This paper investigates the parameter learning problem for the probabilistic Boolean control networks (PBCNs) with input-output data. Firstly, an algebraic expression of the PBCNs is obtained by taking advantage of the semi-tensor product technique, and then, the parameter learning problem is transformed into an optimal problem to reveal the parameter matrices of a linear system in a computationally efficient way. Secondly, two recursive semi-tensor product based algorithms are designed to calculate the forward and backward probabilities. Thirdly, the expectation maximization algorithm is proposed as an elaborate technique to address the parameter learning problem. In addition, a useful index is introduced to describe the performance of the proposed parameter learning algorithm. Finally, two numerical examples are employed to demonstrate the reliability of the proposed parameter learning approach.
- Open Access
- Article
Parameter Learning of Probabilistic Boolean Control Networks with Input-Output Data
- Hongwei Chen 1, *,
- Qi Chen 1,
- Bo Shen 1,
- Yang Liu 2
Author Information
Received: 23 Sep 2023 | Accepted: 27 Nov 2023 | Published: 26 Mar 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
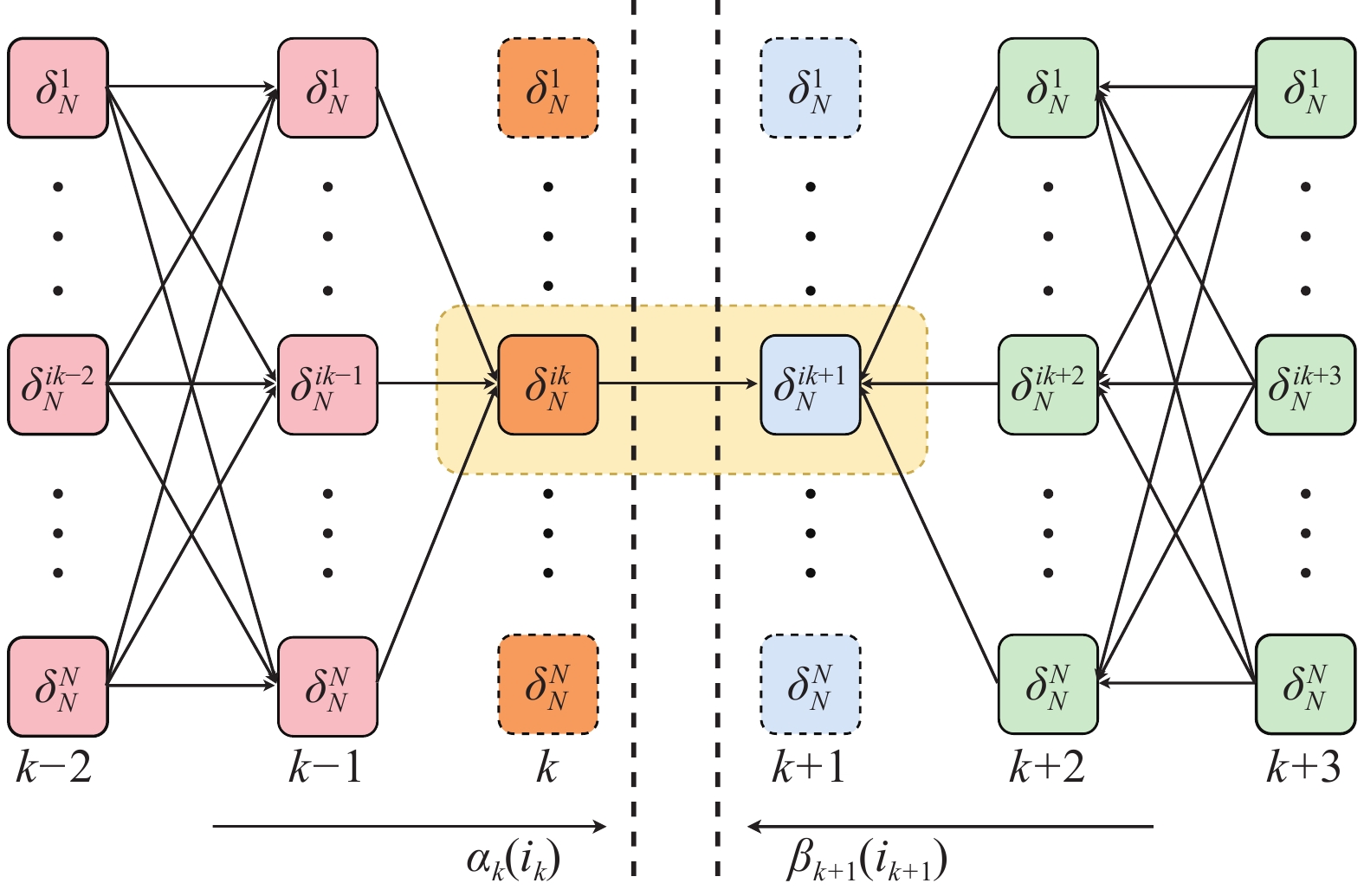
Keywords
probabilistic boolean control networks | parameter learning | semi-tensor product | forward and backward probabilities | expectation maximization algorithm
References
- 1.Kauffman, S.A. Metabolic stability and epigenesis in randomly constructed genetic nets. J. Theor. Biol., 1969, 22: 437−467. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(69)90015-0
- 2.Thomas, R. Boolean formalization of genetic control circuits. J. Theor. Biol., 1973, 42: 563−585. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(73)90247-6
- 3.Akutsu, T.; Hayashida, M.; Ching, W.K.; et al. Control of Boolean networks: Hardness results and algorithms for tree structured networks. J. Theor. Biol., 2007, 244: 670−679. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2006.09.023
- 4.Cheng, D.Z.; Qi, H.S.; Li, Z.Q.
Analysis and Control of Boolean Networks :A Semi-tensor Product Approach ; Springer: London, UK, 2011. doi: 10.1007/978-0-85729-097-7 - 5.Cheng, D.Z.; Qi, H.S. Controllability and observability of Boolean control networks. Automatica, 2009, 45: 1659−1667. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.03.006
- 6.Yu, Y.Y.; Meng, M.; Feng, J.E.; et al. Observability criteria for Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2022, 67: 6248−6254. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3131436
- 7.Feng, J.E.; Li, Y.L.; Fu, S.H.; et al. New method for disturbance decoupling of Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2022, 67: 4794−4800. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3161609
- 8.Zhao, R.; Feng, J.E.; Wang, B.; et al. Disturbance decoupling of Boolean networks via robust indistinguishability method. Appl. Math. Comput., 2023, 457: 128220. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2023.128220
- 9.Li, R.; Chu, T.G. Complete synchronization of Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2012, 23: 840−846. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2190094
- 10.Chen, H.W.; Liang, J.L. Local synchronization of interconnected Boolean networks with stochastic disturbances. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2020, 31: 452−463. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2904978
- 11.Fornasini, E.; Valcher, M.E. Optimal control of Boolean control networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2014, 59: 1258−1270. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2294821
- 12.Laschov, D.; Margaliot, M. Minimum-time control of Boolean networks. SIAM J. Control Optim., 2013, 51: 2869−2892. doi: 10.1137/110844660
- 13.Li, H.T.; Xie, L.H.; Wang, Y.Z. Output regulation of Boolean control networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2017, 62: 2993−2998. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2606600
- 14.Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Cheng, D.Z. Output tracking of Boolean control networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2020, 65: 2730−2735. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2944903
- 15.Zhang, Q.L.; Feng, J.E.; Wang, B.; et al. Event-triggered mechanism of designing set stabilization state feedback controller for switched Boolean networks. Appl. Math. Comput., 2020, 383: 125372. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2020.125372
- 16.Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Fault detection and pinning control of Boolean networks. Appl. Math. Comput., 2022, 429: 127232. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2022.127232
- 17.Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Lou, J.G.; et al. Robust minimal strong reconstructibility problem of Boolean control networks. Appl. Math. Comput., 2023, 458: 128209. doi: 10.1016/J.AMC.2023.128209
- 18.Li, H.T.; Xu, X.J.; Ding, X.Y. Finite-time stability analysis of stochastic switched Boolean networks with impulsive effect. Appl. Math. Comput., 2019, 347: 557−565. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2018.11.018
- 19.Shmulevich, I.; Dougherty, E.R.; Kim, S.; et al. Probabilistic Boolean networks: A rule-based uncertainty model for gene regulatory networks. Bioinformatics, 2002, 18: 261−274. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.261
- 20.Chen, H.W.; Liang, J.L.; Lu, J.Q.; et al. Synchronization for the realization-dependent probabilistic Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2018, 29: 819−831. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2647989
- 21.Li, H.T.; Yang, X.R.; Wang, S.L. Perturbation analysis for finite-time stability and stabilization of probabilistic Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2021, 51: 4623−4633. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3003055
- 22.Chen, H.W.; Wang, Z.D.; Shen, B.; et al. Model evaluation of the stochastic Boolean control networks. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control, 2022, 67: 4146−4153. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3106896
- 23.Li, R.; Yang, M.; Chu, T.G. State feedback stabilization for probabilistic Boolean networks. Automatica, 2014, 50: 1272−1278. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2014.02.034
- 24.Wu, Y.H.; Guo, Y.Q.; Toyoda, M. Policy iteration approach to the infinite horizon average optimal control of probabilistic Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2021, 32: 2910−2924. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3008960
- 25.Li, F.F.; Xie, L.H. Set stabilization of probabilistic Boolean networks using pinning control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2019, 30: 2555−2561. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2881279
- 26.Ding, X.Y.; Li, H.T.; Yang, Q.Q.; et al. Stochastic stability and stabilization of n-person random evolutionary Boolean games. Appl. Math. Comput., 2017, 306: 1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2017.02.020
- 27.Lähdesmäki, H.; Shmulevich, I.; Yli-Harja, O. On learning gene regulatory networks under the Boolean network model. Mach. Learn., 2003, 52: 147−167. doi: 10.1023/A:1023905711304
- 28.Nam, D.; Seo, S.; Kim, S. An efficient top-down search algorithm for learning Boolean networks of gene expression. Mach. Learn., 2006, 65: 229−245. doi: 10.1007/s10994-006-9014-z
- 29.Apostolopoulou, I.; Marculescu, D. Tractable learning and inference for large-scale probabilistic Boolean networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2019, 30: 2720−2734. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2886207
- 30.Akutsu, T.; Melkman, A.A. Identification of the structure of a probabilistic Boolean network from samples including frequencies of outcomes. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2019, 30: 2383−2396. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2018.2884454
- 31.Cheng, D.Z.; Qi, H.S.; Li, Z.Q. Model construction of Boolean network via observed data. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw., 2011, 22: 525−536. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2106512
- 32.Cheng, D.Z.; Zhao, Y. Identification of Boolean control networks. Automatica, 2011, 47: 702−710. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.01.083
- 33.Zhang, X.H.; Han, H.X.; Zhang, W.D. Identification of Boolean networks using premined network topology information. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst., 2017, 28: 464−469. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2514841
- 34.Leifeld, T.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, P. Identification of Boolean network models from time series data incorporating prior knowledge. Front. Physiol., 2018, 9: 695. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00695
- 35.Cui, L.B.; Li, W.; Ching, W.K. On Construction of sparse probabilistic Boolean networks from a prescribed transition probability matrix. In
Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computational Systems Biology ,Suzhou ,China ,9–11 September 2010 ; ORSC & APORC, 2010; pp. 227–234. - 36.Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. Roy. Stat. Soc.: Ser. B (Methodol.), 1977, 39: 1−22. doi: 10.1111/j.2517-6161.1977.tb01600.x
- 37.Chaves, M. Methods for qualitative analysis of genetic networks. In
Proceedings of the European Control Conference ,Budapest ,Hungary ,23–26 August 2009 ; IEEE: New York, 2009; pp. 671–676. doi: 10.23919/ECC.2009.7074480
How to Cite
Chen, H.; Chen, Q.; Shen, B.; Liu, Y. Parameter Learning of Probabilistic Boolean Control Networks with Input-Output Data. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2024, 3 (1), 100005. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2024.100005.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


