Cognitive computing is recognized as the next era of computing. In order to make hardware and software systems more human-like, emotion artificial intelligence (AI) and cognitive AI which simulate human intelligence are the core of real AI. The current boom of sentiment analysis and affective computing in computer science gives rise to the rapid development of emotion AI. However, the research of cognitive AI has just started in the past few years. In this visionary paper, we briefly review the current development in emotion AI, introduce the concept of cognitive AI, and propose the envisioned future of cognitive AI, which intends to let computers think, reason, and make decisions in similar ways that humans do. The important aspect of cognitive AI in terms of engagement, regulation, decision making, and discovery are further discussed. Finally, we propose important directions for constructing future cognitive AI, including data and knowledge mining, multi-modal AI explainability, hybrid AI, and potential ethical challenges.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
From Emotion AI to Cognitive AI
- Guoying Zhao *,
- Yante Li,
- Qianru Xu
Author Information
Received: 22 Sep 2022 | Accepted: 28 Nov 2022 | Published: 22 Dec 2022
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
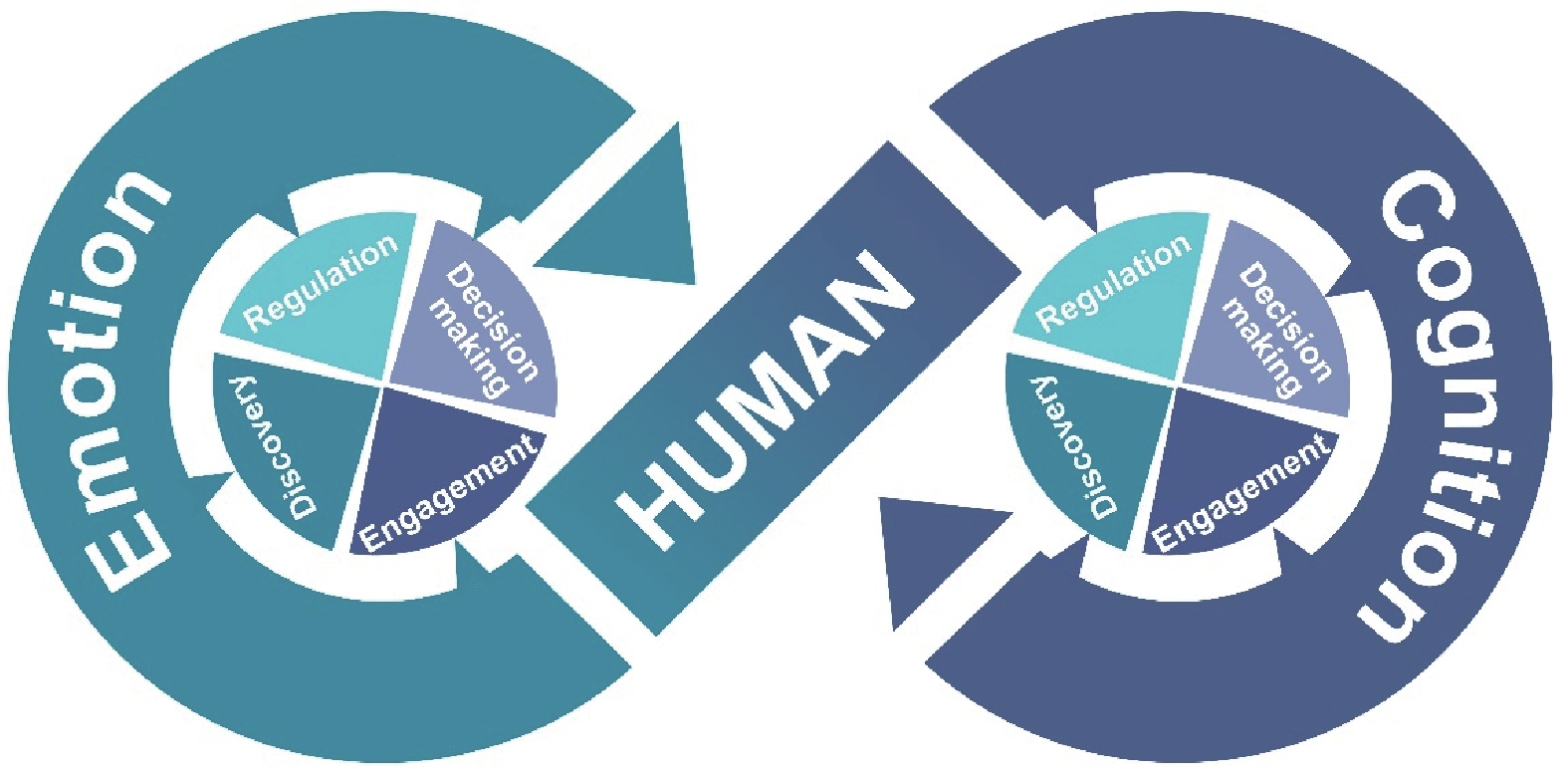
Keywords
emotion | cognition | human intelligence | artificial intelligence
References
- 1.Luckin, R.
Machine Learning and Human Intelligence: The Future of Education for the 21st Century ; UCL IOE Press, London, 27, July,2018 . doi:10.1177/14782103221117655 - 2.Phelps, E.A, Emotion AND cognition: Insights from studies of the human amygdala. Annu. Rev. Psychol., 2006, 57: 27−53.
- 3.Isaacowitz, D.M.; Charles, S.T.; Carstensen, L.L. Emotion and cognition. In
The Handbook of Aging and Cognition ; Salthouse, T.A., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc.: Mahwah,2000 ; pp. 593–631. - 4.Jessica A.Sommerville. Social Cognition. Encyclopedia of Infant and Early Childhood Development,
2020 , pp.196-206, Elsevier. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-809324-5.21640-4. - 5.Jian, M.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Yu, H.; et al, Saliency detection based on directional patches extraction and principal local color contrast. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent., 2018, 57: 1−11.
- 6.Jian, M.W., Qi, Q., Dong, J.Y.; et al, Integrating QDWD with pattern distinctness and local contrast for underwater saliency detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent., 2018, 53: 31−41.
- 7.Jian, M.W.; Lam, K.M.; Dong, J.Y.; et al, Visual-patch-attention-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2015, 45: 1575−1586.
- 8.Schmid, U, Cognition and AI. Fachbereich 1 Künstliche Intelligenz der Gesellschaft für Informatik e.V., GI., 2008, 1: 5.
- 9.Scherer, K.R. On the nature and function of emotion: A component process approach. In
Approaches to Emotion ; Scherer, K.R.; Ekman, P., Eds.; Psychology Press: New York,1984 ; p. 26. - 10.Lazarus, R.S. The cognition-emotion debate: A bit of history. In
Handbook of Cognition and Emotion ; Dalgleish, T.; Power, M.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York,1999 ; pp. 3–19. - 11.Pessoa, L.
The Cognitive-Emotional Brain: From Interactions to Integration ; MIT Press: Cambridge, 2013. - 12.Okon-Singer, H.; Hendler, T.; Pessoa, L.; et al, The neurobiology of emotion–cognition interactions: Fundamental questions and strategies for future research. Front. Hum. Neurosci., 2015, 9: 58.
- 13.Dolcos, F.; Katsumi, Y.; Moore, M.; et al, Neural correlates of emotion-attention interactions: From perception, learning, and memory to social cognition, individual differences, and training interventions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 2020, 108: 559−601.
- 14.Shackman, A.J.; Salomons, T.V.; Slagter, H.A.; et al, The integration of negative affect, pain and cognitive control in the cingulate cortex. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2011, 12: 154−167.
- 15.Young, M.P.; Scanneil, J.W.; Burns, G.A.P.C.; et al, Analysis of connectivity: Neural systems in the cerebral cortex. Rev. Neurosci., 1994, 5: 227−250.
- 16.Pessoa, L, On the relationship between emotion and cognition. Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2008, 9: 148−158.
- 17.Martı́nez-Miranda, J.; Aldea, A, Emotions in human and artificial intelligence. Comput. Hum. Behav., 2005, 21: 323−341.
- 18.Tao, J.H.; Tan, T.N. Affective computing: A review. In
Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Beijing, China, October 22–24, ; Springer: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 981–995. doi:10.1007/11573548_1252005 - 19.Schuller, D.; Schuller, B.W, The age of artificial emotional intelligence. Computer, 2018, 51: 38−46.
- 20.Saxena, A.; Khanna, A.; Gupta, D, Emotion recognition and detection methods: A comprehensive survey. J. Artif. Intell. Syst., 2020, 2: 53−79.
- 21.Li, Y.T.; Wei, J.S.; Liu, Y.; et al. 2022, Deep learning for micro-expression recognition: A survey. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput., 2022, 13: 2028−2046.
- 22.Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.Z.; Li, X.; et al, Graph-based Facial Affect Analysis: A Review. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput., 2022, 19: 1−20.
- 23.Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhou, J.Z.; et al, SG-DSN: A Semantic Graph-based Dual-Stream Network for facial expression recognition. Neurocomputing, 2021, 462: 320−330.
- 24.Chen, H.Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.B.; et al. Analyze spontaneous gestures for emotional stress state recognition: A micro-gesture dataset and analysis with deep learning. In
Proceedings of 2019 14th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2019), Lille, France, 14–18 May 2019 ; IEEE: Lille, France,2019 ; pp. 1–8. doi:10.1109/FG.2019.8756513 - 25.Liu, X.; Shi, H.L.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. iMiGUE: An identity-free video dataset for micro-gesture understanding and emotion analysis. In
Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021 ; IEEE: Nashville, USA,2021 ; pp. 10631–10642. doi:10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01049 - 26.Koolagudi, S.G.; Rao, K.S, Emotion recognition from speech: A review. Int. J. Speech Technol., 2012, 15: 99−117.
- 27.Zhou, Z.H.; Zhao, G.Y.; Hong, X.P.; et al, A review of recent advances in visual speech decoding. Image Vis. Comput., 2014, 32: 590−605.
- 28.Yu, Z.T.; Li, X.B.; Zhao, G.Y, Facial-Video-Based Physiological Signal Measurement: Recent advances and affective applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 2021, 38: 50−58.
- 29.Shu, L.; Xie, J.Y.; Yang, M.Y.; et al, A review of emotion recognition using physiological signals. Sensors, 2018, 18: 2074.
- 30.Li, X.B.; Cheng, S.Y.; Li, Y.T.; et al. 4DME: A spontaneous 4D micro-expression dataset with multimodalities.
IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput .2022 , in press. doi:10.1109/TAFFC.2022.3182342 - 31.Huang, X.H.; Kortelainen, J.; Zhao, G.Y.; et al, Multi-modal emotion analysis from facial expressions and electroencephalogram. Comput. Vis. Image Underst., 2016, 147: 114−124.
- 32.Saleem, S.M.; Abdullah, A.; Ameen, S.Y.A.; et al, Multimodal emotion recognition using deep learning. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends, 2021, 2: 52−58.
- 33.Lisetti, C.L. Emotion synthesis: Some research directions. In
Proceedings of the Working Notes of the AAAI Fall Symposium Series on Emotional and Intelligent: The Tangled Knot of Cognition, Orlando, FL, USA, October 22–24, ; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, USA, 1998; pp. 109–115.1998 - 34.Hudlicka, E, Guidelines for designing computational models of emotions. Int. J. Synth. Emotions (IJSE), 2011, 2: 26−79.
- 35.Strömfelt, H.; Zhang, Y.; Schuller, B.W. 2017. Emotion-augmented machine learning: Overview of an emerging domain. In
Proceedings of 2017 Seventh International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), San Antonio, TX, USA, 23–26 October 2017 ; IEEE: San Antonio, USA,2017 ; pp. 305–312. doi:10.1109/ACII.2017.8273617 - 36.Khashman, A. A modified backpropagation learning algorithm with added emotional coefficients, IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 2008, 19: 1896−1909.
- 37.Hwang, K.; Chen, M. Big-Data Analytics for Cloud,
IoT and Cognitive Computing ; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA,2017 . - 38.Wang, Y.X, A cognitive informatics reference model of autonomous agent systems (AAS). Int. J. Cognit. Inf. Nat. Intell., 2009, 3: 1−16.
- 39.Li, J.H.; Mei, C.L.; Xu, W.H.; et al. Concept learning via granular computing: A cognitive viewpoint.
Inf. Sci . 2015,298 , 447–467. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2014.12.010 - 40.Chen, M.; Herrera, F.; Hwang, K, Cognitive computing: Architecture, technologies and intelligent applications. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 19774−19783.
- 41.Gudivada, V.N, Cognitive computing: Concepts, architectures, systems, and applications. Handb. Stat., 2016, 35: 3−38.
- 42.Sreedevi, A.G.; Harshitha, T.N.; Sugumaran, V.; et al. Application of cognitive computing in healthcare, cybersecurity, big data and IoT: A literature review.
Inf. Process. Manage . 2022,59 , 102888. doi:10.1016/J.IPM.2022.102888 - 43.Ferrucci, D.A, Introduction to “This is Watson”. IBM J. Res. Dev., 2012, 56: 1.1−1.5.
- 44.Hurwitz, J.S.; Kaufman, M.; Bowles, A.
Cognitive Computing and Big Data Analytics ; John Wiley & Sons: Indianapolis, IN, USA,2015 . - 45.Fairclough, S.H.; Venables, L, Prediction of subjective states from psychophysiology: A multivariate approach. Biol. Psychol., 2006, 71: 100−110.
- 46.Teixeira, T.; Wedel, M.; Pieters, R, Emotion-induced engagement in internet video advertisements. J. Mark. Res., 2012, 49: 144−159.
- 47.Skinner, E.; Pitzer, J.; Brule, H. The role of emotion in engagement, coping, and the development of motivational resilience. In
International Handbook of Emotions in Education ; Pekrun, R.; Linnenbrink-Garcia, L., Eds.; Routledge: New York,2014 ; pp. 331–347. - 48.Mathur, A.; Lane, N.D.; Kawsar, F. Engagement-aware computing: Modelling user engagement from mobile contexts. In
Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016 ; ACM: Heidelberg, Germany,2016 ; pp. 622–633. doi:10.1145/2971648.2971760 - 49.Renninger, K.A.; Hidi, S.E.
The Power of Interest for Motivation and Engagement ; Routledge: New York,2015 . - 50.Klie, L, IBM’s Watson brings cognitive computing to customer engagement. Speech Technol. Mag., 2014, 19: 38−42.
- 51.Behera, R.K.; Bala, P.K.; Dhir, A, The emerging role of cognitive computing in healthcare: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Med. Inf., 2019, 129: 154−166.
- 52.Bandura, A, Social cognitive theory of self-regulation. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process., 1991, 50: 248−287.
- 53.Schunk, D.H.; Greene, J.A. Historical, contemporary, and future perspectives on self-regulated learning and performance. In
Handbook of Self-Regulation of Learning and Performanc e; Schunk, D.H.; Greene, J.A., Eds.; Routledge: New York,2018 ; pp. 1–15. doi:10.4324/9781315697048-1 - 54.McRae, K.; Gross, J.J, Emotion regulation. Emotion, 2020, 20: 1−9.
- 55.Bandura, A.
Social Foundations of Thought and Action ; Prentice Hall, New York,2002 . Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1985-98423-000(accessed on 5 November 2022). - 56.Azevedo, R.; Gašević, D, Analyzing multimodal multichannel data about self-regulated learning with advanced learning technologies: Issues and challenges. Comput. Hum. Behav., 2019, 96: 207−210.
- 57.Wilson, R.A.; Keil, F.C.
The MIT Encyclopedia of the Cognitive Sciences ; A Bradford Book, West Yorkshire, UK, 2001. - 58.Forgas, J.P, Mood effects on decision making strategies. Aust. J. Psychol., 1989, 41: 197−214.
- 59.Loewenstein, G.; Lerner, J.S. The role of affect in decision making. In
Handbook of Affective Science ; Davidson, R.; Goldsmith, H.; Scherer, K., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford,2003 ; pp. 619–642. - 60.Gliozzo, A.; Ackerson, C.; Bhattacharya, R.; et al.
Building Cognitive Applications with IBM Watson Services: Volume 1 Getting Started ; IBM Redbooks, IBM Garage, United States,2017 . Available online:https://www.redbooks.ibm.com/abstracts/sg248387.html (accessed on 6 November 2022). - 61.Iyengar, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Steinmuller, C.; et al, Preventing future oil spills with software-based event detection. Computer, 2010, 43: 95−97.
- 62.Commissiong, M.A. Student Engagement, Self-Regulation, Satisfaction, and Success in Online Learning Environments. Ph.D. Thesis, Walden University, Minneapolis, USA,
2020 . - 63.Starkey, K.; Hatchuel, A.; Tempest, S, Management research and the new logics of discovery and engagement. J. Manage. Stud., 2009, 46: 547−558.
- 64.Araujo, T.; Helberger, N.; Kruikemeier, S.; et al, In AI we trust? Perceptions about automated decision-making by artificial intelligence AI Soc., 2020, 35: 611−623.
- 65.Chirapurath, J.
Knowledge Mining: The Next Wave of Artificial Intelligence-Led Transformation ; Harward Business Review, Harvard Business Publishing, Watertown, Massachusetts, 21.11.2019 . Available online:https://hbr.org/sponsored/2019/11/knowledge-mining-the-next-wave-of-artificial-intelligence-led-transformation (accessed on 11 November 2022). - 66.Sagiroglu, S.; Sinanc, D. Big data: A review. In
Proceedings of 2013 International Conference on Collaboration Technologies and Systems (CTS), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–24 May 2013 ; IEEE: San Diego, USA,2013 ; pp. 42–47. doi:10.1109/CTS.2013.6567202 - 67.Sarker, I.H, Machine learning: Algorithms, real-world applications and research directions. SN Comput. Sci., 2021, 2: 160.
- 68.Peng, W.; Varanka, T.; Mostafa, A.; et al, Hyperbolic deep neural networks: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2022, 44: 10023−10044.
- 69.Li, Z.M.; Tian, W.W.; Li, Y.T.; et al. A more effective method for image representation: Topic model based on latent dirichlet allocation. In
Proceedings of 2015 14th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design and Computer Graphics (CAD/Graphics), Xi'an, China, 26–28 August 2015 ; IEEE: Xi'an, China,2015 ; pp. 143–148. doi:10.1109/CADGRAPHICS.2015.19 - 70.Jarrahi, M.H, Artificial intelligence and the future of work: Human-AI symbiosis in organizational decision making. Bus. Horiz., 2018, 61: 577−586.
- 71.Wyant, D.K.; Bingi, P.; Knight, J.R.; et al. DeTER framework: A novel paradigm for addressing cybersecurity concerns in mobile healthcare. In
Research Anthology on Securing Medical Systems and Records ; Information Resources Management Association, Ed.; IGI Global, Chocolate Ave. Hershey, PA 17033, USA,2022 ; pp. 381–407. doi:10.4018/978-1-6684-6311-6.ch019 - 72.Arrieta, A.B.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N.; Del Ser, J.; et al, Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible AI. Inf. Fusion, 2020, 58: 82−115.
- 73.Holzinger, A, Explainable AI and multi-modal causability in medicine. i-com, 2021, 19: 171−179.
- 74.Ravindran, N.J.; Gopalakrishnan, P. Predictive analysis for healthcare sector using big data technology. In
Proceedings of 2018 Second International Conference on Green Computing and Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), Bangalore, India ,16–18 August 2018; IEEE: Bangalore, India,2018 ; pp. 326–331. doi:10.1109/ICGCIoT.2018.8753090 - 75.Lin, S.J.; Hsu, M.F. Incorporated risk metrics and hybrid AI techniques for risk management.
Neural Comput . Appl.2017 ,28 , 3477–3489. doi:10.1007/s00521-016-2253-4 - 76.Peeters, M.M.M.; van Diggelen, J.; van den Bosch, K.; et al, Hybrid collective intelligence in a human–AI society. AI Soc., 2021, 36: 217−238.
- 77.Jobin, A.; Ienca, M.; Vayena, E, The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat. Mach. Intell., 2019, 1: 389−399.
How to Cite
Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q. From Emotion AI to Cognitive AI. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2022, 1 (1), 65–72. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0101006.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2022 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


