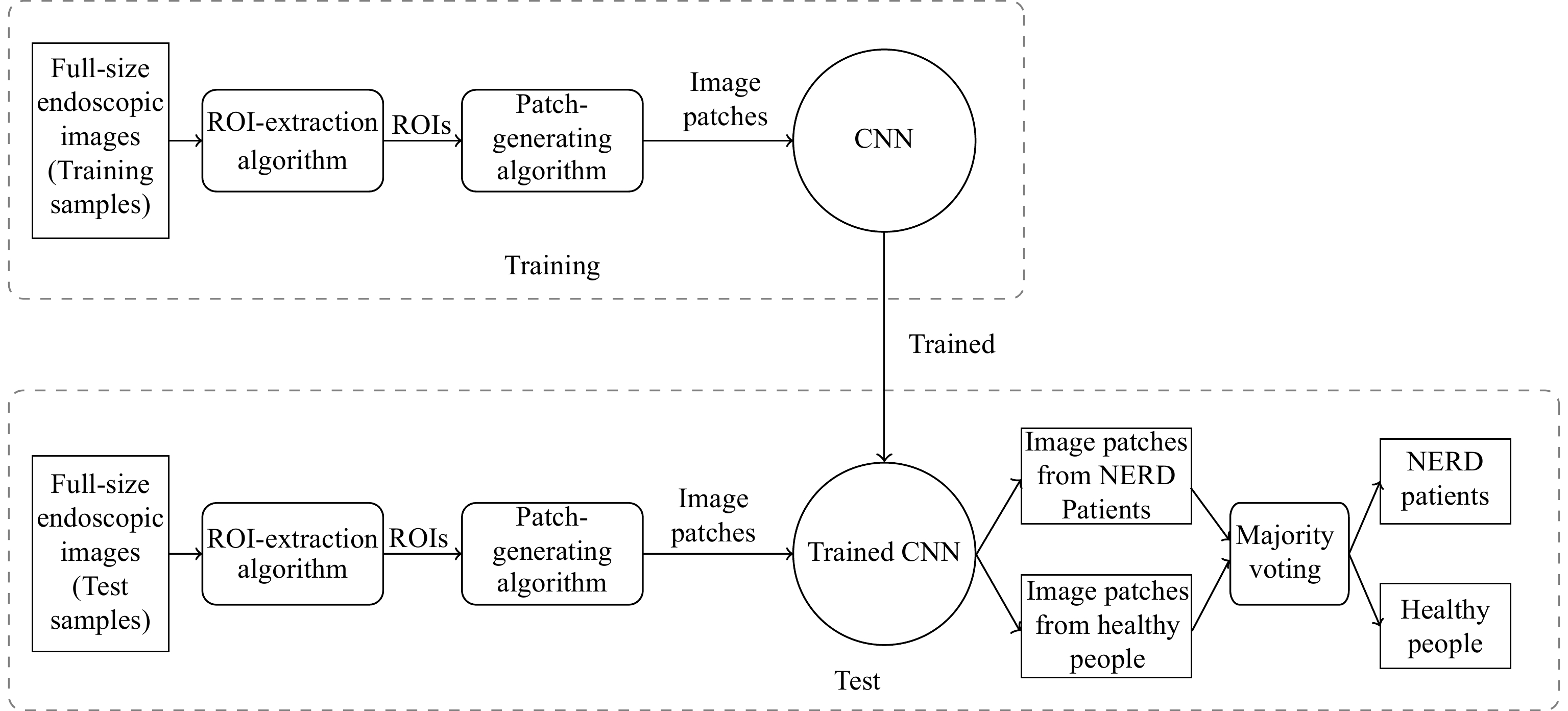
The nonerosive reflux disease (NERD) is a common condition, the symptoms of which mainly include heartburn, regurgitation, dysphagia and odynophagia. The conventional diagnosis of NERD needs the endoscopic examination, biopsy of the lining of the esophagus (mucosa), and ambulatory pH testing over 24 to 96 hours, which is complex and time-consuming. To address this problem, a computer-aided diagnosis system for NERD (named NERD-CADS) has been proposed in our previous paper. The NERD-CADS offers a more convenient and efficient approach to diagnosing NERD, which only requires the input of endoscopic images into the computer to produce a nearly instant diagnostic result. The NERD-CADS uses a convolutional neural network (CNN) as a classifier and can classify the endoscopic images captured in the esophagus of both healthy people and NERD patients. This is, in fact, a classification problem of two classes: non-NERD and NERD. We conduct ten-fold cross-validation to verify the classification accuracy of the NERD-CADS. The experiment shows that the mean of ten-fold classification accuracy of the NERD-CADS test reaches 77.8%. In this paper, we aim to improve the classification accuracy of the NERD-CADS. We add the contrastive self-supervised learning as an additional component to the NERD-CADS (named NERD-CADS-CSSL), and investigate whether it can learn the capability of extracting representations to improve the classification accuracy. This paper combines the contrastive self-supervised learning with transfer learning, which first employs massive public image data to train the CNN by the contrastive self-supervised learning, and then uses the endoscopic images to fine-tune the CNN. In this way, the capability of extracting representations (learned by the contrastive self-supervised learning) can be transferred into the downstream task (NERD diagnosis). The experiment shows that the NERD-CADS-CSSL can obtain a higher mean (80.6%) in tests than the NERD-CADS (77.8%).
- Open Access
- Article
Improved Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Nonerosive Reflux Disease Using Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning with Transfer Learning
- Junkai Liao 1,
- Hak-Keung Lam 1, *,
- Shraddha Gulati 2,
- Bu Hayee 2
Author Information
Received: 05 Feb 2023 | Accepted: 21 Jul 2023 | Published: 26 Sep 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
deep learning | convolutional neural network (CNN) | contrastive self-supervised learning | transfer learning | nonerosive reflux disease (NERD)
References
- 1.Martinez, S.D.; Malagon, I.B.; Garewal, H.S.; et al. Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) - acid reflux and symptom patterns. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther., 2003, 17: 537−545.
- 2.Narayani, R.I.; Burton, M.P.; Young, G.S. Utility of esophageal biopsy in the diagnosis of nonerosive reflux disease. Dis. Esophagus, 2003, 16: 187−192.
- 3.Modlin, I.M.; Hunt, R.H.; Malfertheiner, P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of non-erosive reflux disease - the vevey NERD consensus group. Digestion, 2009, 80: 74−88.
- 4.Chen, C.L.; Hsu, P.I. Current advances in the diagnosis and treatment of nonerosive reflux disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract., 2013, 2013: 653989.
- 5.Khan, M.Q.; Alaraj, A.; Alsohaibani, F.; et al. Diagnostic utility of impedance-pH monitoring in refractory non-erosive reflux disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil., 2014, 20: 497−505.
- 6.Barrett, C.; Choksi, Y.; Vaezi, M.F. Mucosal impedance: A new approach to diagnosing gastroesophageal reflux disease and eosinophilic esophagitis. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep., 2018, 20: 33.
- 7.Liao, J.K.; Lam, H.K.; Jia, G.; et al. A case study on computer-aided diagnosis of nonerosive reflux disease using deep learning techniques. Neurocomputing, 2021, 445: 149−166.
- 8.Huang, C.R.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, W.Y.; et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease diagnosis using hierarchical heterogeneous descriptor fusion support vector machine. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng., 2016, 63: 588−599.
- 9.Fass, R.; Fennerty, B.M.; Vakil, N. Nonerosive reflux disease - current concepts and dilemmas. Am. J. Gastroenterol., 2001, 96: 303−314.
- 10.Fass, R. Erosive esophagitis and nonerosive reflux disease (NERD): Comparison of epidemiologic, physiologic, and therapeutic characteristics. J. Clin. Gastroenterol., 2007, 41: 131−137.
- 11.Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Norouzi, M.; et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 13–18 July 2020; JMLR.org, 2020; pp. 1597–1607.
- 12.Chen, T.; Kornblith, S.; Swersky, K.; et al. Big self-supervised models are strong semi-supervised learners. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, 2020; pp. 22243–22255.
- 13.He, K.M.; Fan, H.Q.; Wu, Y.X.; et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; IEEE: New York, 2020; pp. 9726–9735. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00975
- 14.Chen, X.L.; Fan, H.Q.; Girshick, R.; et al. Improved baselines with momentum contrastive learning. arXiv: 2003.04297, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2003.04297
- 15.Chen, X.L.; Xie, S.N.; He, K.M. An empirical study of training self-supervised vision transformers. In Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; IEEE: New York, 2021; pp. 9620–9629. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00950
- 16.Grill, J.B.; Strub, F.; Altché, F.; et al. Bootstrap your own latent a new approach to self-supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 6–12 December 2020; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, 2020; pp. 21271–21284.
- 17.Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; JMLR.org, 2015; pp. 448–456.
- 18.Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted Boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; Omnipress, 2010; pp. 807–814.
- 19.Lillicrap, T.P.; Hunt, J.J.; Pritzel, A.; et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Juan, USA, 2–4 May 2016; ICLR: Ithaca, 2015. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1509.02971
- 20.Tian, Y.D.; Yu, L.T.; Chen, X.L.; et al. Understanding self-supervised learning with dual deep networks. arXiv: 2010.00578v1, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2010.00578
- 21.Richemond, P.H.; Grill, J.B.; Altché, F.; et al. BYOL works even without batch statistics. arXiv: 2010.10241, 2020. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2010.10241
- 22.Pan, S.J.; Yang, Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., 2010, 22: 1345−1359.
- 23.Torrey, L.; Shavlik, J. Transfer learning. In Handbook of Research on Machine Learning Applications and Trends: Algorithms, Methods, and Techniques; Olivas, E.S; Guerrero, J.D.M.; Martinez-Sober, M.; et al., Eds.; IGI Global: Hershey, 2010; pp. 242–264. doi: 10.4018/978-1-60566-766-9.ch011
- 24.Szegedy, C.; Ioffe, S.; Vanhoucke, V.; et al. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, USA, 4–9 February 2017; AAAI: Palo Alto, 2017; pp. 4278–4284.
- 25.Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; et al. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: New York, 2009; pp. 248–255. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
- 26.Coates, A.; Ng, A.; Lee, H. An analysis of single-layer networks in unsupervised feature learning. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, USA, 11–13 April 2011; PMLR, 2011; pp. 215–223.
- 27.Metz, C.E. Basic principles of ROC analysis. Semin. Nucl. Med., 1978, 8: 283−298.
How to Cite
Liao, J.; Lam, H.-K.; Gulati, S.; Hayee, B. Improved Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Nonerosive Reflux Disease Using Contrastive Self-Supervised Learning with Transfer Learning. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (3), 100010. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2023.100010.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


