The adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) technology has been widely used benefiting from its recursive structure in forward and the prospective conception of reinforcement learning. Furthermore, ADP-based control issues with communication constraints arouse ever-increasing research consideration in theoretical analysis and engineering applications due mainly to the wide participation of digital communications in industrial systems. The latest development of ADP-based optimal control with communication constraints is systematically surveyed in this paper. To this end, the development of ADP-based dominant methods is first investigated from their structures and implementation. Then, technical challenges and corresponding approaches are comprehensively and thoroughly discussed and the existing results are reviewed according to the constraint types. Furthermore, some applications of the ADP method in practical systems are summarized. Finally, future topics are lighted on ADP-based control issues.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Networked Control Systems Under Communication Constraints: A Survey of Trends and Techniques
- Xueli Wang 1,
- Ying Sun 1, *,
- Derui Ding 2
Author Information
Received: 22 Sep 2022 | Accepted: 28 Nov 2022 | Published: 22 Dec 2022
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
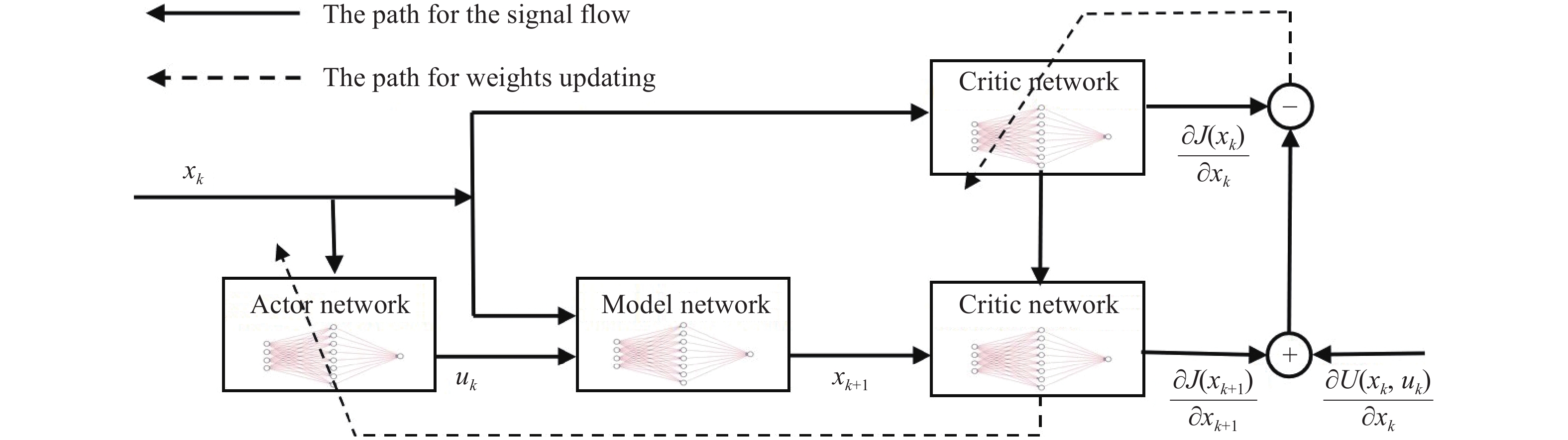
Keywords
optimal control | adaptive dynamic programming | communication protocols | networkinduced phenomena | networked control systems
References
- 1.Walsh, G.C.; Ye, H.; Bushnell, L.G, Stability analysis of networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol., 2002, 10: 438−446.
- 2.Liu, Y.J.; Tang, L.; Tong, S.C.; et al, Reinforcement learning design-based adaptive tracking control with less learning parameters for nonlinear discrete-time MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2015, 26: 165−176.
- 3.Wang, D.; He, H.B.; Zhong, X.N.; et al, Event-driven nonlinear discounted optimal regulation involving a power system application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2017, 64: 8177−8186.
- 4.Wang, T.; Gao, H.J.; Qiu, J.B, A combined adaptive neural network and nonlinear model predictive control for multirate networked industrial process control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2016, 27: 416−425.
- 5.Werbos, P.J, Foreword-ADP: The key direction for future research in intelligent control and understanding brain intelligence. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern., Part B (Cybern.), 2008, 38: 898−900.
- 6.Song, R.Z.; Wei, Q.L.; Zhang, H.G.; et al, Discrete-time non-zero-sum games with completely unknown dynamics. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2021, 51: 2929−2943.
- 7.Yang, X.; He, H.B.; Zhong, X.N, Adaptive dynamic programming for robust regulation and its application to power systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2018, 65: 5722−5732.
- 8.Zhong, X.N.; He, H.B.; Wang, D.; et al, Model-free adaptive control for unknown nonlinear zero-sum differential game. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2018, 48: 1633−1646.
- 9.Li, B.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Distributed quasiconsensus control for stochastic multiagent systems under Round-Robin protocol and uniform quantization. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2022, 52: 6721−6732.
- 10.Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.D.; Zou, L.; et al, H∞ PID control for discrete-time fuzzy systems with infinite-distributed delays under Round-Robin communication protocol. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst., 2022, 30: 1875−1888.
- 11.Song, J.; Wang, Z.D.; Niu, Y.G.; et al, Observer-based sliding mode control for state-saturated systems under weighted try-once-discard protocol. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, 2020, 30: 7991−8006.
- 12.Geng, H.; Wang, Z.D.; Chen, Y.; et al, Variance-constrained filtering fusion for nonlinear cyber-physical systems with the denial-of-service attacks and stochastic communication protocol. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin., 2022, 9: 978−989.
- 13.Liu, H.J.; Wang, Z.D.; Fei, W.Y.; et al, On finite-horizon H∞ state estimation for discrete-time delayed memristive neural networks under stochastic communication protocol. Inf. Sci., 2021, 555: 280−292.
- 14.Luo, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, D.R.; et al, Event-triggered optimal control with performance guarantees using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2020, 31: 76−88.
- 15.Ge, X.H.; Han, Q.L, Consensus of multiagent systems subject to partially accessible and overlapping Markovian network topologies. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2017, 47: 1807−1819.
- 16.Wang, Z.D.; Wang, L.C.; Liu, S, Encoding-decoding-based control and filtering of networked systems: Insights, developments and opportunities. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin., 2018, 5: 3−18.
- 17.Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, R.Q.; et al, Remote estimator design for time-delay neural networks using communication state information. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2018, 29: 5149−5158.
- 18.Wang, L.C.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Synchronization control for a class of discrete-time dynamical networks with packet dropouts: A cording-decoding-based approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2018, 48: 2437−2448.
- 19.Liu, S.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, L.C.; et al, H∞ pinning control of complex dynamical networks under dynamic quantization effects: A coupled backward Riccati equation approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2022, 52: 7377−7387.
- 20.Wang, X.L.; Ding, D.R.; Dong, H.L.; et al. PI-based security control against joint sensor and controller attacks and applications in load frequency control. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3190005
- 21.Zhao, D.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Proportional-integral observer design for uncertain time-delay systems subject to deception attacks: An outlier-resistant approach. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2022, 52: 5152−5164.
- 22.Zhang, H.G.; Luo, Y.H.; Liu, D.R, Neural-network-based near-optimal control for a class of discrete-time affine nonlinear systems with control constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 2009, 20: 1490−1503.
- 23.Al-Tamimi, A.; Lewis, F.L.; Abu-Khalaf, M, Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: Convergence proof. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern., Part B (Cybern.), 2008, 38: 943−949.
- 24.Heydari, A, Stability analysis of optimal adaptive control under value iteration using a stabilizing initial policy. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2018, 29: 4522−4527.
- 25.Powell, W.B. Approximate Dynamic Programming: Solving the Curses of Dimensionality; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007.
- 26.Prokhorov, D.V.; Wunsch, D.C, Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 1997, 8: 997−1007.
- 27.Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998.
- 28.Bellman, R. Dynamic Programming; Princeton University Press: Princeton, 1957.
- 29.White, D.A.; Sofge, D.A. Handbook of Intelligent Control: Neural, Fuzzy, and Adaptive Approaches; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, 1992.
- 30.Padhi, R.; Unnikrishnan, N.; Wang, X.H.; et al, A single network adaptive critic (SNAC) architecture for optimal control synthesis for a class of nonlinear systems. Neural Netw., 2006, 19: 1648−1660.
- 31.He, H.B.; Ni, Z.; Fu, J, A three-network architecture for on-line learning and optimization based on adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing, 2012, 78: 3−13.
- 32.Xu, X.; Hou, Z.S.; Lian, C.Q.; et al, Online learning control using adaptive critic designs with sparse kernel machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2013, 24: 762−775.
- 33.Bertsekas, D.P, Value and policy iterations in optimal control and adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2017, 28: 500−509.
- 34.Pang, B.; Bian, T.; Jiang, Z.P, Robust policy iteration for continuous-time linear quadratic regulation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2022, 67: 504−511.
- 35.Jiang, H.Y.; Zhou, B, Bias-policy iteration based adaptive dynamic programming for unknown continuous-time linear systems. Automatica, 2022, 136: 110058.
- 36.Ha, M.M.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.R. A novel value iteration scheme with adjustable convergence rate. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3143527
- 37.Vamvoudakis, K.G.; Lewis, F.L, Online actor-critic algorithm to solve the continuous-time infinite horizon optimal control problem. Automatica, 2010, 46: 878−888.
- 38.Yang, X.; Liu, D.R.; Ma, H.W.; et al, Online approximate solution of HJI equation for unknown constrained-input nonlinear continuous-time systems. Inf. Sci., 2016, 328: 435−454.
- 39.Liu, D.R.; Wang, D.; Li, H.L, Decentralized stabilization for a class of continuous-time nonlinear interconnected systems using online learning optimal control approach. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2014, 25: 418−428.
- 40.Zhang, Y.W.; Zhao, B.; Liu, D.R.; et al. Adaptive dynamic programming-based event-triggered robust control for multiplayer nonzero-sum games with unknown dynamics 1-4mmPlease verify and confirm the term “Multi-Player” has been changed to “Multiplayer” in the title of this article. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3175650
- 41.Xue, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.R, Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for unmatched uncertain nonlinear continuous-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2021, 32: 2939−2951.
- 42.Tse, D.; Viswanath, P. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, U.K., 2005.
- 43.Xu, H.; Zhao, Q.M.; Jagannathan, S, Finite-horizon near-optimal output feedback neural network control of quantized nonlinear discrete- time systems with input constraint. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2015, 26: 1776−1788.
- 44.Zhao, Q.; Xu, H.; Jagannathan, S, Optimal control of uncertain quantized linear discrete-time systems. Int. J. Adapt .Control Signal Process., 2015, 29: 325−345.
- 45.Fan, Q.Y.; Yang, G.H.; Ye, D, Quantization-based adaptive actor-critic tracking control with tracking error constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2018, 29: 970−980.
- 46.Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, H.G.; Luo, Y.H.; et al, Model-free optimal control design for a class of linear discrete-time systems with multiple delays using adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing, 2014, 135: 163−170.
- 47.Zhang, H.G.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, G.Y.; et al, Data-based adaptive dynamic programming for a class of discrete-time systems with multiple delays. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2020, 50: 432−441.
- 48.Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.G.; Yu, R.; et al, H∞ tracking control of discrete-time system with delays via data-based adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2020, 50: 4078−4085.
- 49.Zhang, H.G.; Ren, H.; Mu, Y.F.; et al, Optimal consensus control design for multiagent systems with multiple time delay using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2022, 52: 12832−12842.
- 50.Li, S.; Ding, L.; Gao, H.B.; et al, ADP-based online tracking control of partially uncertain time-delayed nonlinear system and application to wheeled mobile robots. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2020, 50: 3182−3194.
- 51.Chen, Y.G.; Wang, Z.D.; Qian, W.; et al, Asynchronous observer-based H∞ control for switched stochastic systems with mixed delays under quantization and packet dropouts. Nonlinear Anal.: Hybrid Syst., 2018, 27: 225−238.
- 52.Sheng, L.; Wang, Z.D.; Wang, W.B.; et al, Output-feedback control for nonlinear stochastic systems with successive packet dropouts and uniform quantization effects. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern. Syst., 2017, 47: 1181−1191.
- 53.Jiang, Y.; Liu, L.; Feng, G. Adaptive optimal control of networked nonlinear systems with stochastic sensor and actuator dropouts based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3183020.
- 54.Xu, H.; Jagannathan, S.; Lewis, F.L, Stochastic optimal control of unknown linear networked control system in the presence of random delays and packet losses. Automatica, 2012, 48: 1017−1030.
- 55.Jiang, Y.; Fan, J.L.; Chai, T.Y.; et al, Tracking control for linear discrete-time networked control systems with unknown dynamics and dropout. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2018, 29: 4607−4620.
- 56.Gao, W.N.; Deng, C.; Jiang, Y.; et al, Resilient reinforcement learning and robust output regulation under denial-of-service attacks. Automatica, 2022, 142: 110366.
- 57.Wang, X.L.; Ding, D.R.; Ge, X.H.; et al, Neural-network-based control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with denial-of-service attack: The adaptive event-triggered case. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32: 2760−2779.
- 58.Huang, X.; Dong, J.X, ADP-based robust resilient control of partially unknown nonlinear systems via cooperative interaction design. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2021, 51: 7466−7474.
- 59.Song, J.; Huang, L.Y.; Karimi, H.R.; et al, ADP-based security decentralized sliding mode control for partially unknown large- scale systems under injection attacks. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap., 2020, 67: 5290−5301.
- 60.Lian, B.S.; Xue, W.Q.; Lewis, F.L.; et al, Online inverse reinforcement learning for nonlinear systems with adversarial attacks. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, 2021, 31: 6646−6667.
- 61.Dong, L.; Zhong, X.N.; Sun, C.Y.; et al, Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for continuous-time systems with control constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2017, 28: 1941−1952.
- 62.Xue, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.R, Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for zero-sum game of partially unknown continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2020, 50: 3189−3199.
- 63.Xue, S.; Luo, B.; Liu, D.R.; et al, Constrained event-triggered H∞ control based on adaptive dynamic programming with concurrent learning. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2022, 52: 357−369.
- 64.Cui, L.L.; Xie, X.P.; Guo, H.Y.; et al, Dynamic event-triggered distributed guaranteed cost FTC scheme for nonlinear interconnected systems via ADP approach. Appl. Math. Comput., 2022, 425: 127082.
- 65.Dong, L.; Zhong, X.N.; Sun, C.Y.; et al, Adaptive event-triggered control based on heuristic dynamic programming for nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2017, 28: 1594−1605.
- 66.Zhang, P.; Yuan, Y.; Guo, L, Fault-tolerant optimal control for discrete-time nonlinear system subjected to input saturation: A dynamic event-triggered approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2021, 51: 2956−2968.
- 67.Zhang, Y.W.; Zhao, B.; Liu, D.R.; Zhang, S.C, Event-triggered control of discrete-time zero-sum games via deterministic policy gradient adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2022, 52: 4823−4835.
- 68.Zhao, S.W.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, H.Y.; et al, Goal representation adaptive critic design for discrete-time uncertain systems subjected to input constraints: The event-triggered case. Neurocomputing, 2022, 492: 676−688.
- 69.Zhao, S.W.; Wang, J.C, Robust optimal control for constrained uncertain switched systems subjected to input saturation: The adaptive event- triggered case. Nonlinear Dyn., 2022, 110: 363−380.
- 70.Zhong, X.N.; He, H.B, An event-triggered ADP control approach for continuous-time system with unknown internal states. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2017, 47: 683−694.
- 71.Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.H.; Dong, N.; et al, Decentralized event-driven constrained control using adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2022, 33: 5830−5844.
- 72.Wang, D.; Ha, M.M.; Qiao, J.F, Self-learning optimal regulation for discrete-time nonlinear systems under event-driven formulation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2020, 65: 1272−1279.
- 73.Zou, L.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Ultimate boundedness control for networked systems with Try-Once-Discard protocol and uniform quantization effects. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control, 2017, 62: 6582−6588.
- 74.Liu, K.; Fridman, E.; Hetel, L, Stability and L2-gain analysis of networked control systems under Round-Robin scheduling: A time-delay approach. Syst. Control Lett., 2012, 61: 666−675.
- 75.Zou, L.; Wang, Z.D.; Gao, H.J, Observer-based H∞ control of networked systems with stochastic communication protocol: The finite-horizon case. Automatica, 2016, 63: 366−373.
- 76.Ding, D.R.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Neural-network-based output-feedback control under round-robin scheduling protocols. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2019, 49: 2372−2384.
- 77.Zou, L.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L.; et al, Full information estimation for time-varying systems subject to round-robin scheduling: A recursive filter approach. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern.: Syst., 2021, 51: 1904−1916.
- 78.Yuan, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, L.; et al, A resilient consensus strategy of near-optimal control for state-saturated multiagent systems with round-robin protocol. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, 2019, 29: 3200−3216.
- 79.Yuan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.D.; et al, Noncooperative event-triggered control strategy design with round-robin protocol: Applications to load frequency control of circuit systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2020, 67: 2155−2166.
- 80.Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Zhang, P.; et al, Near-optimal resilient control strategy design for state-saturated networked systems under stochastic communication protocol. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2019, 49: 3155−3167.
- 81.Ding, D.R.; Wang, Z.D.; Han, Q.L, Neural-network-based output-feedback control with stochastic communication protocols. Automatica, 2019, 106: 221−229.
- 82.Wang, X.L.; Ding, D.R.; Dong, H.L.; et al, Neural-network-based control for discrete-time nonlinear systems with input saturation under stochastic communication protocol. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin., 2021, 8: 766−778.
- 83.Wang, D.; Hu, L.Z.; Zhao, M.M.; et al. Adaptive critic for event-triggered unknown nonlinear optimal tracking design with wastewater treatment applications. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, in press. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3135405
- 84.Wei, Q.L.; Liu, D.R, Adaptive dynamic programming for optimal tracking control of unknown nonlinear systems with application to coal gasification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2014, 11: 1020−1036.
- 85.Wei, Q.L.; Liu, D.R.; Lewis, F.L.; et al, Mixed iterative adaptive dynamic programming for optimal battery energy control in smart residential microgrids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2017, 64: 4110−4120.
- 86.Wei, Q.L.; Lu, J.W.; Zhou, T.M.; et al, Event-triggered near-optimal control of discrete-time constrained nonlinear systems with application to a boiler-turbine system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf., 2022, 18: 3926−3935.
- 87.Yi, J.; Chen, S.; Zhong, X.N.; et al, Event-triggered globalized dual heuristic programming and its application to networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf., 2019, 15: 1383−1392.
- 88.Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Barragan-Alcantar, D.; Collado-Gonzalez, I.; et al, Adaptive dynamic programming and deep reinforcement learning for the control of an unmanned surface vehicle: Experimental results. Control Eng. Pract., 2021, 111: 104807.
- 89.Heydari, A, Optimal impulsive control using adaptive dynamic programming and its application in spacecraft rendezvous. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2021, 32: 4544−4552.
- 90.Liu, F.; Jiang, C.P.; Xiao, W.D, Multistep prediction-based adaptive dynamic programming sensor scheduling approach for collaborative target tracking in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2021, 18: 693−704.
- 91.Zhao, J.; Wang, T.Y.; Pedrycz, W.; et al, Granular prediction and dynamic scheduling based on adaptive dynamic programming for the blast furnace gas system. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2021, 51: 2201−2214.
- 92.Hu, C.F.; Zhao, L.X.; Qu, G, Event-triggered model predictive adaptive dynamic programming for road intersection path planning of unmanned ground vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., 2021, 70: 11228−11243.
- 93.Liang, L.; Song, J.B.; Li, H.S, Dynamic state aware adaptive source coding for networked control in cyberphysical systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol., 2017, 66: 10000−10010.
- 94.Zhao, S.W.; Wang, J.C.; Xu, H.T.; et al. Composite observer-based optimal attitude-tracking control with reinforcement learning for hypersonic vehicles. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3192871
- 95.Dou, L.Q.; Cai, S.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; et al, Event-triggered-based adaptive dynamic programming for distributed formation control of multi-UAV. J. Franklin Inst., 2022, 359: 3671−3691.
- 96.Gao, Y.X.; Liu, C.S.; Duan, D.D.; et al, Distributed optimal event-triggered cooperative control for nonlinear multi-missile guidance systems with partially unknown dynamics. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32: 8369−8396.
- 97.Wang, X.L.; Ding, D.R.; Ge, X.H.; et al. Neural-network-based control with dynamic event-triggered mechanisms under DoS attacks and applications in load frequency control. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 2022, in press. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3206370
- 98.Wang, X.L.; Ding, D.R.; Ge, X.H.; et al, Supplementary control for quantized discrete-time nonlinear systems under goal representation heuristic dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2022.
How to Cite
Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Ding, D. Adaptive Dynamic Programming for Networked Control Systems Under Communication Constraints: A Survey of Trends and Techniques. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2022, 1 (1), 85–98. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0101008.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2022 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


