The disassembly complexity of end-of-life products increases continuously. Traditional methods are facing difficulties in solving the decision-making and control problems of disassembly operations. On the other hand, the latest development in reinforcement learning makes it more feasible to solve such kind of complex problems. Inspired by behaviorism psychology, reinforcement learning is considered as one of the most promising directions to achieve universal artificial intelligence (AI). In this context, we first review the basic ideas, mathematical models, and various algorithms of reinforcement learning. Then, we introduce the research progress and application subjects in the field of disassembly and recycling, such as disassembly sequencing, disassembly line balancing, product transportation, disassembly layout, etc. In addition, the prospects, challenges and applications of reinforcement learning based disassembly and recycling are also comprehensively analyzed and discussed.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
Reinforcement Learning for Disassembly System Optimization Problems: A Survey
- Xiwang Guo 1, 2, *,
- Zhiliang Bi 2,
- Jiacun Wang 1,
- ShuJin Qin 3,
- ShiXin Liu 4,
- Liang Qi 5
Author Information
Received: 16 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 28 Nov 2022 | Published: 27 Mar 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
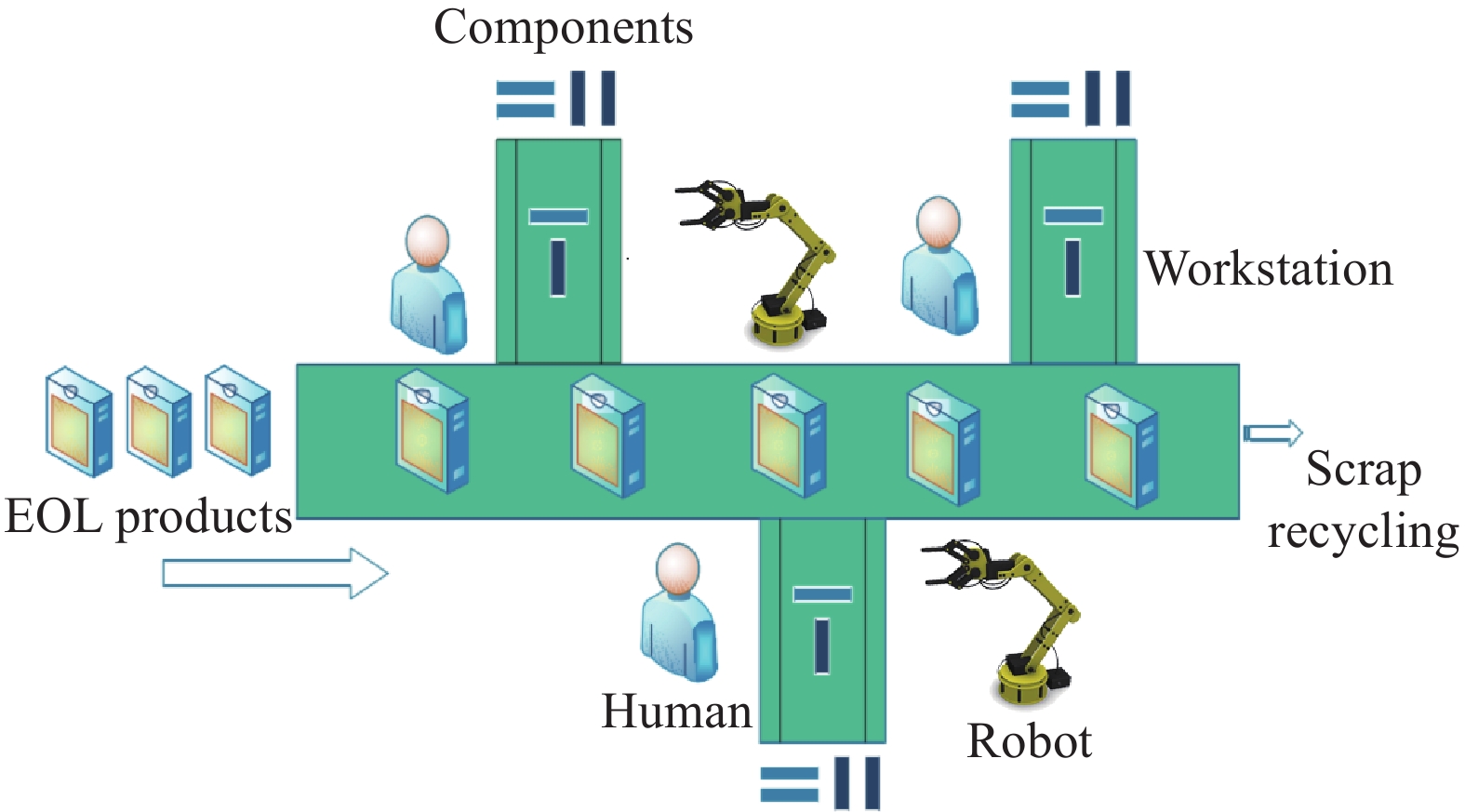
Keywords
disassembly lines | reinforcement learning | Q-learning | deep Q-learning
References
- 1.Liu, Z.Y.; Li, C.; Fang, X.Y.; et al. Energy consumption in additive manufacturing of metal parts. Procedia Manuf., 2018, 26: 834−845.
- 2.Azaria, A.; Richardson, A.; Kraus, S.; et al. Behavioral analysis of insider threat: A survey and bootstrapped prediction in imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst., 2014, 1: 135−155.
- 3.Mete, S.; Serin, F. A reinforcement learning approach for disassembly line balancing problem. In Proceedings of 2021 International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT), Amman, Jordan, 14–15 July 2021; IEEE: Amman, Jordan, 2021; pp. 424–427. doi: 10.1109/ICIT52682.2021.9491689
- 4.Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, Z.D.; Pham, D.T.; et al. Collaborative optimization of robotic disassembly sequence planning and robotic disassembly line balancing problem using improved discrete Bees algorithm in remanufacturing. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf., 2020, 61: 101829.
- 5.Igarashi, K.; Yamada, T.; Gupta, S.M.; et al. Disassembly system modeling and design with parts selection for cost, recycling and CO2 saving rates using multi criteria optimization. J. Manuf. Syst., 2016, 38: 151−164.
- 6.Baazouzi, S.; Rist, F.P.; Weeber, M.; et al. Optimization of disassembly strategies for electric vehicle batteries. Batteries, 2021, 7: 74.
- 7.Battaïa, O.; Dolgui, A.; Heragu, S.S.; et al. Design for manufacturing and assembly/disassembly: Joint design of products and production systems. Int. J. Prod. Res., 2018, 56: 7181−7189.
- 8.Tian, G.D.; Zhou, M.C.; Li, P.G. Disassembly sequence planning considering fuzzy component quality and varying operational cost. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2018, 15: 748−760.
- 9.Guo, X.W.; Zhang, Z.W.; Qi, L.; et al. Stochastic hybrid discrete grey wolf optimizer for multi-objective disassembly sequencing and line balancing planning in disassembling multiple products. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2022, 19: 1744−1756.
- 10.Guo, X.W.; Zhou, M.C.; Liu, S.X.; et al. Multiresource-constrained selective disassembly with maximal profit and minimal energy consumption. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2021, 18: 804−816.
- 11.Harib, K.H.; Sivaloganathan, S.; Ali, H.Z.; et al. Teaching assembly planning using AND/OR graph in a design and manufacture lab course. In Proceedings of 2020 ASEE Virtual Annual Conference, 22 Jun 2020-26 Jun 2020; 2020.
- 12.Tian, G.D.; Ren, Y.P.; Feng, Y.X.; et al. Modeling and planning for dual-objective selective disassembly using and/or graph and discrete artificial bee colony. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform., 2019, 15: 2456−2468.
- 13.Barrett, T.; Clements, W.; Foerster, J.; et al. Exploratory combinatorial optimization with reinforcement learning. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intelli., 2020, 34: 3243−3250.
- 14.Qu, S.H. Dynamic Scheduling in Large-Scale Manufacturing Processing Systems Using Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. Ph.D. Thesis, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2019.
- 15.Chang, M.M.L.; Ong, S.K.; Nee, A.Y.C. Approaches and challenges in product disassembly planning for sustainability. Procedia CIRP, 2017, 60: 506−511.
- 16.Aguinaga, I.; Borro, D.; Matey, L. Parallel RRT-based path planning for selective disassembly planning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2008, 36: 1221−1233.
- 17.Tseng, H.E.; Chang, C.C.; Lee, S.C.; et al. A Block-based genetic algorithm for disassembly sequence planning. Expert Syst. Appl., 2018, 96: 492−505.
- 18.Wu, H.; Zuo, H.F. Using genetic annealing simulated annealing algorithm to solve disassembly sequence planning. J. Syst. Eng. Electron., 2009, 20: 906−912.
- 19.Guo, X.W.; Zhou, M.C.; Abusorrah, A.; et al. Disassembly sequence planning: A survey. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin., 2021, 8: 1308−1324.
- 20.Wang, H.; Xiang, D.; Duan, G.H. A genetic algorithm for product disassembly sequence planning. Neurocomputing, 2008, 71: 2720−2726.
- 21.Xing, Y.F.; Wang, C.E.; Liu, Q. Disassembly sequence planning based on Pareto ant colony algorithm. J. Mech. Eng., 2012, 48: 186−192.
- 22.Chapman, D.; Kaelbling, L.P. Input generalization in delayed reinforcement learning: An algorithm and performance comparisons. In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Artificial intelligence, Sydney New South Wales Australia, 24–30 August 1991; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Sydney New South Wales Australia, 1991; pp. 726–731.
- 23.Guo, X.W.; Zhou, M.C.; Liu, S.X.; et al. Lexicographic multiobjective scatter search for the optimization of sequence-dependent selective disassembly subject to multiresource constraints. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2020, 50: 3307−3317.
- 24.Guo, X.W.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, M.C.; et al. Disassembly sequence optimization for large-scale products with multiresource constraints using scatter search and petri nets. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2016, 46: 2435−2446.
- 25.Ji, Y.J.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, M.C.; et al. A machine learning and genetic algorithm-based method for predicting width deviation of hot-rolled strip in steel production systems. Inf. Sci., 2022, 589: 360−375.
- 26.Zhao, Z.Y.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, M.C.; et al. Decomposition method for new single-machine scheduling problems from steel production systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2020, 17: 1376−1387.
- 27.Zhao, Z.Y.; Zhou, M.C.; Liu, S.X. Iterated greedy algorithms for flow-shop scheduling problems: A tutorial. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2022, 19: 1941−1959.
- 28.Zhang, R.; Lv, Q.B.; Li, J.; et al. A reinforcement learning method for human-robot collaboration in assembly tasks. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf., 2022, 73: 102227.
- 29.de Mello, L.S.H.; Sanderson, A.C. AND/OR graph representation of assembly plans. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom., 1990, 6: 188−199.
- 30.Xia, K.; Gao, L.; Li, WD.; et al. A Q-learning based selective disassembly planning service in the cloud based remanufacturing system for WEEE. In Proceedings of the ASME 2014 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference collocated with the JSME 2014 International Conference on Materials and Processing and the 42nd North American Manufacturing Research Conference, Detroit, Michigan, USA, 9–13 June 2014; ASME: Detroit, USA, 2014; pp. V001T04A012. doi: 10.1115/MSEC2014-4008
- 31.Wurster, M.; Michel, M.; May, M.C.; et al. Modelling and condition-based control of a flexible and hybrid disassembly system with manual and autonomous workstations using reinforcement learning. J. Intell. Manuf., 2022, 33: 575−591.
- 32.Mao, H.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Qiu, C. Adaptive disassembly sequence planning for VR maintenance training via deep reinforcement learning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, in press. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-08290-x
- 33.McGovern, S.M.; Gupta, S.M. A balancing method and genetic algorithm for disassembly line balancing. Eur. J. Oper. Res., 2007, 179: 692−708.
- 34.Guo, X.W.; Liu, S.X.; Zhou, M.C.; et al. Dual-objective program and scatter search for the optimization of disassembly sequences subject to multiresource constraints. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng., 2018, 15: 1091−1103.
- 35.Bentaha, M.L.; Battaïa, O.; Dolgui, A. An exact solution approach for disassembly line balancing problem under uncertainty of the task processing times. Int. J. Prod. Res., 2015, 53: 1807−1818.
- 36.Mei, K.; Fang, Y.L. Multi-robotic disassembly line balancing using deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the ASME 2021 16th International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, 21–25 June 2021; ASME, 2021; pp. V002T07A005. doi: 10.1115/MSEC2021-63522
- 37.Tuncel, E.; Zeid, A.; Kamarthi, S. Solving large scale disassembly line balancing problem with uncertainty using reinforcement learning. J. Intell. Manuf., 2014, 25: 647−659.
- 38.Serrano-Muñoz, A.; Arana-Arexolaleiba, N.; Chrysostomou, D.; et al. Learning and generalising object extraction skill for contact-rich disassembly tasks: An introductory study. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, in press. doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-08086-z
- 39.Tuncel, E.; Zeid, A.; Kamarthi, S. Inventory management in multi-product, multi-demand disassembly line using reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, Istanbul, Turkey, 3–6 July 2012; Istanbul, Turkey, 2012; pp. 1866–1873.
- 40.Zheng, P.; Xia, L.Q.; Li, C.X.; et al. Towards self-X cognitive manufacturing network: An industrial knowledge graph-based multi-agent reinforcement learning approach. J. Manuf. Syst., 2021, 61: 16−26.
- 41.Wurster, M.; Michel, M.; May, M.C.; et al. Modelling and condition-based control of a flexible and hybrid disassembly system with manual and autonomous workstations using reinforcement learning. J. Intell. Manuf., 2022, 33: 575−591.
- 42.Wiering, M.; van Otterlo, M. Reinforcement Learning; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-27645-3.
- 43.Kaiser, L.; Babaeizadeh, M.; Milos, P.; et al. Model based reinforcement learning for Atari. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26–30 April 2020; OpenReview.net: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2020.
- 44.Rafati, J.; Noelle, D. C. Learning representations in model-free hierarchical reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Third AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Thirty-First Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference and Ninth AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, 27 January–1 February 2019; AAAI Press: Honolulu, 2019; p. 1303.
- 45.Watkins, C.J.C.H.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 279–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00992698
- 46.Osband, I.; Blundell, C.; Pritzel, A.; et al. Deep exploration via bootstrapped DQN. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; Curran Associates Inc.: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; pp. 4033–4041.
- 47.van Hasselt, H. Double Q-learning. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver British, Columbia, Canada, 6–9 December 2010; Curran Associates Inc.: Vancouver British, Canada, 2010; pp. 2613–2621.
- 48.Clifton, J.; Laber, E. Q-learning: Theory and applications. Annu. Rev. Stat. Appl., 2020, 7: 279−301.
- 49.Montazeri, M.; Kebriaei, H.; Araabi, B.N. Learning Pareto optimal solution of a multi-attribute bilateral negotiation using deep reinforcement. Electron. Commer. Res., 2020, 43: 100987.
- 50.Er, M.J.; Deng, C. Online tuning of fuzzy inference systems using dynamic fuzzy Q-learning. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern., Part B Cybern., 2004, 34: 1478−1489.
- 51.Melo, F.S. Convergence of Q-Learning: A Simple Proof; Institute of Systems and Robotics: Lisboa, 2001; pp. 1–4.
- 52.Zhang, S.T.; Sutton, R.S. A deeper look at experience replay. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1712.01275, 2017. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1712.01275.
- 53.Fedus, W.; Ramachandran, P.; Agarwal, R.; et al. Revisiting fundamentals of experience replay. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, 13–18 July 2020; PMLR, 2020; pp. 3061–3071.
- 54.Zhao, X.K.; Li, C.B.; Tang, Y.; et al. Reinforcement learning-based selective disassembly sequence planning for the end-of-life products with structure uncertainty. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett., 2021, 6: 7807−7814.
- 55.Liu, Z.H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.H.; et al. Task-level decision-making for dynamic and stochastic human-robot collaboration based on dual agents deep reinforcement learning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2021, 115: 3533−3552.
- 56.Zhang, H.J.; Liu, P.S.; Guo, X.W.; et al. An improved Q-learning algorithm for solving disassembly line balancing problem considering carbon emission. In Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; IEEE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2022; 872–877. doi: 10.1109/SMC53654.2022.9945321
- 57.Chen, S.K.; Fang, S.L.; Tang, R.Z. A reinforcement learning based approach for multi-projects scheduling in cloud manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res., 2019, 57: 3080−3098.
- 58.Liu, Y.Z.; Zhou, M.C.; Guo, X.W. An improved q-learning algorithm for human-robot collaboration two-sided disassembly line balancing problems. In Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; IEEE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2022; 568–573. doi: 10.1109/SMC53654.2022.9945263
- 59.Bi, Z.L.; Guo, X.W.; Wang, J.C.; et al. A Q-learning-based selective disassembly sequence planning method. In Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; IEEE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2022; pp. 3216–3221. doi: 10.1109/SMC53654.2022.9945073
- 60.Reveliotis, S.A. Modelling and controlling uncertainty in optimal disassembly planning through reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April 2004-1 May 2004; IEEE: New Orleans, USA, 2004; pp. 2625–2632. doi: 10.1109/ROBOT.2004.1307457
- 61.Kristensen, C.B.; Sørensen, F.A.; Nielsen, H.B.; et al. Towards a robot simulation framework for E-waste disassembly using reinforcement learning. Procedia Manuf., 2019, 38: 225−232.
- 62.Wang, H.X.; Sarker, B.R.; Li, J.; et al. Adaptive scheduling for assembly job shop with uncertain assembly times based on dual Q-learning. Int. J. Prod. Res., 2021, 59: 5867−5883.
- 63.Cai, W.B.; Guo, X.W.; Wang, J.C.; et al. An improved advantage actor-critic algorithm for disassembly line balancing problems considering tools deterioration. In Proceedings of 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 9–12 October 2022; IEEE: Prague, Czech Republic, 2022; 3336–3341. doi: 10.1109/SMC53654.2022.9945173
- 64.Zhong, Z.K.; Guo, X.W.; Zhou, M.C.; et al. Proximal policy optimization algorithm for multi-objective disassembly line balancing problems. In Proceedings of 2022 Australian & New Zealand Control Conference, Gold Coast, Australia, 24–25 November 2022; IEEE: Gold Coast, Australia, 2022; pp. 207–212. doi: 10.1109/ANZCC56036.2022.9966864
- 65.Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Xu, W.J.; et al. Human-robot collaboration in disassembly for sustainable manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res., 2019, 57: 4027−4044.
- 66.Schoettler, G.; Nair, A.; Luo, J.L.; et al. Deep reinforcement learning for industrial insertion tasks with visual inputs and natural rewards. In Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October 2020-24 January 2021; IEEE: Las Vegas, USA, 2020; pp. 5548–5555. doi: 10.1109/IROS45743.2020.9341714
- 67.Lowe, G.; Shirinzadeh, B. Dynamic assembly sequence selection using reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, New Orleans, LA, USA, 26 April 2004-1 May 2004; IEEE: New Orleans, USA, 2004; pp. 2633–2638. doi: 10.1109/ROBOT.2004.1307458
- 68.Zhao, M.H.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X.B.; et al. ASPW-DRL: Assembly sequence planning for workpieces via a deep reinforcement learning approach. Assem. Autom., 2020, 40: 65−75.
- 69.Li, B.C.; Zhou, Y.F. Multi-component maintenance optimization: An approach combining genetic algorithm and multiagent reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of 2020 Global Reliability and Prognostics and Health Management (PHM-Shanghai), Shanghai, China, 16–18 October 2020; IEEE: Shanghai, China, 2020; pp. 1–7. doi: 10.1109/PHM-Shanghai49105.2020.9280997
- 70.Yang, H.B.; Li, W.C.; Wang, B. Joint optimization of preventive maintenance and production scheduling for multi-state production systems based on reinforcement learning. Reliab. Engin. Syst. Saf., 2021, 214: 107713.
- 71.Chu, T.S.; Wang, J.; Codecà, L. et al. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning for large-scale traffic signal control. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., 2020, 21: 1086−1095.
- 72.Heuillet, A.; Couthouis, F.; Díaz-Rodríguez, N. Explainability in deep reinforcement learning. Knowl.-Based Syst., 2021, 214: 106685.
- 73.Saleh, I.K.; Beshaw, F.G.; Samad, N.M. Deep reinforcement learning WITH a path-planning communication approach for adaptive disassembly. J. Optoelectronics Laser, 2022, 41: 307−314.
- 74.Cobbe, K.; Klimov, O.; Hesse, C.; et al. Quantifying generalization in reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, California, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: Long Beach, 2019; pp. 1282–1289.
- 75.Arulkumaran, K.; Deisenroth, M.P.; Brundage, M.; et al. Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey. IEEE Signal Process. Mag., 2017, 34: 26−38.
- 76.Sitcharangsie, S.; Ijomah, W.; Wong, T.C. Decision makings in key remanufacturing activities to optimise remanufacturing outcomes: A review. J. Clean. Prod., 2019, 232: 1465−1481.
How to Cite
Guo, X.; Bi, Z.; Wang, J.; Qin, S.; Liu, S.; Qi, L. Reinforcement Learning for Disassembly System Optimization Problems: A Survey. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0201001.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


