The concept of Internet of Things (IoT) greatly extends the coverage area that human being is able to perceive, access, and even control. By connecting various “Things” to the Internet, the IoT makes it possible to measure and manage the physical world as needed. As one of the most widely adopted Low Power Wide Area network technologies, the Long-Range-Radio (LoRa) has the features of long range, low power, and robustness, and thus plays an important role in building IoT applications where IoT objects are connected to the internet at affordable costs. Since the development of LoRa, many IoT applications have adopted LoRa and achieved success in the market. Currently, IoT technologies keep evolving towards different fields, giving rise to multifarious IoT applications including industrial IoT, smart city IoT, healthcare IoT, and direct-to-satellite IoT. In the meantime, LoRa also keeps developing and finding its position in various IoT applications either as a main or complementary player. The objective of this survey is to (1) provide a fundamental understanding of the LoRa technology; (2) explore research activities studying LoRa based communication systems for new IoT applications; and (3) demonstrate how the LoRa technology works together with other technologies to deliver better IoT services to end users.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
A Survey on Evolved LoRa-Based Communication Technologies for Emerging Internet of Things Applications
- Fang Yao 1, 3,
- Yulong Ding 2, 3, *,
- Shengguang Hong 2, 4,
- Shuang-Hua Yang 2, 5, *
Author Information
Received: 17 Sep 2022 | Accepted: 17 Oct 2022 | Published: 22 Dec 2022
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
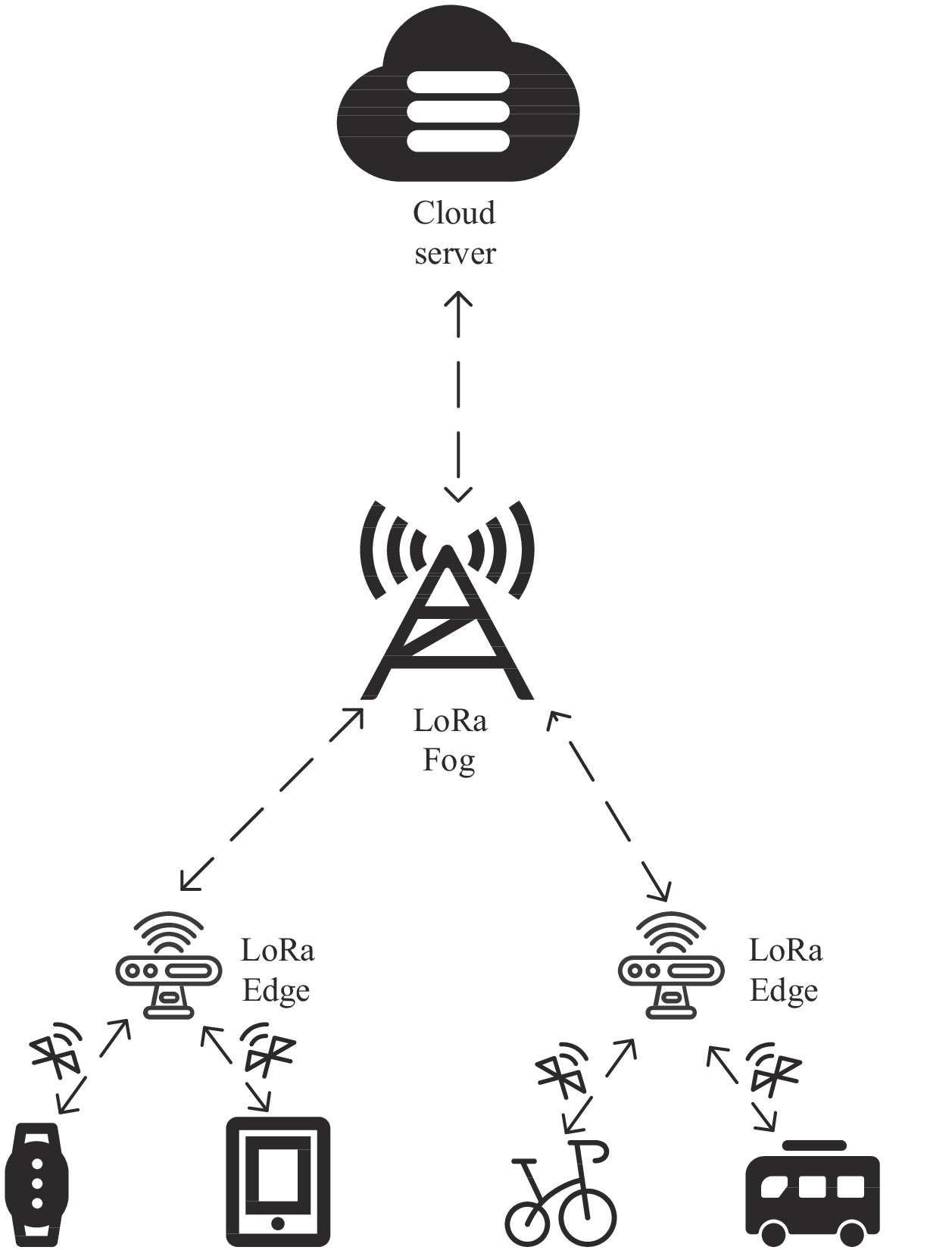
References
- 1.Elijah, O.; Rahman, T. A.; Orikumhi, I.; et al, An overview of internet of things (IoT) and data analytics in agriculture: Benefits and challenges. IEEE Internet Things J., 2018, 5: 3758−3773.
- 2.A shton, K. That ‘Internet of Things’ Things. RFID Journal, 2009. Available online: http://www.itrco.jp/libraries/RFIDjournal-That%20Internet%20of%20Things%20Thing.pdf. (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- 3.Serials Y: Global Information Infrastructure, Internet Protocol Aspects, and Next-Generation Networks. Recommendation ITU-Y Y. 2060, 2012. Available online: https://kipdf.com/series-y-global-information-infrastructure-internet-protocol-aspects-and-next-ge_5ae57e537f8b9ad98a8b4649.html. (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- 4.SEMTECH. Real-world LoRaWANTM Network Capacity for Electrical Metering Applications. Semtech White Paper, 2017.Available online: https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/2507363/Semtech_Network_Capacity_White_Paper.pdf. (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- 5.de Castro Tomé, M.; Nardelli, P.H.J.; Alves, H, Long-range low-power wireless networks and sampling strategies in electricity metering. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., 2019, 66: 1629−1637.
- 6.Magrin, D.; Centenaro, M.; Vangelista, L. Performance evaluation of LoRa networks in a smart city scenario. In
2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) ,Paris ,France ,21–25 May 2017 ; IEEE: Paris, 2017; pp. 1–7. doi:10.1109/ICC.2017.7996384 - 7.Huang, P.; Xiao, L.; Soltani, S.; et al, The evolution of MAC protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, 2013, 15: 101−120.
- 8.Raza, U.; Kulkarni, P.; Sooriyabandara, M, Low power wide area networks: An overview. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, 2017, 19: 855−873.
- 9.Farrell, S. Low-Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) Overview. Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), 2018. Available online: https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc8376.
- 10.Tikhvinsky, V. LPWAN Narrowband Technologies (LoRaWAN, SigFox, etc. ) for M2M Networks and Internet of Things Design. ITU Regional Forum on “Internet of Things, Telecommunication Networks and Big Data as basic infrastructure for Digital Economy”. Russia: Saint-Petersburg, 2018. Available online: https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-T/Workshops-and-Seminars/20180604/Documents/V_Tikhvinskiy.pdf (accessed on 8 November 2022).
- 11.ROHM. The Latest Technology Trends of Wi-SUN Wireless Communication Modules. ROHM Semiconductor, White Paper, 2021. Available online: https://fscdn.rohm.com/en/products/databook/white_paper/module/power_module/specified_low_power/wi-sun-han1_wp-e.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- 12.Sinha, R.S.; Wei, Y.Q.; Hwang, S.H, A survey on LPWA technology: LoRa and NB-IoT. ICT Express, 2017, 3: 14−21.
- 13.Sun, Z.H.; Yang, H.Q.; Liu, K.; et al, Recent advances in LoRa: A comprehensive survey. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw., 2022, 18: 67.
- 14.Gkotsiopoulos, P.; Zorbas, D.; Douligeris, C, Performance determinants in LoRa networks: A literature review. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, 2021, 23: 1721−1758.
- 15.Li, C. N.; Cao, Z.C, LoRa networking techniques for large-scale and long-term IoT: A down-to-top survey. ACM Comput. Surv., 2023, 55: 52.
- 16.Sharma, N.; Shamkuwar, M.; Singh, I. The history, present and future with IoT. In
Internet of Things and Big Data Analytics for Smart Generation ; Balas, V. ; Solanki, V. ; Kumar, R. ;et al , Eds. ; Springer: Cham, 2019; pp. 27–51. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-04203-5_3 - 17.Goudos, S. K.; Dallas, P. I.; Chatziefthymiou, S.; et al, A survey of IoT key enabling and future technologies: 5G, mobile IoT, sematic web and applications. Wireless Pers. Commun., 2017, 97: 1645−1675.
- 18.Savaglio, C.; Ganzha, M.; Paprzycki, M.; et al, Agent-based internet of things: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Future Gener. Comput. Syst., 2020, 102: 1038−1053.
- 19.Glaroudis, D.; Iossifides, A.; Chatzimisios, P, Survey, comparison and research challenges of IoT application protocols for smart farming. Comput. Netw., 2020, 168: 107037.
- 20.Mekki, K.; Bajic, E.; Chaxel, F.; et al, A comparative study of LPWAN technologies for large-scale IoT deployment. ICT Express, 2019, 5: 1−7.
- 21.Adelantado, F.; Vilajosana, X.; Tuset-Peiro, P.; et al, Understanding the limits of LoRaWAN. IEEE Commun. Mag., 2017, 55: 34−40.
- 22.Devalal, S.; Karthikeyan, A. LoRa technology-an overview. In
2018 Second International Conference on Electronics ,Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA) ,Coimbatore ,India ,29–31 March 2018 ; IEEE: Coimbatore, 2018; pp. 284–290. doi:10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474715 - 23.Chaudhari, B. S.; Zennaro, M.; Borkar, S, LPWAN technologies: Emerging application characteristics, requirements, and design considerations. Future Internet, 2020, 12: 46.
- 24.Perwej, Y.; Haq, K.; Parwej, F.; et al, The internet of things (IoT) and its application domains. Int. J. Comput. Appl., 2019, 182: 36−49.
- 25.LoRa. Platform for IoT. Available online: https://www.semtech.com/lora/. (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- 26.Semtech Corporation. LoRa® and LoRaWAN®: A Technical Overview. Technical Paper, 2020. Available online: https://lora-developers.semtech.com/uploads/documents/files/LoRa_and_LoRaWAN-A_Tech_Overview-Downloadable.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- 27.Lavric, A.; Petrariu, A.I. LoRaWAN communication protocol: The new era of IoT. In
2018 International Conference on Development and Application Systems (DAS) ,Suceava ,Romania ,24 –26 May 2018 ; IEEE: Suceava, 2018; pp. 74–77. doi:10.1109/DAAS.2018.8396074 - 28.Jouhari, M.; Amhoud, E.M.; Saeed, N.;
et al . A survey on scalable LoRaWAN for massive IoT: Recent advances, potentials, and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2202.11082, 2022. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.11082.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022). - 29.Siddique, A.; Prabhu, B.; Chaskar, A.; et al, A review on intelligent agriculture service platform with LoRa based wireless sensor network. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol., 2019, 6: 2539−2542.
- 30.Vejlgaard, B.; Lauridsen, M.; Nguyen, H.;
et al . Coverage and capacity analysis of Sigfox, LoRa, GPRS, and NB-IoT. In2017 IEEE 85th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring) ,Sydney ,NSW ,Australia ,04–07 June 2017 ; IEEE: Sydney, 2017; pp. 1–5. doi:10.1109/VTCSpring.2017.8108666 - 31.Naik, N. LPWAN technologies for IoT systems: Choice between ultra narrow band and spread spectrum. In
2018 IEEE International Systems Engineering Symposium (ISSE) ,Rome ,Italy ,01–03 October 2018 ; IEEE: Rome, 2018; pp. 1–8. doi:10.1109/SysEng.2018.8544414 - 32.Tsotsolas, N.; Komisopoulos, F.; Papadopoulos, P.;
et al . An integrated LoRa-based IoT platform serving smart farming and agro-logistics.Emerging Ecosystem-Centric Business Models for Sustainable Value Creation . IGI Global,2022 : 132−158. - 33.SEMTECH. SX1276/77/78/79–137 MHz to 1020 MHz Low Power Long Range Transceiver. 2020. Available online: https://www.mouser.com/datasheet/2/761/sx1276-1278113.pdf (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- 34.Petäjäjärvi, J.; Mikhaylov, K.; Pettissalo, M.;
et al . Performance of a low-power wide-area network based on LoRa technology: Doppler robustness, scalability, and coverage.Int .J .Distrib .Sens .Netw .2017 , in press. doi:10.1177/1550147717699412 - 35.Mroue, H.; Nasser, A.; Parrein, B.;
et al . Analytical and simulation study for LoRa modulation. In2018 25th International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT) ,Saint-Malo ,France ,26–28 June 2018 ; IEEE: Saint-Malo, 2018; pp. 655–659. doi:10.1109/ICT.2018.8464879 - 36.Pasolini, G, On the LoRa chirp spread spectrum modulation: Signal properties and their impact on transmitter and receiver architectures. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun., 2022, 21: 357−369.
- 37.Croce, D.; Gucciardo, M.; Mangione, S.; et al, Impact of LoRa imperfect orthogonality: Analysis of link-level performance. IEEE Commun. Lett., 2018, 22: 796−799.
- 38.Semtech Corporation. LoRa Modulation Basics. 2015.
- 39.Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, H.H.; Barton, R.; et al, Efficient design of chirp spread spectrum modulation for low-power wide-area networks. IEEE Internet Things J., 2019, 6: 9503−9515.
- 40.de Almeida, I.B.F.; Chafii, M.; Nimr, A.; et al, Alternative chirp spread spectrum techniques for LPWANs. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw., 2021, 5: 1846−1855.
- 41.Hanif, M.; Nguyen, H.H, Frequency-shift chirp spread spectrum communications with index modulation. IEEE Internet Things J., 2021, 8: 17611−17621.
- 42.Augustin, A.; Yi, J. Z.; Clausen, T.; et al, A study of LoRa: Long range & low power networks for the internet of things. Sensors, 2016, 16: 1466.
- 43.Ferre, G. Collision and packet loss analysis in a LoRaWAN network. In
2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO) ,Kos ,Greece ,28 August 2017–02 September 2017 ; IEEE: Kos, 2017; pp. 2586–2590. doi:10.23919/EUSIPCO.2017.8081678 - 44.Sørensen, R.B.; Kim, D.M.; Nielsen, J.J.; et al, Analysis of latency and MAC-layer performance for class a LoRaWAN. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., 2017, 6: 566−569.
- 45.Boquet, G.; Tuset-Peiró, P.; Adelantado, F.; et al, LR-FHSS: Overview and performance analysis. IEEE Commun. Mag., 2020, 59: 30−36.
- 46.Semtech. Application note: LR-FHSS system performance. Available online:https://lora-developers.semtech.com/library/product-documents/. (accessed on 8 Octomber 2022).
- 47.Boyes, H.; Hallaq, B.; Cunningham, J.; et al, The industrial internet of things (IIoT): An analysis framework. Comput. Ind., 2018, 101: 1−12.
- 48.Bartolomeu, P.; Alam, M.; Ferreira, J.; et al, Supporting deterministic wireless communications in industrial IoT. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf., 2018, 14: 4045−4054.
- 49.Wang, W.B.; Capitaneanu, S.L.; Marinca, D.; et al, Comparative analysis of channel models for industrial IoT wireless communication. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 91627−91640.
- 50.Foukalas, F.; Pop, P.; Theoleyre, F.;
et al . Dependable wireless industrial IoT networks: Recent advances and open challenges. In2019 IEEE European Test Symposium (ETS) ,Baden-Baden ,Germany ,27 –31 May 2019 ; IEEE: Baden-Baden, 2019; pp. 1–10. doi:10.1109/ETS.2019.8791551 - 51.Rizzi, M.; Ferrari, P.; Flammini, A.;
et al . Using LoRa for industrial wireless networks. In2017 IEEE 13th International Workshop on Factory Communication Systems (WFCS) ,Trondheim ,Norway ,31 May 2017–02 June 2017 ; IEEE: Trondheim, 2017; pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/WFCS.2017.7991972 - 52.Leonardi, L.; Battaglia, F.; Lo Bello, L, RT-LoRa: A medium access strategy to support real-time flows over LoRa-based networks for industrial IoT applications. IEEE Internet Things J., 2019, 6: 10812−10823.
- 53.Hoang, Q.L.; Jung, W.S.; Yoon, T.; et al, A real-time LoRa protocol for industrial monitoring and control systems. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 44727−44738.
- 54.Jörke, P.; Böcker, S.; Liedmann, F.;
et al . Urban channel models for smart city IoT-networks based on empirical measurements of LoRa-links at 433 and 868 MHz. In2017 IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal ,Indoor ,and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC) ,Montreal ,QC ,Canada ,08–13 October 2017 ; IEEE: Montreal, 2017; pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/PIMRC.2017.8292708 - 55.Premsankar, G.; Ghaddar, B.; Slabicki, M.; et al, Optimal configuration of LoRa networks in smart cities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf., 2020, 16: 7243−7254.
- 56.Lavric, A, LoRa (long-range) high-density sensors for internet of things. J. Sens., 2019, 2019: 3502987.
- 57.Lee, H.C.; Ke, K.H, Monitoring of large-area IoT sensors using a LoRa wireless mesh network system: Design and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 2018, 67: 2177−2187.
- 58.Almeida, N.C.; Rolle, R.P.; Godoy, E.P.;
et al . Proposal of a hybrid LoRa Mesh/LoRaWAN network. In2020 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4 .0 & IoT ,Roma ,Italy ,03–05 June 2020 ; IEEE: Roma, 2020; pp. 702–707. doi:10.1109/MetroInd4.0IoT48571.2020.9138206 - 59.Hong, S. G.; Yao, F.; Ding, Y. L.; et al, A hierarchy-based energy-efficient routing protocol for LoRa-mesh network. IEEE Internet Things J., 2022, 9: 22836−22849.
- 60.Huh, H.; Kim, J.Y. LoRa-based mesh network for IoT applications. In
2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT) ,Limerick ,Ireland ,15–18 April 2019 ; IEEE: Limerick, 2019; pp. 524–527. doi:10.1109/WF-IoT.2019.8767242 - 61.Osorio, A.; Calle, M.; Soto, J. D.; et al, Routing in LoRaWAN: Overview and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag., 2020, 58: 72−76.
- 62.Centelles, R. P.; Freitag, F.; Meseguer, R.; et al, Beyond the star of stars: An introduction to multihop and mesh for LoRa and LoRaWAN. IEEE Pervas. Comput., 2021, 20: 63−72.
- 63.Fraire, J.A.; Céspedes, S.; Accettura, N. Direct-to-satellite IoT - a survey of the state of the art and future research perspectives. In
18th International Conference on Ad-Hoc Networks and Wireless on Ad-Hoc ,Mobile ,and Wireless Networks ,Luxembourg ,Luxembourg ,October 1–3 ,2019 ; Springer: Luxembourg, 2019; pp. 241–258. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-31831-4_17 - 64.Fraire, J.A.; Henn, S.; Dovis, F.;
et al . Sparse satellite constellation design for LoRa-based direct-to-satellite internet of things. InGLOBECOM 2020 - 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference ,Taipei ,China ,07–11 December 2020 ; IEEE: Taipei, China, 2020; pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/GLOBECOM42002.2020.9348042 - 65.Fernandez, L.; Ruiz-De-Azua, J. A.; Calveras, A.; et al, Assessing LoRa for satellite-to-earth communications considering the impact of ionospheric scintillation. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 165570−165582.
- 66.Álvarez, G.; Fraire, J. A.; Hassan, K. A.; et al, Uplink transmission policies for LoRa-based direct-to-satellite IoT. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 72687−72701.
- 67.Satellite Based LoRa Unlocks Europe-Wide IoT. White Paper, EchoStar Mobile. Available online: https://www.echostarmobile.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/EchoStar_Mobile_White_Paper_compressed.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2022).
- 68.Ullah, M. A.; Mikhaylov, K.; Alves, H, Analysis and simulation of LoRaWAN LR-FHSS for direct-to-satellite scenario. IEEE Wireless Commun. Lett., 2022, 11: 548−552.
- 69.Chaari, L.; Fourati, M.; Rezgui, J. Heterogeneous LoRaWAN & LEO satellites networks concepts, architectures and future directions. In
2019 Global Information Infrastructure and Networking Symposium (GIIS) ,Paris ,France ,18–20 December 2019 ; IEEE: Paris, 2019; pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/GIIS48668.2019.9044966 - 70.Doroshkin, A. A.; Zadorozhny, A. M.; Kus, O. N.; et al, Experimental study of LoRa modulation immunity to Doppler effect in CubeSat radio communications. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 75721−75731.
- 71.Colavolpe, G.; Foggi, T.; Ricciulli, M.; et al, Reception of LoRa signals from LEO satellites. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst., 2019, 55: 3587−3602.
- 72.Dimitrievski, A.; Filiposka, S.; Melero, F.J.; et al, Rural healthcare IoT architecture based on low-energy LoRa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2021, 18: 7660.
- 73.Wu, F.; Qiu, C.K.; Wu, T.Y.; et al, Edge-based hybrid system implementation for long-range safety and healthcare IoT applications. IEEE Internet Things J., 2021, 8: 9970−9980.
- 74.Adebusola, J.A.; Ariyo, A.A.; Elisha, O.A.;
et al . An overview of 5G technology. In2020 International Conference in Mathematics ,Computer Engineering and Computer Science (ICMCECS) ,Ayobo ,Nigeria ,18–21 March 2020 ; IEEE: Ayobo, 2020; pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICMCECS47690.2020.240853 - 75.Rao, V.C.S.; Kumarswamy, P.; Phridviraj, M.S.B.;
et al . 5G enabled industrial internet of things (IIoT) architecture for smart manufacturing. InData Engineering and Communication Technology ; Reddy, K.A.; Devi, B.R.; George, B.;et al , Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 193–201. doi:10.1007/978-981-16-0081-4_20 - 76.Larrañaga, A.; Lucas-Estañ, M. C.; Martinez, I.;
et al . Analysis of 5G-TSN integration to support industry 4.0. In2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA) ,Vienna ,Austria ,08–11 September 2020 ; IEEE: Vienna, 2020; pp. 1111–1114. doi:10.1109/ETFA46521.2020.9212141 - 77.Nasrallah, A.; Thyagaturu, A.S.; Alharbi, Z.; et al, Ultra-low latency (ULL) networks: The IEEE TSN and IETF DetNet standards and related 5G ULL research. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials, 2019, 21: 88−145.
- 78.Gundall, M.; Huber, C.; Rost, P.;
et al . Integration of 5G with TSN as prerequisite for a highly flexible future industrial automation: Time synchronization based on IEEE 802.1AS. InIECON 2020 The 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society ,Singapore ,18–21 October 2020 ; IEEE: Singapore, 2020; pp. 3823–3830. doi:10.1109/IECON43393.2020.9254296 - 79.Liu, F.; Tang, G. M.; Li, Y.; et al, A survey on edge computing systems and tools. Proc. IEEE, 2019, 107: 1537−1562.
- 80.Sarker, V.K. ; Queralta, J.P.; Gia, T.N.;
et al . A survey on LoRa for IoT: Integrating edge computing. In:2019 Fourth International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing (FMEC) ,Rome ,Italy ,10–13 June 2019 ; IEEE: Rome, 2019; pp. 295–300. doi:10.1109/FMEC.2019.8795313 - 81.Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X. F.; et al, A survey on the edge computing for the internet of things. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 6900−6919.
- 82.Drăgulinescu, A.M.C.; Manea, A.F.; Fratu, O.; et al, LoRa-based medical IoT system architecture and testbed. Wireless Pers Commun, 2022, 126: 25−47.
- 83.Gia, T.N.; Qingqing, L.; Queralta, J.P.;
et al . Edge AI in smart farming IoT: CNNs at the edge and fog computing with LoRa. In2019 IEEE AFRICON ,Accra ,Ghana ,25–27 September 2019 ; IEEE: Accra, 2019; pp. 1–6. doi:10.1109/AFRICON46755.2019.9134049 - 84.Hou, L.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Z. M.; et al, Design and prototype implementation of a blockchain-enabled LoRa system with edge computing. IEEE Internet Things J., 2021, 8: 2419−2430.
- 85.Kumari, P.; Mishra, R.; Gupta, H.P.;
et al . An energy efficient smart metering system using edge computing in LoRa network.IEEE Trans .Sustainable Comput .2021 , in press. doi:10.1109/TSUSC.2021.3049705 - 86.Queralta, J.P.; Gia, T.N.; Tenhunen, H.;
et al . Edge-AI in LoRa-based health monitoring: Fall detection system with fog computing and LSTM recurrent neural networks. In2019 42nd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP) ,Budapest ,Hungary ,01–03 July 2019 ; IEEE: Budapest, 2019; pp. 601–604. doi:10.1109/TSP.2019.8768883 - 87.Ferreira, C.M.S.; Oliveira, R.A.R.; Silva, J.S. Low-energy smart cities network with LoRa and Bluetooth. In
2019 7th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Cloud Computing ,Services ,and Engineering (MobileCloud) ,Newark ,CA ,USA ,04–09 April 2019 ; IEEE: Newark, 2019; pp. 24–29. doi:10.1109/MobileCloud.2019.00011 - 88.Barro, P.A.; Zennaro, M.; Pietrosemoli, E. TLTN – The local things network: On the design of a LoRaWAN gateway with autonomous servers for disconnected communities. In
2019 Wireless Days (WD) ,Manchester ,UK ,24–26 April 2019 ; IEEE: Manchester, 2019; pp. 1–4. doi:10.1109/WD.2019.8734239
How to Cite
Yao, F.; Ding, Y.; Hong, S.; Yang, S.-H. A Survey on Evolved LoRa-Based Communication Technologies for Emerging Internet of Things Applications. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2022, 1 (1), 4–19. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0101002.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2022 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


