Feldmann, M.; et al. Allosteric TYK2 inhibition: Redefining autoimmune disease therapy beyond JAK1-3 inhibitors. eBioMedcine 2023, 97, 104840.
- 79.Armstrong, A.W.; Gooderham, M.; Warren, R.B.; et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled phase 3 POETYK PSO-1 trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 29–39.
- 80.Strober, B.; Thaci, D.; Sofen, H.; et al. Deucravacitinib versus placebo and apremilast in moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Efficacy and safety results from the 52-week, randomized, double-blinded, phase 3 program for evaluation of TYK2 inhibitor psoriasis second trial. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 40–51.
- 81.FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warnings-about-increased-riskserious-heart-related-events-cancer-blood-clots-and-death. Accessed on 1 March 2024.
- 82.Summary Safety Review - Xeljanz and Xeljanz XR (tofacitinib) and Jakavi (ruxolitinib) - Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitors - Assessing the Potential Risk of Blood Clots in the Deep Veins (Venous Thromboembolic Events). Published: June 18, 2020. https://hpr-rps.hres.ca/reg-content/summary-safety-review-detail.php?lang=en&linkID=SSR00240#references. Accessed on 1 March 2024.
- 83.Sivaraman, P.; Cohen, S.B. Malignancy and Janus kinase inhibition. Rheum. Dis. Clin. North. Am. 2017, 43, 79–93.
- 84.Curtis, J.R.; Xie, F.; Yun, H.; et al. Real-world comparative risks of herpes virus infections in tofacitinib and biologic-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1843–1847.
- 85.Crowley, E.L.; Nezamololama, N.; Papp, K.; et al. Abrocitinib for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 955–962.
- 86.Miyatake, D.; Shibata, T.; Toyoshima, J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of a single oral dose of peficitinib (ASP015K) in Japanese subjects with normal and impaired hepatic function. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 699–708.
- 87.Pardanani, A.; Harrison, C.; Cortes, J.E.; et al. Safety and efficacy of fedratinib in patients with primary or secondary myelofibrosis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 643–651.
How to Cite
Wei, Y.; Zhang, T. Janus Kinases and Autoimmunity: Bridging Pathways to Therapy. International Journal of Drug Discovery and Pharmacology 2024, 3 (2), 100007. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijddp.2024.100007.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


