Federated learning is a newly developing distributed machine learning technology, which makes it possible for users to train machine learning models with decentralized privacy data. Owing to huge communication overhead, the traditional federated learning algorithm samples user data randomly, which may reduce the performance of the model due to the statistical heterogeneity of users. In this paper, we propose a distillation-based user selection algorithm for federated learning in heterogeneous situations. Based on knowledge distillation, the soft targets of users are uploaded to the server as a basis for user selection. Our algorithm reduces the statistical heterogeneity of selected users, resulting in low additional communication and computation overhead. Experiments implemented on MNIST and fashion-MNIST show that the proposed algorithm obtains better model performance as compared to the federated averaging algorithm and several other user selection algorithms.
- Open Access
- Article
Distillation-Based User Selection for Heterogeneous Federated Learning
- Bowen Li,
- Wenling Li *
Author Information
Received: 07 Sep 2023 | Accepted: 09 Nov 2023 | Published: 26 Jun 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
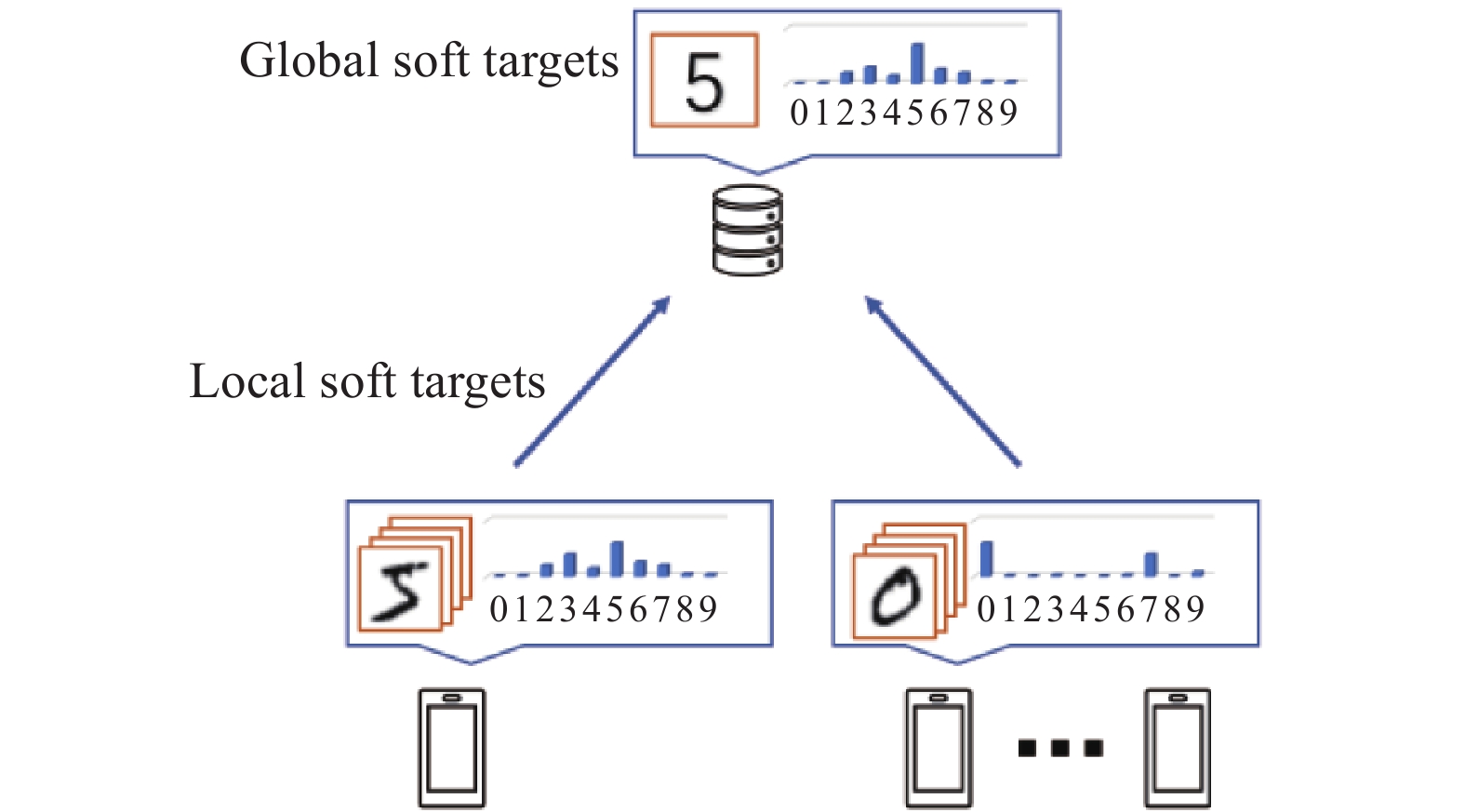
Keywords
federated learning | user selection | knowledge distillation
References
- 1.Li, L.; Fan, Y.X.; Tse, M.; et al. A review of applications in federated learning. Comput. Ind. Eng., 2020, 149: 106854. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106854
- 2.Yao, F.; Ding, Y.L.; Hong, S.G.; et al. A survey on evolved LoRa-based communication technologies for emerging internet of things applications. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intell., 2022, 1: 4−19. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0101002
- 3.Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.Y.; Yang, Z.H.; et al. Robust semisupervised federated learning for images automatic recognition in internet of drones. IEEE Internet Things J., 2023, 10: 5733−5746. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3151945
- 4.Rieke, N.; Hancox, J.; Li, W.Q.; et al. The future of digital health with federated learning. npj Digital Med., 2020, 3: 119. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00323-1
- 5.McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.;
et al . Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. InProceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017 ; PMLR, 2017; pp. 1273–1282. - 6.Abdulrahman, S.; Tout, H.; Ould-Slimane, H.; et al. A survey on federated learning: The journey from centralized to distributed on-site learning and beyond. IEEE Internet Things J., 2021, 8: 5476−5497. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3030072
- 7.Wang, Y.A.; Shen, B.; Zou, L.; et al. A survey on recent advances in distributed filtering over sensor networks subject to communication constraints. Int. J. Network Dyn. Intell., 2023, 2: 100007. doi: 10.53941/ijndi0201007
- 8.Zhang, T.H.; Lam, K.Y.; Zhao, J.;
et al . Joint device scheduling and bandwidth allocation for federated learning over wireless networks.IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun .2023 . doi:10.1109/TWC.2023.3291701 - 9.Cho, Y.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Chirvolu, T.; et al. Communication-efficient and model-heterogeneous personalized federated learning via clustered knowledge transfer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process., 2023, 17: 234−247. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2022.3231527
- 10.Wang, H.; Kaplan, Z.; Niu, D.;
et al . Optimizing federated learning on Non-IID data with reinforcement learning. InIEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–9 July 2020 ; IEEE: New York, 2020; pp. 1698–1707. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM41043.2020.9155494 - 11.Yang, H.B.; Fang, M.H.; Liu, J. Achieving linear speedup with partial worker participation in Non-IID federated learning. In
Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations, 3–7 May 2021 ; ICLR, 2021. - 12.Luo, B.; Xiao, W.L.; Wang, S.Q.;
et al . Tackling system and statistical heterogeneity for federated learning with adaptive client sampling. InIEEE INFOCOM 2022-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, London, UK, 2–5 May 2022 ; IEEE: New York, 2022; pp. 1739–1748. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM48880.2022.9796935 - 13.Fraboni, Y.; Vidal, R.; Kameni, L.;
et al . Clustered sampling: Low-variance and improved representativity for clients selection in federated learning. InProceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 18–24 July 2021 ; PMLR, 2021; pp. 3407–3416. - 14.Wang, S.; Lee, M.; Hosseinalipour, S.;
et al . Device sampling for heterogeneous federated learning: Theory, algorithms, and implementation. InIEEE INFOCOM 2021-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–13 May 2021 ; IEEE: New York, 2021; pp. 1–10. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM42981.2021.9488906 - 15.Cho, Y.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Joshi, G. Client selection in federated learning: Convergence analysis and power-of-choice selection strategies. arXiv: 2010.01243, 2020. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2010.01243
- 16.Hinton, G.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv: 1503.02531, 2015. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1503.02531
- 17.Jeong, E.; Oh, S.; Kim, H.;
et al . Communication-efficient on-device machine learning: Federated distillation and augmentation under non-IID private data. arXiv: 1811.11479, 2018. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1811.11479 - 18.Lin, T.; Kong, L.J.; Stich, S.U.;
et al . Ensemble distillation for robust model fusion in federated learning. InProceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–12 December 2020 ; ACM: Red Hook, 2020; p. 198. doi:10.5555/3495724.3495922 - 19.Itahara, S.; Nishio, T.; Koda, Y.; et al. Distillation-based semi-supervised federated learning for communication-efficient collaborative training with non-IID private data. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput., 2023, 22: 191−205. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2021.3070013
- 20.Wu, C.H.; Wu, F.Z.; Lyu, L.J.; et al. Communication-efficient federated learning via knowledge distillation. Nat. Commun., 2022, 13: 2032. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29763-x
- 21.Zhang, L.; Shen, L.; Ding, L.;
et al . Fine-tuning global model via data-free knowledge distillation for non-IID federated learning. InProceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022 ; IEEE: New York, 2022; pp. 10164–10173. doi:10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00993 - 22.Xing, H.L.; Xiao, Z.W.; Qu, R.; et al. An efficient federated distillation learning system for multitask time series classification. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas., 2022, 71: 2517012. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2022.3201203
- 23.Yan, G.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Seizing critical learning periods in federated learning. In
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 22 February–1 March 2022 ; AAAI: Palo Alto, 2022; pp. 8788–8796. doi:10.1609/aaai.v36i8.20859 - 24.Cui, Y.G.; Cao, K.; Cao, G.T.; et al. Client scheduling and resource management for efficient training in heterogeneous IoT-edge federated learning. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst., 2022, 41: 2407−2420. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2021.3110743
- 25.Ikotun, A.M.; Ezugwu, A.E.; Abualigah, L.; et al. K-means clustering algorithms: A comprehensive review, variants analysis, and advances in the era of big data. Inf. Sci., 2023, 622: 178−210. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.11.139
- 26.Goetz, J.; Malik, K.; Bui, D.;
et al . Active federated learning. arXiv: 1909.12641, 2019. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1909.12641 - 27.Tang, M.X.; Ning, X.F.; Wang, Y.T.;
et al . FedCor: Correlation-based active client selection strategy for heterogeneous federated learning. InProceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022 ; IEEE: New York, 2022; pp. 10092–10101. doi:10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00986 - 28.Li, T.; Sahu, A.K.; Zaheer, M.;
et al . Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks. InProceedings of Machine Learning and Systems 2020, Austin, TX, USA, 2–4 March 2020 ; MLSys, 2020; pp. 429–450.
How to Cite
Li, B.; Li, W. Distillation-Based User Selection for Heterogeneous Federated Learning. International Journal of Network Dynamics and Intelligence 2024, 3 (2), 100007. https://doi.org/10.53941/ijndi.2024.100007.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


