Diabetes retinopathy (DR) is a universal eye disease, which brings irreversible blindness risks to patients in severe cases. Due to the scarcity of professional ophthalmologists, it has become increasingly important to develop computer-aided diagnostic systems for DR grading diagnosis. However, the current mainstream deep learning methods face challenges in accurately classifying the severity of DR, making it difficult for them to provide a reliable reference for clinicians. To tackle this problem, we propose two novel modules to improve the accuracy of DR classification. Specifically, we design a multi-scale feature extraction module to capture tiny lesions in fundus images and differentiate similar lesions simultaneously. In addition, we develop a class attention module to alleviate the adverse impact of intra-class similarity on DR grading. Experimental results show that our proposed modules attain significant performance improvement on the APTOS2019 blind detection dataset, with accuracy and quadratic weighted Kappa metrics achieving 95.98% and 97.12%, respectively.
- Open Access
- Article
Multi-Scale Class Attention Network for Diabetes Retinopathy Grading
- Hongyu Chen 1,
- Ronghua Wu 1,
- Chen Tao 1,
- Wenjing Xu 1,
- Hongzhe Liu 3,
- Cheng Xu 3,
- Muwei Jian 1, 2, *
Author Information
Received: 01 Jun 2023 | Accepted: 21 Jul 2023 | Published: 26 Jun 2024
Abstract
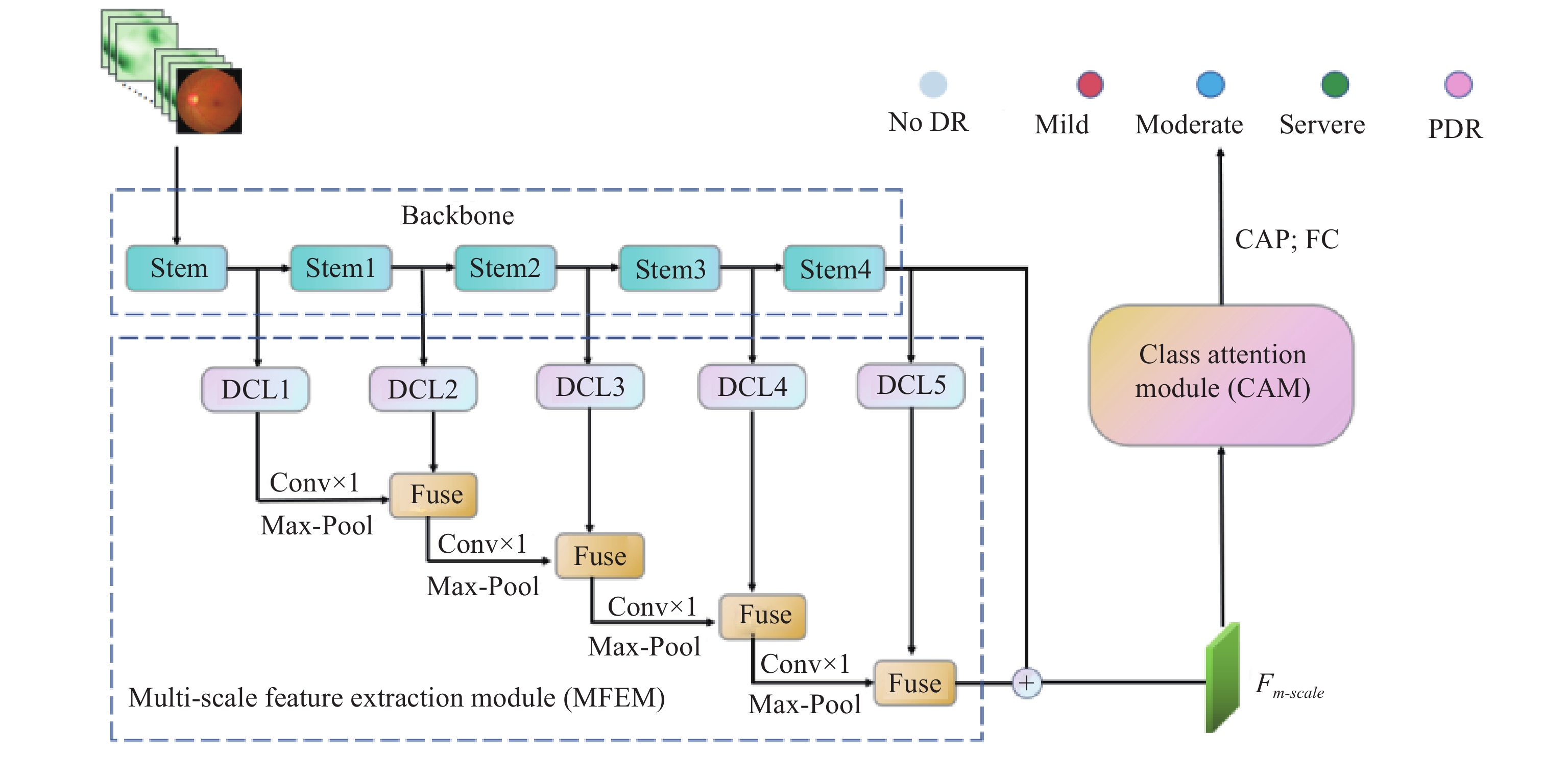
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1.The Royal College of Ophthalmologists. Diabetic Retinopathy Guidelines. Technical Report, 2012.
- 2.Scully, T. Diabetes in numbers. Nature, 2012, 485: S2−S3. doi: 10.1038/485S2a
- 3.Wilkinson, C.P.; Ferris, F.L.; Klein, R.E.; et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology, 2003, 110: 1677−1682. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00475-5
- 4.Jian, M.W.; Wang, J.J.; Yu, H.; et al. Integrating object proposal with attention networks for video saliency detection. Inf. Sci., 2021, 576: 819−830. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.08.069
- 5.Yin, Y.C.; Han, Z.M.; Jian, M.W.; et al. AMSUnet: A neural network using atrous multi-scale convolution for medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med., 2023, 162: 107120. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107120
- 6.Abràmoff, M.D.; Lou, Y.Y.; Erginay, A.; et al. Improved automated detection of diabetic retinopathy on a publicly available dataset through integration of deep learning. Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci., 2016, 57: 5200−5206. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-19964
- 7.Araújo, T.; Aresta, G.; Mendonça, L.; et al. DR|GRADUATE: Uncertainty-aware deep learning-based diabetic retinopathy grading in eye fundus images. Med. Image Anal., 2020, 63: 101715. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2020.101715
- 8.Saleh, E.; Błaszczyński, J.; Moreno, A.; et al. Learning ensemble classifiers for diabetic retinopathy assessment. Artif. Intell. Med., 2018, 85: 50−63. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2017.09.006
- 9.Mahendran, G.; Dhanasekaran, R. Investigation of the severity level of diabetic retinopathy using supervised classifier algorithms. Comput. Electr. Eng., 2015, 45: 312−323. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2015.01.013
- 10.Jian, M.W.; Wu, R.H.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. Dual-branch-UNet: A dual-branch convolutional neural network for medical image segmentation. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci., 2023, 137: 705−716. doi: 10.32604/CMES.2023.027425
- 11.Han, Z.M.; Jian, M.W.; Wang, G.G. ConvUNeXt: An efficient convolution neural network for medical image segmentation. Knowl. Based Syst., 2022, 253: 109512. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109512
- 12.Xu, K.L.; Feng, D.W.; Mi, H.B. Deep convolutional neural network-based early automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using fundus image. Molecules, 2017, 22: 2054. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122054
- 13.Li, X.G.; Pang, T.T.; Xiong, B.; et al. Convolutional neural networks based transfer learning for diabetic retinopathy fundus image classification. In
2017 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing ,BioMedical Engineering and Informatics (CISP-BMEI ),Shanghai ,China ,14 –16 October 2017 ; IEEE: New York, 2017; pp. 1–11. doi:10.1109/CISP-BMEI.2017.8301998 - 14.Chen, H. A novel multi-scale network based on class attention for diabetes retinopathy. In
The 20th IEEE International Conference on Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing (UIC 2023 ), UK. - 15.Zhang, Y.; Lv, P.H.; Lu, X.B.; et al. Face detection and alignment method for driver on highroad based on improved multi-task cascaded convolutional networks. Multimed. Tools Appl., 2019, 78: 26661−26679. doi: 10.1007/s11042-019-07836-2
- 16.Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.Q.; et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Boston ,MA ,USA ,7 –12 June 2015 ; IEEE: New York, 2015; pp. 1–9. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594 - 17.Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In
14th European Conference on Computer Vision ,Amsterdam ,The Netherlands ,11–14 October 2016 ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 21–37. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2 - 18.Niu, Z.Y.; Zhong, G.Q.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing, 2021, 452: 48−62. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.03.091
- 19.Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; et al. Attention is all you need. In
Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems ,Long Beach ,CA ,USA ,4 December 2017 ; Curran Associates: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 6000–6010. doi:10.5555/3295222.3295349 - 20.Wang, X.L.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; et al. Non-local neural networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Salt Lake City ,UT ,USA ,18 –23 June 2018 ; IEEE: New York, 2018; pp. 7794–7803. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2018.00813 - 21.Huang, Z.L.; Wang, X.G.; Huang, L.C.; et al. CCNet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision ,Seoul ,Korea (South ),27 October 2019 –2 November 2019 ; IEEE: New York, 2019; pp. 603–612. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2019.00069 - 22.Zhu, Z.; Xu, M.D.; Bai, S.; et al. Asymmetric non-local neural networks for semantic segmentation. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision ,Seoul ,Korea (South ),27 October 2019 –2 November 2019 ; IEEE: New York, 2019; pp. 593–602. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2019.00068 - 23.Cao, Y.; Xu, J.R.; Lin, S.; et al. GCNet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop ,Seoul ,Korea (South ),27 –28 October 2019 ; IEEE: New York, 2019; pp. 1971–1980. doi:10.1109/ICCVW.2019.00246 - 24.Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Salt Lake City ,UT ,USA ,18 –23 June 2018 ; IEEE: New York, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745 - 25.Li, X.; Wang, W.H.; Hu, X.L.; et al. Selective kernel networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Long Beach ,CA ,USA ,15 –20 June 2019 ; IEEE: New York, 2019; pp. 510–519. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2019.00060 - 26.Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In
Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV ),Munich ,Germany ,8–14 September 2018 ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–19. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_1 - 27.Wang, X.L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, D.R. Adaptive dynamic programming for networked control systems under communication constraints: A survey of trends and techniques. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell., 2022, 1: 85−98. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101008
- 28.Yu, N.X.; Yang, R.; Huang, M.J. Deep common spatial pattern based motor imagery classification with improved objective function. Int. J. Netw. Dyn. Intell., 2022, 1: 73−84. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101007
- 29.Krause, J.; Gulshan, V.; Rahimy, E.; et al. Grader variability and the importance of reference standards for evaluating machine learning models for diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmology, 2018, 125: 1264−1272. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2018.01.034
- 30.Sugeno, A.; Ishikawa, Y.; Ohshima, T.; et al. Simple methods for the lesion detection and severity grading of diabetic retinopathy by image processing and transfer learning. Comput. Biol. Med., 2021, 137: 104795. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104795
- 31.Bellemo, V.; Lim, Z.W.; Lim, G.; et al. Artificial intelligence using deep learning to screen for referable and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in Africa: A clinical validation study. Lancet Digital Health, 2019, 1: e35−e44. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(19)30004-4
- 32.Tymchenko, B.; Marchenko, P.; Spodarets, D. Deep learning approach to diabetic retinopathy detection. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Pattern Recognition Applications and Methods ,Valletta ,Malta ,22 –24 February 2020 ; ICPRAM, 2020; pp. 501–509. - 33.He, A.L.; Li, T.; Li, N.; et al. CABNet: Category attention block for imbalanced diabetic retinopathy grading. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2021, 40: 143−153. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3023463
- 34.Li, X.M.; Hu, X.W.; Yu, L.Q.; et al. CANet: Cross-disease attention network for joint diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema grading. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 2020, 39: 1483−1493. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2951844
- 35.Wu, Z.; Shi, G.L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Coarse-to-fine classification for diabetic retinopathy grading using convolutional neural network. Artif. Intell. Med., 2020, 108: 101936. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2020.101936
- 36.Jian, M.W.; Chen, H.Y.; Tao, C.; et al. Triple-DRNet: A triple-cascade convolution neural network for diabetic retinopathy grading using fundus images. Comput. Biol. Med., 2023, 155: 106631. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106631
- 37.Graham, B. Kaggle Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Competition Report. University of Warwick, pp. 24-26, 2015.
- 38.He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Las Vegas ,NV ,USA ,27 –30 June 2016 ; IEEE: New York, 2016; pp. 770–778. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2016.90 - 39.Xie, S.N.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In
Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,Honolulu ,HI ,USA ,21 –26 July 2017 ; IEEE: New York, 2017; pp. 5987–5995. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2017.634 - 40.Tan, M.X.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In
Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning ,Long Beach ,CA ,USA ,9 –15 June 2019 ; ICML, 2019; pp. 6105–6114. - 41.Chai, R.M.; Chen, D.; Ma, X.; et al. Diabetic retinopathy diagnosis based on transfer learning and improved residual network. In
2022 IEEE 11th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS ),Chengdu ,China ,3 –5 August 2022 ; IEEE: New York, 2022; pp. 941–946. doi:10.1109/DDCLS55054.2022.9858557 - 42.Liu, Z.; Mao, H.Z.; Wu, C.Y.; et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition ,New Orleans ,LA ,USA ,18 –24 June 2022 ; IEEE: New York, 2022; pp. 11966–11976. doi:10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01167
How to Cite
Chen, H.; Wu, R.; Tao, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, C.; Jian, M. Multi-Scale Class Attention Network for Diabetes Retinopathy Grading. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2024, 3 (2), 100012. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2023.100012.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


