With the improvement of hardware computing power and the development of deep learning algorithms, a revolution of "artificial intelligence (AI) + medical image" is taking place. Benefiting from diversified modern medical measurement equipment, a large number of medical images will be produced in the clinical process. These images improve the diagnostic accuracy of doctors, but also increase the labor burden of doctors. Deep learning technology is expected to realize an auxiliary diagnosis and improve diagnostic efficiency. At present, the method of deep learning technology combined with attention mechanism is a research hotspot and has achieved state-of-the-art results in many medical image tasks. This paper reviews the deep learning attention methods in medical image analysis. A comprehensive literature survey is first conducted to analyze the keywords and literature. Then, we introduce the development and technical characteristics of the attention mechanism. For its application in medical image analysis, we summarize the related methods in medical image classification, segmentation, detection, and enhancement. The remaining challenges, potential solutions, and future research directions are also discussed.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
Deep Learning Attention Mechanism in Medical Image Analysis: Basics and Beyonds
- Xiang Li 1,
- Minglei Li 1,
- Pengfei Yan 1,
- Guanyi Li 1,
- Yuchen Jiang 1,
- Hao Luo 1, *,
- Shen Yin 2
Author Information
Received: 16 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 25 Nov 2022 | Published: 27 Mar 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
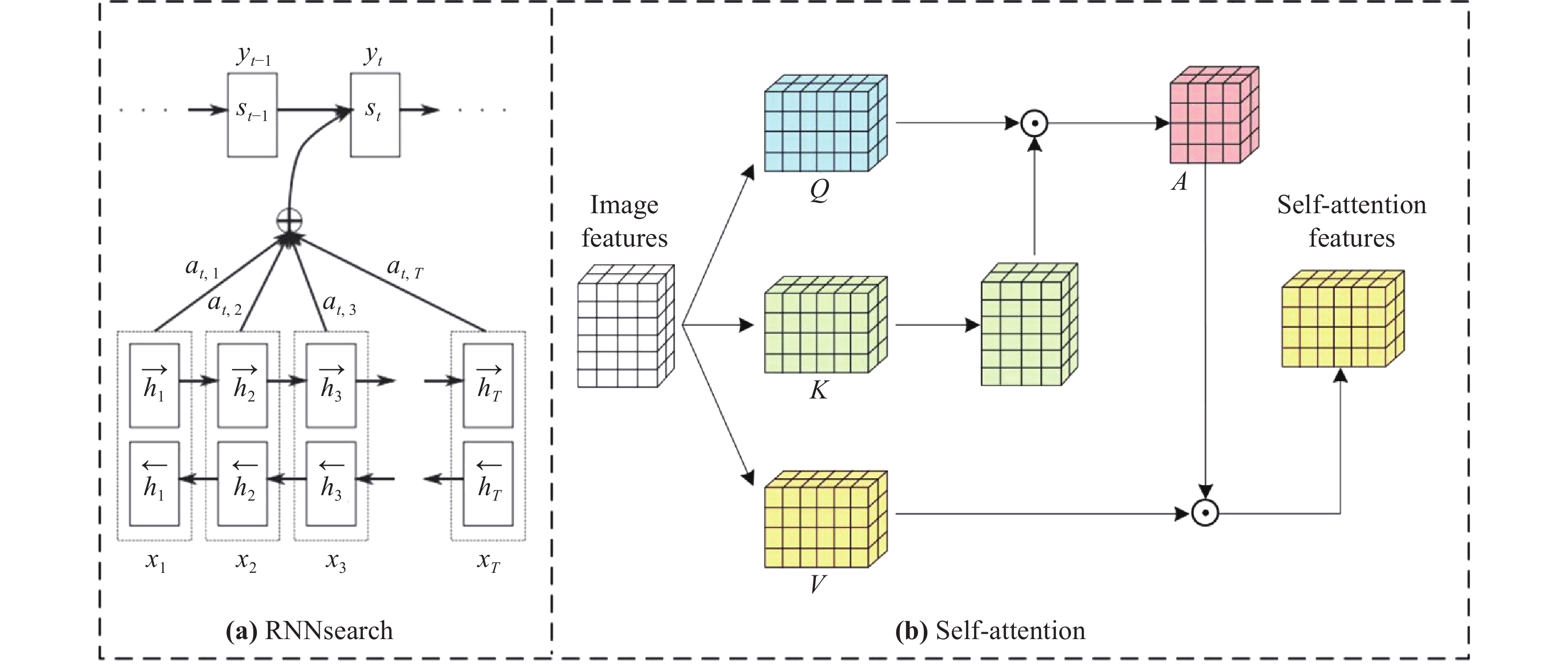
Keywords
References
- 1.Longoni, C.; Bonezzi, A.; Morewedge, C. K. Resistance to medical artificial intelligence. J. Consum. Res., 2019, 46: 629−650.
- 2.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Rodriguez-Andina, J. J.; et al. When medical images meet generative adversarial network: Recent development and research opportunities. Discov. Artif. Intell., 2021, 1: 5.
- 3.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Li, M.L.; et al. MSFR‐Net: Multi‐modality and single‐modality feature recalibration network for brain tumor segmentation.
Med. Phys .2022 , in press. doi: 10.1002/mp.15933 - 4.Chen, L.; Zhao, L.; Chen, C.Y.C. Enhancing adversarial defense for medical image analysis systems with pruning and attention mechanism. Med. Phys., 2021, 48: 6198−6212.
- 5.Wang, Q.C.; Wu, T.Y.; Zheng, H.; et al. Hierarchical pyramid diverse attention networks for face recognition. In
Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020 ; IEEE: Seattle, USA, 2020; pp. 8326–8335. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00835 - 6.Wang, X.; Lv, R.R.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Multi-scale context aggregation network with attention-guided for crowd counting. In
Proceedings of 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 6–9 December 2020 ; IEEE: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 240–245. doi: 10.1109/ICSP48669.2020.9321067 - 7.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Zhang, J.S.; et al. Lesion-attention pyramid network for diabetic retinopathy grading. Artif. Intell. Med., 2022, 126: 102259.
- 8.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Liu, Y.L.; et al. RAGCN: Region aggregation graph convolutional network for bone age assessment from x-ray images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 2022, 71: 4006412.
- 9.Corbetta, M.; Shulman, G. L. Control of goal-directed and stimulus-driven attention in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2002, 3: 201−215.
- 10.Rensink, R. A. The dynamic representation of scenes. Visual Cognit., 2000, 7: 17−42.
- 11.Noton, D.; Stark, L. Scanpaths in saccadic eye movements while viewing and recognizing patterns.
Vision Res .1971 ,11 , 929–942, IN3–IN8. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(71)90213-6 - 12.Hayhoe, M.; Ballard, D. Eye movements in natural behavior. Trends Cogn. Sci., 2005, 9: 188−194.
- 13.Ahmad, S. VISIT: A neural model of covert visual attention. In
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver Colorado, 2–5 December 1991 ; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Denver, USA, 1991; pp. 420–427. - 14.Zhang, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Samaras, D.; et al. A computational model of eye movements during object class detection. In
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver British Columbia Canada, 5–8 December 2005 ; MIT Press: Vancouver British, Canada, 2005; pp. 1609–1616. - 15.Larochelle, H.; Hinton, G. Learning to combine foveal glimpses with a third-order Boltzmann machine. In
Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver British Columbia Canada, 6–9 December 2010; Curran Associates Inc.: Vancouver British, Canada, 2010; pp. 1243–1251. - 16.Bazzani, L.; de Freitas, N.; Larochelle, H.; et al. Learning attentional policies for tracking and recognition in video with deep networks. In
Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, Bellevue Washington USA, 28 June 2011–2 July 2011 ; Omnipress: Bellevue, USA, 2011; pp. 937–944. - 17.Fukushima, K. Neural network model for selective attention in visual pattern recognition and associative recall. Appl. Opt., 1987, 26: 4985−4992.
- 18.Milanese, R.; Wechsler, H.; Gill, S.; et al. Integration of bottom-up and top-down cues for visual attention using non-linear relaxation. In
Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 21–23 June 1994 ; IEEE: Seattle, USA, 1994; pp. 781–785. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.1994.323898 - 19.Paletta, L.; Fritz, G.; Seifert, C. Q-learning of sequential attention for visual object recognition from informative local descriptors. In
Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Machine Learning, Bonn Germany, 7–11 August 2005 ; ACM: Bonn, Germany, 2005; pp. 649–656. doi: 10.1145/1102351.1102433 - 20.Postma, E. O.; van den Herik, H.J.; Hudson, P.T.W. SCAN: A scalable model of attentional selection. Neural Networks, 1997, 10: 993−1015.
- 21.Stollenga, M.F.; Masci, J.; Gomez, F.; et al. Deep networks with internal selective attention through feedback connections. In
Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 8–13 December 2014 ; MIT Press: Montreal, Canada, 2014; pp. 3545–3553. - 22.Salah, A.A.; Alpaydin, E.; Akarun, L. A selective attention-based method for visual pattern recognition with application to handwritten digit recognition and face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2002, 24: 420−425.
- 23.Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015 ; San Diego, 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0473(accessed on 10 October 2022). - 24.Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; et al. Attention is all you need. In
Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, California, USA, 4–9 December 2017 ; Curran Associates Inc.: Long Beach, USA, 2017; pp. 6000–6010. - 25.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Li, M.L.; et al. Lightweight attention convolutional neural network for retinal vessel image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform., 2021, 17: 1958−1967.
- 26.Xiao, T.J.; Xu, Y.C.; Yang, K.Y.; et al. The application of two-level attention models in deep convolutional neural network for fine-grained image classification. In
Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015 ; IEEE: Boston, 2015; pp. 842–850. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298685 - 27.Song, S.J.; Lan, C.L.; Xing, J.L.; et al. An end-to-end spatio-temporal attention model for human action recognition from skeleton data. In
Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, California, USA, 4–9 February 2017 ; AAAI Press: San Francisco, USA, 2017; pp. 4263–4270. - 28.Xie, Q.; Lai, Y.K.; Wu, J.; et al. MLCVNet: Multi-level context VoteNet for 3D object detection. In
Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020 ; IEEE: Seattle, USA, 2020; pp. 10447–10456. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01046 - 29.Hu, X.W.; Yu, L.Q.; Chen, H.; et al. AGNet: Attention-guided network for surgical tool presence detection. In
Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, Québec City, QC, Canada, 14 September 2017 ; Springer: Québec City, Canada, 2017; pp. 186–194. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67558-9_22 - 30.Nie, D.; Gao, Y.Z.; Wang, L.; et al. ASDNet: Attention based semi-supervised deep networks for medical image segmentation. In
Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Springer: Granada, Spain, 2018; pp. 370–378. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-00937-3_43 - 31.Xiao, X.; Lian, S.; Luo, Z.M.; et al. Weighted res-UNet for high-quality retina vessel segmentation. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education, Hangzhou, China, 19–21 October 2018 ; IEEE: Hangzhou, China, 2018; pp. 327–331. doi: 10.1109/ITME.2018.00080 - 32.Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018 ; IEEE: Salt Lake City, USA, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745 - 33.Gao, Z.L.; Xie, J.T.; Wang, Q.L.; et al. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019 ; IEEE: Long Beach, USA, 2019; pp. 3024–3033. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00314 - 34.Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.P.; et al. Context encoding for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018 ; IEEE: Salt Lake City, USA, 2018; pp. 7151–7160. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00747 - 35.Wang, Q.L.; Wu, B.G.; Zhu, P.F.; et al. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In
Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020 ; IEEE: Seattle, USA, 2020; pp. 11531–11539. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01155 - 36.Lee, H.; Kim, H.E.; Nam, H. SRM: A style-based recalibration module for convolutional neural networks. In
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 27 October 2019-2 November 2019 ; IEEE: Seoul, Korea (South), 2019; pp. 1854–1862. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00194 - 37.Yang, Z.X.; Zhu, L.C.; Wu, Y.; et al. Gated channel transformation for visual recognition. In
Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020 ; IEEE: Seattle, USA, 2020; pp. 11794–11803. doi: 10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.01181 - 38.Qin, Z.Q.; Zhang, P.Y.; Wu, F.; et al. FcaNet: Frequency channel attention networks. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021 ; IEEE: Montreal, Canada, 2021; pp. 783–792. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00082 - 39.Guo, X.Q.; Yuan, Y. X. Semi-supervised WCE image classification with adaptive aggregated attention. Med. Image Anal., 2020, 64: 101733.
- 40.Chen, H.Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.Y.; et al. IL-MCAM: An interactive learning and multi-channel attention mechanism-based weakly supervised colorectal histopathology image classification approach. Comput. Biol. Med., 2022, 143: 105265.
- 41.Yao, H.D.; Zhang, X.J.; Zhou, X.B.; et al. Parallel structure deep neural network using CNN and RNN with an attention mechanism for breast cancer histology image classification. Cancers, 2019, 11: 1901.
- 42.Shaik, N.S.; Cherukuri, T. K. Multi-level attention network: Application to brain tumor classification. Signal Image Video Process., 2022, 16: 817−824.
- 43.Wang, Z.K.; Zou, Y.N.; Liu, P. X. Hybrid dilation and attention residual U-Net for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med., 2021, 134: 104449.
- 44.Sinha, A.; Dolz, J. Multi-scale self-guided attention for medical image segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform., 2021, 25: 121−130.
- 45.Gu, R.; Wang, G.T.; Song, T.; et al. CA-Net: Comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2021, 40: 699−711.
- 46.Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Ni, J.J.; et al. TA-Net: Triple attention network for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med., 2021, 137: 104836.
- 47.Ni, J.J.; Wu, J.H.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. Global channel attention networks for intracranial vessel segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med., 2020, 118: 103639.
- 48.Fan, Y.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Yao, R.X.; et al. COVID-19 detection from X-ray images using multi-kernel-size spatial-channel attention network. Pattern Recognit., 2021, 119: 108055.
- 49.Guo, C.L.; Szemenyei, M.; Hu, Y.T.; et al. Channel attention residual U-net for retinal vessel segmentation. In
Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021 ; IEEE: Toronto, Canada, 2021; pp. 1185–1189. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP39728.2021.9414282 - 50.Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; et al. ResUNet++: An advanced architecture for medical image segmentation. In
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM ),San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019 ; IEEE: San Diego, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 225–2255. doi: 10.1109/ISM46123.2019.00049 - 51.Sharif, S.M.A.; Naqvi, R.A.; Biswas, M. Learning medical image denoising with deep dynamic residual attention network. Mathematics, 2020, 8: 2192.
- 52.Rahman, T.; Bilgin, A.; Cabrera, S. Asymmetric decoder design for efficient convolutional encoder-decoder architectures in medical image reconstruction. In
Proceedings of the Multimodal Biomedical Imaging XVⅡ 2022, San Francisco, United States, 22 Jan 2022-27 Jan 2022 ; SPIE: San Francisco, USA, 2022; pp. 7–14. - 53.Yin, X.W.; Qian, W.H.; Xu, D.; et al. An unsupervised dual attention method for 3D medical image registration. In
Proceedings of 2021 7th International Conference on Computer and Communications, Chengdu, China, 10–13 December 2021 ; IEEE: Chengdu, China, 2021; pp. 975–979. doi: 10.1109/ICCC54389.2021.9674730 - 54.Gu, Y.C.; Zeng, Z.T.; Chen, H.B.; et al. MedSRGAN: Medical images super-resolution using generative adversarial networks. Multimed. Tools Appl., 2020, 79: 21815−21840.
- 55.Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In
Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018 ; Springer: Munich, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1 - 56.Muqeet, A.; Iqbal, M.T.B.; Bae, S. H. HRAN: Hybrid residual attention network for single image super-resolution. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 137020−137029.
- 57.Liu, Z.G.; Du, J.; Wang, M.; et al. ADCM: Attention dropout convolutional module. Neurocomputing, 2020, 394: 95−104.
- 58.Guo, N.; Gu, K.; Qiao, J.F.; et al. Improved deep CNNs based on Nonlinear Hybrid Attention Module for image classification. Neural Networks, 2021, 140: 158−166.
- 59.Sheng, J.C.; Lv, G.Q.; Du, G.; et al. Multi-scale residual attention network for single image dehazing. Digital Signal Process., 2022, 121: 103327.
- 60.Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.W.; Chen, Y.P.; et al. Selective kernel convolution deep residual network based on channel-spatial attention mechanism and feature fusion for mechanical fault diagnosis.
ISA Trans .2022 , in press. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.06.035 - 61.Li, G.Q.; Fang, Q.; Zha, L.L.; et al. HAM: Hybrid attention module in deep convolutional neural networks for image classification. Pattern Recognit., 2022, 129: 108785.
- 62.Sun, H.; Zeng, X.X.; Xu, T.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis in histopathological images of the endometrium using a convolutional neural network and attention mechanisms. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform., 2020, 24: 1664−1676.
- 63.Mishra, S.S.; Mandal, B.; Puhan, N. B. Perturbed composite attention model for macular optical coherence tomography image classification. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell., 2022, 3: 625−635.
- 64.Zhao, W.W.; Wang, R.Z.; Qi, Y.L.; et al. BASCNet: Bilateral adaptive spatial and channel attention network for breast density classification in the mammogram. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2021, 70: 103073.
- 65.Wei, Z.H.; Li, Q.; Song, H. Dual attention based network for skin lesion classification with auxiliary learning. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2022, 74: 103549.
- 66.Qin, Z.W.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.H.; et al. 3D convolutional neural networks with hybrid attention mechanism for early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2022, 77: 103828.
- 67.Xu, Z.W.; Ren, H.J.; Zhou, W.; et al. ISANET: Non-small cell lung cancer classification and detection based on CNN and attention mechanism. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2022, 77: 103773.
- 68.Chen, G.P.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, Y.; et al. Asymmetric U-shaped network with hybrid attention mechanism for kidney ultrasound images segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl., 2023, 212: 118847.
- 69.Hu, H.X.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; et al. Parallel deep learning algorithms with hybrid attention mechanism for image segmentation of lung tumors. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform., 2021, 17: 2880−2889.
- 70.Yu, J.K.; Yang, D.D.; Zhao, H. S. FFANet: Feature fusion attention network to medical image segmentation. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2021, 69: 102912.
- 71.Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Ni, J.J.; et al. TA-Net: Triple attention network for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med., 2021, 137: 104836.
- 72.Xu, Z.H.; Liu, S.J.; Yuan, D.; et al. ω-net: Dual supervised medical image segmentation with multi-dimensional self-attention and diversely-connected multi-scale convolution. Neurocomputing, 2022, 500: 177−190.
- 73.Chen, J.D.; Chen, W.R.; Zeb, A.; et al. Segmentation of medical images using an attention embedded lightweight network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., 2022, 116: 105416.
- 74.Cao, L.Y.; Li, J.W.; Chen, S. Multi-target segmentation of pancreas and pancreatic tumor based on fusion of attention mechanism. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2023, 79: 104170.
- 75.Chen, P.H.; Men, S.Y.; Lin, H.B.; et al. Detection of local lesions in tongue recognition based on improved faster R-CNN. In
Proceedings of 2021 6th International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Applications, Xiamen, China, 11–13 June 2021 ; IEEE: Xiamen, China, 2021; pp. 165–168. doi: 10.1109/ICCIA52886.2021.00039 - 76.Li, X.Y.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, K.; et al. Early gastric cancer detection based on the combination of convolutional neural network and attention mechanism. In
Proceedings of 2021 China Automation Congress, Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021 ; IEEE: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 5731–5735. doi: 10.1109/CAC53003.2021.9728413 - 77.Jiang, Z.F.; Liu, X.; Yan, Z.Z.; et al. Improved detection performance in blood cell count by an attention-guided deep learning method. OSA Continuum, 2021, 4: 323−333.
- 78.Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, D.Q. Dual-attention network for acute pancreatitis lesion detection with CT images. In
Proceedings of 2021 International Conference on Medical Imaging and Computer-Aided Diagnosis (MICAD 2021 ); Su, R.D.; Zhang, Y.D.; Liu, H., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 238–250. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-3880-0_25 - 79.Pan, X.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Bai, W.D.; et al. Detection model of nasolaryngology lesions based on multi-scale contextual information fusion and cascading mixed attention. In
Proceedings of 2021 16th International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Knowledge Engineering, Chengdu, China, 26–28 November 2021 ; IEEE: Chengdu, China, 2021; pp. 464–470. doi: 10.1109/ISKE54062.2021.9755353 - 80.Zhao, Y.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, X.M.; et al. A new pulmonary nodule detection based on multiscale convolutional neural network with channel and attention mechanism. In
Signal and Information Processing, Networking and Computers ; Sun, J.D.; Wang, Y.; Huo, M.Y.; Xu, L.X., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023; pp. 1004–1010. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-3387-5_120 - 81.Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.Y.; He, X.D.; et al. DR-GAN: Conditional generative adversarial network for fine-grained lesion synthesis on diabetic retinopathy images. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform., 2022, 26: 56−66.
- 82.Jiang, M.F.; Zhi, M.H.; Wei, L.Y.; et al. FA-GAN: Fused attentive generative adversarial networks for MRI image super-resolution. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph., 2021, 92: 101969.
- 83.Li, M.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhang, F.C.; et al. Deformable medical image registration based on unsupervised generative adversarial network integrating dual attention mechanisms. In
Proceedings of 2021 14th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, Shanghai, China, 23–25 October 2021 ; IEEE: Shanghai, China, 2021; pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/CISP-BMEI53629.2021.9624229 - 84.Zhu, D.M.; Sun, D.G.; Wang, D. B. Dual attention mechanism network for lung cancer images super-resolution. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., 2022, 226: 107101.
- 85.Chi, J.N.; Sun, Z.Y.; Wang, H.; et al. CT image super-resolution reconstruction based on global hybrid attention. Comput. Biol. Med., 2022, 150: 106112.
- 86.Li, Y.C.; Zeng, X.H.; Dong, Q.; et al. RED-MAM: A residual encoder-decoder network based on multi-attention fusion for ultrasound image denoising. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2023, 79: 104062.
- 87.Vaswani, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Srinivas, A.; et al. Scaling local self-attention for parameter efficient visual backbones. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021 ; IEEE: Nashville, TN, USA, 2021; pp. 12889–12899. - 88.Vila, L.C.; Escolano, C.; Fonollosa, J.A.R.; et al. End-to-end speech translation with the transformer. In
Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference, IberSPEECH 2018, Barcelona, Spain, 21–23 November 2018 ; ISCA: Barcelona, Spain, 2018; pp. 60–63. - 89.Chen, L.W.; Rudnicky, A. Fine-grained style control in transformer-based text-to-speech synthesis. In
Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Singapore, Singapore, 23–27 May 2022 ; IEEE: Singapore, Singapore, 2022; pp. 7907–7911. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP43922.2022.9747747 - 90.Egonmwan, E.; Chali, Y. Transformer and seq2seq model for paraphrase generation. In
Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Neural Generation and Translation @EMNLP-IJCNLP 2019, Hong Kong, China, 4 November 2019 ; ACL: Hong Kong, China, 2019; pp. 249–255. - 91.Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In
Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020 ; Springer: Glasgow, UK, 2020; pp. 213–229. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58452-8_13 - 92.Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Event, Austria, 3–7 May 2021 ; OpenReview.net, 2021. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929 (accessed on 10 October 2022). - 93.Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; et al. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. In
Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 18–24 July 2021 ; PMLR, 2021; pp. 10347–10357. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877 (accessed on 10 October 2022). - 94.Wang, W.H.; Xie, E.Z.; Li, X.; et al. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021 ; IEEE: Montreal, Canada, 2021; pp. 568–578. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00061 - 95.Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.T.; Cao, Y.; et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 10–17 October 2021 ; IEEE: Montreal, Canada, 2021; pp. 10012–10022. doi: 10.1109/ICCV48922.2021.00986 - 96.Xia, Z.F.; Pan, X.R.; Song, S.J.; et al. Vision transformer with deformable attention. In
Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022 ; IEEE: New Orleans, USA, 2022; pp. 4794–4803. doi: 10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00475 - 97.He, S.; Grant, P.E.; Ou, Y. M. Global-Local transformer for brain age estimation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2022, 41: 213−224.
- 98.Li, M.L.; Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; et al. Explainable multi-instance and multi-task learning for COVID-19 diagnosis and lesion segmentation in CT images. Knowl. Based Syst., 2022, 252: 109278.
- 99.Wang, S.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Xuan, K.; et al. 3DMeT: 3D medical image transformer for knee cartilage defect assessment. In
Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 347–355. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87589-3_36 - 100.Verenich, E.; Martin, T.; Velasquez, A.; et al. Pulmonary disease classification using globally correlated maximum likelihood: An auxiliary attention mechanism for convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2109.00573, 2021. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.00573 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- 101.Wu, W.J.; Mehta, S.; Nofallah, S., et al. Scale-aware transformers for diagnosing melanocytic lesions. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 163526−163541.
- 102.Barhoumi, Y.; Ghulam, R. Scopeformer: N-CNN-ViT hybrid model for intracranial hemorrhage classification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2107.04575, 2021. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.04575 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- 103.Sun, Q.X.; Fang, N.H.; Liu, Z.; et al. HybridCTrm: Bridging CNN and transformer for multimodal brain image segmentation. J. Healthc. Eng., 2021, 2021: 7467261.
- 104.Hatamizadeh, A.; Nath, V.; Tang, Y.C.; et al. Swin UNETR: Swin transformers for semantic segmentation of brain tumors in MRI images. In
Proceedings of the 7th International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop, Strasbourg, France, 27 September-1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2022; pp. 272–284 doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-08999-2_22 - 105.Gao, Y.H.; Zhou, M.; Metaxas, D.N. UTNet: A hybrid transformer architecture for medical image segmentation. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 61–71. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_6 - 106.Ji, Y.F.; Zhang, R.M.; Wang, H.J.; et al. Multi-compound transformer for accurate biomedical image segmentation. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 326–336. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_31 - 107.Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, R.Y.; et al. TF-Unet: An automatic cardiac MRI image segmentation method. Math. Biosci. Eng., 2022, 19: 5207−5222.
- 108.Xie, Y.T.; Zhang, J.P.; Shen, C.H.; et al. CoTr: Efficiently bridging CNN and transformer for 3D medical image segmentation. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 171–180. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_16 - 109.Ma, X.H.; Luo, G.N.; Wang, W.; et al. Transformer network for significant stenosis detection in CCTA of coronary arteries. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 516–525. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_50 - 110.Jiang, H.; Zhang, P.L.; Che, C.; et al. RDFNet: A fast caries detection method incorporating transformer mechanism. Comput. Math. Methods Med., 2021, 2021: 9773917.
- 111.Kong, Q.R.; Wu, Y.R.; Yuan, C.; et al. CT-CAD: Context-aware transformers for end-to-end chest abnormality detection on X-rays. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 December 2021 ; IEEE: Houston, USA, 2021; pp. 1385–1388. doi: 10.1109/BIBM52615.2021.9669743 - 112.Tao, R.; Zheng, G.Y. Spine-transformers: Vertebra detection and localization in arbitrary field-of-view spine CT with transformers. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 93–103. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87199-4_9 - 113.Chen, L.Y.; You, Z.Y.; Zhang, N.; et al. UTRAD: Anomaly detection and localization with U-Transformer. Neural Networks, 2022, 147: 53−62.
- 114.Feng, C.M.; Yan, Y.L.; Fu, H.Z.; et al. Task transformer network for joint MRI reconstruction and super-resolution. In
Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Strasbourg, France, 27 September–1 October 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 307–317. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87231-1_30 - 115.Wang, D.Y.; Wu, Z.; Yu, H.Y. TED-Net: Convolution-free T2T vision transformer-based encoder-decoder dilation network for low-dose CT denoising. In
Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, Strasbourg, France, 27 September 2021 ; Springer: Strasbourg, France, 2021; pp. 416–425. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-87589-3_43 - 116.Korkmaz, Y.; Dar, S.U.H.; Yurt, M.; et al. Unsupervised MRI reconstruction via zero-shot learned adversarial transformers. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2022, 41: 1747−1763.
- 117.Shin, H.C.; Ihsani, A.; Mandava, S.; et al. GANBERT: Generative adversarial networks with bidirectional encoder representations from transformers for MRI to PET synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2008.04393, 2020. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.04393 (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- 118.Song, L.; Liu, G.X.; Ma, M. R. TD-Net: Unsupervised medical image registration network based on Transformer and CNN. Appl. Intell., 2022, 52: 18201−18209.
- 119.Jiang, Y.C.; Yin, S.; Li, K.; et al. Industrial applications of digital twins. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci., 2021, 379: 20200360.
- 120.Li, X.; Jiang, Y.C.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Playing against deep-neural-network-based object detectors: A novel bidirectional adversarial attack approach. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell., 2022, 3: 20−28.
- 121.Seo, D.; Oh, K.; Oh, I. S. Regional multi-scale approach for visually pleasing explanations of deep neural networks. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 8572−8582.
- 122.Yin, S.; Rodriguez-Andina, J.J.; Jiang, Y. C. Real-time monitoring and control of industrial cyberphysical systems: With integrated plant-wide monitoring and control framework. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag., 2019, 13: 38−47.
- 123.Zhou, Q.; Wang, Q.W.; Bao, Y.C.; et al. LAEDNet: A Lightweight Attention Encoder–Decoder Network for ultrasound medical image segmentation. Comput. Electr. Eng., 2022, 99: 107777.
- 124.Jiang, Y.C.; Li, X.; Luo, H.; et al. Quo vadis artificial intelligence? Discov. Artif. Intell., 2022, 2: 4.
- 125.Saha, A.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Huisman, H. End-to-end prostate cancer detection in bpMRI via 3D CNNs: Effects of attention mechanisms, clinical priori and decoupled false positive reduction. Med. Image Anal., 2021, 73: 102155.
- 126.Sun, K.; He, M.J.; He, Z.C.; et al. EfficientNet embedded with spatial attention for recognition of multi-label fundus disease from color fundus photographs. Biomed. Signal Process. Control, 2022, 77: 103768.
- 127.Shen, N.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, J.; et al. Multi-organ segmentation network for abdominal CT images based on spatial attention and deformable convolution. Expert Syst. Appl., 2023, 211: 118625.
How to Cite
Li, X.; Li, M.; Yan, P.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, H.; Yin, S. Deep Learning Attention Mechanism in Medical Image Analysis: Basics and Beyonds. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (1), 93–116. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0201006.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


