Neural networks serve as a crucial role in critical tasks, where erroneous outputs can have severe consequences. Traditionally, the validation of neural networks has focused on evaluating their performance across a large set of input points to ensure desired outputs. However, due to the virtually infinite cardinality of the input space, it becomes impractical to exhaustively check all possible inputs. Networks exhibiting strong performance on extensive input samples may fail to generalize correctly in novel scenarios, and remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks. This paper presents the general pipeline of neural network robustness and provides an overview of different domains that work together to achieve robustness guarantees. These domains include evaluating the robustness against adversarial attacks, evaluating the robustness formally and applying defense techniques to enhance the robustness when the model is compromised.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
On the Formal Evaluation of the Robustness of Neural Networks and Its Pivotal Relevance for AI-Based Safety-Critical Domains
- Mohamed Ibn Khedher 1, *,
- Houda Jmila 2,
- Mounim A. El-Yacoubi 2
Author Information
Received: 11 Jul 2023 | Accepted: 31 Oct 2023 | Published: 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
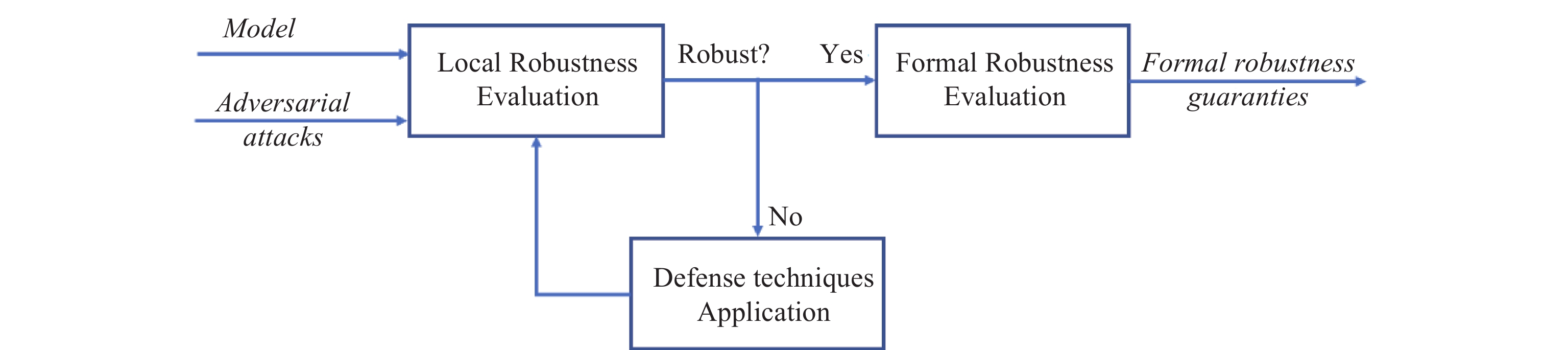
Keywords
neural network verification | adversarial attacks | defense techniques | formal robustness guaranties
References
- 1.Khedher, M.I.; Jmila, H.; El Yacoubi, M.A. Fusion of interest point/image based descriptors for efficient person re-identification. In
Proceedings of 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8 –13 July 2018 ; IEEE: New York, 2018; pp. 1–7. - 2.Qin, H.F.; El-Yacoubi, M.A. Finger-vein quality assessment based on deep features from grayscale and binary images. Int. J. Patt. Recogn. Artif. Intell., 2019, 33: 1940022. doi: 10.1142/s0218001419400226
- 3.Yu, N.X.; Yang, R.; Huang, M.J. Deep common spatial pattern based motor imagery classification with improved objective function. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell., 2022, 1: 73−84. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101007
- 4.Li, X.; Li, M.L.; Yan, P.F.; et al. Deep learning attention mechanism in medical image analysis: Basics and beyonds. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell., 2023, 2: 93−116. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0201006
- 5.Dao, Q.; El-Yacoubi, M.A.; Rigaud, A.S. Detection of Alzheimer disease on online handwriting using 1D convolutional neural network. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 2148−2155. doi: 10.1109/access.2022.3232396
- 6.Jmila, H.; Khedher, M.I.; Blanc, G.;
et al . Siamese network based feature learning for improved intrusion detection. InProceedings of the 26th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 12 –15 December 2019 ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 377–389. - 7.Khedher, M.I.; Mziou, M.S.; Hadji, M. Improving decision-making-process for robot navigation under uncertainty. In
Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, SciTePress, 4–6 February 2021 ; SciTePress, 2021; pp. 1105–1113. - 8.Bunel, R.; Turkaslan, I.; Torr, P.H.S.;
et al . A unified view of piecewise linear neural network verification. InProceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 3–8 December 2018 ; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, 2018; pp. 4795–4804. - 9.Goodfellow, I.J.; Shlens, J.; Szegedy, C. Explaining and harnessing adversarial examples. In
Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015 ; 2015. - 10.Papernot, N.; McDaniel, P.; Jha, S.;
et al . The limitations of deep learning in adversarial settings. InProceedings of 2016 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, Saarbruecken, Germany, 21–24 March 2016 ; IEEE: New York, 2016; pp. 372– 387. - 11.Moosavi-Dezfooli, S.M.; Fawzi, A.; Frossard, P. DeepFool: A simple and accurate method to fool deep neural networks. In
Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016 ; IEEE: New York, 2016; pp. 2574– 2582. - 12.Kurakin, A.; Goodfellow, I.J.; Bengio, S. Adversarial machine learning at scale. In
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017 ; OpenReview.net, 2017. - 13.Madry, A.; Makelov, A.; Schmidt, L.;
et al . Towards deep learning models resistant to adversarial attacks. InProceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018 ; OpenReview.net, 2018. - 14.Bhambri, S.; Muku, S.; Tulasi, A.;
et al . A survey of black-box adversarial attacks on computer vision models. arXiv:1912.01667, 2020. - 15.Chen, P.Y.; Zhang, H.; Sharma, Y.;
et al . ZOO: Zeroth order optimization based black-box attacks to deep neural networks without training substitute models. InProceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas Texas USA, 3 November 2017 ; ACM: New York, 2017; pp. 15–26. - 16.Brendel, W.; Rauber, J.; Bethge, M. Decision-based adversarial attacks: Reliable attacks against black-box machine learning models. In
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018 ; OpenReview.net, 2018. - 17.Chen, J.B.; Jordan, M.I. Boundary attack++: Query-efficient decision-based adversarial attack. arXiv: 1904.02144, 2019.
- 18.Jmila, H.; Khedher, M.I. Adversarial machine learning for network intrusion detection: A comparative study. Comput. Netw., 2022, 214: 109073. doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2022.109073
- 19.Aung, A.M.; Fadila, Y.; Gondokaryono, R.;
et al . Building robust deep neural networks for road sign detection. arXiv: 1712.09327, 2017. - 20.Xiang, W.M.; Tran, H.D.; Johnson, T.T. Reachable set computation and safety verification for neural networks with ReLU activations. arXiv: 1712.08163, 2017.
- 21.Xiang, W.M.; Tran, H.D.; Johnson, T.T. Output reachable set estimation and verification for multilayer neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2017, 29: 5777−5783. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2808470
- 22.Gehr, T.; Mirman, M.; Drachsler-Cohen, D.;
et al . AI2: Safety and robustness certification of neural networks with abstract interpretation. InProceedings of 2018 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 May 2018 ; IEEE: New York, 2018; pp. 3–18. - 23.El Mellouki, O.; Khedher, M.I.; El-Yacoubi, M.A. Abstract layer for leakyReLU for neural network verification based on abstract interpretation. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 33401−33413. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3263145
- 24.Lomuscio, A.; Maganti, L. An approach to reachability analysis for feed-forward ReLU neural networks. arXiv: 1706.07351, 2017.
- 25.Tjeng, V.; Xiao, K.Y.; Tedrake, R. Evaluating robustness of neural networks with mixed integer programming. In
Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019 ; OpenReview.net, 2019. - 26.Ibn-Khedher, H.; Khedher, M.I.; Hadji, M. Mathematical programming approach for adversarial attack modelling. In
Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, SciTePress, 4–6 February 2021 ; SciTePress, 2021; pp. 343–350. - 27.Bastani, O.; Ioannou, Y.; Lampropoulos, L.;
et al . Measuring neural net robustness with constraints. InProceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016 ; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, 2016; pp. 2621–2629. - 28.Dvijotham, K.; Stanforth, R.; Gowal, S.;
et al . A dual approach to scalable verification of deep networks. arXiv: 1803.06567, 2018. - 29.Wong, E.; Kolter, J.Z. Provable defenses against adversarial examples via the convex outer adversarial polytope. In
Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholmsmässan, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018 ; PMLR, 2018; pp. 5283–5292. - 30.Raghunathan, A.; Steinhardt, J.; Liang, P. Certified defenses against adversarial examples. In
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018 ; OpenReview.net, 2018. - 31.Wang, S.Q.; Pei, K.X.; Whitehouse, J.;
et al . Formal security analysis of neural networks using symbolic intervals. InProceedings of the 27th USENIX Conference on Security Symposium, Baltimore, MD, USA, 15–17 August 2018 ; USENIX Association: Berkeley, 2018; pp. 1599–1614. - 32.Bunel, R.; Turkaslan, I.; Torr, P.H.S.;
et al . Piecewise linear neural network verification: A comparative study. arXiv: 1711.00455, 2017. - 33.Katz, G.; Barrett, C.W.; Dill, D.L.;
et al . Reluplex: An efficient SMT solver for verifying deep neural networks. InProceedings of the International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Heidelberg, Germany, 24–28 July 2017 ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 97–117. - 34.Zantedeschi, V.; Nicolae, M.I.; Rawat, A. Efficient defenses against adversarial attacks. In
Proceedings of the 10th ACM Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Dallas, Texas, USA, 3 November 2017 ; ACM: New York, 2017; pp. 39–49. - 35.Nguyen, L.; Wang, S.; Sinha, A. A learning and masking approach to secure learning. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Decision and Game Theory for Security, Seattle, WA, USA, 29–31 October 2018 ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 453–464. - 36.Lee, H.; Han, S.; Lee, J. Generative adversarial trainer: Defense to adversarial perturbations with GAN. arXiv: 1705.03387, 2023.
How to Cite
Khedher, M. I.; Jmila, H.; Mounim A. El-Yacoubi. On the Formal Evaluation of the Robustness of Neural Networks and Its Pivotal Relevance for AI-Based Safety-Critical Domains. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (4), 100018. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2023.100018.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


