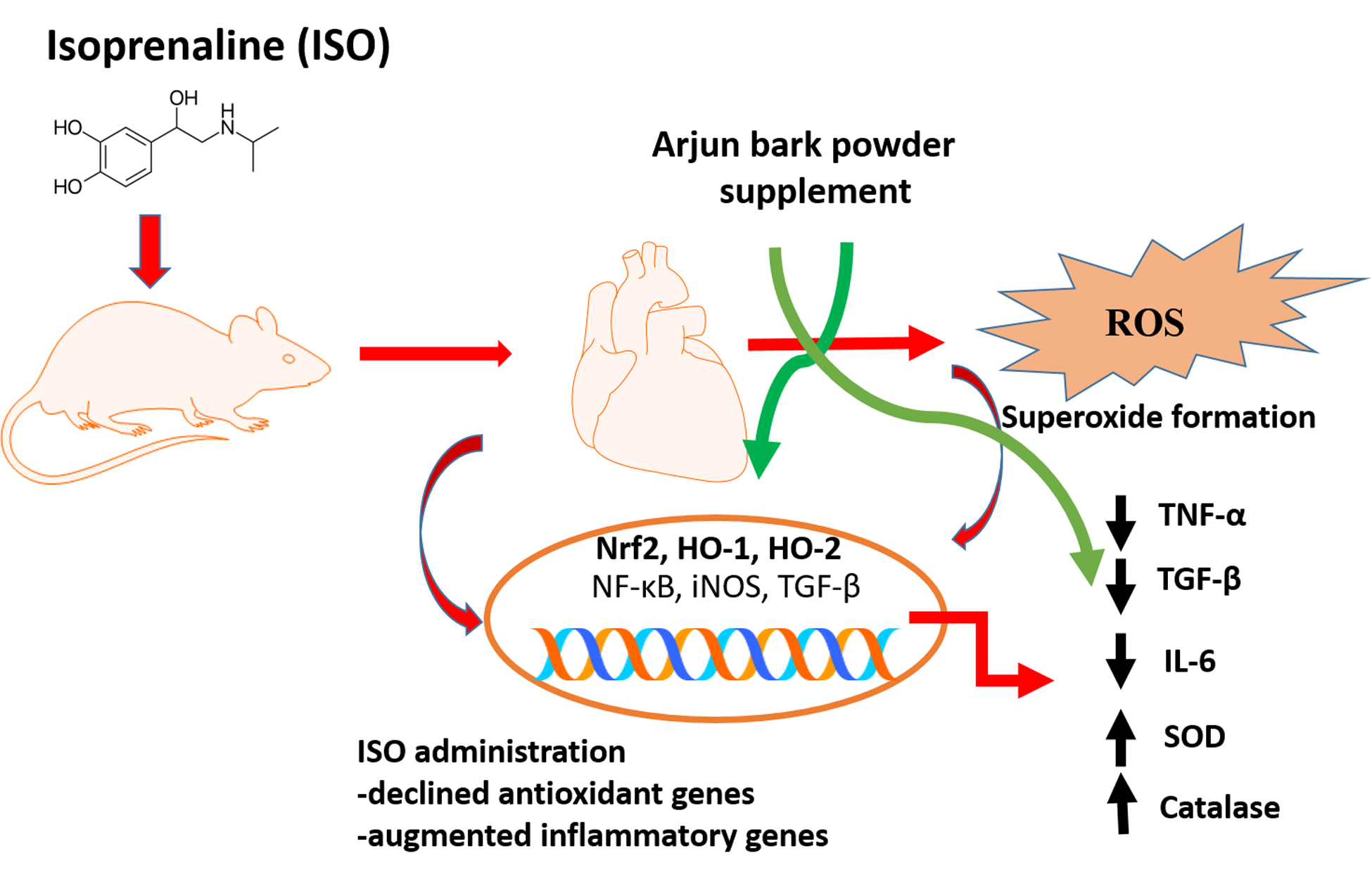
This study was conducted to determine the effect of Terminalia arjuna bark powder supplementation on the oxidative stress of the cardiovascular system. Isoprenaline (ISO) was administered to the rats to develop the cardiac hypertrophy and myocardial infarction (MI). Terminalia arjuna bark powder was mixed with the food powder and provided for two weeks. At the end of the experiment, all rats were sacrificed and tissue samples were collected. ISO administration in rats increased the oxidative stress markers such as malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), advanced oxidation protein product (APOP), and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in plasma and heart. Terminalia arjuna bark powder lowered the MDA, NO, and AOPP concentration level in ISO administered rats. Additionally, Terminalia arjuna restored the antioxidant enzymes (catalase and SOD) activities. Gene expression of antioxidant enzymes and inflammatory markers in the heart were studied. Terminalia arjuna restored Nrf-2, HO-1, HO-2, catalase, SOD, and GPx gene expression in the heart of ISO administered rats. ISO induced increased transcription levels of inflammatory genes such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, TGF-β, iNOS, and NF-κB, which were decreased by Terminalia arjuna bark powder. Histopathology was checked and hematoxylin and eosin and Sirius red staining were performed on heart sections. ISO administration resulted in mononuclear cells infiltration and collagen deposition in the heart which were lowered by Terminalia arjuna bark powder. In conclusion, this study suggests that the Terminalia arjuna bark powder alleviated the oxidative stress by restoring the antioxidant genes and prevented the increase in inflammatory markers in the heart of ISO administered rats.
- Open Access
- Article
Evaluation of Terminalia arjuna Bark Powder Supplementation on Isoprenaline-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Heart of Long Evans Rats, Understanding the Molecular Mechanism of This Old Medicinal Plant
- Mirza Alimullah 1,
- Nafiur Rahman 1,
- Puspa Sornaker 1,
- Kazi Akramuddaula 2,
- Sumaia Sarif 1,
- Shahnaz Siddiqua 3,
- Kaniz Fatima Mitu 1,
- Ishrat Jahan 1,
- Ferdous Khan 1,
- Nusrat Subhan 1,
- Ashraful Alam 1, *
Author Information
Received: 27 Jul 2024 | Revised: 28 Aug 2024 | Accepted: 28 Aug 2024 | Published: 05 Sep 2024
Abstract
Graphical Abstract
Keywords
Terminalia arjuna | isoprenaline | catalase | superoxide dismutase | oxidative stress
References
- 1.Jacob, R.A. Vitamin C nutriture and risk of atherosclerotic heart disease. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 334–337.
- 2.Ceconi, C.; Boraso, A.; Cargnoni, A.; et al. Oxidative stress in cardiovascular disease: Myth or fact? Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 420, 217–221.
- 3.McCord, J.M.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 6049–6055.
- 4.Ferrari, R. The role of free radicals in ischaemic myocardium. Br. J. Clin. Prac. 1990, 44, 301–305.
- 5.Curello, S.; Ceconi, C.; Medici, D.; et al. Oxidative stress during myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion: Experimental and clinical evidence. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1986, 18, 20.
- 6.Ferrari, R.; Ceconi, C.; Curello, S.; et al. Oxygen-mediated myocardial damage during ischameia and reperfusion: Role of the cellular defenses against oxygen toxicity. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1985, 17, 937–945.
- 7.De Bono, D.; Simoons, M.; Tijssen, J.; et al. Effect of early intravenous heparin on coronary patency, infarct size, and bleeding complications after alteplase thrombolysis: Results of a randomised double blind European Cooperative Study Group trial. Heart 1992, 67, 122–128.
- 8.Jordan, J.E.; Zhao, Z.-Q.; Vinten-Johansen, J. The role of neutrophils in myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 1999, 43, 860–878.
- 9.Deten, A.; Volz, H.C.; Hölzl, A.; et al. Effect of propranolol on cardiac cytokine expression after myocardial infarction in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 251, 127–137.
- 10.Hagler, M.A.; Hadley, T.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. TGF-β signalling and reactive oxygen species drive fibrosis and matrix remodelling in myxomatous mitral valves. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 175–184.
- 11.Panda, V.S.; Naik, S.R. Evaluation of cardioprotective activity of Ginkgo biloba and Ocimum sanctum in rodents. Altern. Med. Rev. 2009, 14, 161.
- 12.Kannan, M.M.; Quine, S.D. Ellagic acid inhibits cardiac arrhythmias, hypertrophy and hyperlipidaemia during myocardial infarction in rats. Metabolism 2013, 62, 52–61.
- 13.Mangge, H.; Becker, K.; Fuchs, D.; et al. Antioxidants, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. World J. Cardiol. 2014, 6, 462.
- 14.Akter, N.; Chowdhury, F.I.; Selim, S.; et al. Polyphenolics in ramontchi protect cardiac tissues via suppressing isoprenaline-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in Long-Evans rats. J. Func. Foods 2020, 75, 104250.
- 15.Ulla, A.; Mohamed, M.K.; Sikder, B.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 prevents oxidative stress and fibrosis in isoprenaline induced cardiac remodeling in aged rats. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 29.
- 16.Dwivedi, S.; Chopra, D. Revisiting Terminalia arjuna—An ancient cardiovascular drug. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2014, 4, 224–231.
- 17.Warrier, P.K.; Nambiar, V.P.K.; Ramankutty, C. Indian Medicinal Plants—A Compendium of 500 Species; Orient Longman Private Limited: Chenni, India, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 253–257.
- 18.Jain, S.; Yadav, P.P.; Gill, V.; et al. Terminalia arjuna, a sacred medicinal plant: Phytochemical and pharmacological profile. Phytochem. Rev. 2009, 8, 491–502.
- 19.Maulik, S.K.; Talwar, K.K. Therapeutic potential of Terminalia arjuna in cardiovascular disorders. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2012, 12, 157–163.
- 20.Kapoor, D.; Vijayvergiya, R.; Dhawan, V. Terminalia arjuna in coronary artery disease: Ethnopharmacology, pre-clinical, clinical and safety evaluation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 155, 1029–1045.
- 21.Dwivedi, S. Terminalia arjuna wight & Arn—A useful drug for cardiovascular disorders. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 114–129.
- 22.Dwivedi, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Agarwal, M.; et al. Role of Terminalia arjuna in ischaemic mitral regurgitation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 100, 507–508.
- 23.Pawar, R.; Bhutani, K. Effect of oleanane triterpenoids from Terminalia arjuna—A cardioprotective drug on the process of respiratory oxyburst. Phytomedicine 2005, 12, 391–393.
- 24.Ali, A.; Kaur, G.; Hayat, K.; et al. A novel naphthanol glycoside from Terminalia arjuna with antioxidant and nitric oxide inhibitory activities. Die Pharm. 2003, 58, 932–934.
- 25.Bhatia, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Mahajan, P.; et al. Effect of Terminalia arjuna on blood pressure of anaesthetised dogs. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2000, 32, 159–160.
- 26.Tiwari, A.; Gode, J.; Dubey, G. Effect of Terminalia arjuna on lipid profiles of rabbits fed hypercholesterolemic diet. Int. J. Crude Drug Res. 1990, 28, 43–47.
- 27.Patil, R.H.; Prakash, K.; Maheshwari, V.L. Hypolipidemic effect of Terminalia arjuna (L.) in experimentally induced hypercholesteremic rats. Acta Biol. Szeged. 2011, 55, 289–293.
- 28.Parmar, H.; Panda, S.; Jatwa, R.; et al. Cardio-protective role of Terminalia arjuna bark extract is possibly mediated through alterations in thyroid hormones. Die Pharm. 2006, 61, 793–795.
- 29.Sagor, M.A.T.; Tabassum, N.; Potol, M.A.; et al. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor, allopurinol, prevented oxidative stress, fibrosis, and myocardial damage in isoproterenol induced aged rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 478039.
- 30.Ulla, A.; Alam, M.A.; Sikder, B.; et al. Supplementation of Syzygium cumini seed powder prevented obesity, glucose intolerance, hyperlipidemia and oxidative stress in high carbohydrate high fat diet induced obese rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 289.
- 31.Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; et al. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209.
- 32.Parveen, A.; Babbar, R.; Agarwal, S.; et al. Mechanistic clues in the cardioprotective effect of Terminalia arjuna bark extract in isoproterenol-induced chronic heart failure in rats. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2011, 11, 48–57.
- 33.Mohammad, S.; Sadika, A.; Hossain, I.; et al. Evaluation of in vitro antioxidant activity of bark extracts of Terminalia arjuna. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012, 6, 5286–5298.
- 34.Selim, S.; Akter, N.; Nayan, S.I.; et al. Flacourtia indica fruit extract modulated antioxidant gene expression, prevented oxidative stress and ameliorated kidney dysfunction in isoprenaline administered rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 101012.
- 35.Verma, N.; Vinayak, M. Effect of Terminalia arjuna on antioxidant defense system in cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 159–164.
- 36.Chisty, T.T.E.; Sarif, S.; Jahan, I.; et al. Protective effects of l-carnitine on isoprenaline -induced heart and kidney dysfunctions: Modulation of inflammation and oxidative stress-related gene expression in rats. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25057.
- 37.Sivalokanathan, S.; Ilayaraja, M.; Balasubramanian, M.P. Antioxidant activity of Terminalia arjuna bark extract on N-nitrosodiethylamine induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 281, 87–93.
- 38.Uthirapathy, S. Novel biomarkers of atherogenic diet induced dyslipidemia and metabolic syndrome suppressed by Terminalia arjuna. Int. J. Pharma. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 2528–2536.
- 39.Ali, A.; Kaur, G.; Hamid, H.; et al. Terminoside A, a new triterpene glycoside from the bark of Terminalia arjuna inhibits nitric oxide production in murine macrophages. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2003, 5, 137–142.
- 40.Devi, R.S.; Narayan, S.; Vani, G.; et al. Gastroprotective effect of Terminalia arjuna bark on diclofenac sodium induced gastric ulcer. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2007, 167, 71–83.
- 41.Thomas, T.P.; Grisanti, L.A. The dynamic interplay between cardiac inflammation and fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 529075.
- 42.Feng, W.; Li, W. The study of ISO induced heart failure rat model. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 88, 299–304.
- 43.Dobaczewski, M.; Chen, W.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in cardiac remodeling. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 600–606.
- 44.Kumar, G.; Saleem, N.; Kumar, S.; et al. Transcriptomic validation of the protective effects of aqueous bark extract of Terminalia arjuna (Roxb.) on isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1443. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01443.
- 45.Mythili, P.; Parameswari, C.; Dayana, J. Phytochemical analysis of the bark extract of Terminalia arjuna and its cardioprotective effect. Indian J. Innov. Dev. 2012, 1, 40–42.
How to Cite
Alimullah, M.; Rahman, N.; Sornaker, P.; Akramuddaula, K.; Sarif, S.; Siddiqua, S.; Mitu, K. F.; Jahan, I.; Khan, F.; Subhan, N.; Alam, A. Evaluation of Terminalia arjuna Bark Powder Supplementation on Isoprenaline-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in the Heart of Long Evans Rats, Understanding the Molecular Mechanism of This Old Medicinal Plant. Journal of Medicinal Natural Products 2024, 1 (1), 100004. https://doi.org/10.53941/jmnp.2024.100004.
RIS
BibTex
Copyright & License

Copyright (c) 2024 by the authors.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Contents
References


