Person re-identification at a distance across multiple non-overlapping cameras has been an active research area for years. In the past ten years, short-term Person re-identification techniques have made great strides in accuracy using only appearance features in limited environments. However, massive intra-class variations and inter-class confusion limit their ability to be used in practical applications. Moreover, appearance consistency can only be assumed in a short time span from one camera to the other. Since the holistic appearance will change drastically over days and weeks, the technique, as mentioned above, will be ineffective. Practical applications usually require a long-term solution in which the subject's appearance and clothing might have changed after the elapse of a significant period. Facing these problems, soft biometric features such as Gait has stirred much interest in the past years. Nevertheless, even Gait can vary with illness, ageing and emotional states, walking surfaces, shoe types, clothes types, carried objects (by the subject) and even environment clutters. Therefore, Gait is considered as a temporal cue that could provide biometric motion information. On the other hand, the shape of the human body could be viewed as a spatial signal which can produce valuable information. So extracting discriminative features from both spatial and temporal domains would benefit this research. This article examines the main approaches used in gait analysis for re-identification over the past decade. We identify several relevant dimensions of the problem and provide a taxonomic analysis of current research. We conclude by reviewing the performance levels achievable with current technology and providing a perspective on the most challenging and promising research directions.
- Open Access
- Survey/Review Study
A Review of Techniques on Gait-Based Person Re-Identification
- Babak Rahi 1, *,
- Maozhen Li 1,
- Man Qi 2
Author Information
Received: 16 Oct 2022 | Accepted: 14 Dec 2022 | Published: 27 Mar 2023
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
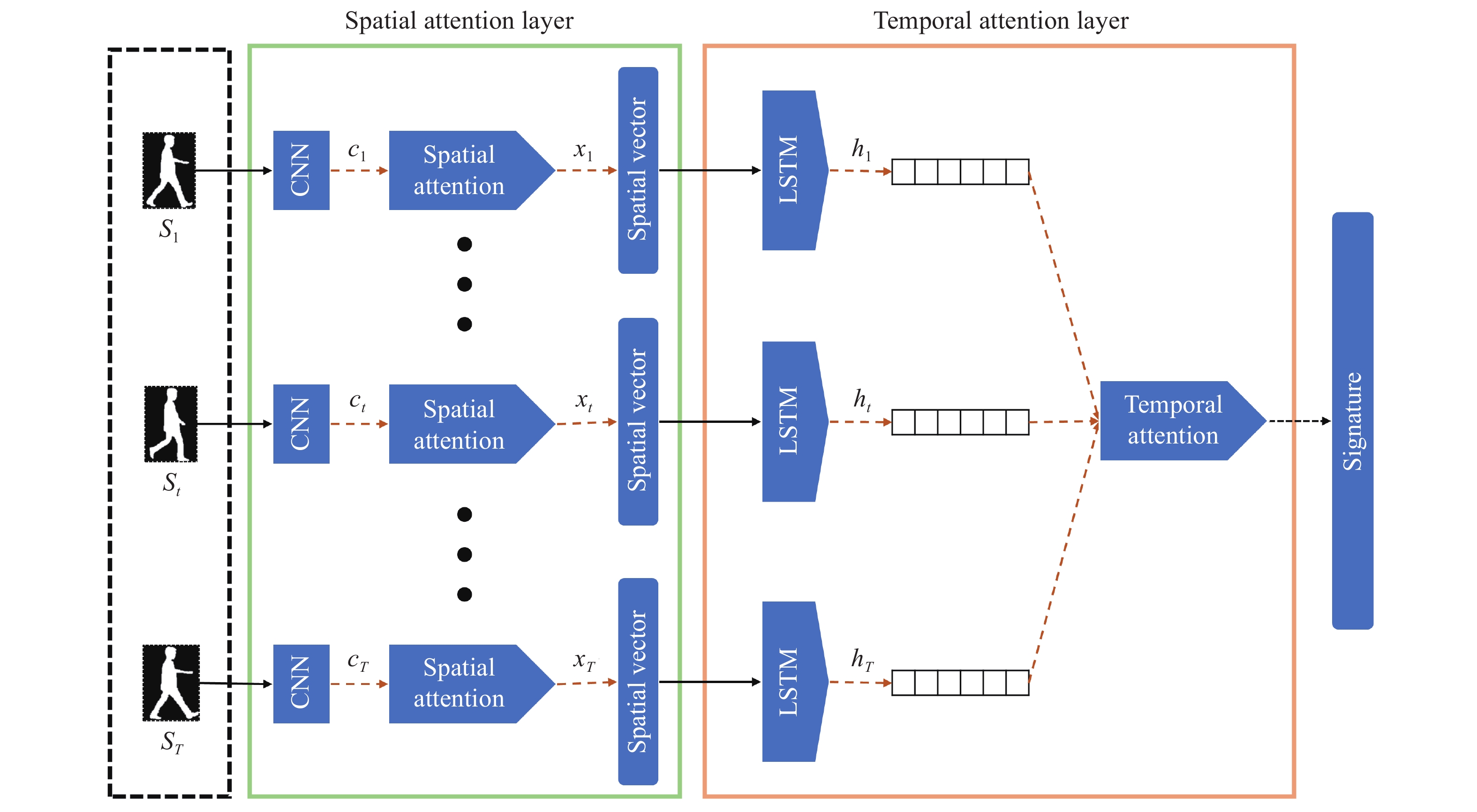
Keywords
gait feature extraction | convolutional neural networks | gait re-identification | gait-recognition | neural networks
References
- 1.Saghafi, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Zaman, H.B.; et al. Review of person re-identification techniques. IET Comput. Vision, 2014, 8: 455−474.
- 2.Bedagkar-Gala, A.; Shah, S.K. A survey of approaches and trends in person re-identification. Image Vision Comput., 2014, 32: 270−286.
- 3.Lavi, B.; Ullah, I.; Fatan, M.; et al. Survey on reliable deep learning-based person re-identification models: Are we there yet? arXiv preprint arXiv: 2005.00355, 2020. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.00355v1 (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- 4.LeCun, Y.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Farabet, C. Convolutional networks and applications in vision. In Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Paris, France, 30 May 2010–2 June 2010; IEEE: Paris, 2010; pp. 253–256. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS.2010.5537907
- 5.Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 2015, 115: 211−252.
- 6.Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Curran Associates Inc.: Lake Tahoe, 2012; pp. 1097–1105.
- 7.Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Zurich, 2014; pp. 818–833. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10590-1_53
- 8.Felzenszwalb, P.F.; Girshick, R.B.; McAllester, D.; et al. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2010, 32: 1627−1645.
- 9.Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 779–788. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.91
- 10.Li, J.N.; Liang, X.D.; Shen, S.M.; et al. Scale-aware fast R-CNN for pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2018, 20: 985−996.
- 11.Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, 2015; pp. 1440–1448. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.169
- 12.Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Amsterdam, 2016; pp. 21–37. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_2
- 13.Dehghan, A.; Assari, S.M.; Shah, M. GMMCP tracker: Globally optimal generalized maximum multi clique problem for multiple object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 07–12 June 2015; IEEE: Boston, 2015; pp. 4091–4099. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7299036
- 14.Son, J.; Baek, M.; Cho, M.; et al. Multi-object tracking with quadruplet convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Honolulu, 2017; pp. 3786–3795. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.403
- 15.Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, N.; et al. Online multi-object tracking with dual matching attention networks. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Munich, 2018; pp. 379–396. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1_23
- 16.Xu, J.R.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Spatial-temporal relation networks for multi-object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; IEEE: Seoul, 2019; pp. 3987–3997. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00409
- 17.Zhang, Q.; Cheng, H.J.; Lai, J.H.; et al. DHML: Deep heterogeneous metric learning for VIS-NIR person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 14th Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition, Zhuzhou, China, 12–13 October 2019; Springer: Zhuzhou, 2019; pp. 455–465. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-31456-9_50
- 18.Martini, M.; Paolanti, M.; Frontoni, E. Open-world person re-identification with RGBD camera in top-view configuration for retail applications. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 67756−67765.
- 19.Liciotti, D.; Paolanti, M.; Frontoni, E.; et al. Person re-identification dataset with RGB-D camera in a top-view configuration. In International Workshop on Video Analytics for Audience Measurement in Retail and Digital Signage, Cancun, Mexico, 4 December 2016; Springer: Cancun, 2016; pp. 1–11. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56687-0_1
- 20.Li, W.; Zhao, R.; Xiao, T.; et al. DeepReiD: Deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, USA, 23–28 June 2014; IEEE: Columbus, 2014; pp. 152–159. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2014.27
- 21.Mehta, D.; Sridhar, S.; Sotnychenko, O.; et al. Vnect: Real-time 3D human pose estimation with a single RGB camera. ACM Trans. Graphics, 2017, 36: 44.
- 22.Zhao, L.M.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.T.; et al. Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Venice, 2017; pp. 3239–3248. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.349
- 23.Hirzer, M.; Beleznai, C.; Roth, P.M.; et al. Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In Proceedings of the 17th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Ystad, Sweden, May 2011; Springer: Ystad, 2011; pp. 91–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21227-7_9
- 24.Köstinger, M.; Hirzer, M.; Wohlhart, P.; et al. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Providence, 2012; pp. 2288–2295. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247939
- 25.Liao, S.C.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; et al. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 7–12 June 2015; IEEE: Boston, 2015; pp. 2197–2206. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298832
- 26.Sun, Y.F.; Zheng, L.; Li, Y.L.; et al. Learning part-based convolutional features for person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2021, 43: 902−917.
- 27.Li, W.; Zhu, X.T.; Gong, S.G. Harmonious attention network for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 2285–2294. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00243
- 28.Chen, D.P.; Li, H.S.; Xiao, T.; et al. Video person re-identification with competitive snippet-similarity aggregation and co-attentive snippet embedding. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 1169–1178. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00128
- 29.Wang, T.Q.; Gong, S.G.; Zhu, X.T.; et al. Person re-identification by discriminative selection in video ranking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2016, 38: 2501−2514.
- 30.McLaughlin, N.; Del Rincon, J.M.; Miller, P. Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1325–1334. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.148
- 31.Zhu, X.K.; Jing, X.Y.; You, X.E.; et al. Video-based person re-identification by simultaneously learning intra-video and inter-video distance metrics. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2018, 27: 5683−5695.
- 32.Zheng, L.; Bie, Z.; Sun, Y.F.; et al. MARS: A video benchmark for large-scale person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Amsterdam, 2016; pp. 868–884. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46466-4_52
- 33.Liu, K.; Ma, B.P.; Zhang, W.; et al. A spatio-temporal appearance representation for video-based pedestrian re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, 2015; pp. 3810–3818. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.434
- 34.You, J.J.; Wu, A.C.; Li, X.; et al. Top-push video-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1345–1353. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.150
- 35.Subramaniam, A.; Nambiar, A.; Mittal, A. Co-segmentation inspired attention networks for video-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October 2019–2 November 2019; IEEE: Seoul, 2019; pp. 562–572. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2019.00065
- 36.Hirzer, M.; Roth, P.M.; Köstinger, M.; et al. Relaxed pairwise learned metric for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012; Springer: Florence, 2012; pp. 780–793. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33783-3_56
- 37.Wu, S.X.; Chen, Y.C.; Li, X.; et al. An enhanced deep feature representation for person re-identification. In 2016 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Lake Placid, USA, 7–10 March 2016; IEEE: Lake Placid, 2016; pp. 1–8. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2016.7477681
- 38.Xiong, F.; Gou, M.R.; Camps, O.; et al. Person re-identification using kernel-based metric learning methods. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Zurich, 2014; pp. 1–16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_1
- 39.Zheng, W.S.; Gong, S.G.; Xiang, T. Towards open-world person re-identification by one-shot group-based verification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2016, 38: 591−606.
- 40.Gray, D.; Tao, H. Viewpoint invariant pedestrian recognition with an ensemble of localized features. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; Springer: Marseille, 2008; pp. 262–275. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-88682-2_21
- 41.Kuo, C.H.; Khamis, S.; Shet, V. Person re-identification using semantic color names and rankboost. In 2013 IEEE workshop on applications of computer vision (WACV), Clearwater Beach, USA, 15–17 January 2013; IEEE: Clearwater Beach, 2013; pp. 281–287. doi: 10.1109/WACV.2013.6475030
- 42.Cheng, D.; Gong, Y.H.; Zhou, S.P.; et al. Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1335–1344. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.149
- 43.Xiao, T.; Li, H.S.; Ouyang, W.L.; et al. Learning deep feature representations with domain guided dropout for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1249–1258. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.140
- 44.Pedagadi, S.; Orwell, J.; Velastin, S.; et al. Local fisher discriminant analysis for pedestrian re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 23–28 June 2013; IEEE: Portland, 2013; pp. 3318–3325. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.426
- 45.Sugiyama, M. Local fisher discriminant analysis for supervised dimensionality reduction. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, USA, 25–29 June 2006; ACM: Pittsburgh, 2006; pp. 905–912. doi: 10.1145/1143844.1143958
- 46.Weinberger, K.Q.; Saul, L.K. Distance metric learning for large margin nearest neighbor classification. J. Mach. Learn. Res., 2009, 10: 207−244.
- 47.Zhang, L.; Xiang, T.; Gong, S.G. Learning a discriminative null space for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1239–1248. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.139
- 48.Lu, M. Ranked: The world’s most surveilled cities. Oct 2022. Available online: https://www.visualcapitalist.com/ranked-the-worlds-most-surveilled-cities/#:~:text=IHS%20Markit%20estimates%20that%20as,billion%20sureillance%20cameras%20installed%20worldwide (accessed on 3 December 2022).
- 49.BBC.co.uk. CCTV: Too many cameras useless, warns surveillance watchdog tony porter. Jan 2015. Available online: https://www.timefortruth.eu/cctv-too-many-cameras-useless-warns-surveillance-watchdog-tony-porter/ (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- 50.Cong, D.N.T.; Achard, C.; Khoudour, L.; et al. Video sequences association for people re-identification across multiple non-overlapping cameras. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing, Vietri sul Mare, Italy, 8–11 September 2009; Springer: Vietri sul Mare, 2009; pp. 179–189. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-04146-4_21
- 51.Guermazi, R.; Hammami, M.; Hamadou, A.B. Violent web images classification based on MPEG7 color descriptors. In 2009 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, San Antonio, USA, 11–14 October 2009; IEEE: San Antonio, 2009; pp. 3106–3111. doi: 10.1109/ICSMC.2009.5346149
- 52.Zheng, L.; Shen, L.Y.; Tian, L.; et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, 2015; pp. 1116–1124. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.133
- 53.Lyons, M.J.; Budynek, J.; Akamatsu, S. Automatic classification of single facial images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 1999, 21: 1357−1362.
- 54.Álvarez-Aparicio, C.; Guerrero-Higueras, Á.M.; González-Santamarta, M.Á.; et al. Biometric recognition through gait analysis. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12: 14530.
- 55.Alobaidi, H.; Clarke, N.; Li, F.D.; et al. Real-world smartphone-based gait recognition. Comput. Secur., 2022, 113: 102557.
- 56.Maloney, L.T.; Wandell, B.A. Color constancy: A method for recovering surface spectral reflectance. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 1986, 3: 29−33.
- 57.Qian, X.L.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Long-term cloth-changing person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 15th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 30 November–4 December 2020; Springer: Kyoto, 2020; pp. 71–88. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-69535-4_5
- 58.Hirzer, M.; Beleznai, C.; Roth, P.M.; et al. Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In Proceedings of the 17th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Ystad, Sweden, May 2011; Springer: Ystad, 2011; pp. 91–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21227-7_9
- 59.Li, M.X.; Zhu, X.T.; Gong, S.G. Unsupervised person re-identification by deep learning tracklet association. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14, September 2018; Springer: Munich, 2018; pp. 772–788. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01225-0_45
- 60.Zheng, Z.D.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Y. Unlabeled samples generated by gan improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; IEEE: Venice, 2017; pp. 3774–3782. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2017.405
- 61.Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; et al. Generative adversarial nets. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal Canada, 8–13 December 2014; MIT Press: Montreal, 2014; pp. 2672–2680.
- 62.Wei, L.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Gao, W.; et al. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 79–88. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00016
- 63.Dai, C.Q.; Peng, C.; Chen, M. Selective transfer cycle GAN for unsupervised person re-identification. Multimed. Tools Appl., 2020, 79: 12597−12613.
- 64.Qian, X.L.; Fu, Y.W.; Xiang, T.; et al. Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Munich, 2018; pp. 661–678. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-01240-3_40
- 65.Fan, H.H.; Zheng, L.; Yan, C.G.; et al. Unsupervised person re-identification: Clustering and fine-tuning. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput., Commun., Appl., 2018, 14: 83.
- 66.Lin, Y.T.; Dong, X.Y.; Zheng, L.; et al. A bottom-up clustering approach to unsupervised person re-identification. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., 2019, 33: 8738−8745.
- 67.Ding, Y.H.; Fan, H.H.; Xu, M.L.; et al. Adaptive exploration for unsupervised person re-identification. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput., Commun., Appl., 2020, 16: 3.
- 68.Pala, F.; Satta, R.; Fumera, G.; et al. Multimodal person reidentification using rgb-d cameras. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., 2016, 26: 788−799.
- 69.Kniaz, V.V.; Knyaz, V.A.; Hladůvka, J.; et al. Thermalgan: Multimodal color-to-thermal image translation for person re-identification in multispectral dataset. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Munich, 2018; pp. 606–624. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-11024-6_46
- 70.Elsken, T.; Metzen, J.H.; Hutter, F. Correction to: Neural architecture search. In Automated Machine Learning; Hutter, F.; Kotthoff, L.; Vanschoren, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, 2019; p. C1. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-05318-5_11
- 71.Zhou, K.Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Cavallaro, A.; Xiang, T. Learning generalisable Omni-scale representations for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1910.06827, 2019. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.06827 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 72.Ross, A.; Shah, J.; Jain, A.K. From template to image: Reconstructing fingerprints from minutiae points. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2007, 29: 544−560.
- 73.Dantcheva, A.; Dugelay, J.L.; Elia, P. Soft biometrics systems: Reliability and asymptotic bounds. In 2010 Fourth IEEE International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Washington, USA, 27–29 September 2010; IEEE: Washington, 2010; pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/BTAS.2010.5634534
- 74.Nixon, M.S.; Tan, T.; Chellappa, R. Human Identification Based on Gait; Springer Science & Business Media, 2010; pp. 4. Available online: https://link.springer.com/referenceworkentry/10.1007/978-0-387-31439-6_375 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 75.Cordina, C. Face blindness. MMSA, 2020. Available online: https://www.um.edu.mt/library/oar/handle/123456789/52399 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 76.Bate, S.; Bennetts, R.J. The rehabilitation of face recognition impairments: A critical review and future directions. Front. Hum. Neurosci., 2014, 8: 491.
- 77.DeGutis, J.M.; Chiu, C.; Grosso, M.E.; et al. Face processing improvements in prosopagnosia: Successes and failures over the last 50 years. Front. Hum. Neurosci., 2014, 8: 561.
- 78.Di Biase, L.; Di Santo, A.; Caminiti, M.L.; et al. Gait analysis in Parkinson’s disease: An overview of the most accurate markers for diagnosis and symptoms monitoring. Sensors, 2020, 20: 3529.
- 79.White, H.; Augsburger, S. Gait evaluation for patients with cerebral palsy. In Orthopedic Care of Patients with Cerebral Palsy; Nowicki, P.D., Ed., Springer: Cham, 2020; pp. 51–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-46574-2_4
- 80.Li, M.X.; Tian, S.S.; Sun, L.L.; et al. Gait analysis for post-stroke hemiparetic patient by multi-features fusion method. Sensors, 2019, 19: 1737.
- 81.Whittle, M.W. Clinical gait analysis: A review. Human Mov. Sci., 1996, 15: 369−387.
- 82.Zijlstra, W.; Hof, A.L. Assessment of spatio-temporal gait parameters from trunk accelerations during human walking. Gait Posture, 2003, 18: 1−10.
- 83.Roy, A.; Sural, S.; Mukherjee, J. A hierarchical method combining gait and phase of motion with spatiotemporal model for person re-identification. Pattern Recognit. Lett., 2012, 33: 1891−1901.
- 84.Ariyanto, G.; Nixon, M.S. Model-based 3D gait biometrics. In 2011 International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Washington, USA, 11–13 October 2011; IEEE: Washington, 2011; pp. 1–7. doi: 10.1109/IJCB.2011.6117582
- 85.Goffredo, M.; Bouchrika, I.; Carter, J.N.; et al. Self-calibrating view-invariant gait biometrics. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man, Cybern., Part B (Cybern.), 2010, 40: 997−1008.
- 86.Lombardi, S.; Nishino, K.; Makihara, Y.; et al. Two-point gait: Decoupling gait from body shape. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; IEEE: Sydney, 2013; pp. 1041–1048. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2013.133
- 87.Lu, H.P.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Venetsanopoulos, A.N. A layered deformable model for gait analysis. In 7th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (FGR06), Southampton, 10–12 April 2006; IEEE: Southampton, 2006; pp. 249–254. doi: 10.1109/FGR.2006.11
- 88.Khamsemanan, N.; Nattee, C.; Jianwattanapaisarn, N. Human identification from freestyle walks using posture-based gait feature. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., 2018, 13: 119−128.
- 89.Bouchrika, I.; Carter, J.N.; Nixon, M.S. Towards automated visual surveillance using gait for identity recognition and tracking across multiple non-intersecting cameras. Multimed. Tools Appl., 2016, 75: 1201−1221.
- 90.Yandell, M.B.; Quinlivan, B.T.; Popov, D.; et al. Physical interface dynamics alter how robotic exosuits augment human movement: Implications for optimizing wearable assistive devices. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil, 2017, 18(40).
- 91.Muybridge, E. Animal locomotion: An Electro-photographic investigation of consecutives phases of animal movement: Prospectus and catalogue of plates.. Males (nude). I., 1969. Available online: https://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/266429 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 92.Dagognet, F. Lanimal selon condillac, introd. a eb de condillac, traité des animaux, Vrin, j.; Paris; pp. 7–131, 1987. Available online: https://philpapers.org/rec/DAGLSC (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 93.Balazia, M.; Sojka, P. Gait recognition from motion capture data. ACM Trans. Multimedia Comput., Commun., Appl., 2018, 14: 22.
- 94.Josiński, H.; Michalczuk, A.; Kostrzewa, D.; et al. Heuristic method of feature selection for person re-identification based on gait motion capture data. In Proceedings of the 6th Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems, Bangkok, Thailand, 7–9 April 2014; Springer: Bangkok, 2014; pp. 585–594. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-05458-2_60
- 95.Nambiar, A.M.; Bernardino, A.; Nascimento, J.C.; et al. Towards view-point invariant person re-identification via fusion of anthropometric and gait features from kinect measurements. In Proceedings of the 12th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, Porto, Portugal, 27 February–1 March 2017; VISAPP: Porto, 2017; pp. 108–119.
- 96.Hofmann, M.; Geiger, J.; Bachmann, S.; et al. The TUM gait from audio, image and depth (GAID) database: Multimodal recognition of subjects and traits. J. Visual Commun. Image Representat., 2014, 25: 195−206.
- 97.Bedagkar-Gala, A.; Shah, S.K. Gait-assisted person re-identification in wide area surveillance. In Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Singapore, 1–2 November 2014; Springer: Singapore, 2014; pp. 633–649. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16634-6_46
- 98.Wei, L.; Tian, Y.H.; Wang, Y.W.; et al. Swiss-system based cascade ranking for gait-based person re-identification. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Austin Texas, USA, 25–30 January 2015; AAAI Press: Austin Texas, 2015; pp. 1882–1888.
- 99.Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.X.; Wu, Q.; et al. Enhancing person re-identification by integrating gait biometric. Neurocomputing, 2015, 168: 1144−1156.
- 100.Iwashita, Y.; Baba, R.; Ogawara, K.; et al. Person identification from spatio-temporal 3D gait. In 2010 International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies, Canterbury, UK, 6–7 September 2010; IEEE: Canterbury, 2010; pp. 30–35. doi: 10.1109/EST.2010.19
- 101.Nambiar, A.; Bernardino, A.; Nascimento, J.C.; et al. Context-aware person re-identification in the wild via fusion of gait and anthropometric features. In 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, USA, 30 May 2017–3 June 2017; IEEE: Washington, 2017; pp. 973–980. doi: 10.1109/FG.2017.121
- 102.John, V.; Englebienne, G.; Krose, B. Person re-identification using height-based gait in colour depth camera. In 2013 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; IEEE: Melbourne, 2013; pp. 3345–3349. doi: 10.1109/ICIP.2013.6738689
- 103.Nambiar, A.; Nascimento, J.C.; Bernardino, A.; et al. Person re-identification in frontal gait sequences via histogram of optic flow energy image. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Lecce, Italy, 24–27 October 2016; Springer: Lecce, 2016; pp. 250–262. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48680-2_23
- 104.Chattopadhyay, P.; Sural, S.; Mukherjee, J. Information fusion from multiple cameras for gait-based re-identification and recognition. IET Image Process., 2015, 9: 969−976.
- 105.Kawai, R.; Makihara, Y.; Hua, C.S.; et al. Person re-identification using view-dependent score-level fusion of gait and color features. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR2012), Tsukuba, Japan, 11–15 November 2012; IEEE: Tsukuba, 2012; pp. 2694–2697.
- 106.Wang, T.Q.; Gong, S.G.; Zhu, X.T.; et al. Person re-identification by video ranking. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Zurich, 2014; pp. 688–703. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-10593-2_45
- 107.Zhang, S.X.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chai, T.R.; et al. Realgait: Gait recognition for person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2201.04806, 2022. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.04806 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 108.Balazia, M.; Sojka, P. You are how you walk: Uncooperative MoCap gait identification for video surveillance with incomplete and noisy data. In 2017 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB), Denver, USA, 1–4 October 2017; IEEE: Denver, 2017; pp. 208–215. doi: 10.1109/BTAS.2017.8272700
- 109.Nambiar, A.M.; Bernardino, A.; Nascimento, J.C. Cross-context analysis for long-term view-point invariant person re-identification via soft-biometrics using depth sensor. In Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications, Funchal, Portugal, 27–29 January 2018; VISAPP: Funchal, 2018; pp. 105–113.
- 110.Stöckel, T.; Jacksteit, R.; Behrens, M.; et al. The mental representation of the human gait in young and older adults. Front. Psychol., 2015, 6: 943.
- 111.Burnfield, M. Gait analysis: Normal and pathological function. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 353.
- 112.Gabel, M.; Gilad-Bachrach, R.; Renshaw, E.; et al. Full body gait analysis with kinect. In 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, USA, 28 August 2012–1 September 2012; IEEE: San Diego, 2012; pp. 1964–1967. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346340
- 113.Bobick, A.F.; Davis, J.W. The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2001, 23: 257−267.
- 114.Balazia, M.; Plataniotis, K.N. Human gait recognition from motion capture data in signature poses. IET Biom., 2017, 6: 129−137.
- 115.Han, J.; Bhanu, B. Individual recognition using gait energy image. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2006, 28: 316−322.
- 116.Lam, T.H.W.; Cheung, K.H.; Liu, J.N.K. Gait flow image: A silhouette-based gait representation for human identification. Pattern Recognit., 2011, 44: 973−987.
- 117.Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jimenez, M.J.; Medina-Carnicer, R. Pyramidal fisher motion for multiview gait recognition. In 2014 22nd International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Stockholm, Sweden, 24–28 August 2014; IEEE: Stockholm, 2014; pp. 1692–1697. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2014.298
- 118.Tang, J.; Luo, J.; Tjahjadi, T.; et al. Robust arbitrary-view gait recognition based on 3D partial similarity matching. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2017, 26: 7−22.
- 119.Connie, T.; Goh, M.K.O.; Teoh, A.B.J. A grassmannian approach to address view change problem in gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern., 2017, 47: 1395−1408.
- 120.Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.D.; et al. Siamese neural network based gait recognition for human identification. In 2016 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing (ICASSP), Shanghai, China, 20–25 March 2016; IEEE: Shanghai, 2016; pp. 2832–2836. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2016.7472194
- 121.Wu, Z.F.; Huang, Y.Z.; Wang, L.; et al. A comprehensive study on cross-view gait based human identification with deep CNNs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2017, 39: 209−226.
- 122.Chopra, S.; Hadsell, R.; LeCun, Y. Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification. In 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, USA, 20–25 June 2005; IEEE: San Diego, 2005; pp. 539–546. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.202
- 123.Shen, C.; Jin, Z.M.; Zhao, Y.R.; et al. Deep Siamese network with multi-level similarity perception for person re-identification. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Mountain, USA, 23–27 October 2017; ACM: Mountain, 2017; pp. 1942–1950. doi: 10.1145/3123266.3123452
- 124.Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.B.; et al. Where-and-when to look: Deep Siamese attention networks for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2019, 21: 1412−1424.
- 125.Zheng, M.; Karanam, S.; Wu, Z.Y.; et al. Re-identification with consistent attentive siamese networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: Long Beach, 2019; pp. 5728–5737. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.00588
- 126.Bromley, J.; Bentz, J.W.; Bottou, L.; et al. Signature verification using a “Siamese” time delay neural network. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell., 1993, 7: 669−688.
- 127.Lu, T.; Zhou, Q.; Fang, W.H.; et al. Discriminative metric learning for face verification using enhanced Siamese neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl., 2021, 80: 8563−5880.
- 128.Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, H.D.; et al. Learning efficient spatial-temporal gait features with deep learning for human identification. Neuroinformatics, 2018, 16: 457−471.
- 129.Li, S.Q.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.D.; et al. Beyond view transformation: Cycle-consistent global and partial perception gan for view-invariant gait recognition. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), San Diego, USA, 23–27 July 2018; IEEE: San Diego, 2018; pp. 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICME.2018.8486484
- 130.Carley, C.; Ristani, E.; Tomasi, C. Person re-identification from gait using an autocorrelation network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, USA, 16–17 June 2019; IEEE: Long Beach, 2019; pp. 2345–2353. doi: 10.1109/CVPRW.2019.00288
- 131.He, Y.W.; Zhang, J.P.; Shan, H.M.; et al. Multi-task GANs for view-specific feature learning in gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., 2019, 14: 102−113.
- 132.Wang, X.H.; Feng, S.L.; Yan, W.Q. Human gait recognition based on self-adaptive hidden Markov model. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf., 2021, 18: 963−972.
- 133.Xu, Y.J.; Han, Y.H.; Hong, R.C.; et al. Sequential video VLAD: Training the aggregation locally and temporally. IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2018, 27: 4933−4944.
- 134.Zhao, S.C.; Liu, Y.B.; Han, Y.H.; et al. Pooling the convolutional layers in deep convnets for video action recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol., 2018, 28: 1839−1849.
- 135.Nguyen, P.; Han, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Weakly supervised action localization by sparse temporal pooling network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 6752–6761. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00706
- 136.Chao, H.Q.; He, Y.W.; Zhang, J.P.; et al. GaitSet: Regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., 2019, 33: 8126−8133.
- 137.Li, S.Q.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.D. Attentive spatial–temporal summary networks for feature learning in irregular gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimedia, 2019, 21: 2361−2375.
- 138.Hu, B.Z.; Gao, Y.; Guan, Y.; et al. Robust cross-view gait identification with evidence: A discriminant gait GAN (DiGGAN) approach on 10000 people. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1811.10493, 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.10493 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 139.Wang, Y.Y.; Song, C.F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Learning view invariant gait features with two-stream GAN. Neurocomputing, 2019, 339: 245−254.
- 140.Zhang, Z.Y.; Tran, L.; Liu, F.; et al. On learning disentangled representations for gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2022, 44: 345−360.
- 141.Liao, R.J.; Yu, S.Q.; An, W.Z.; et al. A model-based gait recognition method with body pose and human prior knowledge. Pattern Recognit., 2020, 98: 107069.
- 142.Burges, C.J.C. Dimension Reduction: A Guided Tour; Now Publishers Inc: Boston, 2010.
- 143.Avraham, T.; Lindenbaum, M. Learning appearance transfer for person re-identification. In Person Re-Identification; Gong, S.G.; Cristani, M.; Yan, S.C., et al, Eds.; Springer: London, 2014; pp. 231–246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-6296-4_11
- 144.Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Guil, N.; et al. Evaluation of CNN architectures for gait recognition based on optical flow maps. In 2017 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 20–22 September 2017; IEEE: Darmstadt, 2017; pp. 1–5. doi: 10.23919/BIOSIG.2017.8053503
- 145.Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Guil, N. Multimodal features fusion for gait, gender and shoes recognition. Mach. Vision Appl., 2016, 27: 1213−1228.
- 146.He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 770–778. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90
- 147.Wang, H.; Kläser, A.; Schmid, C.; et al. Action recognition by dense trajectories. In CVPR 2011, Colorado Springs, USA, 20–25 June 2011; IEEE: Colorado Springs, 2011; pp. 3169–3176. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995407
- 148.Rahi, B. View-Invariant Gait Person Re-Identification with Spatial and Temporal Attention. Ph.D. Thesis, Brunel University London, 2021. Available online: https://bura.brunel.ac.uk/handle/2438/24380 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 149.Jain, M.; Jégou, H.; Bouthemy, P. Better exploiting motion for better action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 23–28 June 2013; IEEE: Portland, 2013; pp. 2555–2562. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.330
- 150.Perronnin, F.; Larlus, D. Fisher vectors meet neural networks: A hybrid classification architecture. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 7–12 June 2015; IEEE: Boston, 2015; pp. 3743–3752. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298998
- 151.Perronnin, F.; Sánchez, J.; Mensink, T. Improving the fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; Springer: Heraklion, 2010; pp. 143–156. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_11
- 152.Jaakkola, T.S.; Haussler, D. Exploiting generative models in discriminative classifiers. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, USA, 1–3 December 1998; MIT Press: Denver, 1999; pp. 487–493.
- 153.Castro, F.M.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J.; Guil, N.; et al. Automatic learning of gait signatures for people identification. In Proceedings of the 14th International Work-Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Cadiz, Spain, 14–16 June 2017; Springer: Cadiz, 2017; pp. 257–270. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-59147-6_23
- 154.Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; MIT Press: Montreal, 2014; pp. 568–576.
- 155.Zhang, B.W.; Wang, L.M.; Wang, Z.; et al. Real-time action recognition with enhanced motion vector CNNs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 2718–2726. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.297
- 156.Piergiovanni, A.J.; Ryoo, M.S. Representation flow for action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: Long Beach, 2019; pp. 9937–9945. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2019.01018
- 157.Farnebäck, G. Two-frame motion estimation based on polynomial expansion. In Proceedings of the 13th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Halmstad, Sweden, 29 June–2 July 2003; Springer: Halmstad, 2003; pp. 363–370. doi: 10.1007/3-540-45103-X_50
- 158.Horn, B.K.P.; Schunck, B.G. Determining optical flow. In Proceedings of SPIE 0281, Techniques and Applications of Image Understanding, Washington, USA, 12 November1981; SPIE: Washington, 1981; pp. 319–331. doi: 10.1117/12.965761
- 159.Lucas, B.D.; Kanade, T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, Canada, 24–28 August 1981; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: Vancouver, 1981; pp. 674–679.
- 160.Brox, T.; Bruhn, A.; Papenberg, N.; et al. High accuracy optical flow estimation based on a theory for warping. In Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; Springer: Prague, 2004; pp. 25–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-24673-2_3
- 161.Papenberg, N.; Bruhn, A.; Brox, T.; et al. Highly accurate optic flow computation with theoretically justified warping. Int. J. Comput. Vision, 2006, 67: 141−158.
- 162.Brox, T.; Malik, J. Large displacement optical flow: Descriptor matching in variational motion estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2010, 33: 500−513.
- 163.Hui, T.W.; Chung, R. Determining motion directly from normal flows upon the use of a spherical eye platform. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, USA, 23–28 June 2013; IEEE: Portland, 2013; pp. 2267–2274. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2013.294
- 164.Hui, T.W.; Chung, R. Determining shape and motion from monocular camera: A direct approach using normal flows. Pattern Recognit., 2015, 48: 422−437.
- 165.Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; et al. FlowNet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, 2015; pp. 2758–2766. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.316
- 166.Ilg, E.; Mayer, N.; Saikia, T.; et al. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Honolulu, 2017; pp. 1647–1655. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2017.179
- 167.Hui, T.W.; Tang, X.O.; Loy, C.C. LiteFlowNet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for optical flow estimation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 8981–8989. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00936
- 168.Feichtenhofer, C.; Pinz, A.; Zisserman, A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Las Vegas, 2016; pp. 1933–1941. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.213
- 169.Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; IEEE: Santiago, 2015; pp. 4489–4497. doi: 10.1109/ICCV.2015.510
- 170.Yu, S.Q.; Chen, H.F.; Wang, Q.; et al. Invariant feature extraction for gait recognition using only one uniform model. Neurocomputing, 2017, 239: 81−93.
- 171.Goferman, S.; Zelnik-Manor, L.; Tal, A. Context-aware saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2012, 34: 1915−1926.
- 172.Ba, J.; Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Multiple object recognition with visual attention. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 7–9 May 2015; ICLR: San Diego, 2014.
- 173.Bazzani, L.; Larochelle, H.; Torresani, L. Recurrent mixture density network for spatiotemporal visual attention. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017; ICLR: Toulon, 2017.
- 174.Sharma, S.; Kiros, R.; Salakhutdinov, R. Action recognition using visual attention. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1511.04119, 2015. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.04119 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 175.Sepas-Moghaddam, A.; Etemad, A. View-invariant gait recognition with attentive recurrent learning of partial representations. IEEE Trans. Biom., Behav., Identity Sci, 2021, 3: 124−137.
- 176.Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 7–9 May 2015; ICLR: San Diego, 2015.
- 177.Vinyals, O.; Kaiser, L.; Koo, T.; et al. Grammar as a foreign language. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; MIT Press: Montreal, 2015; pp. 2773–2781.
- 178.Chan, W.; Jaitly, N.; Le, Q.V.; et al. Listen, attend and spell. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1508.01211, 2015. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.01211 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 179.Guan, Q.J.; Huang, Y.P.; Zhong, Z.; et al. Diagnose like a radiologist: Attention guided convolutional neural network for thorax disease classification. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.09927, 2018. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.09927 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 180.Yao, L.; Poblenz, E.; Dagunts, D.; et al. Learning to diagnose from scratch by exploiting dependencies among labels. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.10501, 2017. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/1710.10501 (accessed on 5 December 2022).
- 181.Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 18–23 June 2018; IEEE: Salt Lake City, 2018; pp. 7132–7141. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2018.00745
- 182.Cheng, J.P.; Dong, L.; Lapata, M. Long short-term memory-networks for machine reading. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, USA, 1–4 November 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Austin, 2016; pp. 551–561. doi: 10.18653/v1/D16-1053
- 183.Xu, K.; Ba, J.L.; Kiros, R.; et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Lille, France, 6–11 July 2015; JMLR.org: Lille, 2015; pp. 2048–2057.
- 184.Ramachandran, P.; Parmar, N.; Vaswani, A.; et al. Stand-alone self-attention in vision models. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Curran Associates Inc.: Vancouver, 2019; p. 7.
- 185.Bansal, V.; Foresti, G.L.; Martinel, N. Cloth-changing person re-identification with self-attention. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops, Waikoloa, USA, 4–8 January 2022; IEEE: Waikoloa, 2022; pp. 602–610. doi: 10.1109/WACVW54805.2022.00066
- 186.Luong, T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Lisbon, Portugal, 17–21 September 2015; Association for Computational Linguistics: Lisbon, 2015; pp. 1412–1421. doi: 10.18653/v1/D15-1166
- 187.Yu, S.Q.; Tan, D.L.; Tan, T.N. A framework for evaluating the effect of view angle, clothing and carrying condition on gait recognition. In 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; IEEE: Hong Kong, China, 2006; pp. 441–444. doi: 10.1109/ICPR.2006.67
- 188.Iwama, H.; Okumura, M.; Makihara, Y.; et al. The OU-ISIR gait database comprising the large population dataset and performance evaluation of gait recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur., 2012, 7: 1511−1521.
- 189.Rao, H.C.; Wang, S.Q.; Hu, X.P.; et al. A self-supervised gait encoding approach with locality-awareness for 3D skeleton based person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 2022, 44: 6649−6666.
- 190.Chen, Y.; Xia, S.X.; Zhao, J.Q.; et al. Adversarial learning-based skeleton synthesis with spatial-channel attention for robust gait recognition. Multimedia Tools Appl., 2023, 82: 1489−1504.
- 191.Ben, X.Y.; Zhang, P.; Meng, W.X.; et al. On the distance metric learning between cross-domain gaits. Neurocomputing, 2016, 208: 153−164.
- 192.Ma, H.D.; Liu, W. A progressive search paradigm for the internet of things. IEEE MultiMedia, 2018, 25: 76−86.
- 193.Montero-Odasso, M.; Schapira, M.; Soriano, E.R.; et al. Gait velocity as a single predictor of adverse events in healthy seniors aged 75 years and older. J. Gerontol. Ser. A, 2005, 60: 1304−1309.
How to Cite
Rahi, B.; Li, M.; Qi, M. A Review of Techniques on Gait-Based Person Re-Identification. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2023, 2 (1), 66–92. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi0201005.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2023 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


