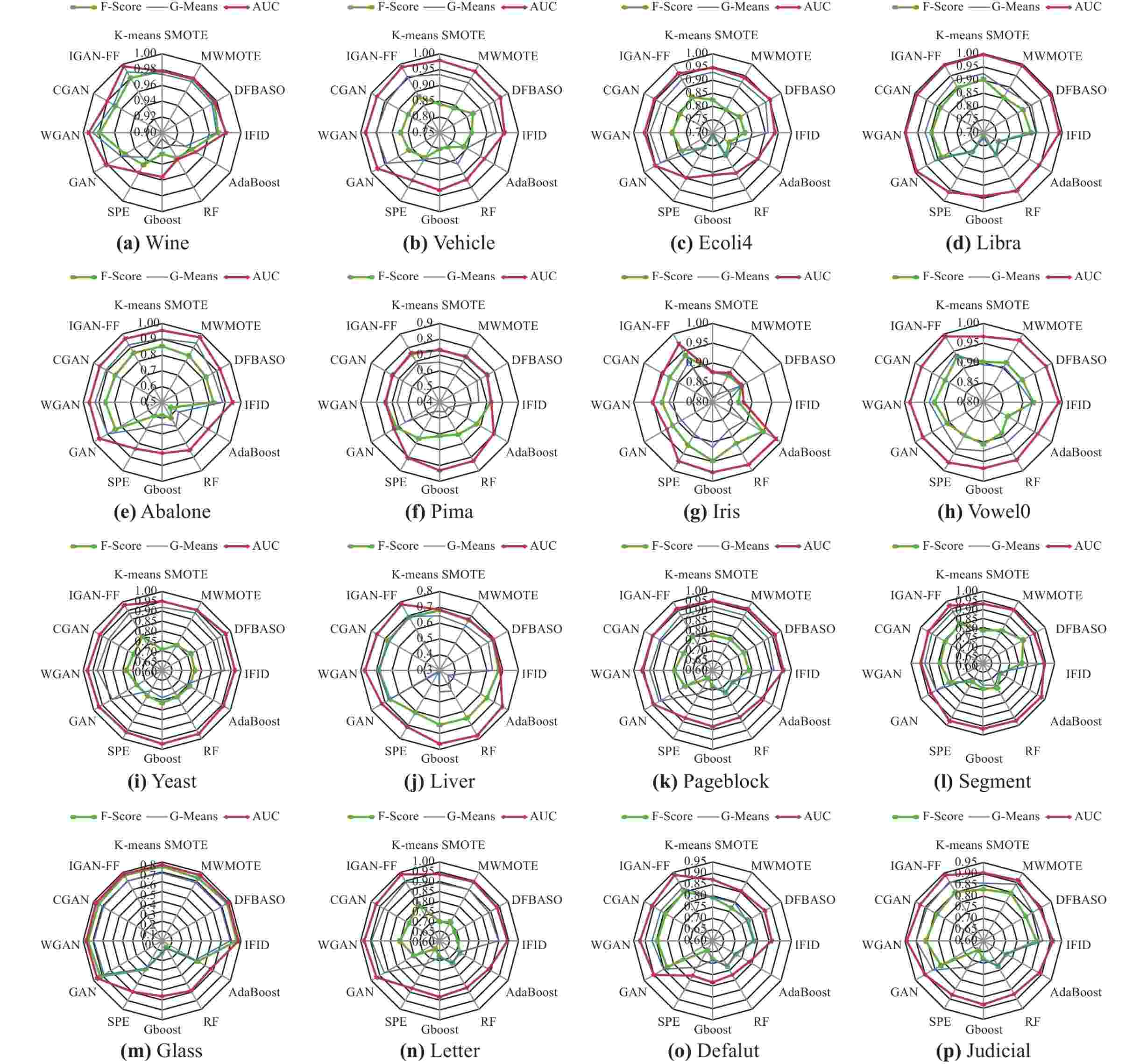
Generative adversarial network (GAN) is an overwhelming yet promising method to address the data imbalance problem. However, most existing GANs that are usually inspired by computer vision techniques have not yet taken the significance and redundancy of features into consideration delicately, probably producing rough samples with overlapping and incorrectness. To address this problem, a novel GAN called improved GAN with feature filtering (IGAN-FF) is proposed, which establishes a new loss function for the model training by replacing the traditional Euclidean distance with the Mahalanobis distance and taking the ℓ1,2-norm regularization term into consideration. The remarkable merits of the proposed IGAN-FF can be highlighted as follows: 1) the utilization of the Mahalanobis distance can make a fair evaluation of different attributes without neglecting any trivial/small-scale but significant ones. In addition, it can mitigate the disturbance caused by the correlation between features; 2) the embedding of ℓ1,2-norm regularization term into the loss function contributes greatly to the feature filtering by guaranteeing the data sparsity as well as helps reduce risk of overfitting. Finally, empirical experiments on 16 well-known imbalanced datasets demonstrate that our proposed IGAN-FF performs better at most evaluation metrics than the other 11 state-of-the-art methods.
- Open Access
- Article
An Improved Generative Adversarial Network with Feature Filtering for Imbalanced Data
- Jun Dou 1,
- Yan Song 2, *
Author Information
Received: 07 Oct 2023 | Accepted: 31 Oct 2023 | Published: 21 Dec 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
imbalanced data | generative adversarial network | ℓ1,2 -norm regularization | mahalanobis distance
References
- 1.Wang, L.; Ye, X.; Li, J.L.; et al. GAN-based dual active learning for nosocomial infection detection. IEEE Trans. Network Sci. Eng., 2022, 9: 3282−3291. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3100322
- 2.Lu, P.; Song, B.Y.; Xu, L. Human face recognition based on convolutional neural network and augmented dataset. Syst. Sci. Control Eng., 2021, 9: 29−37. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2020.1836526
- 3.Wang, C.; Wang, Z.D.; Ma, L.F.;
et al . Subdomain-alignment data augmentation for Pipeline fault diagnosis: An adversarial self-attention network.IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat .2023 , in press. - 4.Wang, C.; Wang, Z.D.; Ma, L.F.; et al. A novel contrastive adversarial network for minor-class data augmentation: Applications to pipeline fault diagnosis. Knowledge-Based Syst., 2023, 271: 110516. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110516
- 5.Yang, D.D.; Lu, J.Y.; Dong, H.L.; et al. Pipeline signal feature extraction method based on multi-feature entropy fusion and local linear embedding. Syst. Sci. Control Eng., 2022, 10: 407−416. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2022.2063202
- 6.Sun, J.; Li, H.; Fujita, H.; et al. Class-imbalanced dynamic financial distress prediction based on Adaboost-SVM ensemble combined with SMOTE and time weighting. Inf. Fus., 2020, 54: 128−144. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.07.006
- 7.Su, Y.F.; Cai, H.; Huang, J. The cooperative output regulation by the distributed observer approach. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intellig., 2022, 1: 20−35. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101003
- 8.Liu, Y.H.; Huang, F.H.; Yang, H. A fair dynamic content store-based congestion control strategy for named data networking. Syst. Sci. Control Eng., 2022, 10: 73−78. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2022.2031335
- 9.Dou, J.; Song, Y.; Wei, G.L.; et al. Fuzzy information decomposition incorporated and weighted Relief-F feature selection: When imbalanced data meet incompletion. Inf. Sci., 2022, 584: 417−432. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.10.057
- 10.He, H.B; Bai, Y.; Garcia, E.A.;
et al . ADASYN: Adaptive synthetic sampling approach for imbalanced learning. In2008 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence ),Hong Kong, China, 01 –08 June 2008 ; IEEE: Hong Kong, China, 2008; pp. 1322–1328. - 11.Dou, J.; Wei, G.L.; Song, Y.;
et al . Switching triple-weight-SMOTE in empirical feature space for imbalanced and incomplete data.IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng .2023 , in press. - 12.Hu, J.; Jia, C.Q.; Liu, H.J.; et al. A survey on state estimation of complex dynamical networks. Int. J. Syst. Sci., 2021, 52: 3351−3367. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2021.1995528
- 13.Zhang, Q.C.; Zhou, Y.Y. Recent advances in non-Gaussian stochastic systems control theory and its applications. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intellig., 2022, 1: 111−119. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101010
- 14.Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.; Hall, L.O.; et al. SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J. Artif. Intellig. Res., 2002, 16: 321−357. doi: 10.1613/jair.953
- 15.Douzas, G.; Bacao, F.; Last, F. Improving imbalanced learning through a heuristic oversampling method based on k-means and smote. Inf. Sci., 2018, 465: 1−20. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.06.056
- 16.Barua, S.; Islam, M.; Yao, X.; et al. MWMOTE-majority weighted minority oversampling technique for imbalanced data set learning. IEEE Trans. Knowledge Data Eng., 2014, 26: 405−425. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2012.232
- 17.Dai, F.F.; Song, Y.; Si, W.Y.; et al. Improved CBSO: A distributed fuzzy-based adaptive synthetic oversampling algorithm for imbalanced judicial data. Inf. Sci., 2021, 569: 70−89. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.04.017
- 18.Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.;
et al . Generative adversarial nets. InProceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, December 2014 ; MIT Press: Montreal, Canada, 2014; pp. 2672–2680. - 19.Douzas, G.; Bacao, F. Effective data generation for imbalanced learning using conditional generative adversarial networks. Exp. Syst. Appl., 2018, 91: 464−471. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.09.030
- 20.Gao, X.; Deng, F.; Yue, X.H. Data augmentation in fault diagnosis based on the Wasserstein generative adversarial network with gradient penalty. Neurocomputing, 2020, 396: 487−494. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.10.109
- 21.Wei, G.L.; Mu, W.M.; Song, Y.; et al. An improved and random synthetic minority oversampling technique for imbalanced data. Knowledge-Based Syst., 2022, 248: 108839. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.108839
- 22.Yu, N.X.; Yang, R.; Huang, M.J. Deep common spatial pattern based motor imagery classification with improved objective function. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intellig., 2022, 1: 73−84. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101007
- 23.Dou, J.; Gao, Z.H.; Wei, G.L.; et al. Switching synthesizing-incorporated and cluster-based synthetic oversampling for imbalanced binary classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intellig., 2023, 123: 106193. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106193
- 24.Wang, X.L.; Sun, Y.; Ding, D.R. Adaptive dynamic programming for networked control systems under communication constraints: A survey of trends and techniques. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intellig., 2022, 1: 85−98. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101008
- 25.Shakiba, F.M.; Shojaee, M.; Azizi, S.; et al. Real-time sensing and fault diagnosis for transmission lines. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intellig., 2022, 1: 36−47. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101004
- 26.Barua, S.; Islam, M.M.; Murase, K. A novel synthetic minority oversampling technique for imbalanced data set learning. In
18th International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Shanghai, China, 13 –17 November 2011 ; Springer: Shanghai, China, 2011; pp. 735–744. - 27.Ting, K.M. An instance-weighting method to induce cost-sensitive trees. IEEE Trans. Knowledge Data Eng., 2002, 14: 659−665. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2002.1000348
- 28.Jia, J.; Zhai, L.M.; Ren, W.X.; et al. An effective imbalanced jpeg steganalysis scheme based on adaptive cost-sensitive feature learning. IEEE Trans. Knowledge Data Eng., 2022, 34: 1038−1052. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2995070
- 29.Suykens, J.A.K.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett., 1999, 9: 293−300. doi: 10.1023/A:1018628609742
- 30.Wang, Z.R.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.R. An intelligent diagnosis scheme based on generative adversarial learning deep neural networks and its application to planetary gearbox fault pattern recognition. Neurocomputing, 2018, 310: 213−222. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.024
- 31.Guo, Q.W.; Li, Y.B.; Song, Y.; et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis method based on full 1-D convolutional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat., 2020, 16: 2044−2053. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2934901
- 32.Zhang, H.C.; Zhang, Y.N.; Nasrabadi, N.M.; et al. Joint-structured-sparsity-based classification for multiple-measurement transient acoustic signals. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. Part B Cybernet., 2012, 42: 1586−1598. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2196038
- 33.Tropp, J.A. Algorithms for simultaneous sparse approximation. Part II: Convex relaxation. Signal Process., 2006, 86: 589−602. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2005.05.031
- 34.Xu, Z.B.; Chang, X.Y.; Xu, F. M.; et al. L1 /2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst., 2012, 23: 1013−1027. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2197412
- 35.Maesschalck, R.; Jouan-Rimbaud, D.; Massart, D. The mahalanobis distance. Chemometr. Intellig. Lab. Syst., 2000, 50: 1−18. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(99)00047-7
- 36.Daffertshofer, A.; Lamoth, C.J.C.; Meijer, O.G.; et al. PCA in studying coordination and variability: A tutorial. Clin. Biomech., 2004, 19: 415−428. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2004.01.005
- 37.Xu, L.; Song, B.Y.; Cao, M.Y. An improved particle swarm optimization algorithm with adaptive weighted delay velocity. Syst. Sci. Control Eng., 2021, 9: 188−197. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2021.1891153
- 38.Qu, L.; Zhu, H.S.; Zheng, R.Q.;
et al . ImGAGN: Imbalanced network embedding via generative adversarial graph networks. InProceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining ),Singapore, 14–18 August 2021 ; ACM: Singapore, 2021; pp. 1390–1398. - 39.Lichman, M. UCI machine learning repository. Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (accessed on 2016).
- 40.Tao, X.M.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.J.; et al. Self-adaptive cost weights-based support vector machine cost-sensitive ensemble for imbalanced data classification. Inf. Sci., 2019, 487: 31−56. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.062
- 41.Mao, J.Y.; Sun, Y.; Yi, X.J.; et al. Recursive filtering of networked nonlinear systems: A survey. Int. J. Syst. Sci., 2021, 52: 1110−1128. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2020.1868615
- 42.Ju, Y.M.; Tian, X.; Liu, H.J.; et al. Fault detection of networked dynamical systems: A survey of trends and techniques. Int. J. Syst. Sci., 2021, 52: 3390−3409. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2021.1998722
- 43.Zong, W.W.; Huang, G.B.; Chen, Y.Q. Weighted extreme learning machine for imbalance learning. Neurocomputing, 2013, 101: 229−242. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.08.010
- 44.Wen, P.Y.; Li, X.R.; Hou, N.; et al. Distributed recursive fault estimation with binary encoding schemes over sensor networks. Syst. Sci. Control Eng., 2022, 10: 417−427. doi: 10.1080/21642583.2022.2063203
- 45.Li, H.; Wu, P.S.; Zeng, N.Y.; et al. Liu and Alsaadi, F.E. A survey on parameter identification, state estimation and data analytics for lateral flow immunoassay: From systems science perspective. Int. J. Syst Sci, 2022, 53: 3556−3576. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2022.2083262
- 46.Freund, J. Boosting a weak learning algorithm by majority. Inf. Comput., 1995, 121: 256−285. doi: 10.1006/inco.1995.1136
- 47.Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn., 2001, 45: 5−32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324
- 48.Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobot., 2013, 7: 21. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2013.00021
- 49.Liu, Z.N.; Cao, W.; Gao, Z.F.;
et al . Self-paced ensemble for highly imbalanced massive data classification. InIEEE 36th International Conference on Data Engineering, Dallas, TX, USA, 20 –24 April 2020 ; IEEE: Dallas, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 841–852. - 50.De Winter, J.F.C.; Dodou, D. Five-point likert items: T test versus Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon. Pract. Assessm. Res. Evaluat., 2010, 15: 1−12. doi: 10.7275/bj1p-ts64
How to Cite
Dou, J.; Song, Y. An Improved Generative Adversarial Network with Feature Filtering for Imbalanced Data. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (4), 100017. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2023.100017.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


